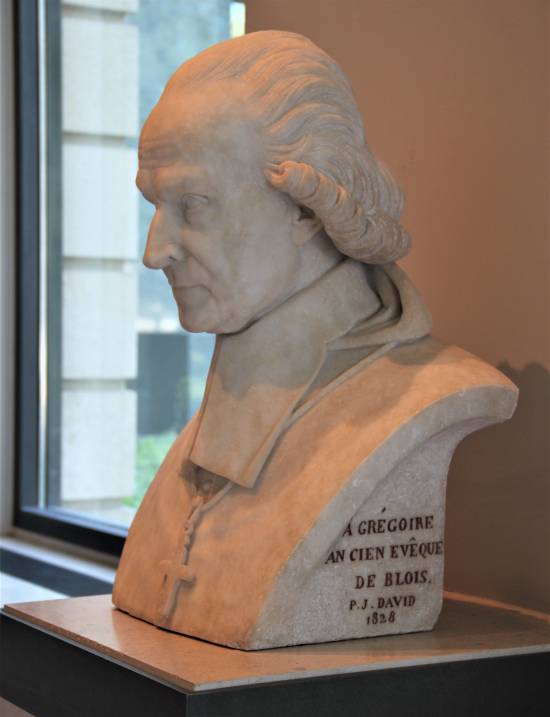
Étiquette : Shakespeare
Shakespeare’s lesson in Economics

Cet article en FR

by Karel Vereycken
As early as 1913, the very year that a handful of major Anglo-American banks set up the Federal Reserve to prevent that any form of national bank in the US fixes the rules for money and credit, Henry Farnam 1 , an economist at Yale University, noted that « if one examines the dramas of Shakespeare, one will notice that quite often in his plays the action turns entirely or partly on economic questions. »
The comedy The Merchant of Venice (circa 1596) is undoubtedly the most striking example. While the plot of the story is generally well known, the deeper meaning of this play, which can be read on different levels, is often overlooked. The sequence of events (the story itself) is one, what they reveal (the principles) is another.
The narrative
To help out his protégé Bassanio and enable him to engage with his beloved Portia, a Catholic Venetian merchant and shipowner named Antonio borrows money from a Jewish moneylender, Shylock.
Shylock hates Antonio, the very archetype of the hypocritical Christian, because the latter treats him with contempt. Antonio, on the other hand, hates Shylock because he is Jewish and because he is a usurer: he lends at interest.
Shakespeare makes us understand that the prosperity of Venice is based on the mutual hatred fueled by the oligarchs between Jews and Christians, according to the famous principle of « Divide and rule. » 2
Double-dealing
The Venetian oligarchy never lacked imagination in circumventing the standards it imposed on its adversaries.
Indeed, among both Jews and Christians, financial usury is condemned and even punished. Interest, which is simply defined as the remuneration of a creditor by his debtor for having lent him capital, is a very ancient concept that probably dates back to the Sumerians and is also found in other ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians or the Romans.
Now, let us recall here that Judaism, which is the first of the Abrahamic religions, clearly prohibits lending at interest. We encounter numerous passages that condemn interest in the Torah, such as the book of Exodus 22:25-27, Leviticus 25:36-37 and Deuteronomy 23:20-21.
However, this prohibition only applies to loans within the Jewish community. In Deuteronomy 23:20-21, it is stated that
« When you lend money, food, or anything else to a fellow countryman, you shall not charge him interest. You may charge interest when you lend to a foreigner, but you shall not lend at interest to your fellow countrymen. »
Initially, the same rule applied among Christians. It was not until the First Council of Nicaea (in 325) that lending at interest was prohibited. At the time, many churches were held by lineages of priests , just as nearby castles were controlled by lineages of lords, the two often being related. While its condemnation had been relatively mild in Christianity before then, interest became a serious sin and was heavily punished from the 1200s onwards.
The exploitation of Jews
Italy has been home to Jews since ancient times. They were dependent on popes, princes, or merchant republics. Rome, Sicily, and the Kingdom of Naples had large communities, and popes sometimes hired Jewish doctors. In the 13th century, some cities granted Jewish bankers, with papal license, a monopoly on pawnbroking.
Venice welcomed Jews but forbade them from practicing any profession other than lending for interest. Initially, the Jews publicly enriched themselves in Venice, drawing the ire of the rest of the population.
To « protect » the Jews, the Doge of Venice created the first ghetto (a Venetian word), offering, it must be said, the most unsanitary district of the lagoon to these Jews whom he detested while cherishing the financing they provided for Venetian colonial expeditions and the slave trade that « Catholic » Venice practiced without any qualms.
The Merchant of Venice
This is the essence of the Venetian system that Shakespeare unmasks in his comedy The Merchant of Venice . 3
So, when Antonio goes to ask Shylock for a loan of 3000 ducats for a period of three months, he first tells him:
« Shylock, I normally don’t lend or borrow money with interest, but in order to help my needy friend, I’ll break my custom. » 4
Shylock then replies:
« Sir Antonio, many times you have criticized me about my money and habit of charging interest in the Rialto. I have endured it all with patience and a shrug, because we Jews are known for our ability to endure. You say I believe in the wrong religion, call me a cut-throat dog, and spit on my Jewish clothing, all because I use my own money to make profit. And now it appears that you need my help. Okay, then!
You come to me and you say, « Shylock, I need money. » You tell me this! You who spat on my beard and kicked me as you’d kick a stray dog away from your threshold! You ask for money. What should I say to you? Shouldn’t I say, « Does a dog have money? Is it possible for a dog to lend you three thousand ducats? » Or should I get bend to my knees and with bated breath humbly whisper, « Fair sir, you spat on me last Wednesday; you spurned me then; another time you called me a dog—and for all this courtesy you’ve shown me, I will gladly lend you this much money? » 5
To which Antonio retorts:
« I am likely to call you such names again, spit on you again, and spurn you, too. If you decide to lend this money, don’t do it as if we are your friends. After all, when have friends ever charged each other interest? Lend me the money as your enemy and if I break my part of the agreement you can more happily punish me. » 6

Offended, Shylock replies:
« Why, look at your temper! I would be friends with you and have your affection, forget about how you have shamed me, lend you what you need and take no interest—but you won’t listen to me! I’m giving you a kind offer. » 7
Shylock, to escape from the mutual hatred, offers to lend him (according to the Jewish and Christian rule), as a friend, without interest.
But the « good » Catholic Antonio refuses to become friends with the Jew. He asserts that in business, one should not have friends , and demands that he lend to him as an enemy because it is easier to sanction in case of non-compliance with the contract.
As Churchill said, an empire has no friends, only interests. This principle would later be theorized by Nazi crown jurist Carl Schmidt to become the rule of today’s oligarchy: to exist, one needs an enemy, and if you lack one, hurry up to invent one!
The Venitian’s double game
As we can see, Shakespeare points out the hypocrisy of this Venetian system which bases its prosperity on a « win-win » policy, not between friends, but as a cynical game between concurring mafias.
Let us recall here that, although it was regularly at war with the Turks, Venice also created a ghetto for Turkish merchants and even a « Foundation », that is to say a functional trade representation in the city.

If a Venetian ambassador was reproached for this trade with the Ottomans which threatened the West, he would reply: « As merchants, we cannot live without them. »
The Ottomans sold wheat, spices, raw silk, cotton, and ash (essential for glassmaking) to the Venetians, while Venice supplied them with finished products such as soap, paper, textiles, and… weapons. Although this was explicitly forbidden by the Pope, countries as France, England, the Low Countries, but especially Venice, Genoa, and Florence sold firearms and gunpowder to the Levant and the Turks. 8
Venice supplied the Turks with cannons and military engineers with its left hand, while renting ships at high prices to Christians who wanted to fight them with its right hand. Added to this was the rivalry with Genoa, which had allied itself with the Palaeologus dynasty but which the Ottomans defeated in favor of the Venetians.
In 1452, a year before the fall of Constantinople, the Hungarian engineer and founder Urban (or Orban), a specialist in large bombards, entered the service of the Ottomans. These cannons, he entrusted to the Sultan, were so powerful that they would bring down « the walls of Babylon. » We know what happened next in 1453.

When the Franks wanted to hire ships in Venice to go on crusade, they lacked money.
No problem: Venice finds the right arrangement. To pay for the ships’ rental, the Franks are invited to make a small detour along the route and begin the crusade by liberating Constantinople, which Venice wants to retake from the Ottomans. And it works! Venice increases its trading posts and military bases in Constantinople to expand its financial and commercial empire.
A Pound of Flesh
Faced with Antonio’s foolish and arrogant response, Shylock pushes his logic to the point of absurdity and, jokingly, suggests that if his debtor does not repay his debt on time, he would have the right to take a pound of flesh from him.
This can be seen as a literal and wacky interpretation of what was written on the « bonds » or « receipts of debt » of the time. Antonio, who is convinced that his ships will return to Venice in time to provide him with enough to repay Shylock, accepts the terms of the contract, almost laughing at their surreal nature.
This is where Shakespeare poses a fundamental question and offers us a beautiful lesson in economics, in the form of a tragic and paradoxical metaphor. In most ancient civilizations, failure to repay a debt could lead you to slavery, cost you your life, or send you to prison for the rest of your life. From monetary slavery, we thus moved on to physical slavery. 9
Later, for example, we find in the archives of the Antwerp courts the text of a trial in 1567 concerning an obligation between Coenraerd Schetz and Jan Spierinck:
« I, Jan Spierinck, confess and declare with my own hand that I owe the honorable Lord Coenraerdt Schetz the sum of four hundred Flemish pounds, and this on the basis of the equal sum that I have received from him to my satisfaction. I promise to pay in full the said Lord Coenraerdt Schetz or the bearer of this present, on the fourth day of the next month of August without any delay, by pledging myself and all my property now and in the future. In the year 1565, on the 11th of June. »
You read that right: « by pledging myself. » Taken literally, the debtor pledges his person as surety to his creditor. Let us also recall that in France, imprisonment for private debts was instituted by a royal ordinance of Philip the Fair in March 1303. Apart from two periods of abolition, from 1793 to 1797 and in 1848, the imprisonment of debtors persisted in France until its abolition in 1867.
During the Renaissance, the Christian humanism of Petrarch, Erasmus, Rabelais, and Thomas More combined Socrates’ notion of justice with that of love for others, and a new principle emerged: the life of each individual is sacred and has a value immeasurably greater than any financial debt.
It is a questioning of this principle that turns Shakespeare’s comedy into a drama. Little by little, the spectator learns that Antonio’s ships have all been swept away by storms and other misfortunes. He therefore does not have the necessary means to repay his debt in time.
The Merchant of Venice must therefore accept that Shylock takes a pound of flesh from him as stipulated in the debt title he signed… a financial claim duely validated by a notary and the laws of the Venetian Republic.

To save Antonio’s life, his friends then offer the lender double the initial sum borrowed, but Shylock, driven by a sense of revenge, will not listen, angry moreover at the fact that his daughter has left his house with a young Christian merchant, taking with her a tidy sum of ducats and family jewels.
Shylock viciously responds to the Doge’s request to show mercy, saying that he is asking for nothing more… than the application of the law. He also reminds the Venetians that they are in no position to give moral lessons, because in Venice one can « buy » people:
« What judgment shall I dread, doing no wrong? You have among you many a purchased slave, Which—like your asses and your dogs and mules— You use in abject and in slavish parts. Because you bought them. Shall I say to you, “Let them be free! Marry them to your heirs! Why sweat they under burdens? Let their beds Be made as soft as yours and let their palates Be seasoned with such viands”? You will answer, “The slaves are ours.” So do I answer you. The pound of flesh which I demand of him Is dearly bought. ‘Tis mine and I will have it. If you deny me, fie upon your law— There is no force in the decrees of Venice. 105 I stand for judgment. Answer, shall I have it? » 10
To this, the impotent Doge offers no counterargument. He himself must obey the laws of the city. The only thing he has the right to do is to allow a doctor of law who has examined the case to deliver his expert opinion.
Turnaround of the situation
Here Shakespeare introduces Portia, who, disguised as a law doctor and acting in the name of a higher principle, love for humanity and good, will succeed in turning the tide. 11
Having acknowledged the validity of Shylock’s claim, she turns the tables with the kind of audacity we lack today. Regarding the claim, she notes an important detail concerning the implementation of the sanction:
« Hold on a second. There’s something else. This agreement doesn’t give you any drop of blood. The literal words are « a pound of flesh. » So take what is yours, take your pound of flesh, but if in cutting it off you shed one drop of Christian blood, your lands and goods will be confiscated by the state of Venice by the city’s laws. » 12

