Étiquette : Wessel Gansfort
Devotio Moderna, Brothers of the Common Life: the cradle of humanism in the North


Presentation of Karel Vereycken, founder of Agora Erasmus, at a meeting with friends in the Netherlands on September 10, 2011.
The current financial system is bankrupt and will collapse in the coming days, weeks, months or years if nothing is done to end the paradigm of financial globalization, monetarism and free trade.
To exit this crisis implies organizing a break-up of the banks according to principles of the Glass-Steagall Act, an indispensable lever to recreate a true credit system in opposition to the current monetarist system. The objective is to guarantee real investments generating physical and human wealth, thanks to large infrastructure projects and highly qualified and well-paid jobs.
Can this be done? Yes, we can! However, the true challenge is neither economic, nor political, but cultural and educational: how to lay the foundations of a new Renaissance, how to effect a civilizational shift away from green and Malthusian pessimism towards a culture that sets itself the sacred mission of fully developing the creative powers of each individual, whether here, in Africa, or elsewhere.
Is there a historical precedent? Yes, and especially here, from where I am speaking to you this morning (Naarden, Netherlands) with a certain emotion. It probably overwhelms me because I have a rather well informed and precise sense of the role that several key individuals from the region where we are gathered this morning have played and how, in the fourteenth century, they made Deventer, Zwolle and Windesheim an intellectual hotbed and the cradle of the Renaissance of the North which inspired so many worldwide.
Let me summarize for you the history of this movement of lay clerics and teachers: the Brothers and Sisters of the Common Life, a movement that nurished our beloved Erasmus of Rotterdam, the humanist giant from whom we borrowed the name to create our political movement in Belgium.
As very often, it all begins with an individual decision of someone to overcome his shortcomings and give up those « little compromises » that end up making most of us slaves. In doing so, this individual quickly appears as a « natural » leader. Do you want to become a leader? Start by cleaning up your own mess before giving lessons to others!
Geert Groote, the founder

The spiritual father of the Brothers is Geert Groote, born in 1340 and son of a wealthy textile merchant in Deventer, which at that time, like Zwolle, Kampen and Roermond, were prosperous cities of the Hanseatic League.
In 1345, as a result of the international financial crash, the Black Death spread throughout Europe and arrived in the Netherlands around 1449-50. Between a third and a half of the population died and, according to some sources, Groote lost both parents. He abhorred the hypocrisy of the hordes of flagellants who invaded the streets and later advocated a less conspicuous, more interior spirituality.
Groote had talent for intellectual matters and was soon sent to study in Paris. In 1358, at the age of eighteen, he obtained the title of Master of Arts, even though the statutes of the University stipulated that the minimum age required was twenty-one.
He stayed eight years in Paris where he taught, while making a few excursions to Cologne and Prague. During this time, he assimilated all that could be known about philosophy, theology, medicine, canon law and astronomy. He also learned Latin, Greek and Hebrew and was considered one of the greatest scholars of the time.
Around 1362 he became canon of Aachen Cathedral and in 1371 of that of Utrecht. At the age of 27, he was sent as a diplomat to Cologne and to the Court of Avignon to settle the dispute between the city of Deventer and the bishop of Utrecht with Pope Urban V. In principle, he could have met the Italian humanist Petrarch who was there at that time.
Full of knowledge and success, Groote got a big head. His best friends, conscious of his talents, kindly suggested him to detach himself from his obsession with « Earthly Paradise ». The first one was his friend Guillaume de Salvarvilla, the choirmaster of Notre-Dame of Paris. The second was Henri Eger of Kalkar (1328-1408) with whom Groote shared the benches of the Sorbonne.
In 1374, Groote got seriously ill. However, the priest of Deventer refused to administer the last sacraments to him as long as he refused to burn some of the books in his possession. Fearing for his life (after death), he decided to burn his collection of books on black magic. Finally, he felt better and healed. He also gave up living in comfort and lucre through fictitious jobs that allowed him to get rich without working too hard.
After this radical conversion, Groote decides to selfperfect. In his Conclusions and Resolutions he wrote:
« It is to the glory, honor and service of God that I propose to order my life and the salvation of my soul. (…) In the first place, not to desire any other benefit and not to put my hope and expectation from now on in any temporal profit. The more goods I have, the more I will probably want more. For according to the primitive Church, you cannot have several benefits. Of all the sciences of the Gentiles, the moral sciences are the least detestable: many of them are often useful and profitable both for oneself and for teaching others. The wisest, like Socrates and Plato, brought all philosophy back to ethics. And if they spoke of high things, they transmitted them (according to St. Augustine and my own experience) by moralizing them lightly and figuratively, so that morality always shines through in knowledge… ».
Groote then undertakes a spiritual retreat at the Carthusian monastery of Monnikshuizen near Arnhem where he devotes himself to prayer and study.
However, after a three-year stay in isolation, the prior, his Parisian friend Eger of Kalkar, told him to go out and teach :
« Instead of remaining cloistered here, you will be able to do greater good by going out into the world to preach, an activity for which God has given you a great talent. »
Ruusbroec, the inspirer

Groote accepted the challenge. However, before taking action, he decided to make a last trip to Paris in 1378 to obtain the books he needed.
According to Pomerius, prior of Groenendael between 1431 and 1432, he undertook this trip with his friend from Zwolle, the teacher Joan Cele (around 1350-1417), the historical founder of the excellent Dutch public education system, the Latin School.
On their way to Paris, they visit Jan van Ruusbroec (1293-1381), a Flemish “mystic” who lived in the Groenendael Priory on the edge of the Soignes Forest near Brussels.
Groote, still living in fear of God and the authorities, initially tries to make « more acceptable » some of the old sage’s writings while recognizing Ruusbroec as closer to the Lord than he is. In a letter to the community of Groenendael, he requested the prayer of the prior:
« I would like to recommend myself to the prayer of your provost and prior. For the time of eternity, I would like to be ‘the prior’s stepladder’, as long as my soul is united to him in love and respect.” (Note 1)
Back in Deventer, Groote concentrated on study and preaching. First he presented himself to the bishop to be ordained a deacon. In this function, he obtained the right to preach in the entire bishopric of Utrecht (basically the whole part of today’s Netherlands north of the great rivers, except for the area around Groningen).
First he preached in Deventer, then in Zwolle, Kampen, Zutphen and later in Amsterdam, Haarlem, Gouda and Delft. His success is so great that jealousy is felt in the church. Moreover, with the chaos caused by the great schism (1378 to 1417) installing two popes at the head of the church, the believers are looking for a new generation of leaders.
As early as 1374, Groote offered part of his parents’ house to accommodate a group of pious women. Endowed with a by-law, the first house of sisters was born in Deventer. He named them « Sisters of the Common Life », a concept developed in several works of Ruusbroec, notably in the final paragraph Of the Shining Stone (Van den blinckende Steen)
« The man who is sent from this height to the world below, is full of truth, and rich in all virtues. And he does not seek his own, but the honor of the one who sent him. And that is why he is upright and truthful in all things. And he has a rich and benevolent foundation grounded in the riches of God. And so he must always convey the spirit of God to those who need it; for the living fountain of the Holy Spirit is not a wealth that can be wasted. And he is a willing instrument of God with whom the Lord works as He wills, and how He wills. And it is not for sale, but leaves the honor to God. And for this reason he remains ready to do whatever God commands; and to do and tolerate with strength whatever God entrusts to him. And so he has a common life; for to him seeing [via contemplativa] and working [via activa] are equal, for in both things he is perfect.”
Radewijns, the organizer

Following one of his first sermons, Groote recruited Florens Radewijns (1350-1400). Born in Utrecht, the latter received his training in Prague where, also at the early age of 18, he was awarded the title of Magister Artium.
Groote then sent him to the German city of Worms to be consecrated priest there. In 1380 Groote moved with about ten pupils to the house of Radewijns in Deventer; it would later be known as the « Sir Florens House” (Heer Florenshuis), the first house of the Brothers and above all its base of operation?
When Groote died of the plague in 1384, Radewijns decided to expand the movement which became the Brothers and Sisters of the Common Life. Soon it will be branded the Devotio Moderna (Modern Devotion).
Books and beguinages


