Étiquette : labor
Posted by: Karel Vereycken | on décembre 4, 2023
Victor Hugo and the awakening of the colossus

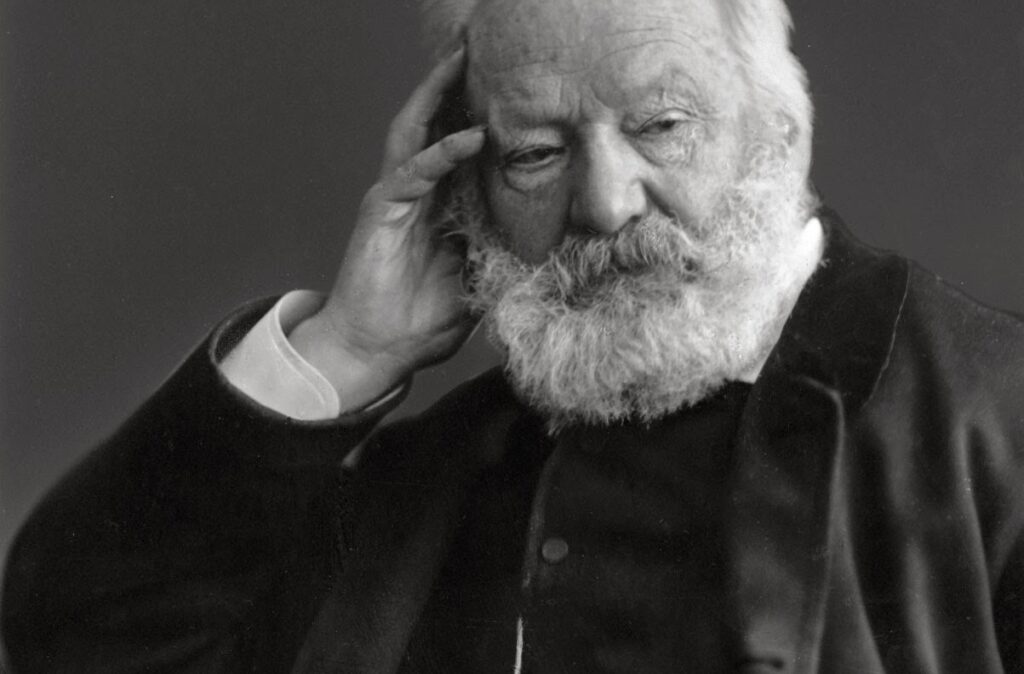
As Christophe Hardy notes in an article on the website L’Eléphant (April 2014), from which I drew heavily, the author of Les Misérables rightly passes for a man who, in his writings and commitments, « defended the cause of the people. »
Steeped in a worldview of Christian humanism and love for the other, the french state sman, critic, author and poet Victor Hugo (1802-1885) felt challenged by the people and the misery in which they found themselves, without falling for a purely idealized or romantic vision. And when he sees the people rise, Hugo takes the measure of their colossal power, be it for good or for evil.
In his poem To the People (Les Châtiments, Book VI), he uses the powerful metaphor of the Ocean to characterize this often unpredictable force. In evoking it, Hugo addresses the people:
« It resembles you; it is terrible and peaceful (…)
Its wave, where one hears like shocks of armors,
Fills the dark night with monstrous murmurs,
And one feels that this wave, like you, human abyss,
Having roared tonight, will devour tomorrow. »
During the first half of his life, Hugo witnessed several popular uprisings. The years 1830 are particularly agitated. Riots and strikes broke out in the big cities, in Paris, Lyon, Marseille, provoked by the harshness of life that was aggravated by the crisis in agricultural production. Generally speaking, the rigor of working conditions was the result of absurd market mechanisms: faced with the collapse of industrial prices (1817-1851), entrepreneurs decided purely and simply to reduce wages!
Pauperization exploded and the workers rebelled against this dramatic decrease in their income. In Paris, Hugo had before his eyes the spectacle of a laboring mass, coming from the provinces to crowd into the center of the capital, uprooted, living in insalubrity and precariousness, exposed to epidemics (cholera in 1832), quick to riot (February and September 1831, June 1832, April 1834).
However, the workers, who represented only a small minority in a largely agricultural and peasant country, struggled to assert their demands, especially for shorter working days. Not yet structured, their fragmentation prevented them from acquiring a true consciousness of class solidarity. This battered mass, regularly agitated by brutal shocks, frightened the notables and the owners, who saw it as a dangerous class threatening their privileges.
Love stronger than pity
Hugo is very early aware that the misery of the people is the main “social question”. This sensitivity to the fate of the poorest is not that of the hypocritical lady-do-rightly, it is the bottom of his soul. And when, elected deputy, he evokes it in the Assembly, the conservatives of which he thought he was close until 1849, started to yell.
« All my thoughts, Hugo said, I could summarize them in one sentence: vigorous hatred of anarchy, tender and deep love of the people! »
The misery of the working classes, the poet knew and had reported on it: misery of the prison (visit to the Conciergerie, in Choses vues, September 1846), misery of working-class life (visit to the cellars of Lille in February 1851, speech not delivered that will inspire the poem of the Châtiments « Joyful life »). He is convinced that it can be eradicated.