This is another beautiful lesson Shakespeare teaches us. How many excellent laws are worthless simply because their authors didn’t bother to specify their implementation? Do you know the laws that allow you to defend yourself against the injustices the system inflicts on you? Because if the devil is in the details, the good Lord is sometimes not far away. It’s up to you to go and find him.
Shakespeare reminds us that economics is not limited to law and mathematics. Every economic choice remains a societal choice. In reality, only « political economy » should be taught in our universities and theaters.
Presenting the science of economics and finance as an « objective » reality and not as a reality of human choices is the best proof that we are subject to propaganda.
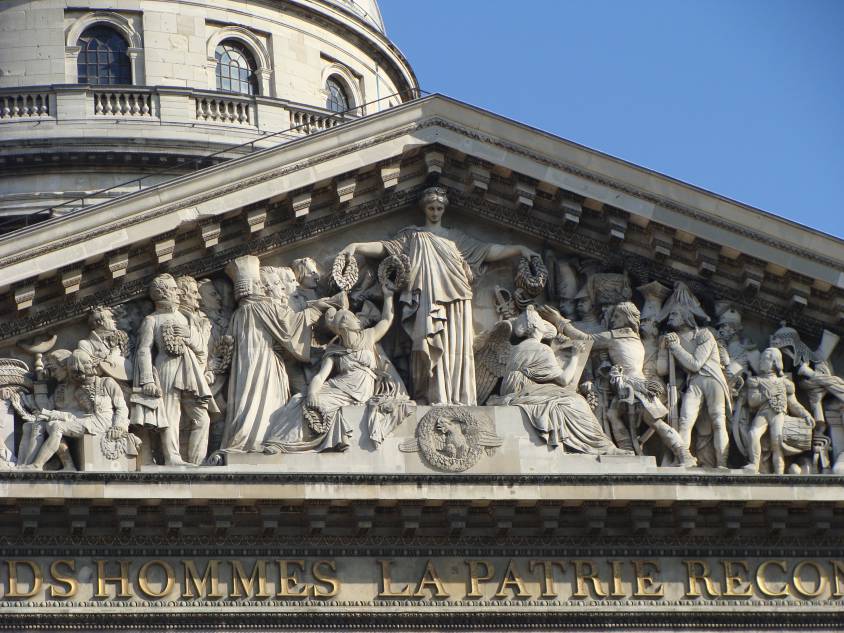
In conclusion, let us emphasize that unlike Christopher Marlowe‘s play, The Jew of Malta (circa 1589), the main actor in Shakespeare’s play is not the evil Jew Shylock (as claimed by anti-Semites who performed distorted versions of the play during the dark periods of our history), but rather the very Catholic merchant of Venice who, as we have seen, uses the Jews for his own interests. Let us recall that in the Jewish ghetto of Venice, the Jews were only allowed to deal with finance but nothing else…
Finally, in The Merchant of Venice , Shakespeare unmasks the workings of a mad and criminal finance which knows how to use formal interpretations of law (the appearance of justice) to satisfy its greed (true injustice).
NOTES:
- Henry Farnam, Shakespeare as an economist, p. 437, Yale Publishing Association, New Haven; ↩︎
- See Sinan Guven, The Conflict Between Interest and Abrahamic Religions , HEConomist, the student newspaper; ↩︎
- All the following quotes from Shakespeare’s The Merchant of Venice are taken from the website Litcharts; ↩︎
- Act 1, Scene 3; ↩︎
- Act 1, Scene 3; ↩︎
- Act 1, Scene 3; ↩︎
- Act 1, Scene 3; ↩︎
- Salim Aydoz, Artillery Trade of the Ottoman Empire, Muslim Heritage website, Sept. 2006; ↩︎
- A case in point is the history of Haiti. See Invade Haiti, Wall Street urged, New York Times, 2022. ↩︎
- Act 4, Scene 1; ↩︎
- The principle of a « Promethean » woman intervening disguised as a man for the good of humanity will be, with the person of Leonore, at the center of Fidelio, Beethoven’s unique opera; ↩︎
- Act 4, Scene 1; ↩︎
La leçon d’économie de Shakespeare

This article in EN

par Karel Vereycken
Déjà en 1913, l’année même où une poignée de grandes banques anglo-américaines constituait la Réserve fédérale pour fixer les règles de la monnaie et du crédit, Henry Farnam 1, un économiste de l’Université de Yale, faisait remarquer que « si l’on examine les drames de Shakespeare, on remarquera qu’assez souvent, dans ses pièces, l’action tourne entièrement ou en partie autour de questions économiques ».
La comédie Le marchand de Venise (vers 1596) en est sans doute l’exemple le plus éclatant. Si l’on connaît généralement le déroulé de l’histoire, on passe assez souvent à côté du sens profond de cette pièce qui se lit à différents niveaux. L’enchaînement des faits (la petite histoire) en est un, ce qu’ils dévoilent (des principes) en est un autre.
La petite histoire
Pour rendre service à son protégé Bassanio et lui permettre d’épouser sa bien-aimée Portia, un marchand et armateur vénitien catholique du nom d’Antonio emprunte de l’argent à un prêteur juif Shylock. Ce dernier déteste Antonio car celui-ci, l’archétype même du chrétien hypocrite, le traite avec mépris. Antonio, quant à lui, déteste Shylock parce qu’il est juif et parce qu’il est un usurier : il prête avec intérêt.
Shakespeare nous fait comprendre que la prospérité de Venise repose sur la séparation et sur la détestation mutuelle entre Juifs et Chrétiens, selon son célèbre principe de « Diviser pour régner ». 2
L’oligarchie vénitienne n’a jamais manqué d’imagination pour contourner les normes qu’elle faisait appliquer à ses adversaires.
L’usure
En effet, aussi bien chez les Juifs que chez les Chrétiens, l’usure financière est condamnée et même punie. L’intérêt qu’on définit simplement comme la rémunération d’un créancier par son débiteur pour lui avoir prêté du capital, est un concept très ancien qui date probablement des Sumériens et qu’on retrouve aussi dans d’autres civilisations antiques comme les Égyptiens ou les Romains.
Or, rappelons ici que le Judaïsme, qui est la première des religions abrahamiques, interdit clairement le prêt à intérêt. On rencontre de nombreuses fois des passages qui condamnent l’intérêt dans la Torah comme le livre de l’Exode 22:25-27, le Lévitique 25:36-37 et le Deutéronome 23:20-21.
Cependant, cette interdiction ne concerne que les prêts dans la communauté juive. Dans le Deutéronome 23:20-21, il est dit que
« lorsque vous prêterez de l’argent, des vivres ou toute autre chose à un compatriote, vous n’exigerez pas d’intérêt de sa part. Vous pouvez exiger des intérêts lorsque vous faites un prêt à un étranger, mais vous ne prêterez pas à intérêt à vos compatriotes ».
Initialement, la même règle s’appliquait chez les Chrétiens. Ce n’est qu’à partir du premier Concile de Nicée (en 325) que le prêt à intérêt est interdit. A l’époque, de nombreuses églises sont tenues par des lignages de prêtres, tout comme les châteaux voisins sont contrôlés par des lignages de seigneurs, les deux étant souvent apparentés. Alors que sa condamnation était relativement modérée dans le Christianisme auparavant, l’intérêt devient un grave péché lourdement puni à partir des années 1200.
L’exploitation des juifs
L’Italie abrite des Juifs depuis l’Antiquité. Ils dépendent soit des papes, soit des princes, soit des républiques marchandes. Rome, la Sicile, le royaume de Naples comprennent de larges communautés et les papes engagent parfois des médecins juifs. Au XIIIe siècle, certaines villes accordent à des banquiers juifs, avec licence pontificale, le monopole du prêt sur gages.
Venise accueille les Juifs mais leur interdit de pratiquer tout autre métier que prêteur contre intérêt. Dans un premier temps, les Juifs s’enrichissent au grand jour à Venise et s’attirent les foudres du reste de la population.
Pour « protéger » les Juifs, le doge de Venise crée le premier « ghetto » (un mot vénitien), offrant, il faut le préciser, le quartier le plus insalubre de la lagune à ces Juifs qu’il déteste tout en chérissant le financement qu’ils permettent aux expéditions coloniales vénitiennes et au trafic d’esclaves que Venise la « Catholique » pratique sans complexes.
Le marchand de Venise
Voilà l’essence du système vénitien que Shakespeare démasque dans sa comédie Le marchand de Venise. 3
Ainsi, lorsqu’Antonio va solliciter auprès de Shylock un prêt de 3000 ducats pour une période de trois mois, il lui précise dans un premier temps :
« Shylock, quoique je ne prête ni n’emprunte à intérêt, cependant pour fournir aux besoins pressants d’un ami, je dérogerai à ma coutume ».
Shylock répond alors :
« Seigneur Antonio, mainte et mainte fois vous m’avez fait des reproches au Rialto sur mes prêts et mes usances. Je n’y ai jamais répondu qu’en haussant patiemment les épaules, car la patience est le caractère distinctif de notre nation. Vous m’avez appelé mécréant, chien de coupe-gorge, et vous avez craché sur ma casaque de juif, et tout cela parce que j’use à mon gré de mon propre bien. Maintenant il paraît que vous avez besoin de mon secours, c’est bon.
Vous venez à moi alors, et vous dites : ‘Shylock, nous voudrions de l’argent.’ Voilà ce que vous me dites, vous qui avez expectoré votre rhume sur ma barbe ; qui m’avez repoussé du pied, comme vous chasseriez un chien étranger venu sur le seuil de votre porte. C’est de l’argent que vous demandez ! Je devrais vous répondre, dites, ne devrais-je pas vous répondre ainsi : ‘Un chien a-t-il de l’argent ? Est-il possible qu’un roquet prête trois mille ducats ?’ Ou bien irai-je vous saluer profondément, et dans l’attitude d’un esclave, vous dire d’une voix basse et timide : ‘Mon beau monsieur, vous avez craché sur moi mercredi dernier, vous m’avez donné des coups de pied un tel jour, et une autre fois vous m’avez appelé chien ; en reconnaissance de ces bons traitements, je vais vous prêter tant d’argent’ ? »
A quoi Antonio rétorque :
« Je suis tout prêt à t’appeler encore de même, à cracher encore sur toi, à te repousser encore de mon pied. Si tu nous prêtes cet argent, ne nous le prête pas comme à des amis, car l’amitié a-t-elle jamais exigé qu’un stérile métal produisît pour elle dans les mains d’un ami ? mais prête plutôt ici à ton ennemi. S’il manque à son engagement, tu auras meilleure grâce à exiger sa punition ».

Offusqué, Shylock répond :
« Eh ! mais voyez donc comme vous vous emportez ! Je voudrais être de vos amis, gagner votre affection, oublier les avanies que vous m’avez faites, subvenir à vos besoins présents, et ne pas exiger un denier d’usure pour mon argent, et vous ne voulez pas m’entendre ! »
Shylock, pour sortir de la détestation mutuelle propose de lui prêter (selon la règle juive et chrétienne), en ami, sans intérêt. Mais le « bon » catholique Antonio refuse de devenir ami avec le Juif. Il affirme qu’en affaires, il ne faut pas avoir d’amis, et exige qu’on lui prête en tant qu’ennemi car c’est plus facile à sanctionner en cas de non-respect du contrat.
Comme le disait Churchill, un Empire n’a pas d’amis, il n’a que des intérêts. Ce principe sera théorisé ensuite par Carl Schmidt pour devenir la règle de l’oligarchie d’aujourd’hui : pour exister, il faut un ennemi et s’il en manque, dépêchons-nous d’en inventer un !
Le double jeu des Vénitiens
Comme on le voit, Shakespeare pointe sur l’hypocrisie de ce système vénitien qui base sa prospérité sur une politique « gagnant-gagnant » non pas entre amis mais entre ennemis.
Rappelons ici que, bien qu’elle soit régulièrement en guerre contre les Turcs, Venise crée également un ghetto pour les marchands turcs et même une « fondation », c’est-à-dire une représentation commerciale fonctionnelle.

Si l’on reprochait à un ambassadeur vénitien ce commerce avec les Ottomans qui menaçaient l’Occident, celui-ci répondait : « En tant que marchands, nous ne pouvons vivre sans eux. »
Les Ottomans vendaient du blé, des épices, de la soie grège, du coton et de la cendre (pour la fabrication du verre) aux Vénitiens, tandis que Venise leur fournissait des produits finis tels que du savon, du papier, des textiles et… des armes. Bien que cela soit explicitement interdit par le pape, la France, l’Angleterre, les Pays-bas, mais surtout Venise, Gênes, et Florence vendaient des armes à feu et de la poudre à canon au Levant et aux Turcs. 4
Venise fournit de sa main gauche des canons et des ingénieurs militaires aux Turcs tout en louant à prix fort, de sa main droite, des navires aux Chrétiens voulant les combattre. A cela s’ajoute la rivalité avec Gênes qui s’était alliée à la dynastie des Paléologues mais que les Ottomans ont battue au profit des Vénitiens.
En 1452, un an avant la chute de Constantinople, l’ingénieur et fondeur hongrois Urban (ou Orban), spécialiste des grosses bombardes, se met au service des Ottomans. Ces canons confie-t-il au Sultan, sont si puissants qu’ils feraient chuter « les murs de Babylone ». On connaît la suite en 1453.