A number of parallels can be drawn with the phenomenon of the Beguines which flourished from the 13th century onward. (Note 2)
The first beguines were independent women, living alone (without a man or a rule), animated by a deep spirituality and daring to venture into the enormous adventure of a personal relationship with God. (Note 3)
Operating outside the official religious hierarchy, they didn’t beg but worked various jobs to earn their daily bread. The same goes for the Brothers of the Common Life, except that for them, books were at the center of all activities. Thus, apart from teaching, the copying and production of books represented a major source of income while allowing spreading the word to the many.
Lay Brothers and Sisters focused on education and their priests on preaching. Thanks to the scriptorium and printing houses, their literature and music will spread everywhere.
Windesheim
To protect the movement from unfair attacks and criticism, Radewijns founded a congregation of canons regular obeying the Augustinian rule.
In Windesheim, between Zwolle and Deventer, on land belonging to Berthold ten Hove, one of the members, a first cloister is erected. A second one, for women this time, is built in Diepenveen near Arnhem. The construction of Windesheim took several years and a group of brothers lived temporarily on the building site, in huts.
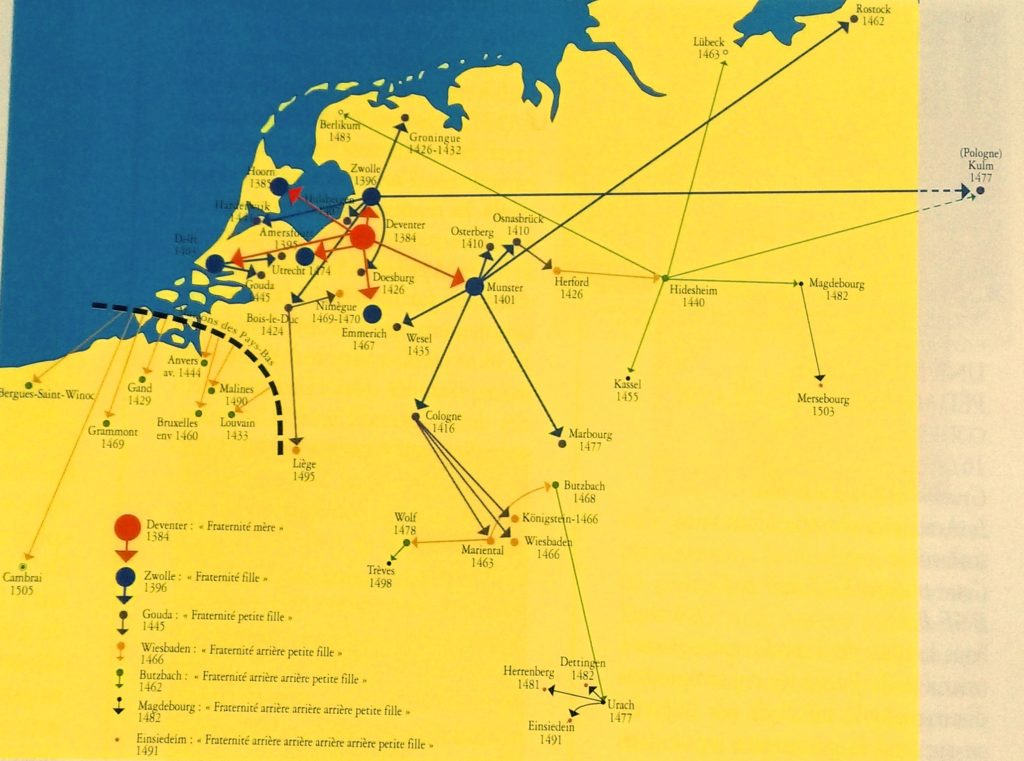
In 1399 Johannes van Kempen, who had stayed at Groote’s house in Deventer, became the first prior of the cloister of Mont Saint-Agnès near Zwolle and gave the movement new momentum. From Zwolle, Deventer and Windesheim, the new recruits spread all over the Netherlands and Northern Europe to found new branches of the movement.
In 1412, the congregation had 16 cloisters and their number reached 97 in 1500: 84 priories for men and 13 for women. To this must be added a large number of cloisters for canonesses which, although not formally associated with the Windesheim Congregation, were run by rectors trained by them.
Windesheim was not recognized by the Bishop of Utrecht until 1423 and in Belgium, Groenendael, associated with the Red Cloister and Korsendonc, wanted to be part of it as early as 1402.
Thomas a Kempis, Cusanus and Erasmus

Johannes van Kempen was the brother of the famous Thomas a Kempis (1379-1471). The latter, trained in Windesheim, animated the cloister of Mont Saint-Agnès near Zwolle and was one of the towering figures of the movement for seventy years. In addition to a biography he wrote of Groote and his account of the movement, his Imitatione Christi (The Imitation of Christ) became the most widely read work in history after the Bible.
Both Rudolf Agricola (1444-1485) and Alexander Hegius (1433-1498), two of Erasmus’ tutors during his training in Deventer, were direct pupils of Thomas a Kempis. The Latin School of Deventer, of which Hegius was rector, was the first school in Northern Europe to teach the ancient Greek language to children.

While no formal prove exists, it is tempting to believe that Cusanus (1401-1464), who protected Agricola and, in his last will, via his Bursa Cusanus, offered a scholarship for the training of orphans and poor students of the Brothers of the Common Life in Deventer, was also trained by this humanist network.
What is known is that when Cusanus came in 1451 to the Netherlands to put the affairs of the Church in order, he traveled with his friend Denis the Carthusian (van Rijkel) (1402-1471), a disciple of Ruusbroec, whom he commissioned to carry on this task.
A native of Limburg, trained at the famous Cele school in Zwolle, Dionysius the Carthusian also became the confessor of the Duke of Burgundy and is thought to be the “theological advisor” of the Duke’s ambassador and court painter, Jan Van Eyck. (Note 4)
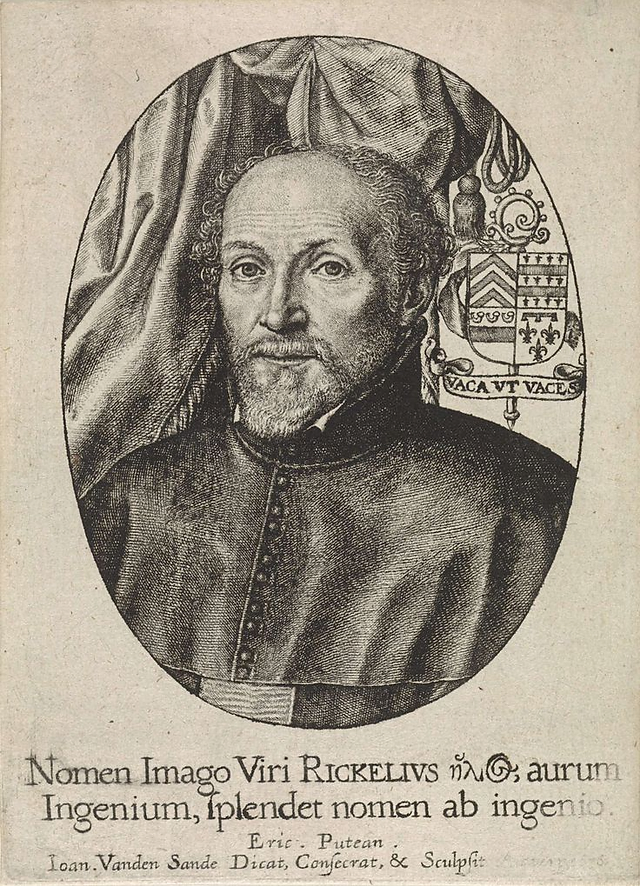
Gansfort

Wessel Gansfort (1419-1489), another exceptional figure of this movement was at the service of the Greek Cardinal Bessarion, the main collaborator of Nicolas of Cusa (Cusanus) at the Council of Ferrara-Florence of 1437. Gansfort, after attending the Brothers’ school in Groningen, was also trained by Joan Cele‘s Latin school in Zwolle.
The same goes for the first and only Dutch pope, Adrianus VI, who was trained in the same school before completing his training with Hegius in Deventer. This pope was very open to Erasmus’ reformist ideas… before arriving in Rome.
Hegius, in a letter to Gansfort, which he calls Lux Mundi (Light of the World), wrote:
« I send you, most honorable lord, the homilies of John Chrysostom. I hope that you will enjoy reading them, since the golden words have always been more pleasing to you than the pieces of this metal. As you know, I went to the library of Cusanus. There I found some books that I didn’t know existed (…) Farewell, and if I can do you a favor, let me know and consider it done.”
Rembrandt