Contradicting the conservatives, the working classes are not, in his eyes, « dangerous classes ». They are even in danger, and the fact that they are in danger threatens the stability of the whole society:
« I denounce to you the misery, which is the scourge of one class and a danger for all! I denounce to you the misery which is not only the suffering of the individual, which is the ruin of the society. »
(Speech of July 9, 1849.)
If he abandons his convictions as a young Royalist to become a passionate Republican of progress, Hugo fears chaos and needless bloodshed. Although he did not live through 1793 and the Terror, he is obsessed with the memory of the bloody days of the French Revolution, when the guillotine was in full swing.
Reporting on the insurrection, in 1832, more than the violence as such, he denounced the extremists who, for personal calculations and not to fight against injustice, excite the masses to revolt and announce for the end of the month « four beautiful permanent guillotines on the four main squares of Paris”.
Hugo considers this strategy as a political dead end (« Don’t ask for rights as long as the people ask for heads »), while understanding its legitimacy:
« It is of the essence of the revolutionary riot, which should not be confused with other kinds of riots, to be almost always wrong in form and right in substance. »
With irony, he points out to the powerful that « the most excellent symbol of the people is the pavement. You walk on it until it falls on your head. » (Things Seen, 1830 to 1885.)
Like the German poet Friedrich Schiller, Hugo believes that the role of the artist and the poet is to elevate the debate. Art, like the polar star shining in the night for sailors lost on the ocean, is essential to guide the people to safety.
Magnanimous
Politically, in order to lay the foundations of a peaceful and harmonious future destiny, he affirms that compassion and forgiveness must prevail over hatred and vengeance.
« He who murdered on the highways who, better directed,
would have been the most excellent servant of the city.
This head of the common man,
cultivate it, clear it, water it, fertilize it,
enlighten it, moralize it, use it;
you will not need to cut it off.”
(Claude Gueux, novel, 1834.)
Lucid, the poet declares that « to open a school is to close a prison, » for « when the people are intelligent, only then will the people be sovereign. »
This is the treatment applied to Jean Valjean, the main hero of Les Misérables: the poor thief, an escaped convict, will eventually become the great soul that his host of one evening, Monsignor Myriel, had been able to detect in him while the rest of society proved unable to identify it … Hugo will spend his life to de-demonize « the beggars » (les gueux), that is to say the people.
In 1812, in his song Les gueux, the popular chansonnier Pierre-Jean de Béranger*, whom he admired, intoned:
« Let us sing the praise of the beggars.
How many beggars are good men!
It is necessary that finally the spirit
avenges the honest man who has nothing.”
In one of his greatest speeches (in July 1851, on the reform of the Constitution), Hugo claimed for the people (and for all) the right to material life (assured work, organized assistance, abolition of the death penalty) and the right to intellectual life (compulsory and free education, freedom of conscience, freedom of expression, freedom of the press).
In short, in embryo, the vision of a Jaurès and a De Gaulle that we will find in « Les Jours heureux » (The Happy Days), the program of the National Council of the Resistance (CNR), and the antithesis of the financial globalization that is inflicted on us today.
A whistleblower

In 1527, in a letter to his friend Thomas More, the humanist Erasmus of Rotterdam warned the powerful: if the Church of Rome does not adopt the measures of progressive and peaceful reform that he, Erasmus, proposes, they will be guilty of having provoked a century of violence.
In Les années funestes (1852), knowing the power of the colossus, Victor Hugo also warned the oligarchy. A warning that keeps its topicality:
« You have not taken heed of the people that we are.
With us, in the great days, the children are men,
The men are heroes, the old men are giants.
Oh, how stupid and gaping you will be,
The day when you will see, laughable escogriffs,
This great people of France escape from your claws!
The day when you will see fortune, dignities,
Powers, places, honors, beautiful pledges well counted,
All the heaps of your fierce pride,
Fall at the first step that the colossus will make!
Confounded, furious, vainly clinging
To the wavering debris of your collapse,
You will still try to shout, to proscribe,
To insult, and History will burst out laughing. »
NOTE:
*Christine Bierre: « Pierre-Jean de Béranger : la chanson, une arme républicaine » in Nouvelle Solidarité N°07/2022.
Posted in Comprendre, Etudes historiques, politiques et scientifiques | Commentaires fermés sur Victor Hugo and the awakening of the colossus
Tags: agricultural, artist, artkarel, Béranger, Châtiments, cholera, Choses Vues, Christian, colosse, colossus, dangerous, De Gaulle, Erasmus, fragmentation, goya, gueux, guillotine, humanism, insalubrity, Jaurès, Karel, Karel Vereycken, labor, livelihood, Love, metaphor, Misérables, misery, National Council of the Resistance, ocean, pity, poet, poverty, power, prison, renaissance, revolution, riot, schiller, uprising, Valjean, Vereycken, Victor Hugo, wages, working-class