Lorsque les Francs veulent louer des navires à Venise pour partir en croisade, l’argent leur fait défaut.
Pas de souci : Venise trouve l’arrangement qui convient. Pour payer la location des navires, les Francs sont invités à faire un petit détour sur le trajet, et commencer la croisade par la libération de Constantinople que Venise veut reprendre aux Ottomans. Et ça marche ! Venise multiplie ses comptoirs et ses bases militaires à Constantinople pour étendre son empire financier et commercial.
Une livre de chair
Face à la réponse sotte et arrogante d’Antonio, Shylock pousse la logique jusqu’à l’absurde et, sur le ton de la plaisanterie, propose alors que dans l’éventualité où son débiteur ne rembourserait pas sa dette en temps et en heure, il aurait le droit de prélever sur celui-ci une livre de chair.
On peut y voir une interprétation littérale et loufoque de ce qui s’écrivait sur les « obligations » ou « reconnaissances de dette » de l’époque. Antonio, qui est convaincu que ses navires rentreront à temps à Venise pour lui fournir de quoi rembourser Shylock, accepte les conditions du contrat, presque en riant de leur caractère surréaliste.
C’est là que Shakespeare pose une question fondamentale et nous offre une belle leçon d’économie, sous la forme d’une métaphore tragique et paradoxale. Dans la plupart des civilisations de l’Antiquité, le non-remboursement d’une dette pouvait vous conduire en esclavage, vous coûter la vie ou vous envoyer en prison pour le reste de vos jours. De l’esclavage monétaire on passait ainsi à l’esclavage physique.
Plus tard, on trouve, par exemple, dans les archives des tribunaux d’Anvers le texte d’un procès en 1567 concernant une obligation entre Coenraerd Schetz et Jan Spierinck :
« Moi, Jan Spierinck, confesse et déclare de ma propre main devoir à l’honorable seigneur Coenraerdt Schetz la somme de quatre cents livres flamandes, et ce sur la base de la somme égale que j’ai reçue de lui à ma satisfaction. Je promets de payer intégralement ledit seigneur Coenraerdt Schetz ou le porteur de la présente, le quatrième jour du prochain mois d’août sans aucun retard, en engageant ma personne et tous mes biens maintenant et à l’avenir. En l’an 1565, le 11 juin ». Vous avez bien lu : « en engageant ma personne ».
Pris à la lettre, le débiteur gage sa personne en caution à son créancier. Rappelons également qu’en France la prison pour dettes privées est instituée par une ordonnance royale de Philippe Le Bel de mars 1303. En dehors de deux périodes de suppression, de 1793 à 1797 et en 1848, la contrainte par corps des débiteurs a persisté en France jusqu’à son abolition en 1867.
A la Renaissance, l’humanisme chrétien de Pétrarque, d’Erasme, de Rabelais et de Thomas More allie la notion de justice de Socrate avec celle de l’amour d’autrui, et un nouveau principe émerge : la vie de chaque individu est sacrée et a une valeur incommensurablement supérieure à tous les titres de dette financière.
C’est une remise en question de ce principe qui fait tourner la comédie de Shakespeare au drame. Petit à petit, le spectateur apprend que les navires d’Antonio ont tous été emportés par des tempêtes et d’autres déconvenues. Il ne dispose donc pas en temps et en heure des moyens nécessaires pour s’acquitter de sa dette.
Le marchand de Venise doit donc accepter que Shylock lui prenne une livre de chair comme le stipule la reconnaissance de dette qu’il a signée… un titre de dette validé par les lois de la République.

Pour sauver la vie d’Antonio, ses amis proposent alors au prêteur le double de la somme initiale empruntée, mais Shylock, animé par un sentiment de vengeance, ne veut rien entendre, fâché de surcroît du fait que sa fille est partie de sa maison avec un jeune marchand chrétien emportant une coquette somme de ducats et des bijoux de famille.
Shylock répond vicieusement au Doge qui lui demande d’être clément, qu’il ne réclame rien d’autre que l’application de la loi. Au passage il rappelle aux Vénitiens qu’ils sont mal placés pour donner des leçons de moralité, car à Venise on peut « acheter » des personnes :
« Quel jugement aurais-je à redouter, puisque je ne fais point de mal ? Vous avez chez vous un grand nombre d’esclaves que comme vos ânes, vos chiens et vos mulets, vous employez aux travaux les plus abjects et les plus vils, parce que vous les avez achetés. Irai-je vous dire : rendez-leur la liberté, faites leur épouser vos héritières ? Pourquoi suent-ils sous des fardeaux ? Donnez-leur des lits aussi doux que les vôtres. Que leur palais soit flatté par les mêmes mets que le vôtre. Vous me répondez : ces esclaves sont à nous. Je vous réponds de même : la livre de chair que j’exige de lui m’appartient : je l’ai chèrement payée, et je la veux. Si vous me refusez, honte à vos lois ! Il n’y a plus aucune force dans les décrets du sénat de Venise. — J’attends que vous me rendiez justice. Parlez : l’aurai-je ? »
A cela, le Doge impuissant n’apporte aucun contre-argument. Lui-même doit obéir aux lois de la cité. L’unique chose qu’il a le droit de faire, c’est de laisser la parole à un docteur en droit qui a examiné l’affaire, pour qu’il livre son avis d’expert.
Retournement de la situation
Ici, Shakespeare fait intervenir Portia qui, déguisée en homme de loi et agissant au nom d’un principe supérieur, l’amour pour l’humanité et le bien, prend la parole. 5
Une fois reconnue la validité de la demande de Shylock, elle retourne la situation avec le genre d’audace qui nous manque aujourd’hui. A propos de la créance, elle relève un détail important concernant la mise en œuvre de la sanction :
« Le billet ne t’accorde pas une goutte de sang : les termes sont exprès ; une livre de chair. Prends ce qui t’est dû ; prends ta livre de chair. Mais si, en la coupant, tu verses une seule goutte de sang chrétien, les lois de Venise ordonnent la confiscation de tes terres et de tes biens au profit de la république. »

C’est une autre belle leçon que nous donne Shakespeare. Combien de lois excellentes ne valent rien du simple fait que leurs auteurs n’ont pas pris la peine d’en spécifier la mise en œuvre ? Connaissez-vous les lois vous permettant de vous défendre contre les injustices que le système vous inflige ? Car si le diable est dans les détails, le bon Dieu n’est parfois pas loin. A vous d’aller le chercher.
Shakespeare nous rappelle que l’économie ne se réduit pas au droit et aux mathématiques. Tout choix économique reste un choix de société. En réalité, seule « l’économie politique » devrait être enseignée dans nos facultés et nos théâtres.
Présenter la science de l’économie et de la finance comme une réalité « objective » et non pas comme une réalité des choix humains, est la meilleure preuve que nous sommes soumis à de la propagande.
Pour conclure, soulignons que contrairement à la pièce de Christopher Marlowe, Le Juif de Malte (vers 1589), l’acteur principal de la pièce de Shakespeare n’est pas le Juif maléfique Shylock (comme le prétendaient des antisémites qui faisaient jouer des versions dénaturées de la pièce durant les périodes noires de notre histoire), mais bien le très catholique marchand de Venise qui, on l’a vu, se sert des Juifs pour son propre intérêt. Rappelons que dans le ghetto juif de Venise, les Juifs n’avaient que le droit de s’occuper de finance mais de rien d’autre…
Enfin, dans Le marchand de Venise, Shakespeare démasque le fonctionnement d’une finance folle et criminelle qui sait utiliser des interprétations formelles du droit (l’apparence de la justice) pour satisfaire sa cupidité (la véritable injustice).
NOTES:
- Henry Farnam, Shakespeare as an economist, p. 437, Yale Publishing Association, New Haven ; ↩︎
- Voir à ce propos Sinan Guven, Le conflit entre l’intérêt et les religions abrahamiques, HEConomist, le journal des étudiants ; ↩︎
- Toutes les citations qui suivent du Marchand de Venise de Shakespeare sont tirées de la version en lecture libre sur le site Atramenta. ↩︎
- Salim Aydoz, Artillery Trade of the Ottoman Empire, Muslim Heritage website, Sept. 2006 ; ↩︎
- Le principe d’une femme « prométhéenne » intervenant déguisée en homme pour le bien de l’humanité sera, avec la personne de Leonore, au centre de Fidelio, l’unique opéra de Beethoven ; ↩︎
ARTKAREL AUDIO GUIDE: How Bosch’s Ship of Fools drove the Jester out of business (Paris)


Liste:
To the audio on this website;
Read:
- With Hieronymous Bosh on the track of the Sublime;
- Comment la folie d’Erasme sauva notre civilisation (FR en ligne) + NL pdf (Agora Erasmus) + EN pdf (Schiller Institute Archive Website) + DE pdf (Neue Solidarität).
- Le rêve d’Erasme: le Collège des Trois Langues de Louvain (FR en ligne)
- Erasmus‘ dream: the Leuven Three Language College (EN online)
- ENTRETIEN: Jan Papy: Erasme, le grec et la Renaissance des sciences (FR en ligne)
- Dirk Martens, l’imprimeur d’Erasme qui diffusa le livre de poche (FR en ligne).
- 1512-2012 : Mercator et Frisius, des cosmographes aux cosmonautes + NL pdf (Agora Erasmus) + EN pdf (Schiller Institute Archive Website).
- La nef des fous de Sébastian Brant (FR en ligne), un livre d’une grande actualité !
- Avec Jérôme Bosch sur la trace du Sublime (FR en ligne) + EN pdf.
- Joachim Patinir et l’invention du paysage en peinture (FR en ligne).
- Joachim Patinir and the invention of landscape painting (EN online)
- Exposition de Lille : ce que nous apprennent les fabuleux paysages flamands (FR en ligne).
- Portement de croix: redécouvrir Bruegel grâce au livre de Michael Gibson (FR en ligne) + EN pdf (Fidelio).
- ENTRETIEN Michael Gibson: Pour Bruegel, le monde est vaste (FR en ligne) + EN pdf (Fidelio)
- Pierre Bruegel l’ancien, Pétrarque et le Triomphe de la Mort (FR en ligne) + EN online.
- A propos du film « Bruegel, le moulin et la croix » (FR en ligne).
- L’ange Bruegel et la chute du cardinal Granvelle (FR en ligne).
- Albrecht Dürer contre la mélancolie néo-platonicienne + EN pdf.
Rembrandt and the Light of Agapè

Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn. Don’t count on me here to tell his story in a few lines! (*1) In any case, since the romantics, all, and nearly to much has been said and written about the rediscovered Dutch master of light inelegantly thrown into darkness by the barbarians of neo-classicism.