A quick look on Rembrandt’s intellectual training indicates that he too was a late product of this educational epic. In 1609, Rembrandt, barely three years old, entered elementary school where, like other boys and girls of his generation, he learned to read, write and… draw.
The school opened at 6 in the morning, at 7 in the winter, and closes at 7 in the evening. Classes begin with prayer, reading and discussion of a passage from the Bible followed by the singing of psalms. Here Rembrandt acquired an elegant writing style and much more than a rudimentary knowledge of the Gospels.
The Netherlands wanted to survive. Its leaders take advantage of the twelve-year truce (1608-1618) to fulfill their commitment to the public interest.
In doing so, the Netherlands at the beginning of the XVIIth century became the first country in the world where everyone had the chance to learn to read, write, calculate, sing and draw.
This universal educational system, no matter what its shortcomings, available to both rich and poor, boys and girls alike, stands as the secret behind the Dutch « Golden Century ». This high level of education also created those generations of active Dutch emigrants a century later in the American Revolution.
While others started secondary school at the age of twelve, Rembrandt entered the Leyden Latin School at the age of 7. There, the students, apart from rhetoric, logic and calligraphy, learn not only Greek and Latin, but also foreign languages such as English, French, Spanish or Portuguese. Then, in 1620, at the age of 14, with no laws restricting young talents, Rembrandt enrolled in University. The subject he chose was not Theology, Law, Science or Medicine, but… Literature.
Did he want to add to his knowledge of Latin the mastery of Greek or Hebrew philology, or possibly Chaldean, Coptic or Arabic? After all, Arabic/Latin dictionaries were already being published in Leiden at a time the city was becoming a major printing center in the world.
Thus, one realizes that the Netherlands and Belgium, first with Ruusbroec and Groote and later with Erasmus and Rembrandt, made an essential contribution in the not so distant past to the kind of humanism that can raise today humanity to its true dignity.
Hence, failing to extend our influence here, clearly seems to me something in the realm of the impossible.

Footnotes:
- Geert Groote, who discovered Ruusbroec’s work during his spiritual retreat at the Carthusian monastery of Monnikshuizen, near Arnhem, has translated at least three of his works into Latin. He sent The Book of the Spiritual Tabernacle to the Cistercian Cloister of Altencamp and his friends in Amsterdam. The Spiritual Marriage of Ruusbroec being under attack, Groote personally defends it. Thus, thanks to his authority, Ruusbroec’s works are copied in number and carefully preserved. Ruusbroec’s teaching became popularized by the writings of the Modern Devotion and especially by the Imitation of Christ.
- At the beginning of the 13th century the Beguines were accused of heresy and persecuted, except… in the Burgundian Netherlands. In Flanders, they are cleared and obtain official status. In reality, they benefit from the protection of two important women: Jeanne and Margaret of Constantinople, Countess of Flanders. They organized the foundation of the Beguinages of Louvain (1232), Gent (1234), Antwerp (1234), Kortrijk (1238), Ypres (1240), Lille (1240), Zoutleeuw (1240), Bruges (1243), Douai (1245), Geraardsbergen (1245), Hasselt (1245), Diest (1253), Mechelen (1258) and in 1271 it was Jan I, Count of Flanders, in person, who deposited the statutes of the great Beguinage of Brussels. In 1321, the Pope estimated the number of Beguines at 200,000.
- The platonic poetry of the Beguine, Hadewijch of Antwerp (XIIIth Century) has a decisive influence on Jan van Ruusbroec.
- It is significant that the first book printed in Flanders in 1473, by Erasmus’ friend and printer Dirk Martens, is precisely a work of Denis the Carthusian.
Erasmus’ dream: the Leuven Three Language College


In autumn 2017, a major exhibit organized at the University library of Leuven and later in Arlon, also in Belgium, attracted many people. Showing many historical documents, the primary intent of the event was to honor the activities of the famous Three Language College (Collegium Trilingue), founded in 1517 by the efforts of the Christian Humanist Erasmus of Rotterdam (1467-1536) and his allies. Though modest in size and scope, Erasmus’ initiative stands out as one of the cradles of European civilization, as you will discover here.

Revolutionary political figures, such as William the Silent (1533-1584), organizer of the Revolt of the Netherlands against the Habsburg tyranny, humanist poets and writers such as Thomas More, François Rabelais, Miguel Cervantes and William Shakespeare, all of them, recognized their intellectual debt to the great Erasmus of Rotterdam, his exemplary fight, his humor and his great pedagogical project.
For the occasion, the Leuven publishing house Peeters has taken through its presses several nice catalogues and essays, published in Flemish, French as well as English, bringing together the contributions of many specialists under the wise (and passionate) guidance of Pr Jan Papy, a professor of Latin literature of the Renaissance at the Leuven University, with the assistance of a “three language team” of Latinists which took a fresh look at close to all the relevant and inclusively some new documents scattered over various archives.
“The Leuven Collegium Trilingue: an appealing story of courageous vision and an unseen international success. Thanks to the legacy of Hieronymus Busleyden, counselor at the Great Council in Mechelen, Erasmus launched the foundation of a new college where international experts would teach Latin, Greek and Hebrew for free, and where bursaries would live together with their professors”, reads the back cover of one of the books.

For the researchers, the issue was not necessarily to track down every detail of this institution but rather to answer the key question: “What was the ‘magical recipe’ which attracted rapidly to Leuven between three and six hundred students from all over Europe?”
Erasmus’ initiative was unprecedented. Having an institution, teaching publicly Latin and, on top, for free, Greek and Hebrew, two languages considered “heretic” by the Vatican, was already tantamount to starting a revolution.
Was it that entirely new? Not really. As early as the beginning of the XIVth century, for the Italian humanists in contact with Greek erudites in exile in Venice, the rigorous study of Greek, Hebraic and Latin sources as well as the Fathers and the New Testament, was the method chosen by the humanists to free mankind from the Aristotelian worldview suffocating Christianity and returning to the ideals, beauty and spirit of the “Primitive Church”.
For Erasmus, as for his inspirer, the Italian humanist Lorenzo Valla (1403-1457), the « Philosophy of Christ » (agapic love), has to come first and opens the road to end the internal divisions of Christianity and to uproot the evil practices of greed (indulgences, simony) and religious superstition (cult of relics) infecting the Church from the top to the bottom, and especially the mendicant orders.
To succeed, Erasmus sets out to clarify the meaning of the Holy Writings by comparing the originals written in Greek, Hebrew and Latin, often polluted following a thousand years of clumsy translations, incompetent copying and scholastic commentaries.
Brothers of the Common Life
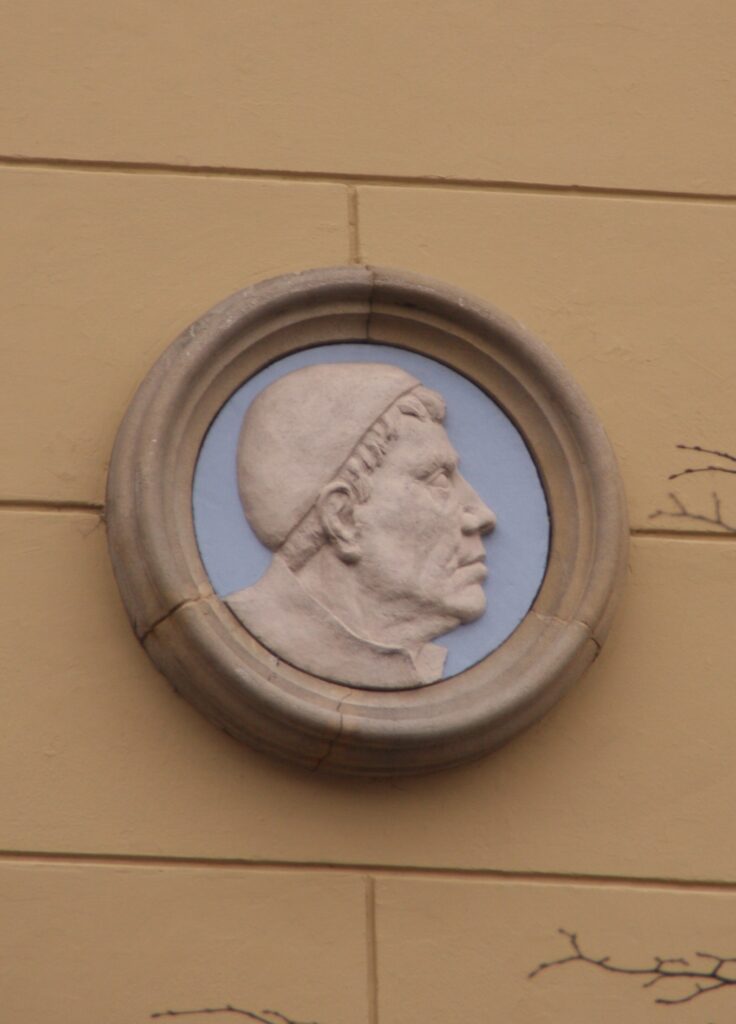



My own research allows me to recall that Erasmus was a true disciple of the Sisters and Brothers of the Common Life of Deventer in the Netherlands, a hotbed of humanism in Northern Europe. The towering figures that founded this lay teaching order are Geert Groote (1340-1384), Florent Radewijns (1350-1400) and Wessel Gansfort (1420-1489), all three said to be fluent in precisely these three languages.
The religious faith of this current, also known as the “Modern Devotion”, centered on interiority, as beautifully expressed in the little book of Thomas a Kempis (1380-1471), the Imitation of Christ. This most read book after the Bible, underlines the importance for the believer to conform one owns life to that of Christ who gave his life for mankind.
Rudolph Agricola
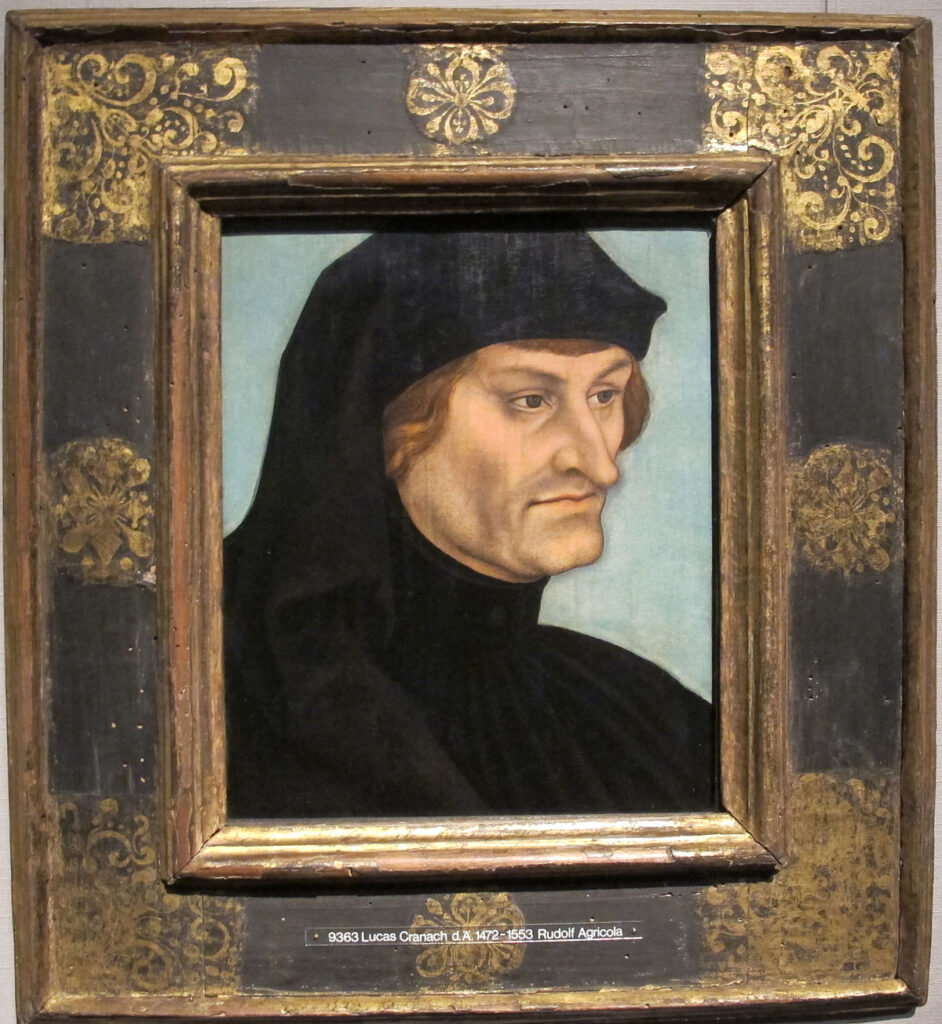

Hence, in 1475, Erasmus father, fluent in Greek and influenced by famous Italian humanists, sends his son to the chapter of the Brothers of the Common Life in Deventer, at that time under the direction of Alexander Hegius (1433-1499), himself a pupil of the famous Rudolph Agricola (1442-1485) which Erasmus had the chance to listen to and which he calls a “divine intellect”.
Follower of the cardinal-philosopher Nicolas of Cusa (1401-1464), enthusiastic advocate of the Italian Renaissance and the Good Letters, Agricola would tease his students by saying:
“Be cautious in respect to all that you learned so far. Reject everything! Start from the standpoint you will have to un-learn everything, except that what is based on your sovereign authority, or on the basis of decrees by superior authors, you have been capable of re-appropriating yourself”.
Erasmus, with the foundation of the Collegium Trilingue will carry this ambition at a level unreached before. To do so, Erasmus and his friend apply a new pedagogy. Hence, instead of learning by heart medieval commentaries, pupils are called to formulate their proper judgment and take inspiration of the great thinkers of the Classical period, especially “Saint Socrates”. Latin, a language that degenerated during the Roman Empire, will be purified from barbarisms.
With this approach, for pupils, reading a major text in its original language is only the start. An explorative work is required: one has to know the history and the motivations of the author, his epoch, the history of the laws of his country, its geography, cosmography, all considered to be indispensable instruments to put each text in its specific literary and historical context and allowing reading, beyond the words, the intention of their author.

This “modern” approach (questioning, critical study of sources, etc.) of the Collegium Trilingue, after having demonstrated its efficiency by clarifying the message of the Gospel, will rapidly travel over Europe and reach many other domains of knowledge, notably scientific issues! By uplifting young talents, out of the small and sleepy world of scholastic certitudes, this institution rapidly grew into a hotbed for creative minds.
For the ignorant reader who often considers Erasmus as some kind of comical writer praising madness which lost it after an endless theological dispute with Martin Luther, such a statement might come as a surprise.
Scientific Renaissance

While Belgium’s contributions to science, under Emperor Charles Vth, are broadly recognized and respected, few are those understanding the connection uniting Erasmus with a mathematician as Gemma Frisius and his pupil and friend Gerard Mercator, an anatomist such as Andreas Vesalius or a botanist such as Rembert Dodonaeus.
Hence, as already thoroughly documented in 2011 by Professor Jan Papy in a remarkable article, the scientific renaissance which bloomed in the Netherlands and Belgium in the early XVIth century, could not have taken place if it were for the “linguistic revolution” provoked by the Collegium Trilingue.
Because, beyond the mastery of their vernacular languages (French and Dutch), hundreds of youth, by studying Greek, Latin and Hebrew, suddenly got access to all the scientific treasures of Greek Philosophy and the best authors in those newly discovered languages.

At last, they could read Plato in the text, but also Anaxagoras, Heraclites, Thales of Millet, Eudoxus of Cnidus, Pythagoras, Eratosthenes, Archimedes, Galen, Vitruvius, Pliny the elder, Euclid and Ptolemy whose work they will master and eventually correct.
As the books published by Peeters account in great detail, during the first century of its existence, the Collegium Trilingue had a rough time confronting political uproar and religious strife. Heavy critique came especially form the “traditionalists”, a handful of theologians for which the Greeks were nothing but schismatics and the Jews the assassins of Christ and esoterics.
The opposition was such that Erasmus himself never could teach at the Collegium and, while keeping in close contact, decided to settle in Basel, Switzerland, in 1521.
Despite all of this, the Erasmian revolution conquered Europe overnight and a major part of the humanists of that period were trained or influenced by this institution. From abroad, hundreds of pupils arrived to follow classes given by professors of international reputation.
27 European universities integrated pupils of the Collegium in their teaching staff: among them stood Jena, Wittenberg, Cologne, Douai, Bologna, Avignon, Franeker, Ingolstadt, Marburg, etc.
Teachers at the Collegium were secured a decent income so that they weren’t obliged to give private lectures to secure a living and could offer public classes for free. As was the common practice of the Brothers of the Common Life in Deventer, a system of bursa allowed talented though poor students, including many orphans, to have access to higher learning. “Something not necessarily unusual those days, says Pr Jan Papy, and done for the sake of the soul of the founder (of the Collegium, reference to Busleyden)”.

While visiting Leuven and contemplating the worn-out steps of the spiral staircase (wentelsteen), one of the last remains of the building that had a hard time resisting the assaults of time and ignorance, one can easily imagine those young minds jumping down the stairs with enthusiasm going from the dormitory to the classroom. Looking at the old shopping list of the school’s kitchen one can conclude the food was excellent with lots of meat, poultry but also vegetables and fruits, and sometimes wine from Beaune in Burgundy, especially when Erasmus came for a visit! While over the years, of course, the quality of the learning transmitted, would vary in accordance with the excellence of its teachers, the Collegium Trilingue, whose activity would last till the French revolution, gave its imprint in history by giving birth to what some have called the “Little Renaissance” of the first half of the XVIth century.
In France, the Sorbonne University reacted with fear and in 1523, the study of Greek was outlawed in France.