By Karel Vereycken, June 2001.
The uneasy task that imparts me here is like that of Apelles of Cos, the Greek painter who, when challenged, painted a line evermore thinner than the abysmal line painted by his rival. In order to draw that line, tracing the horizons of the political and philosophical battles who raged that epoch will unveil new and surprising angles throwing unusual light on the genius of our painter-philosopher.
First, we will show that Rembrandt (1606-1669) was « the painter of the Thirty years War » (1618-1648), a terrible continental conflict unfolding during a major part of his life, challenging his philosophical, religious and political commitment in favor of peace and unity of mankind.
Secondly, we will inquire into the origin of that commitment and worldview. Did Rembrandt met the person and ideas of the Czech humanist Jan Amos Komensky (« Comenius ») (1592-1670), one of the organizers of the revolt of Bohemia? This militant for peace, predecessor of Leibniz in the domain of pansophia (universal wisdom), traveled regularly to the Netherlands where he settled definitively in 1656. A strong communion of ideas seems to unite the painter with the great Moravian pedagogue.
Also, isn’t it astonishing that the treaties of Westphalia, who put an end to the atrocious war, are precisely based on the notions of repentance and pardon so dear to Comenius and sublimely evoked in Rembrandt’s art?
Finally, we will dramatize the subject matter by sketching the stark contrast opposing Rembrandt’s oeuvre with that of one of the major war propagandist: (Sir) Peter Paul Rubens (1577-1640).
Rembrandt, who finished rejecting any quest for earthly glory could not but paint his work away from that of the fashion-styled Flemish courtier painter. Moreover, Rubens was in high gear mobilizing all his virtuoso energy in support of the oligarchy whose Counter Reformation crusades and Jesuitical fanaticism were engulfing the continent with gallows, fire and innocent blood.
What Rembrandt advises us for his painting also applies to his life: if you stick your head to close to the canvass, the toxic odors will sharply irritate your nose and eyes. But taking some distance will permit you to discover sublime and unforgettable beauty.
What Art?
Since the triumph of Immanuel Kant‘s modernist thesis, the Critique of the Faculty of Judgment, it has not been « politically correct » to assert that art has a political dimension. And with good reason! If art can influence the course of history and shape it through its power, it is because it is a vector of ideas! An impossibility, according to the Kantian thesis, because art is a gratuitous act, free of everything, including meaning. The ultimate freedom! You either like it or you don’t, it’s all a matter of taste.
Following in the footsteps of the German poet Friedrich Schiller, we’re here to convince you otherwise, and abolish the tyranny of taste. For us, art is an eminently political act, although the work of art has nothing in common with a mere political manifesto, and the artist can in no way be reduced to an ordinary « activist ».
His domain, that of the poet, the musician or the visual artist, is to be a guide for mankind. To enable people to identify within themselves what makes them human, i.e. to strengthen that part of their soul, of their divine creativity, which places them entirely at the zenith of their responsibility for the whole of creation.
To achieve this, and we’ll develop this here, what counts in art is the type of conception of love it communicates. By making this « universal » sensitive, sublime art makes the most elevated conception of love accessible.
Such art, which forces us think, employs enigmas, ambiguities, metaphores and ironies to give us access to the idea beyond the visible. For art that limits itself to theatricality and the beauty of form fatally sinks into erotic, romantic love, depriving man of his humanity and therefore of his revolutionary power.
Rubens will be the ambassador of the great un-powers of his time: the glory of the empire and the magnificent financial strength of those days « new economy », the « tulip bubble ». In short, the oligarchy.
Rembrandt, in turn, will be the ambassador of the have-nots: the weak, the sick, the humiliated, the refugees; he will live in the image of the living Christ as the ambassador of humanity. It might seem strange to you to call such a man the « the painter of the thirty years war. »
Paradoxically, his historical period underscores the fact that very often mankind only wakes up and mobilizes its best resources for genius when confronted with the terrible menace of extinction. Today, when the Cheney’s, the Rumsfeld’s and the Kissinger’s want to plunge the world into a « post-Westphalian epoch », in reality a new dark age of « perpetual war », Rembrandt will be one of our powerful weapons of mass education.
Historical context and the origins of the war
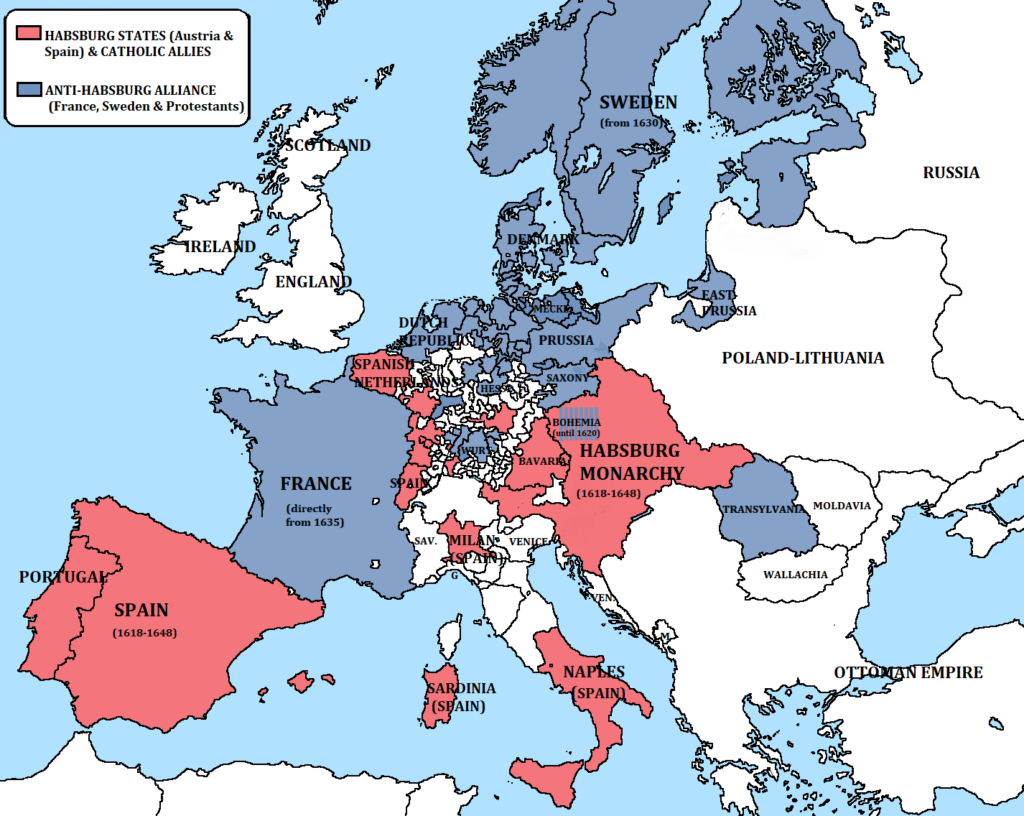
Before entering Rembrandt, it is indispensable to know what was at stake those days. The academic name « Thirty Years War » indicates only the last period of a far longer period of « religious » conflict which was taking place around the globe during the sixteenth century, mainly centered in central Europe, on the territory of today’s Germany.
While 1618 refers to the revolt of Bohemia, the 1648 peace of Westphalia defines a reality far beyond the apparent religious pretext: the utter ruin of the utopian imperial dream of Habsburg and the birth of modern Europe composed of nation-states (*2)
On the reasons for « religious » warfare, let us look at the first half of the sixteenth century. At the eighteen years long Council of Trent (1545-1563), the Roman Catholic Church discarded stubbornly all the wise advise given earlier to avoid all conflict by one of its most ardent, but most critical supporters: Erasmus of Rotterdam.
As Erasmus forewarned, by choosing as main adversary the radical anti-semite demagogue Martin Luther, the church degraded itself to sterile and intolerant dogmatism, opening each day new highways for « the Reformation ».
The religious power-sharing of the « Peace of Augsburg » of 1555, between Rome and the protestant princes, temporarily calmed down the situation, but the ambiguous terms of that treaty incorporated all the germs of the new conflicts to come. Note that « freedom of religion » meant above all « freedom of possession ». The « peace » solely applied to Catholics and Lutherans, authorizing both to possess churches and territories, while ostracizing all the others, very often abusively labeled « Calvinists ».
Playing diabolically on internal divisions, some evil Jesuits of those days set up Calvinists and Lutherans to combat each other bitterly, by claiming, for example in Germany, that Calvinism was illegal since not explicitly mentioned in the treaty. Furthermore, the citizen obtained no real freedom of religion; he was simply authorized to leave the country or adopt the confessions of his respective lord or prince, which in turn could freely choose.
As a result of a general climate of suspicion, the protestant princes created in 1608 the « Evangelical Union » under the direction of the palatine elector Frederic V. Their eyes and hopes were turned on King Henri IV‘s France, where the Edit of Nantes and other treaties had ended a far long era of religious wars. After Henry IV‘s assassination in 1610, the Evangelical Union forged an alliance with Sweden and England.
The answer of the Catholic side, was the formation in 1609 of a « Holy League » allied with Habsburg’s Spain by Maximilian of Bavaria. Beyond all the religious and political labels, a real war party is created on both sides and the heavy clouds carrying the coming tempest threw their menacing shadows on a sharply divided Europe.
1618: The Revolt of Bohemia
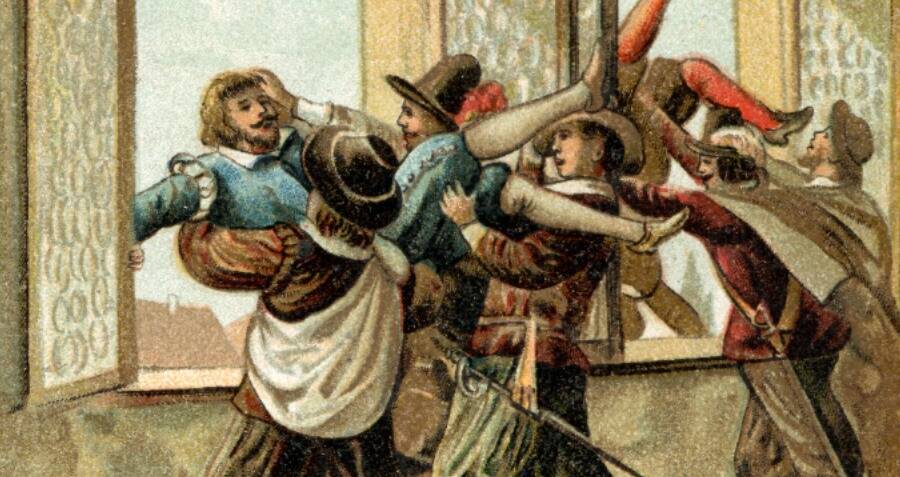

Hence, after the never-ending revolt of the Netherlands, the very idea of an insurrection of Bohemia drove the Habsburgs (and the slave trading Fugger and Welser banking empires controlling them) into total hysteria, since they felt the heath on their plans. If Bohemia would become « a new, but larger Holland », then many other nations, such as Poland, could join the Reformation camp and destabilize the imperial geopolitical power balance forever.
As from 1576, the crown of Bohemia was in the hands of the Catholic Rudolphe II, Holy Roman Emperor. Despite a far-fetched passion for esotericism, Rudolphe II will be the protector of astronomers Tycho Brahe and Johannes Kepler in Prague.
In 1609, the Protestants of Bohemia obtain from him a « Letter of Majesty » offering them certain rights in terms of religion. After his death in 1612, his brother Matthias, Holy Roman Emperor, became his successor and left the direction of the country to cardinal Melchior Klesl, a radical Counter Reformation militant refusing any application of the « letter of majesty ».
This set the conditions for the famous « defenestration of Prague », when two representatives of the imperial power were thrown out of the window and fall on a manure heap, at the end of hot diplomatic negotiations. That highly symbolical act was in reality the first signal for a general uprising, and following the early death of Matthias, the rebels made Frederic V their sovereign instead of accepting Habsburg’s choice.
Charles Zerotina, a protestant nobleman and Comenius, (see box below), a Moravian reverend and respected community leader, masterminded that revolt. Frederic V, for example was crowned in 1619 by Jan Cyrill, who was Zerotina’s confessor, and whose daughter will become Comenius wife.
The insurgents were defeated at the battle of White Mountain, close to Prague, in 1620 by a Catholic coalition, composed of Spanish troops pulled out of Flanders together with Maximilian’s Bavarians. On the scene: French philosopher René Descartes, who paid his own trip and who was part of the war coalition and joined in entering defeated Prague in search for Kepler’s astronomical instruments… (*3)
An arrest warrant immediately targeted Comenius, who escaped with Zerotina from bloody repression. Protestantism was forbidden and the Czech language replaced by German.
Most resistance leaders were arrested and 27 beheaded in public. Their heads were put up on pins and shown on the roof of Prague’s Saint-Charles bridge.
One of them was the famous Jan Jessenius, head of the University of Prague who performed one of Europe’s early public anatomical dissections in 1600 and was a close friend of Tycho Brahe. To warn those who used their speech to encourage « heresy », his tongue was pulled out before he was beheaded, quartered and impaled.
Thirty thousand people went into exile while Frederic V and his court took refuge in Den Haag in the Netherlands. There, but years before, Comenius had a personal encouter with the future « Winterkönig » and his wife Elisabeth Stuart, on their way back from their wedding in England for which Shakespeare had arranged a representation of « The Tempest ».
A World War
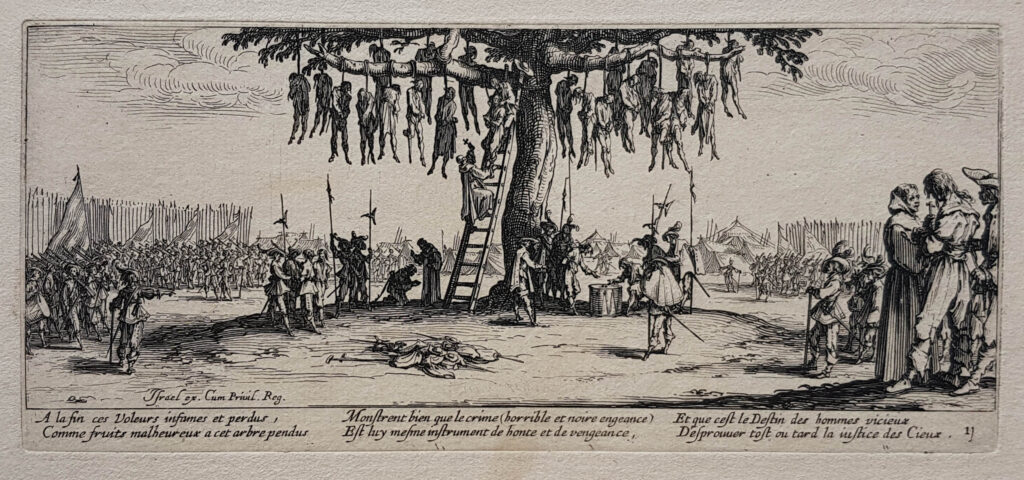

1618 marked the outbreak of an all-out war across Europe, provoked by the imperial drive of Habsburg to reunify all of the continent behind one unique emperor and one single religion.
As of 1625, aided by French and English financial facilities, Christian IV of Denmark and Gustave Adolphus of Sweden intervened on the northern flank against Habsburg descending from the north as far as up till Munich.
Then, France opened another flank on the western front in 1635. Catholic cardinal Richelieu, who defeated the Huguenots at LaRochelle in 1628 (since he « fought their political rights but not their religious ones », will heavily aid the Protestant camp. His fears were that,
« if the protestant party is completely in shambles, the offensive of the house of Austria will come down on France ».
The famous etchings of the Lorraine engraver Jacques Callot, « Misery and calamities of war » of 1633, give an idea how this savage war swept Europe with its cortège of misery, famine, epidemics and desolation.
The estimated population loss on the territory of present day Germany indicates a downturn from 15 to less than 10 million. Hundreds of cities were turned back into simple villages and thousands of communities simply disappeared from the map.
War affected all the colonies of those powers involved in the conflict. Dutch and English pirates would sink any Spanish or Portuguese ships encountered at the other edge of the Earth’s curve. For Spain, loyal pillar of Habsburg, 250 million ducats were spent for the war effort (between 1568 and 1654), despite the state bankruptcy of 1575. That amount represents more than the double of the revenue from the loot of the new world (gold, spices, slaves, etc.) which scarcely amounted only to 121 million ducats…
Rembrandt and Comenius
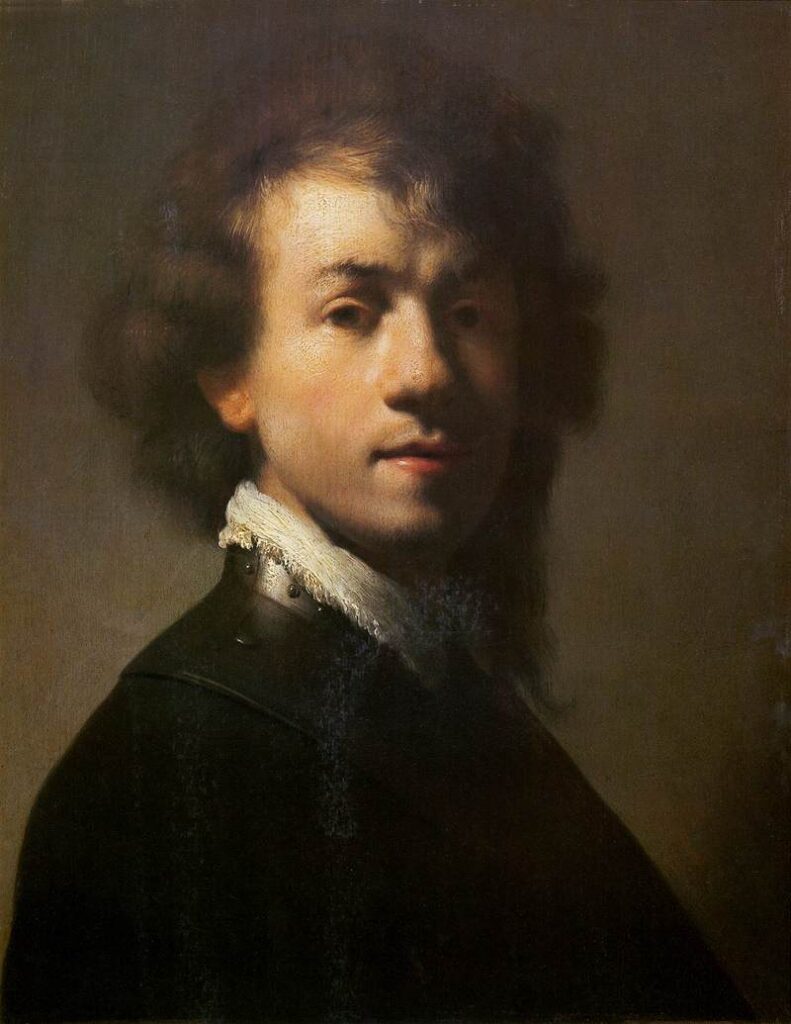