François Rabelais, at that time a monk in Vendée, saw his books confiscated by the prior of his monastery and deserts his order. Later, as a doctor, he translated the medical writings of the Greek scientist Galen from Greek into French. Rabelais’s letter to Erasmus shows the highest possible respect and intellectual debt to Erasmus.
In 1530, Marguerite de Navarre, sister of King Francis, and reader and admirer of Erasmus, at war with the Sorbonne, convinced her brother to allow Guillaume Budé, a friend of Erasmus, to create the “Collège des Lecteurs Royaux” (ancestor of the Collège de France) on the model of the Collegium Trilingue. And to protect its teachers, many coming directly from Leuven, they got the title of “advisors” of the King. The Collège taught Latin, Hebrew and Greek, and rapidly added Arab, Syriac, medicine, botany and philosophy to its curriculum.
Dirk Martens

Also celebrated for the occasion, Dirk Martens (1446-1534), rightly considered as one of the first humanists to introduce printing in the Southern Netherlands.
Born in Aalst in a respected family, the young Dirk got his training at the local convent of the Hermits of Saint William. Eager to know the world and to study, Dirk went abroad. In Venice, at that time a cosmopolite center harboring many Greek erudite in exile, Dirk made his first steps into the art of printing at the workshop of Gerardus de Lisa, a Flemish musician who set up a small printing shop in Treviso, close to Venice.
Back in Aalst, together with his partner John of Westphalia, Martens printed in 1473 the first book in the country with a movable type printing press, a treatise of Dionysius the Carthusian (1401-1471), a friend and collaborator of cardinal-philosopher Nicolas of Cusa, as well as the spiritual advisor of Philip the Good, the Duke of Burgundy and thought to be the occasional « theological » advisor of the latter’s court painter, Jan Van Eyck.
If the oldest printed book known to us is a Chinese Buddhist writing dating from 868, the first movable printing types, made first out of wood and then out of hardened porcelain and metal, came from China and Korea in 1234.

The history of two lovers, a poem written by Aeneas Piccolomini before he became the humanist Pope Pius II, was another early production of Marten’s print shop in Aalst.
Proud to have introduced this new technique allowing a vast increase in the spreading of good and virtuous ideas, Martens wrote in one of the prefaces: “This book was printed by me, Dirk Martens of Aalst, the one who offered the Flemish people all the know-how of Venice”.
After some years in Spain, Martens returned to Aalst and started producing breviaries, psalm books and other liturgical texts. While technically elaborate, the business never reached significant commercial success.
Martens then moved to Antwerp, at that time one of the main ports and cross-roads of trade and culture. Several other Flemish humanists born in Aalst played eminent roles in that city and animate its intellectual and cultural life. Among these:
—Cornelis De Schrijver (1482-1558), the secretary of the City of Aalst, better known under his latin name Scribonius and later as Cornelius Grapheus. Writer, translator, poet, musician and friend of Erasmus, he was accused of heresy and hardly escaped from being burned at the stake.
—Pieter Gillis (1486-1533), known as Petrus Aegidius. Pupil of Martens, he worked as a corrector in his company before becoming Antwerp’s chief town clerk. Friend of Erasmus and Thomas More, he appears with Erasmus in the double portrait painted by another friend of both, Quinten Metsys (1466-1530).
—Pieter Coecke van Aelst (1502-1550), editor, painter and scenographer. After a trip to Italy, he set up a workshop in Antwerp. Pieter will produce patrons for tapestries, translated with the help of his wife the works of the Roman architect Vitruvius into Dutch and trained the young Flemish painter Bruegel the Elder who will marry his daughter.
Invention of pocket books
In Antwerp, Martens became part of this milieu and his workshop became a meeting place for painters, musicians, scientists, poets and writers. With the Collegium Trilingue, Martens opens a second shop, this time in Leuven to work with Erasmus. In order to provide adequate books to the Collegium, Martens proudly became, in the footsteps of the Venetian Printer Aldo Manuce, one of the first printers to concentrate on in-octavo 8° (22 x 12 cm), i.e. “pocket” size books affordable by all and which students could take home !
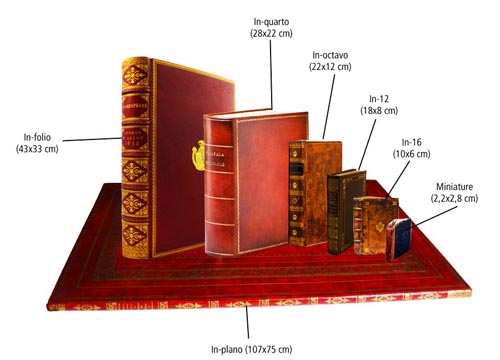
For the specialists of the Erasmus house of Anderlecht, close to Brussels,
“Martens innovated in nearly all domains. As well as in terms of printing types as lay-out. He was the first to introduce Italics, Greek and Hebrew letter types. He also generalized the use of ‘New Roman’ letter type so familiar today. During the first thirty years of the XVIth century, he also operated the revolution in lay-out (chapters and paragraphs) that gave birth to the modern book as we know it today. All this progress, he achieved in close cooperation with Erasmus”.
Thomas More’s Utopia

In 1516, it was Dirk Martens who printed the first edition of Thomas More’s Utopia. Among the hundreds of editions he printed mostly alone, 61 books and writings of Erasmus, notably In Praise of Folly. He also produced More’s edition of the roman satirist Lucian and Columbus’ account of the discovery of the new world. In 1423, Martens printed the complete works of Homer, quite a challenge!
In 1520, a papal bull of Leo X condemned the errors of Martin Luther and ordered the confiscation of his writings to be burned in public in front of the clergy and the people.
For Erasmus, burning books didn’t automatically erased their their content from the minds of the people. “One starts by burning books, one finishes by burning people” Erasmus warned years before Heinrich Heine said that “There, were one burns books, one ends up burning people”.
Printers and friends of Erasmus, especially in France, died on the stake opening the doors for the religious wars that will ravage Europe for the century to come.
What Erasmus feared above all, is that with the Vatican’s brutal war against Luther, it is the entire cultural renaissance and the learning of languages that got threatened with extinction.
In July 1521, confronted with the book burning, the German painter and engraver Albrecht Dürer, who made his living with bible illustrations, left Antwerp with his wife to return to his native Nuremberg.
Thirty years later, in 1552, the great cartographer Gerardus Mercator, a brilliant pupil of the Collegium Trilingue, for having called into question the views of Aristotle, went into exile and settled in Duisbourg, Germany.
In 1521, at the request of his friends who feared for his life, Erasmus left Leuven for Basel and settled in the workshop of another humanist, the Swiss printer Johann Froben.
In 1530, with a foreword of Erasmus, Froben published Georgius Agricola’s inventory of mining techniques, De Re Metallica, a key book that vastly contributed to the industrial revolution of Saxen, Switzerland, Germany and the whole of Europe.
Conclusion
If certain Catholic historians try to downplay the hostility of their Church towards Erasmus, the fact remains that between 1559 and 1900, the full works of Erasmus were on the “Index Vaticanus” and therefore “forbidden readings” for Catholics.
If Thomas More, whom Erasmus considered as his twin brother, was canonized by Pius XI in 1935 and recognized as the patron saint of the political leaders, Erasmus himself was never rehabilitated.
Interrogated by this author in a letter, the Pope Francis returned a polite but evasive answer.
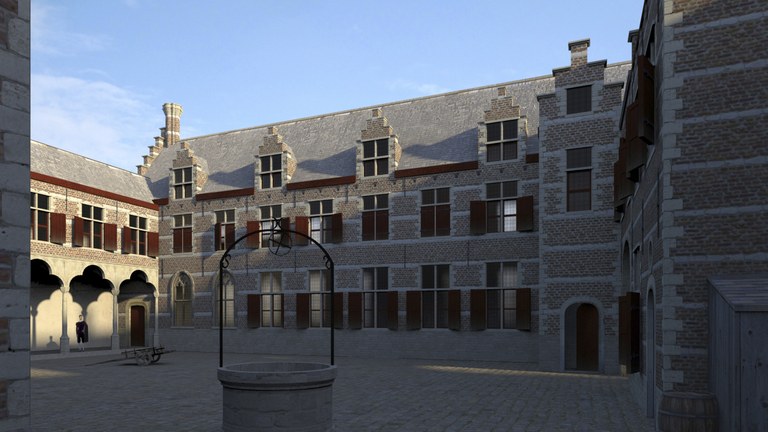

Let’s rebuild the Collegium Trilingue !
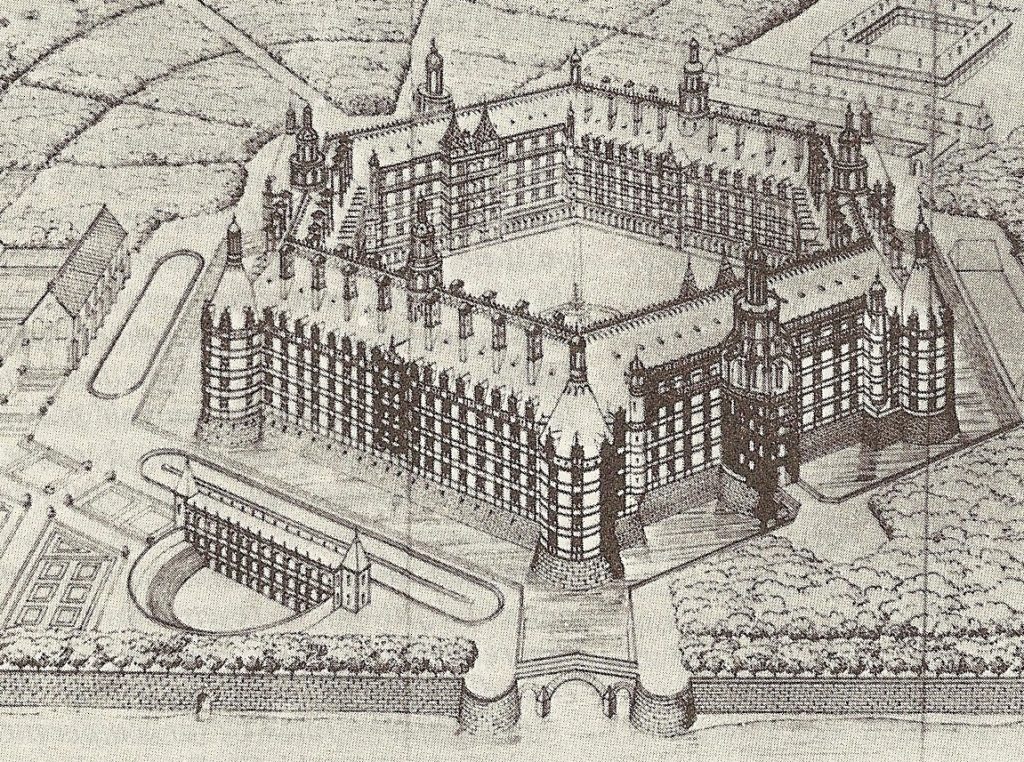
With the exception of the staircase, only a few stones remain of the historical building housing the Collegium Trilingue. In 1909, the University of Louvain planned to buy up and rebuild the site but the First World War changed priorities. Before becoming social housing, part of the building was used as a factory. As a result, today, there is no overwhelming charm. However, seeing the historical value of the site, we cannot but fully support a full reconstruction plan of the building and its immediate environment.
It would make the historical center of Leuven so much nicer, so much more attractive and very much more loyal to its own history. On top, such a reconstruction wouldn’t cost much and might interest private investors. The images in 3 dimensions produced for the Leuven exhibit show a nice Flemish Renaissance building, much in the style of the marvels constructed by architect Rombout II Keldermans.
Every period has the right to honestly “re-write” its own history, without falsifications, according to its own vision of the future.
It has to be noted here that the world famous “Rubenshuis” in Antwerp, is not at all the original building, but a scrupulous reconstruction of the late 1930s.
Le « rêve d’Erasme », le Collège des Trois Langues de Louvain


REVUE DE LIVRE :
Le Collège des Trois Langues de Louvain (1517-1797)
Erasme, les pratiques pédagogiques humanistes et le nouvel institut des langues.
Sous la direction de Jan Papy, avec les contributions de Gert Gielis, Pierre Swiggers, Xander Feys & Dirk Sacré, Raf Van Rooy & Toon Van Hal, Pierre Van Hecke.
Edition Peeters, Louvain 2018.
230 pages, 60 €.
__________________________________________________________________

En Belgique, il y a un an, dans la vieille ville universitaire de Louvain, et ensuite à Arlon, une exposition très intéressante a échappé à notre attention.
Réunissant des documents historiques, gravures et manuscrits de la bibliothèque universitaire ainsi que de nombreuses pièces de l’étranger, du 19 octobre 2017 au 18 janvier 2018, l’évènement a voulu, à l’occasion du 500e anniversaire de sa fondation, retracer l’origine et mettre à honneur l’activité du fameux « Collège Trilingue » érigé en 1517 grâce aux efforts du grand humaniste chrétien Erasme de Rotterdam (1467-1536).
Quand on parle de civilisation européenne, c’est bien cette institution, bien que peu connue et de taille modeste, qui en fut l’un des artisans majeurs.
Car tout comme Guillaume le Taciturne (1533-1584), l’organisateur de la révolte des Pays-Bas contre la tyrannie habsbourgeoise, les visionnaires More, Rabelais, Cervantès et Shakespeare s’inspireront de son combat exemplaire, de sa verve et de son grand projet pédagogique.

L’occasion pour les Editions Peeters de Louvain de consacrer à cet anniversaire un beau catalogue et plusieurs recueils, publiés aussi bien en néerlandais, en français, qu’en anglais, réunissant les contributions de plusieurs spécialistes sous l’œil avisé (et passionné) de Jan Papy, professeur de littérature latine de la Renaissance à l’Université de la ville, appuyé d’une « équipe trilingue louvainiste » qui n’a pas épargné ses efforts pour relire attentivement toutes les publications ayant trait au sujet et explorer des sources nouvelles dans diverses archives d’Europe.
L’histoire de cet établissement humaniste en est une non seulement d’une remarquable visée scientifique et pédagogique, mais aussi d’efforts obstinés, voire de combats courageux, couronnés d’un succès international sans précédent. Mettant à profit le legs de Jérôme de Busleyden (1470-1517), conseiller au Grand Conseil de Malines, décédé en août 1517, Érasme s’attela aussitôt à la création d’un collège où des savants de renommée internationale prodigueraient un enseignement public et gratuit du latin, du grec et de l’hébreu. Dans ce collège ‘trilingue’, étudiants-boursiers et professeurs vivaient ensemble.
peut-on lire sur la jaquette du catalogue de plus de 200 pages.
Pour les chercheurs, il ne s’agissait pas de retracer de façon exhaustive l’histoire de cette entreprise mais de répondre à la question :
Quelle fut la ‘recette magique’ qui a permis d’attirer aussi rapidement à Louvain entre trois et six cents étudiants venant de partout en Europe ?

En tout cas, la chose est inédite, car, à l’époque, rien que le fait d’enseigner et en plus gratuitement, le grec et l’hébreu —considéré par le Vatican comme hérétique— est déjà révolutionnaire. Et ceci, bien que, dès le XIVe siècle, initié par les humanistes italiens au contact des érudits grecs exilés en Italie, l’examen des sources grecques, hébraïques et latines et la comparaison rigoureuse des grands textes aussi bien des pères de l’Eglise que de l’Evangile, est la voie choisie par les humanistes pour libérer l’humanité de la chape de plomb aristotélicienne qui étouffe la Chrétienté et de faire renaître l’idéal, la beauté et le souffle de l’église primitive.
Pour Erasme, comme l’avait fait avant lui Lorenzo Valla (1403-1457), en promouvant ce qu’il appelle « la philosophie du Christ », il s’agit d’unir la chrétienté en mettant fin aux divisions internes résultant de la cupidité (les indulgences, la simonie, etc.) et des pratiques de superstition religieuse (culte des reliques) qui infectent l’Eglise de haut en bas, en particulier les ordres mendiants.
Pour y arriver, Erasme désire reprendre l’Evangile à sa source, c’est-à-dire comparer les textes d’origine en grec, en latin et en hébreux, souvent inconnus ou sinon entièrement pollués par plus de mille ans de copiages et de commentaires scolastiques.
Frères de la Vie Commune

Mes recherches propres me permettent de rappeler qu’Erasme est un disciple des Sœurs et Frères de la Vie commune de Deventer au Pays-Bas. Les figures fondatrices et emblématiques de cet ordre laïc et enseignant sont Geert Groote (1340-1384), Florent Radewijns (1350-1400) et Wessel Gansfort (1420-1489) dont on croit savoir qu’ils maitrisaient précisément ces trois langues.
Le piétisme de ce courant dit de la « Dévotion Moderne », centré sur l’intériorité, s’articule à merveille dans le petit livre de Thomas a Kempis (1380-1471), L’imitation de Jésus Christ. Celui-ci souligne l’exemple personnel à suivre de la passion du Christ tel que nous l’enseigne l’Evangile, message qu’Erasme reprendra.