That the young Rembrandt was totally heckled by the situation of general war which was shaking up Europe is easily visible in the early self-portrait of Nuremberg.
Here he portrays himself divided between two choices. One shoulder reveals the gorget, a piece of armor that invokes the patriotic call for serving the nation calling on every young Dutchman of his generation in age of serving the military, especially after the surprise attack of the Spanish troops on Amersfoort of august 1629.
The other shoulder is nonchalantly caressed by a « liefdelok », the French « cadenette » or lovelock exhibited by amorous adolescents. What to choose? Love the nation, or the beloved?
More and more irritated by the ambitions of Constantijn Huygens, the powerful secretary of the stadholder which got him well-paid orders for the government and made him move from Leiden to Amsterdam, Rembrandt’s thinking and activity gets ever more concentrated and powerful.
Ten years later, the dying away of his wife Saskia in 1642, year of the « Night watch », plunges the painter into a deep personnal existential crisis. Gone, the self-portraits where he paints himself as an Italian courtier, with a glove in one hand carrying a heavy golden chain around his neck fronting for his social status and competing with the court. Suddenly he seems to realize that the totality of the world’s gold will never buy back the lost lives of those once loved.
When interrogated on the matter, Rembrandt would bluntly state he didn’t need to go to Italy, as the tradition used to be, since everything Italy ever produced came to him anyway as it was available in one form or another on the Amsterdam art market. But traveler he was, as drawings of the gates of London indicate, done in the early forties, maybe the year Comenius crossed the channel?
In 1644, the neo-Platonist rabbi and teacher of Spinoza, Menasseh Ben Israel, for which Rembrandt illustrated books, received a letter from Comenius agent John Dury, chaplain of Mary Princess of Orange, starting a discussion on the reintegration of the Jews in England, and Menasseh finally went for negotiations to meet Cromwell in 1655.
The Nightly Conspiracy
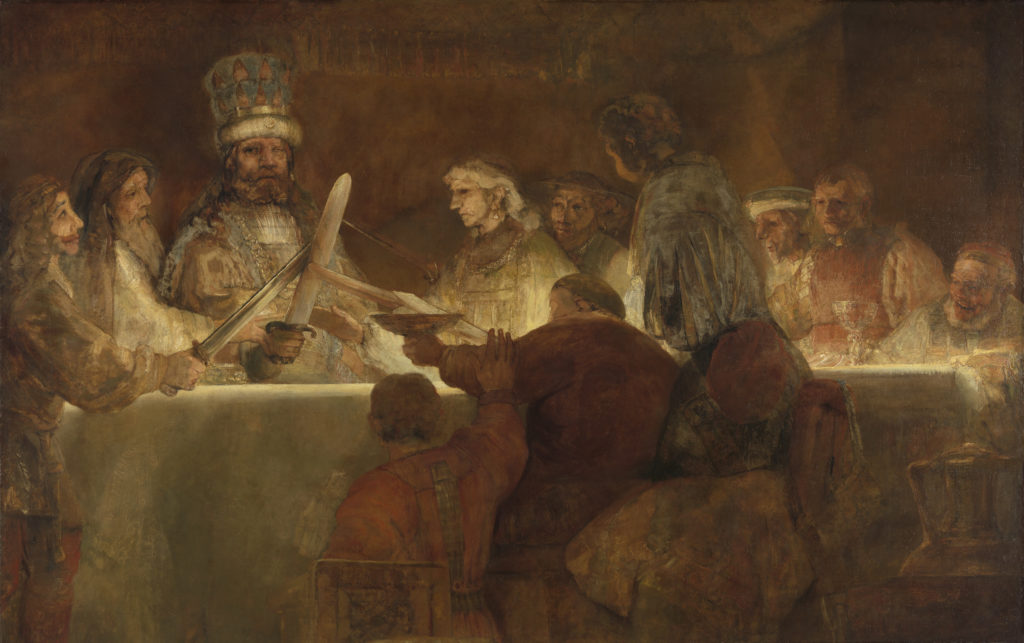

Although some timid hypothesis’ exists concerning Comenius‘ influence on Rembrandt, a rigorous historian’s research could certainly bring more light on this matter.
Although Rembrandt’s worldview evolved in an environment of the Mennonite community, peace-loving Anabaptists miles away from any political commitment, Rembrandt’s passion for the « cause of Bohemia » seems particularly striking in « The nightly conspiracy of Claudius Civilus at the Schakerbos ».
The large painting figured as one in a series planned to decorate the new Amsterdam city hall to celebrate the revolt of the Batavians against the Romans. Starting from historical elements of Tacitus, the story had been cooked up to warm up Dutch patriotism since the reference to Spanish tyranny was clear to all. For reasons unknown today, Rembrandt’s painting was taken down after a couple of months. To mock the cowardice of the ruling elites, Rembrandt seems to have transposed the historical scene into his present timeframe.
One Swedish historian thinks that the leader of the conspiracy here is not Claudius Civilis (the Batavian general who lost an eye in battle), but another general who equally lost an eye in battle and which was non-other than the Hussite general Jan Zizka! (*4).
Remember that Comenius and the revolt of Bohemia strongly identified with John Huss. Looking closely makes you discover that Rembrandt’s Claudius Civilis is indeed dressed up in central European costume. From left to right one sees first a Dutch patrician. Is this a portrait of the then rising republican Jan De Wit?
Next, one sees a monk, without weapons, who poses his hand on Civilus’ arm in a conspiratorial gesture. Is this Comenius resistance movement, the Unity of the Brethren?
According to the historians, the two chalices, one wide, the other narrow, could signify the « Eucharist under the two species », namely that bread and wine be shared with all, which happened to be one of the demands of the Jan Hus tradition.
One also can identify a Jew or rabbi taking place in the conspiracy. Looks pretty weird for a simple Batavian conspiracy! That the establishment was unhappy to see their hero painted as an ugly Cyclops seems probable.
But to be challenged in their flight forward into pompous fantasy in stead of taking up the urgent tasks of their time was another one.
King of Swedish Steel, Louis De Geer
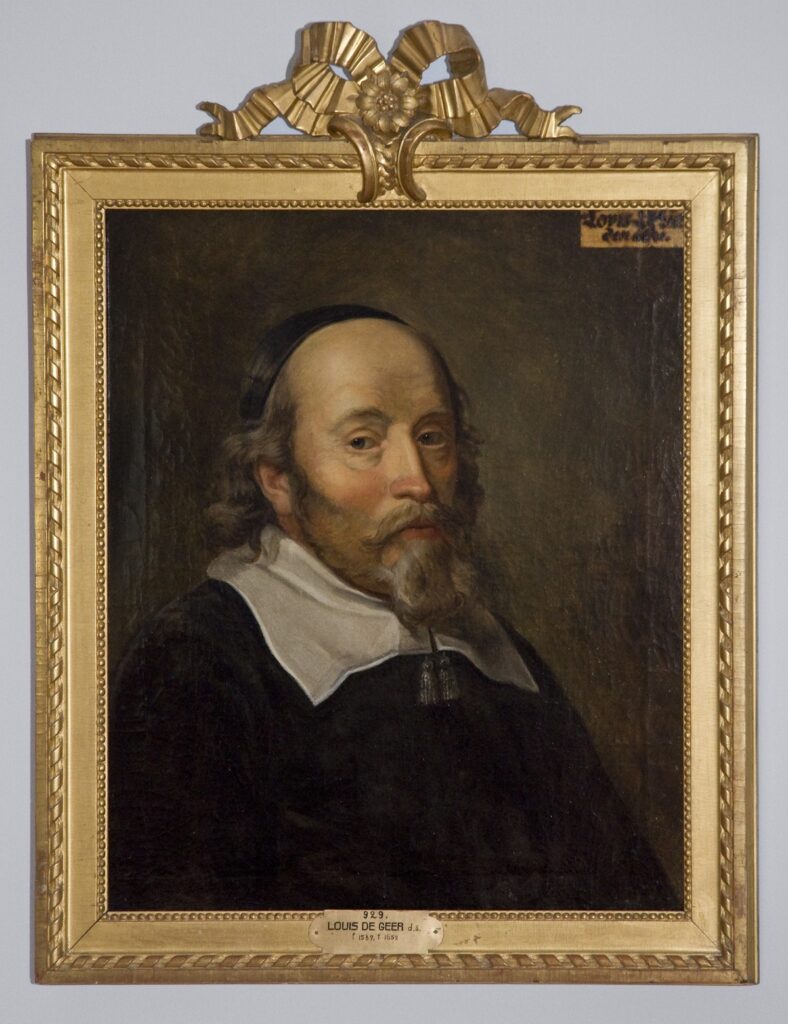

Comenius arrives in Amsterdam on invitation of the de Geer family in 1656, the year of Rembrandt’s bankruptcy (*5).
Louis de Geer, alias « the Steel King » and his son Laurent were the life-long protectors of Comenius for whom they paid the funeral and even build a chapel in the city of Naarden, some miles outside Amsterdam.
Originally from Luik (Liège) in today’s Belgium, that uncompromising Calvinist family settled in Amsterdam. It was the de Geer family who led the foundations of Sweden’s industrial flowering of iron, steel and copper . To do this, de Geer brought three hundred families of Walloon steelworkers to Sweden, and for whom he build hospitals, schools, housing projects and commercial facilities.
De Geer also financed the scottish preacher John Dury and the « intelligencer » Samuel Hartlib, two active friends of Comenius in England. At war with the Royal Society and Francis Bacon, they wanted to render scientific knowledge available to all of the population.
John Milton’s treatise On Education was dedicated to the same Samuel Hartlib. Louis de Geer and Sweden’s prime Minister Johan Skytte, realized Comenius education projects were the best of all possible investment to foster the physical economy. His educational reforms created a labor force of such an exceptional quality and astonishing productivity, that they warmly invited him to Sweden and asked him to reform the nation’s educational system.
That relationship of Comenius with the de Geer family leads us to Rembrandt, since Louis de Geer’s sister, Marghareta, and her husband Jacob Trip, one of the major shareholders of the Swedish copper mines, had their portrait done by Rembrandt, offering him a well paid order during very difficult years.

The City of Amsterdam allotted Comenius a yearly pension, encouraged him to publish his complete works on pedagogy and offered him the keys of the city library. Comenius brought over his family and assistants and installed a library and a printing shop behind the Westerkerk where Rembrandt will be buried.
Comenius, when going every day from his house to his printing shop crossed the street where Rembrandt lived his last days. Since early this century, Czech curators got convinced that Rembrandt’s Portrait of an old man at the Uffizi Gallery in Florence, is in reality a portrait of Comenius (*6).


True or not, one has to realize that Rembrandt demanded to each of his models to sit each day for four hours over a period of three months to paint their portrait, a thing maybe not so evident for the aging Comenius.
But what is known with certainty is the fact that one of Rembrandt’s pupils, Juriaen Ovens, painted Comenius portrait during that period.
The Peace of Westphalia and the « Via Lucis »

Although Bohemia did not gain its long-desired independence at the peace of Westphalia, one cannot underestimate Comenius influence on the negotiations leading to the establishment of the peace-treaty. His work, Cesta Pokoje (Road to peace) of 1630, written in Czech is described as,
« an ethical-religious writing in which love, faith and mutual comprehension are established as the single ethical foundations of a possible peace ».

From 1641 to 1642, right before the start of the first peace negotiations, Comenius wrote the Via Lucis (The path of light), which could have been used as a guiding memorandum for the negotiators.
At the question if this Via Lucis was a millenarist mystical vision, as has been often pretended, we can consider the following.
Asked what could be hoped for and when a major change could take place, Comenius answered that the hope would come with the arrival of a time where the Gospel of the Kingdom would be preached all over the world and universal peace established.
That change could arise as the result of the emergence of a light to which will turn not only the Christian, but all the people of the world.
That light will come, « from the combination of the lanterns of human conscience, of a rational consideration of the works of God or of nature, and from the law or divine will ».
For him, « human enterprise can, through prayer and considerations of pious men imagine the possible ways to unite these rays of light, to irradiate them on the entirety of the human species and to spill similar thoughts in the minds of others » (*7).