En 1475, le père d’Erasme, qui maîtrise le grec et aurait écouté des humanistes réputés en Italie, envoie son fils de neuf ans au chapitre des frères de Deventer, à l’époque dirigé par Alexandre Hegius (1433-1498), élève du célèbre Rudolphe Agricola (1442-1485), qu’Erasme a eu la possibilité d’écouter et qu’il appelle un « intellect divin ».
Disciple du cardinal-philosophe Nicolas de Cues (1401-1464), défenseur enthousiaste de la renaissance italienne et des belles lettres, Agricola a comme habitude de secouer ses élèves en leur lançant :
Soyez méfiant à l’égard de tout ce que vous avez appris jusqu’à ce jour. Rejetez tout ! Partez du point de vue qu’il faut tout désapprendre, sauf ce que, sur la base de votre autorité propre, ou sur la base du décret d’auteurs supérieurs, vous avez été capable de vous réapproprier.
Erasme reprend cet élan et, avec la fondation du Collège Trilingue, le portera à des hauteurs inédites. Pour ce faire, Erasme et ses amis appliqueront une nouvelle pédagogie.
Désormais, au lieu d’apprendre par cœur des commentaires médiévaux, les élèves doivent formuler leur propre jugement en s’inspirant des grands penseurs de l’antiquité classique, notamment « Saint Socrate », et ceci dans un latin purgé de ses barbarismes. Dans cette approche, lire un grand texte dans sa langue originale n’est que la base.
Vient ensuite tout un travail exploratoire : il faut connaître l’histoire et les motivations de l’auteur, son époque, l’histoire des lois de son pays, l’état de la science et du droit, la géographie, la cosmographie, comme des instruments indispensables pour situer les textes dans leur contexte littéraire et historique.

Cette approche « moderne » (questionnement, étude critique des sources, etc.) du Collège Trilingue, après avoir fait ses preuves en clarifiant le message de l’Evangile, se répand alors rapidement à travers toute l’Europe et surtout s’étend à toutes les matières, notamment scientifiques !
En sortant les jeunes talents du monde étroit et endormi des certitudes scolastiques, l’institution devient un formidable incubateur d’esprits créateurs.
Certes, cela peut étonner le lecteur français pour qui Erasme n’est qu’un littéraire comique qui se serait perdu dans une dispute théologique sans fin contre Luther. Si l’on admet généralement que sous Charles Quint, les Pays-Bas et l’actuelle Belgique ont apporté leurs contributions à la science, peu nombreux sont ceux qui comprennent le lien unissant Erasme avec la démarche d’un mathématicien tel que Gemma Frisius, d’un cartographe comme Gérard Mercator, d’un anatomiste comme André Vésale ou d’un botaniste comme Rembert Dodoens.
Or, comme l’avait déjà documenté en 2011 le professeur Jan Papy dans un article remarquable, en Belgique et aux Pays-Bas, la Renaissance scientifique de la première moitié du XVIe siècle, n’a été possible que grâce à la « révolution linguistique » provoquée par le Collège Trilingue.
Car, au-delà de leurs langues vernaculaires, c’est-à-dire le français et le néerlandais, des centaines de jeunes, étudiant le grec, le latin et l’hébreu, accèderont d’un coup, à toutes les richesses scientifiques de la philosophie grecque, des meilleurs auteurs latins, grecs et hébreux. Enfin, ils purent lire Platon dans le texte, mais aussi Anaxagore, Héraclite, Thalès, Eudoxe de Cnide, Pythagore, Ératosthène, Archimède, Galien, Vitruve, Pline, Euclide et Ptolémée dont ils reprennent les travaux pour les dépasser ensuite.

Comme le retracent en détail les œuvres publiées par les Editions Peeters, dans le premier siècle de son existence, le collège dut traverser des moments difficiles à une époque fortement marquée par des troubles politiques et religieux.
Le Collège Trilingue, près du Marché aux poissons, au centre de Louvain, a notamment dû affronter de nombreuses critiques et attaques de la part d’adversaires « traditionalistes », en particulier certains théologiens pour qui, en gros, les Grecs n’étaient que des schismatiques et les Juifs les assassins du Christ et des ésotériques. L’opposition fut telle qu’en 1521, Erasme quitte Louvain pour Bâle en Suisse, sans perdre contact avec l’institution.
En dépit de cela, la démarche érasmienne a d’emblée conquis toute l’Europe et tout ce qui comptait alors parmi les humanistes sortait de cette institution. De l’étranger, des centaines d’étudiants y accouraient pour suivre gratuitement les cours donnés par des professeurs de réputation internationale. 27 universités européennes ont nommé dans leur corps professoral d’anciens étudiants du Trilingue : Iéna, Wittenberg, Cologne, Douai, Bologne, Avignon, Franeker, Ingolstadt, Marburg, etc.
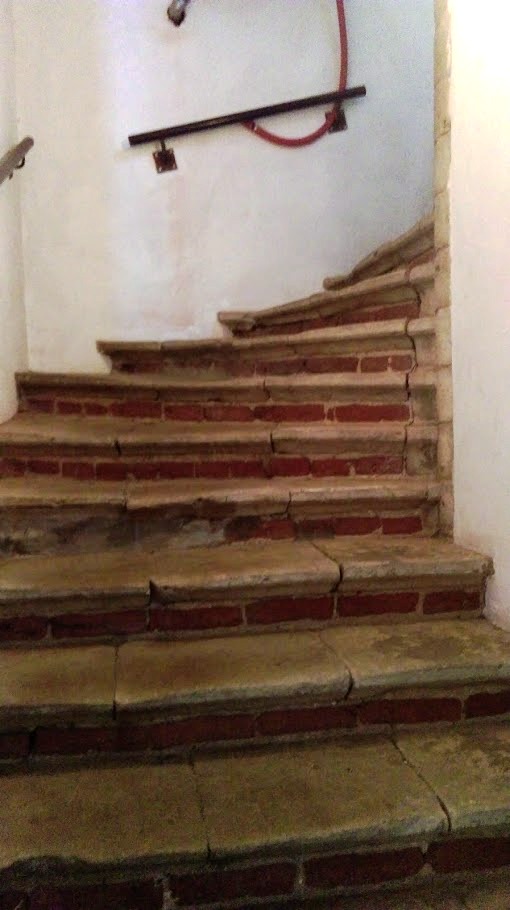

Comme à Deventer chez les Frères de la Vie Commune, un système de bourses permet à des élèves pauvres mais talentueux, notamment les orphelins, d’accéder aux études. « Une chose pas forcément inhabituelle à l’époque, précise Jan Papy, et entreprise pour le salut de l’âme du fondateur (du Collège, c’est-à-dire Jérôme Busleyden) ».
En contemplant les marches usées jusqu’à la corde de l’escalier tournant en pierre (Wentelsteen), l’un des rares vestiges du bâtiment d’alors qui a résisté à l’assaut du temps et du mépris, on imagine facilement les pas enthousiastes de tous ses jeunes élèves quittant leur dortoir situé à l’étage. Comme l’indiquent les registres des achats de la cuisine du Collège Trilingue, pour l’époque, la nourriture y est excellente, beaucoup de viande, de la volaille, mais également des fruits, des légumes, et parfois du vin de Beaune, notamment lorsque Erasme y est reçu.
Avec le temps, la qualité de son enseignement a forcément variée avec celle de ses enseignants, le Collège Trilingue, dont l’activité a perduré pendant longtemps après la mort d’Erasme, a imprimé sa marque sur l’histoire en engendrant ce qu’on qualifie parfois de « petite Renaissance » du XVIe siècle.
Erasme, Rabelais et la Sorbonne
Quitte à nous éloigner du contenu du catalogue, nous nous permettons d’examiner brièvement l’influence d’Erasme et du Collège Trilingue en France.
A Paris, chez les chiens de garde de la bienpensance, c’est la méfiance. La Sorbonne (franciscaine), alarmée par la publication d’Erasme sur le texte grec de L’Evangile de Saint Luc, fait interdire dès 1523 l’étude du grec en France. En Vendée, à Fontenay-le-Comte, les moines du couvent de Rabelais confisquent alors sans vergogne ses livres grecs ce qui incitera l’intéressé à déserter son ordre mais pas ses livres. Médecin, Rabelais traduit par la suite Galien du grec en français. Et, comme le démontre la lettre de Rabelais à Erasme, le premier tient le second en haute estime.
Dans son Gargantua (1534), esquissant les contours d’une Eglise du futur, Rabelais évoque le Collège Trilingue sous le nom d’abbaye de Thélème (Thélème = désir en grec, peut-être une référence à Désiré, prénom d’Erasme), un magnifique bâtiment hexagonal à six étages, digne des plus beaux châteaux de la Loire où l’on puisse retrouver, « les belles grandes librairies, en Grec, Latin, Hébrieu, François, Tuscan et Hespaignol, disparties par les divers estaiges selon langaiges », référence on ne peut plus claire au projet érasmien.

Contre la Sorbonne, en 1530, le Collège Trilingue d’Erasme servira explicitement de modèle pour la création, à l’instigation de Guillaume Budé (ami d’Erasme), du « Collège des lecteurs royaux » (devenu depuis le Collège de France) par François Ier, avec les encouragements de sa sœur Marguerite de Valois reine de Navarre (1492-1549) (grand-mère d’Henri IV), poétesse, femme de lettres et lectrice d’Erasme.
Dans le même élan, en 1539, Robert Estienne est nommé imprimeur du roi pour le latin et l’hébreu, et c’est à sa demande que François Ier fit graver par Claude Garamont une police complète de caractères grecs dits « Grecs du Roi ».
Pour les mettre à l’abri des foudres des sorbonagres et des sorbonicoles, François Ier déclare alors les lecteurs royaux conseillers du roi. A l’ouverture, il s’agit de chaires de lecture publique pour le grec, l’hébreu et les mathématiques mais d’autres chaires suivront dont le latin, l’arabe, le syriaque, la médecine, la botanique et la philosophie. Aujourd’hui, il aurait sans doute ajouté le chinois et le russe.
Ce qui n’empêche pas qu’à peine un an après sa publication, en 1532, Pantagruel, le conte philosophique de Rabelais déchaîne les foudres de la Sorbonne. Accusé d’obscénité, en sus d’apostasie, Rabelais s’en tire de justesse grâce à l’un de ses anciens condisciples, Jean du Bellay (1498-1560), diplomate et évêque de Paris, qui l’emmène à Rome à titre de médecin.
A son retour, les esprits calmés, la bienveillance de François Ier et de Marguerite de Navarre, lui permettent de retrouver son poste à l’Hôtel-Dieu de Lyon.
Si certains historiens de l’Eglise estiment qu’Erasme, à Louvain en particulier, a exagéré et parfois même suscité des réactions hostiles de la part de certains théologiens à son encontre, rappelons tout de même que lors du Concile de Trente (1545-1563), l’œuvre complète d’Erasme, taxée d’hérésie, fut interdite de lecture pour les catholiques et mise à l’Index Vaticanus en 1559 où elle restera jusqu’en 1900 !
Si Thomas More, en qui Erasme voyait son « frère jumeau », a été béatifié en 1886 par le pape Léon XIII, canonisé par Pie XI en 1935 et fait saint patron des responsables de gouvernement et des hommes politiques par Jean-Paul II en l’an 2000, pour Erasme, il va falloir attendre.
Interrogé en 2015 au sujet d’un geste éventuel de réhabilitation en faveur d’un chrétien qui a tant fait pour défendre le christianisme, sa Sainteté le pape François, dans sa réponse écrite, a vivement remercié l’auteur pour ses réflexions.
Reconstruisons le Collège Trilingue !
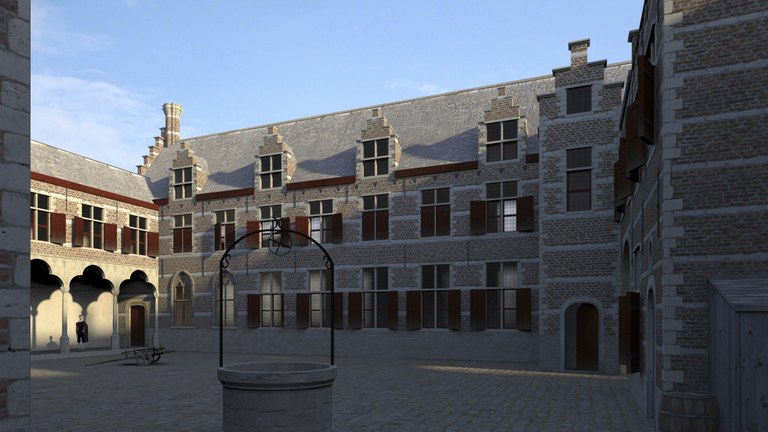


Dans le catalogue de l’exposition, le professeur Jan Papy retrace également le destin qu’ont connu les bâtiments qui abritaient jadis le Collège Trilingue.
Il mentionne notamment la tentative d’un des recteurs de l’Université Catholique de Louvain, de récupérer l’édifice en 1909, un projet qui échoua malheureusement à cause de la Première Guerre mondiale.
Le bâtiment est ensuite transformé en dépôt et en logements sociaux. « Dans la chapelle du Collège Trilingue, on fume alors le hareng et la salle de cours sert d’usine à glace… »
Aujourd’hui, à part l’escalier, rien n’évoque la splendeur historique de cette institution, ce qui fut forcément ressentie lors des commémorations de 2017.
Jan Papy regrette, bien que l’Université ait célébré les 500 ans avec « tout le faste académique requis », que l’ « on ne peut cependant s’empêcher d’éprouver des sentiments équivoques à la pensée que cette même Université n’a toujours pas pris à cœur le sort de cet institut qu’Erasme avait appelé de ses vœux et pour lequel il avait tant œuvré ».
Les restes du bâtiment, certes, dans leur état actuel, n’ont pas grande « valeur », du point de vue « objectif ». Ce n’est qu’en fonction de l’attention subjective que nous leur attribuons, qu’elles ont une valeur inestimable et précieuse comme témoignage ultime d’une partie de notre propre histoire.

A cela s’ajoute que reconstruire le bâtiment, dont il ne reste pas grand-chose, coûterait à peine quelque petits millions d’euros, c’est-à-dire pas grand-chose à l’aube des milliards d’euros que brassent nos banques centrales et nos marchés financiers. Des mécènes privés pourraient également s’y intéresser.

De notre point de vue, la reconstruction effective du Collège Trilingue dans sa forme originale, qui constitue en réalité une partie du cœur urbanistique de la ville de Louvain, serait une initiative souhaitable et incontestablement « un énorme plus » sur la carte de visite de la ville, de son Université, des Flandres, de la Belgique et de toute l’Europe. N’est-il pas un fait regrettable, alors que tous les jeunes connaissent les bourses Erasmus, que la plupart des gens ignorent les idées, l’œuvre et le rôle qu’a pu jouer un si grand humaniste ?
Des images en trois dimensions, réalisées dans la cadre de l’exposition sur la base des données historiques, permettent de visualiser un bel édifice, du même type que ceux construit par l’architecte Rombout II Keldermans à l’époque (Note), apte à remplir des missions multiples.

Enfin, chaque époque est en droit de « ré-écrire » l’histoire en fonction de sa vision de l’avenir sans pour autant la falsifier. Rappelons également, bien qu’on tende à l’oublier, que la Maison de Rubens (Rubenshuis) à Anvers, un Musée qui attire des milliers de visiteurs chaque année, n’est pas du tout le bâtiment d’origine ! Comme le reconnaît le site du Musée actuel :
La maison de Rubens reste sans doute inchangée jusqu’au milieu du 18e siècle, après quoi elle est entièrement transformée. Les façades sur la rue sont démolies et reconstruites selon le goût de l’époque. La demeure du XVIe siècle est aussi en grande partie remplacée par une bâtisse neuve. Le bâtiment est confisqué par les Français en 1798 et devient une prison pour les religieux condamnés au bannissement. La maison est rachetée par un particulier après l’époque napoléonienne. L’idée de faire de la maison un monument naît dans le courant du XIXe siècle. La Ville d’Anvers en fait l’acquisition en 1937. Les années suivantes seront mises à profit pour rendre autant que possible à la demeure son aspect à l’époque de Rubens. Le musée Maison Rubens ouvre ses portes en 1946. C’est la maison que vous visitez aujourd’hui.
L’annonce officielle d’une reconstruction du bâtiment pourrait éventuellement se faire le 18 octobre 2020, date anniversaire du jour où le Collège Trilingue ouvrait ses portes. Moi j’y serais !
Note: On pense à la Cour de Busleyden et le Palais de Marguerite d’Autriche à Malines ou à la Cour des marquis (Markiezenhof) de Bergen-op-Zoom