One identifies exactly that concept in an etching of Rembrandt that Goethe awkwardly used by having it copied as frontispiece for his Faust in 1790 (*8).
The subject here is not at all a man going along to get along with the devil, but light (mirror of Christ) enlightening the life and the mind of the mortals. Way before Voltaire and opposed to the Venetian illuminati, Comenius and Rembrandt made own the metaphor of light.
To get an even more precise idea of Comenius demands for peace, one can read another memorandum called Angelus Pacis (The peace-angel),
« send to the English and Dutch peace Ambassadors at Breda, a writing designated to be sent afterwards to all the Christians of Europe and then to all the nations of the world in order to stop them, that they cease fighting each other ».
Comenius first remarks laconically that England and Holland are morally so degraded that they even don’t need some spiritual difference as a pretext, but fight each other for purely material possessions! As a way out, he proposes a new friendship:
« But how do you conceive that new friendship (or rather reestablishment of your friendship)? Will it be not by the general pardon that you will allow each other? The wise men have always seen the oblivion of received injuries as the surest road leading to peace. Touching too rudely the wounds, is to revivify the pains and to furnish the wounds an occasion for irritation.
« When this is true, it would be to be wished that the river Aa, whose tranquil waters irrigate Breda, would turn for this hour into the river Lethe of which the poets tell us that whoever drinks their water forgets everything of the past.
« The one who is guilty of trouble, God will find him, even when men, for love of peace, spare him. That the just one starts accusing himself; that means that the one whose conscience accuses him of having broken the friendship and witnessed enmity, should, according to justice, be the first one and the most ardent to reestablish friendship. If the offended party neglects that duty of justice, it will be the honor of the offended party to assume that honorable role, according to the word of the philosopher. » (*9)

COMENIUS: TEACH EVERYTHING TO ALL AND EVERYONE
Jan Amos Komensky (« Comenius ») (1592-1670) was above all a militant teacher, practicing « the universal art of teaching everything to everybody » (pan-sophia) and reckless source of inspiring enthusiasm.
One year after his death in 1670, Leibniz wrote of him: « time will come, Comenius, that honors will be offered to your works, to your hopes and even to the objects of your desires ».
In some domains, indeed, Comenius was Leibniz‘s precursor. First, he fought the fossilization of thought resulting from the dominant Aristotelianism: « Little time after that unification between Christ and Aristotle, the church fell into a pitiable state and became filled with the uproar of theological dispute ».
Strong defender of the free will that he didn’t see entirely in contradiction with an Augustinianconcept of predestination, he felt closer to John Huss than to Calvin, while generally labeled a « Calvinist » by historians.
In 1608, Comenius enters the Latin School of Prérov (Moravia), a school reorganized at the demand of Charles Zerotina on the model of the Calvinist school of Sankt-Gall in Switzerland. Zerotina was one of the key figures of the Bohemian nobility, promoter of the Church of Unity of Brethren, organizer of popular education and key leader of the international anti-Habsburg resistance. For example, in 1589 he lends a considerable amount of money to the French King Henri IV, which he meets in Rouen, France, in 1593 in support of ending the religious wars with the the Spanish.
Henri IV’s conversion to Catholicism (« Paris is worth a mass ») ruined Zerotina’s hope to reproach the Unity of Brethren with the French Huguenots. Befriended with Theodore de Bèze, which he met regularly when studying in Basel and Geneva, Zerotina sent Comenius to study at the Herborn University in Nassau. That University was founded in 1584 by Louis of Nassau, brother of William the Silent, the leader of the revolt of the Netherlands against Habsburg’s Spain. Louis of Nassau, a key international coordinator of the revolt was in permanent contact with the humanist Huguenot leader Gaspard de Coligny in France and with Walsingham, the chancellor of England’s Queen Elisabeth Ist.
Together with Zerotina, Comenius unleashed the revolt of Bohemia of 1618. After spending some time with the guerrilla forces for which he drew a map of Moravia, Comenius went into exile, as bishop of his church, the « Unity Brethren of Bohemia ».
Till his death, he was the soul of the Bohemian resistance, the gray eminence of the Diaspora and the guardian that prevented the Czech language from disappearing, since it was replaced by German in Bohemia. Since wars are only possible if large parts of the population remain uneducated, for Comenius education became the leading edge to fight for Peace.
Opposed to the Jesuit educators who consolidated their own power by education the elites only, Comenius, starting from his conviction that every individual is made in the living image of God, elaborated with great passion a very high level curriculum, which he wanted accessible to all, as he develops this in his « The Great Didactic » (1638).
Following the advice of Erasmus and Vivès, Comenius abolishes corporal punishment and decides to bring boys and girls in the same class. With him, a school needs to be available in every village, free of cost and open to everybody.
Breaking the division between intellectual and manual work, the schools were part-time technical workshops, anticipating France’s Ecole Polytechnique and the Arts et Metiers (technical school to perfect working people), completely oriented towards the joy of discovery. Leibniz idea of academies originated in Comenius’ schools and societies of friends.
For him, as for Leibniz, the body of physics couldn’t walk without the legs of metaphysics. Integrating that transcendence, he strongly rejected the very idea that nature was reducible to a mere aggregate defined by formal laws, and he adamantly lambasted Bacon, Galileo and Descartes for doing so. In stead, nature has to be looked to as a dynamic process defined by the becoming. That becoming is not repetitive, but permanent progression and potentialization: nature has a quality of development, tending towards self-accomplishment and harmony.
He was severely attacked by Descartes’ « Judgment of the Pansophical works » and mocked by Voltaire, who made him appear as Candide‘s naive philosophy teacher « Pangloss ».
Founder of modern pedagogy, he realized children are beings of affection, before becoming beings of reason. Up till those days, ignorant children were often seen as possessed by the devil, a devil which had to be beaten out of them. The French cardinal Pierre de Bérulle, founder of the Oratorians, reflected that mindset when he wrote that « infancy is the most vile and abject state of man’s nature after that of death ».
To make knowledge accessible to all, Comenius revolutionized the dogmas of that educational approach. In well-ordered classrooms, beautifully decorated with maps, classes would last only one hour covering all the domains one fiends in an engraving of Comenius: theology, manual works, music, astronomy, geometry, botany, printing, construction, painting and sculpture.
Comenius taught Latin, but was strongly convinced that every pupil had to master first his mother tongue. That was a total revolution, since up till then, Latin was taught in Latin, and to bad for those who didn’t understand already !
He also will also re-introduce illustrated textbooks (« The sensible world in images »)(1653), which had been stupidly banned from schools to « not invite the senses to disturb the intellect ». For Comenius, images have the same role as a telescope, displacing the field of perception beyond immediate limits.
His ideas, and especially the rapid successes of schools adopting his pedagogy attracted all of Europe and beyond. In 1642, Comenius was hired by Johan Skytte, the influential chancellor of the University of Uppsala, to reorganize the Swedish education system according to his principles. Skytte, an erudite Platonist inspired by Erasmus, will be Gustaphe Adolph’s preceptor and his son Bengt Skytte will be an influential teacher of Leibniz.
Before that job, Comenius discarded a similar offer originating from Richelieu of France and the offer that came from John Winthrop Junior from the United States who offered Comenius to preside Harvard University, newly founded in the Massachussetts Bay Colony of America.
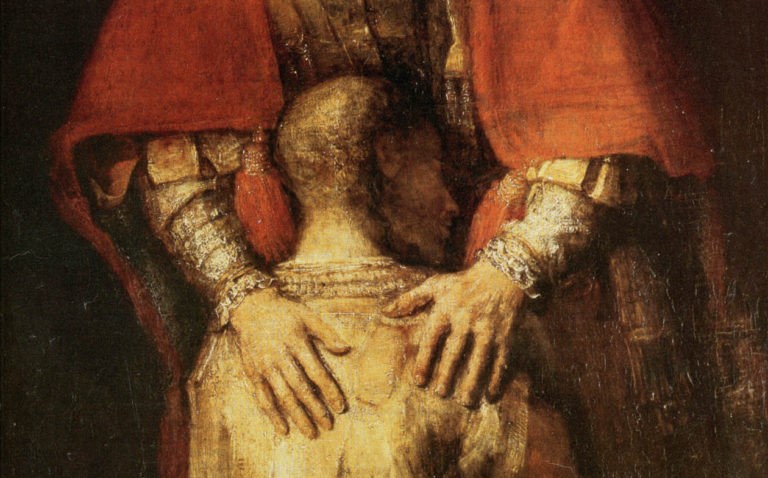
Rembrandt and Forgiveness
To express in art that precise moment where love gives birth to pardon and repentance will be precisely one of Rembrandt’s favorite subjects. The fact that he choose the name Titus for his son, after the roman emperor who supposedly had showed great clemency toward the early Christians, demonstrates that point. But Titus was also the name of a bishop of Creta who was a close collaborator of Apostle Paul.
Rembrandt was fascinated by the figure of Saint-Paul, who used to be after all a roman officer who, through his conversion, showed the possible transformation of each individual for the better, capable of becoming a militant for the good.
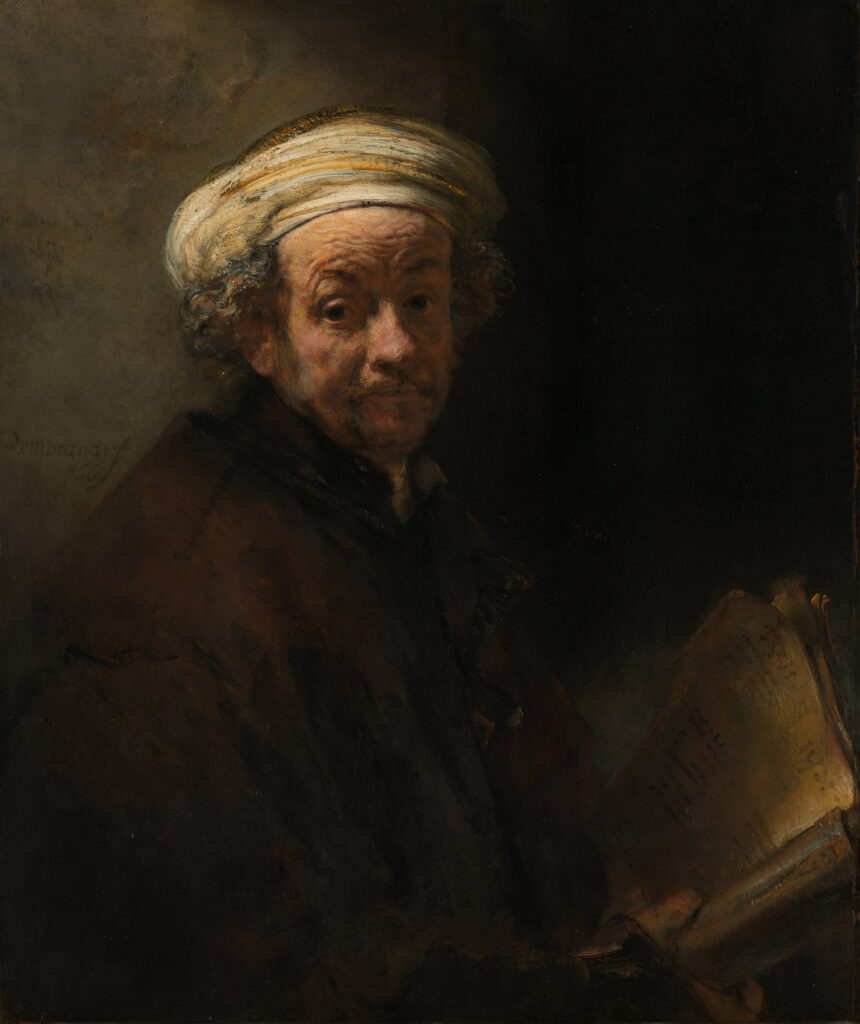

Rembrandt’s self-portrait of the Rijksmuseum, with the famous « ghost-image » of a badly lit dagger nearly planted his breast supposedly represent him as Saint-Paul, traditionally represented defending Christian faith with the scripture in one hand and the sword in the other.
The bible in the armored hand do appear in that painting, but the sword here seems more as a dagger, suggesting an eventual reference to the name given by Erasmus to his Christian’s manual, the « Enchiridion » after the Greek word egkheiridion (dagger).
The Prodigal Son

In one of Rembrandt’s late works, the « Return of the prodigal son », despite the fact that the work was completed by a pupil, we see how profoundly he dealt with precisely that subject. The expressiveness of the figures is amplified by the nearly life-size representation on the wide canvas (262 x 205 cm).
The father’s eyes, plunged in interior vision, look yonder the small passage by which the son hasarrived, as doubting of the happiness that overwhelms him, since his son « who was dead », « came back to life ».
The son, who installs his convicts head on the father’s abdomen, engages in the act of total repentance. The naked foot who leaves behind the rotten shoe, communicates in a metaphorical way that sinners deed of repentance, offering what he has inside. The father embraces his son by putting his pardoning hands on his shoulders, while the jealous brothers stand by wondering and enraged why so much love is given to the son « who had spoiled the fathers good with prostitutes ».
Three observations indicate Comenius person and thought might have inspired this work.
First, according to all available portraits, the face of the father shows heavy resemblance with the treats of Comenius himself, a well known militant for peace based on repentance and pardon which Rembrandt probably met frequently during that period.
Second, and after a second look, the son doesn’t look European at all, but actually Negroid, which would add to the painting some critical thoughts on the widely practiced slavery of the European powers of those days.
To conclude, one could interpret the parable of the prodigal son in a much larger sense: is this not man itself, son of God, who returns to his father after having wandered on the roads of sin? Comenius, after a moment of nearly total desperation uses that same image in his book The labyrinth of the world and the paradise of the hearth (1623).
Similar to the image employed by the Dutch painter Hieronymous Bosch, in his « ambulant salesman », man gets lost in the multiplicity of the world that leads him to self-destruction, but after a crisis decides to regain divine unity.
In order to add still another dimension to the discussion on the quality of love involved in art, it is useful to contrast our master with the works of the most talented belonging to the tradition of his detractors: Peter-Paul Rubens.
Rembrandt, Rubens and other Philistines
But before investigating Rubens, it is appropriate to consider the following. Despite the fact that Rembrandt came out of the immense intellectual ferment of the late sixteenth century University of Leiden, one of the cradle’s of humanism, one cannot escape the fact that his lashing career would have infatuated many.
Remember, Constantijn Huygens « discovered Rembrandt » in 1629, while still a young millers son running a small boutique with Jan Lievens, asking them to come to Amsterdam and work for the government. (*10).
Rembrandt’s « patron » nevertheless would write without blushing in his diary Mijn Jeugd (my youth) that Peter Paul Rubens, the Flemish baroque painter was « one of the seven marvels of the world ».
Rubens was, before everything else, the talented standard bearer of the « enemy » Counterreformation and its Jesuits army, whose admiration made Rembrandt totally uncomfortable. How could this virtuoso painter be seen as the brightest star on the firmament of painting? According to some, Huygens was looking for « a Dutch Rubens », capable of making shine the « elites » of the nation.
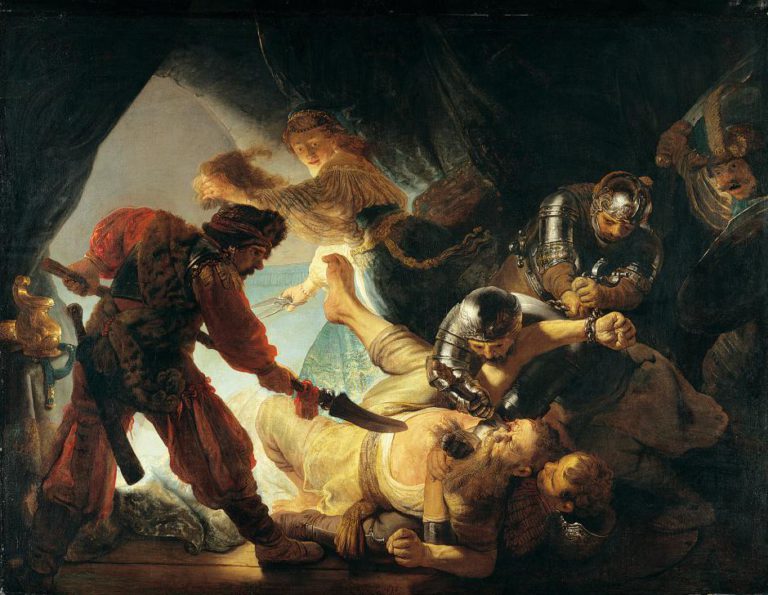

Rembrandt at one point got so irritated with Huygens’ shortsightedness that he
offered him a large painting called Samson blinded by the Philistines. The work, a pastiche of the violent style, painted « à la Rubens », shows roman soldiers gouging out Samson’s eye with a dagger. Did Rembrandt suggest that his Republic (the strong giant) and its representatives were blinded by their own philistinism?
When a little Page becomes a great Leporello
Rembrandt perfectly translates the feeling of revulsion any honest Dutch patriot would have felt in front of Rubens. Had the Dutch elites already forgotten that Peter Paul’s father, Jan Rubens, once a Calvinist city councilor of Antwerp close to the leadership of the revolt of the Netherlands, had severely damaged the integrity of the father of the fatherland by engaging in an extra-conjugal relationship with Anna of Saxen, the unstable spouse of William the Silent?
Humiliated, but with courage and determination, Rubens mother fought as a lioness to free her husband from an uncertain jail. Her son Peter Paul, could not but become the calculated instrument of vengeance against the protestants and an indispensable tool to do away the blame hanging over the family. Hence, at the age of twelve, Peter Paul was sent to the special college of Romualdus Verdonck, a private school specifically designed to train the shock troops of the Counterreformation.
From there on, Rubens becomes a pageboy at the little court of Marguerite de Ligne, countess de Lalaing at Oudenaarde, whose descendants still form the Royal blood of today’s Belgium. As a kid, Rubens copied the biblical images of the woodprints of Holbein and the Swiss engraver Tobias Stimmer. After two waves of iconoclasm (1566 and 1581), the Counterreformation was very eager to recruit image-makers of all kinds, but under strict regulations specified by the final session of the Council of Trent in 1563. (*12).
After a short training by Abraham van Noort, Rubens career was boosted by his entering of the workshop of Otto van Veen. Born in Leiden in 1556 and trained by the Jesuits, « Venius » was the pupil of the master-courtier Federico Zuccari in Rome. Zuccari was the court painter of Habsburg’s Philippe II of Spain and the founder of the « Accademia di San Luca ». Traveling from court to court, Venius succeeded in getting the favors of Alexander Farnèse, the malign Spanish governor in charge of occupying Flanders.
Farnèse, who actually organized the successful assassination of the father of the Netherlands, the erasmian humanist William the Silent in 1584, nominated Venius as his court painter and as engineer of the Royal armies.
Furthermore, Venius will be the man who opened Rubens mind on Antiquity and together they will read and comment classical authors in Latin. Especially, he will show Rubens that an artist, if he wants to attain glory during his lifetime, must appeal a little bit to his talent and a very much to the powerful.
In Italia
In may 1600, Rubens rides his horse to Venice. In June, during Carnival he encounters the Duke of Mantua, Vincent of Gonzague, who is the cousin of archduke Albert who is ruling then Flanders with Isabella since 1598.
The duke of Mantua, the oligarchic type Mozart portrays in his « Don Giovanni » and Verdi explicitly in « Rigoletto », was very fond at the idea to add a « fiamminghi » to his stable.
The court of Mantua, in a competition of magnificence with other courts, notably those of Milan, Florence or Ferrare, employed once the painter Mantegna, the architect Leon Battista Alberti and the codifier of courtly manners Baldassare Castiglione. At the times of Rubens, the court paid the living of poet Torquato Tasso and the composer Monteverdi which wrote in Mantua his « Orpheus » and « Ariane » in 1601.
Galileo was also one of the guests for a short period in 1606. But especially, the Duke had in his possession one of the largest collections of works of art of that period, and his agents in Italy and all over the world were in charge of identifying new works worth becoming part of the collection.

An inventory of 1629 lists three Titian’s, two Raphael’s, one Veronese, one Tintoretto, eleven Giulio Romano’s, three Mantegna’s, two Corregia’s and one Andrea del Sarto amidst others. Similar to Giulio Romano who became the mere instrument of the « scourge of the princes » Pietro Aretino, our Flemish painter became just another Leporello, an obligingly « valet » enslaved by the Duke.
When we look to his self-portrait with his Circle of friends in Mantua, we see a fearful man, who « became somebody » because surrounded by « people who made it » and recognized by the powerful.
In Espagna
Immediately the Duke gave Rubens a truly Herculean task: transport a quite sophisticated present to Philippe III and his prime minister the Duke of Lerma from Mantua to Madrid. On top of a little chariot specially designed for hunting and several boxes of perfume, the core of the present consisted of not less then forty copies of the best paintings of the Duke’s private collection, notably some Raphael‘s and Titians. On top, Rubens’ mission was « to paint the fanciest women of Spain » during his trip. While his patron in Mantua whines for his return, Rubens will deploy his seductive capabilities at the Spanish court which looked far more promising to his career.
Back in Italy, his immediate going to Rome seems an opportune move, since in these days Barocci was held for to old, Guido Reni for to young. Also, Annibale Carracci appeared out of order since suffering from melancholic apoplexies while Caravagio, accused of murder, was hiding on the properties of his patrons, the Colonna’s.
But essentially, Rubens goes to the holy city because he’s enthusiastically promoted there by the Genovese cardinal Giacoma Serra, very impressed by the « splendid portraits » of women Rubens painted for the Spinola-Doria dynasty in Genoa.
Nevertheless, hearing about the imminent death of his mother, Rubens rushes to Antwerp, and after much a hesitation settles his workshop there, far at a distance from the centers of power, but close to the fabulous privileges he obtains from the Spanish regents over the Netherlands, Albrecht and Isabella.
In Antwerpia
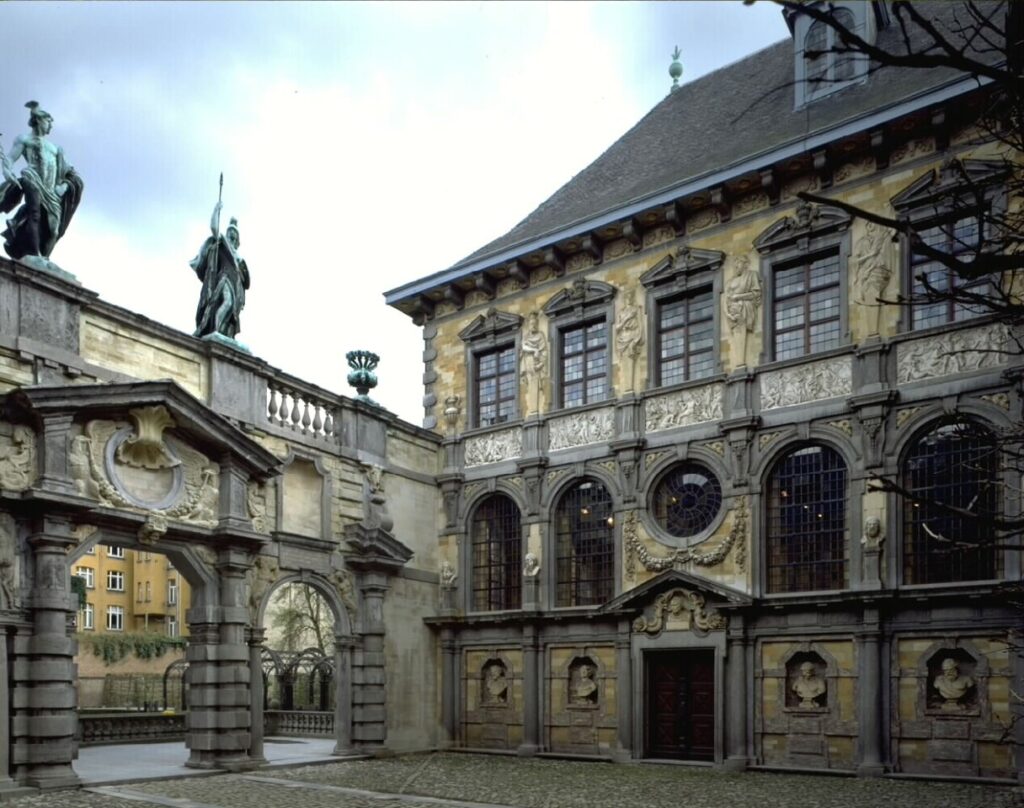

These advantages were such that conspiracy-theorist see them as sufficient proof that there was a blueprint to kill the soul of the Erasmian spirit in Christian painting in the region.
First, Rubens will receive 500 guilders per year without any obligation concerning his artistic output except the double portrait of the rulers, any supplementary order necessitating separate payment.
Next, Rubens obtains a status permitting him to bypass the regulations and obligations of the Saint-Luc painters guild, particularly the rule that limits the number of pupils and the amount of their salary. And since a lot is never enough, Rubens obtains a tax-exemption status in Antwerp! As a real patrician he orders the building of his palace.
Broken down long time ago, and for whatever reasons, one has to observe that it was during the times of Flemish collaboration with Hitler’s Germany (from 1938 to 1946) that his Genovese modeled resort, temporarily recreated in 1910 for the Universal Exposition in Brussels, will be entirely rebuild after the engravings of Jacobus Harrewijn of 1692, decorated as the original and the interior filled with fitting old furniture (*14).
It is true that his enthusiasm for opulent blondes and violent action was interpreted by Nazi historians as the expression of profound sympathy for the Nordic races, while his visual energy was seen as the antithesis of « degenerated » art. The Rubens cult in Antwerp might tell us something interesting about the recurrent rise of rightwing extremism in that city.
Propaganda Genius
Rubens feat was to « merchandize » the ruling taste of the oligarchy of his time. Similar to the German filmmaker Leni Riefenstahl under Hitler, Rubens became the genial producer of their propaganda. Precocious child and brilliant draughtsman, he had spent hours and hours working after Italian collections and bas-reliefs in the ruins of Rome.
Since the « Warrior-pope » Julius II and Leo X took over the Vatican, art had to submit to the dictatorship of the degenerated taste of imperial Rome. Eight years of work, from 1600 to 1608, in Genoa, Mantua, Florence, Rome, without forgetting Madrid, with free access to nearly all the great collections of antiquities and paintings of the old families, enabled Rubens to constitute a « data-base », whose fructification will generate the bulk of his fortune.
Specialists do point easily to the unending stream of visual quotes identified in his works. A group of Michelangelo in « The Baptism of Christ » (Koninklijk Museum voor Schone Kunsten, Antwerp); a pose of Raphael’s Aristotle in the School of Athens in his « St-Gregory with St-Domitilla, St-Maurus and Papianus » (Gemäldegalerie, Berlin) or one of his Madonna’s in « The fall of man » (Rubenshuis, Antwerp), without forgetting a head of the Laocone in the « Elevation of the Cross » (Cathedral, Antwerp) or the « contraposto » of a Venus coming straight away from a roman statuary in « The union of Earth and Water » (Hermitage, Saint-Petersburg). (*11).
The Tulip, Seneca plus Ultra

The desire to be accepted by the ruling oligarchs becomes even clearer when we discover his admiration for Seneca.
Through his education and under the influence of his brother Philippe, Peter Paul Rubens will become a fanatical follower of the Roman neo-stoic Seneca (4 BC – 65 AC). In his painting The four philosophers, Rubens paints himself standing, once again « on the map » with those who got a chair at the table.
With a view on the palatine hill in the background, site of the Apollo cult considered the authentic Rome, we see his brother Philippe, a renowned jurist, sitting across the leading stoic ideologue of those days, Justus Lipsius and his pupil Wowerius, all situated beneath a niche filled with a bust of Seneca honored by a vase with four tulips, two of them closed, and the other two opened.
Originally from Persia, the tulip bulb was brought from Turkey to Europe by an Antwerp diplomat in 1560. Its culture degenerated rapidly from a hobby for gentleman-botanist into the immense collective folly known as the Tulip Mania and « tulip-bubble » or « Windhandel » (wind-trade).
That gigantic speculative bubble bursted in Haarlem on February 2, 1637, while some days earlier, a tulip with the name of « vice-roy » went for 2500 guilders, paid in real goods being two units of wheat and four of rye, four fat calves, eight pigs, a dozen of sheep, two barrels of wine, four tons of butter, a thousand pounds of cheese, a bed and a silver kettle drum (*14).

As can be seen in his painting Rubens in his garden with Helena Fourment, Rubens was not indifferent to that highly profitable business. Behind the master and his spouse, appears discretely behind a tree in Rubens garden a rich field of tulips!
But in the « Four philosophers », the tulip is nothing else than a metaphor of the « Brevity of life », an essay of Seneca.
The latter, tutor of Nero, preached a Roman form of sharp cynicism known under the label of fatum (fatality): to rise to (Roman) grandeur, man must cultivate absolute resignation. By an active retreat of oneself on oneself and by a obstinate denegation of a threatening and absurd world, man discovers his over-powerful self. That power even increases, if the self decides that death means nothing.
At the opposite of Socrates, who accepted to die for giving birth to the truth, Seneca makes his suicide his main existential deed. Waiting for his hour, his job is to steer his boredom by managing alternating pleasures and pains in a world where good and bad have no more sense.
As all cases of radical Aristotelianism, that philosophy, or « art of life » steers us in the hell of dualism, separating « reason », cleaned from any emotion, from the unbridled horses driving our senses. These two ways of being unfree makes us a double fool. Rubens fronts for that philosophy in his work Drunk Silenus.

The excess of alcohol evacuates all reason and brings man back to his bestial state, a state which Rubens considers natural. Instead of being a polemic, the painting reveals all the complacency of the painter-courtier with the concept of man being enslaved by blind passion. Instead of fighting it, as Friedrich Schiller outlines the case repeatedly and most explicitly in his « On the Esthetical Education of Mankind », Rubens cultivates that dualism and takes pleasure in it. And sincerely tries to recruit the viewer to that obscene and degrading worldview.
Peace IS war

As an example of « allegories », let us look for a moment at Rubens canvas Peace and War.
Above all, that painting is nothing but a glittering « business-card » as one understands knowing the history of the painting. At one point, Rubens, who had become a diplomat thanks to his international relations, organized successfully the conclusion of a peace-treaty between Spain and England (which collapsed fairly soon).
Repeating that for him « peace » was based on the unilateral capitulation of the Netherlands (reunification of the Catholic south with the North ordered to abandon Protestantism), he succeeded entering the Spanish diplomatic servicesomething pretty unusual for a Flemish subject, in particular during the revolt of the Netherlands.
Following this diplomatic success, the painter is threefold knighted: by the Court of Madrid to which he presents a demand to obtain Spanish nationality; by the Court of Brussels and also by the King of England!
Before leaving that country, he offers his painting « Peace and War » to King Charles. The canvas goes as follows: Mars is repelled by wisdom, represented as Minerva, the goddess protecting Rome. Peace is symbolized by a woman directing the flow of milk spouting out of her breast towards the mouth of a little Pluto. In the mean time a satyr with goat hooves displays the corn of abundance…
On the far left, a blue sky enters on stage while on the right the clouds glide away as carton accessories of a theatre. Rubens main argument here for peace is not a desire for justice, but the increase of pleasures and gratifications resulting from the material objects which men could accumulate under peace arrangements! Ironically, seen the cupidity of the ruling Dutch elites, which Rembrandt would lambaste uncompromisingly, it seems that Rubens might have succeeded in convincing these elites to sell the Republic for a handful of tulips. If only his art would have been something else then self-glorification! Here, his style is purely didactical, copied from the Italian mannerism Leonardo despised so much.
Instead of using metaphors capable to make people think and discover ideas, the art of Rubens is to illustrate symbolized allegories. The beauty of an invisible idea has never, and can not be brought to light by this insane iconographical approach. His « style » will be so impersonal that dozens of assistants, real slave laborers, will be generously used for the expansion of his enterprise.
King Christian IV’s physician, Otto Sperling, who visits Rubens in 1621 reported:
« While still painting he was hearing Tacitus read aloud to him and at the same time was dictating a letter. When we kept silent so as not to disturb him with our talk, he himself began to talk to us while still continuing to work, to listen to the reading and to dictate his letter, answering our questions and then displaying his astonishing power. »
« Then he charged a servant to lead us through his magnificent palace and to show us his antiquities and Greek and Roman statues which he possessed in considerable number. We then saw a broad studio without windows, but which captured the light of the day through an aperture in the ceiling. There, were united a considerable amount of young painters occupied each with a different work of which M. Rubens had produced the design by his pencil, heightened with colors at certain points. These models had to be executed completely in paint by the young people till finally, M. Rubens administered with his own hand the final touch.
« All these works came along as painted by Rubens himself, and the man, not satisfied to merely accumulate an immense fortune by operating in this manner, has been overwhelmed with honors and presents by kings and princes ». (*15).
We know, for example, that between 1609 and 1620, not less than sixty three altars were fabricated by « Rubens, Inc. ». In 1635, in a letter to his friend Pereisc, when the thirty years war is ravaging Europe, Rubens states cynically « let us leave the charge of public affairs to those who’s job it is ».
The painter asks and obtains a total discharge of his public responsibilities the same year while retiring to enjoy a private life with his new young partner.
Painter of Agapè, versus painter of Eros
Being a human, Rembrandt correctly had thousand reasons to be allergic to Rubens. The latter was not simply « on the wrong side » politically, but produced an art inspiring nothing but lowness: portraits designated to flatter the pride of the mighty by making shine and glitter some shabby gentry; history scenes being permanent apologies of Roman fascism where, under the varnish of pseudo-Catholicism, the alliance of the violent forces of nature and iron-cold reason dominated. Behind the « art of living » of Seneca, there stood the brutal methods of manipulation of the perfect courtier described by Baldassare Castiglione in his « Courtier ». For courtly ethics, everything stands with balance (sprezzatura) and appearance, and behind the mask of nice epithets operates the savage passions of seduction, possession, rape and power-games.
On the opposite, Rembrandt is the pioneer of interiority, of the creative sovereignty of each individual. To show the beauty of that interiority, why not underline paradoxically exterior ugliness?
In the « Old man and young boy » of Domenico Ghirlandajo, an imperfect appearance unveils a splendid beauty. The old man has a terribly looking nose, but the visual exchange between him and the boy shows a quality of love which transcends both of them. At the opposite of Seneca, they don’t contemplate the « brevity of life », but the longevity or « immortality of the soul ».
Martin Luther King, in a sermon tries equally to define these different species of love. After defining Eros (carnal love), and Philia (brotherly love), he says:
« And then the Greek language comes out with another word. It’s the word agape. Agape is more than Eros; it’s more than an aesthetic or romantic love; it is more than friendship. Agape is understanding, creative, redemptive goodwill for all men. It is an overflowing love which seeks nothing in return. Theologians would say that it is the love of God operating in the human heart. And so when one rises to love on this level, he loves every man, not because he likes him, not because his ways appeal to him, but he loves every man because God loves him, and he rises to the level of loving the person who does an evil deed, while hating the deed that the person does. » (*17)
Then, King shows how that love intervenes into the political domain:
« If I hit you and you hit me and I hit you back and you hit me back and go on, you see, that goes on ad infinitum. It just never ends. Somewhere somebody must have a little sense, and that’s the strong person.
The strongperson is the person who can cut off the chain of hate, the chain of evil. And that is the tragedy of hate, that it doesn’t cut it off. It only intensifies the existence of hate and evil in the universe. Somebody must have religion enough and morality enough to cut it off and inject within the very structure of the universe that strong and powerful element of love. »
You probably understood our point here. Martin Luther King, in his battle for justice, was living in the same « temporal eternity » as Rembrandt and Comenius opposing the thirty years war. Isn’t that a most astonishing truth: that the most powerful political weapon at man’s disposal is nothing but transforming universal love, over more available to everyone on simple demand? But to become a political weapon, that universal love cannot remain a vague sentiment or fancy romantic concept. Strengthened by reason, Agapè can only reach height with the wings of philosophy.
Rembrandt and Comenius knew that « secret », which will remain a secret for the oligarchs, if they remain what they are. »
The Little Fur
Another comparison between two paintings will make the difference even more clearer between Eros and Agapè: Het pelsken (the little fur) of Rubens (left) and Hendrickje bathing in a river of Rembrandt (right).
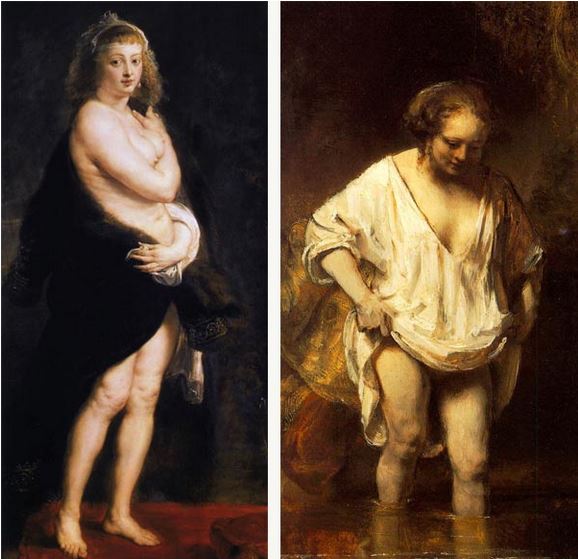

That comparison has a particular significance since the two paintings show the young wives of both painters. At the age of fifty-three Rubens remarried the sixteen year old Helena Fourment, while Rembrandt settled at the age of forty-three with the twenty-two year old Hendrickje Stoffels.
The naked Helena Fourment, with staring eyes, and while effecting an hopeless gesture of pseudo-chastity, pulls a black fur coat over her shoulders. The stark color contrast between the pale body skin and the deep dark fur, a typical baroque dramatic touch of Rubens, unavoidably evokes basic instincts. No wonder that this canvas was baptized the « little fur » by those who composed the catalogues.
However, paradoxically, Hendrickje is lifting her skirt to walk in the water, but entirely free from any erotic innuendo! Her hesitating, tender steps in the refreshing water seem dominated by her confident smile. Here, the viewer is not some « Peeping Tom » intruding into somebody’s private life, but another human being invited to share a moment of beauty and happiness.
Suzanne and the Elderly
Another excellent example is the way the two painters paint the story of Suzanne and the elderly. Comenius, was so impassioned by this story that in 1643 he called his daughter Zuzanna in 1646 his son Daniel. This Biblical parable (Daniel 13) deals with a strong notion of justice, quite similar to the one already developed in Greece by Sophocles Antigone. In both cases, in the name of a higher law, a young woman defies the laws of the city.
In her private garden, far from intruding viewers, the beautiful Suzanne gets watched on by two judges which will try to blackmail her: or you submit to our sexual requests, or we will accuse you of adultery with a young man which just escaped from here! Suzanne starts shouting and refuses to submit to their demands. The next day, Suzanne gets accused publicly by the judges (the strongest) in front of her family, but Daniel, a young man convinced of her innocence, takes her defense and unmasks the false proofs forged by the judges. At the end, the judges receive the sentence initially slated for Suzanne.

In the Rubens painting, a voluptuous Suzanne lifts her desperate eyes imploring divine help from heaven. The image incarnates the dominant but
insane ideology of both Counterreformation Catholicism and radical Protestantism: the denial of the free will, and thus of the incapacity to obtain divine grace through one’s acting for the good. For the Calvinist/protestant ideologues, the soul was predestinated for good or evil. Reacting by a simple inversion to the crazy indulgences, it was « logical » that no earthly action could « buy » divine grace. So whatever one did, whatever our commitment for doing the good on earth, nothing could derail God’s original design. The Counterreformation Catholics thought pretty much the same, except that one could claim God’s indulgence in the context of the rites of the Roman Catholic Church, especially by paying the indulgences: « No salvation outside the church ».

In a spectacular way, Rembrandt’s Suzanne and the elderly reinstates the real evangelical Christian humanist standpoint: a chaste Suzanne looks straight in the eyes of the viewer which is witnessing the terrible injustice happening right under his nos. So, will you be the new Daniel? Will you find the courage to intervene against the laws of the State to defend a « Divine » justice? Hence, agapè is that infinite love for justice and truth, that leads you to courageous action and makes you a sublime personality capable of changing history, in the same way Antigone, Jeanne d’Arc, or Suzanne did before.
Plato versus Aristotle
The fact that Rembrandt was a philosopher is regularly put into question, even denied. The inventory of his goods, established when his enemies forced him into bankruptcy in 1654, doesn’t mention any book outside a huge bible, supposedly establishing a legitimate suspicion of him being near to illiteracy. While romanticized biographies portray him as an accursed poet, a narcissistic genius or the simple-minded mystical visionary son of a miller, a comment in 1641 from the artist Philips Angel underscores, not his painting, but Rembrandt’s « elevated and profound reflection ».

It is Aristotle contemplating Homer’s bust, which demonstrates once and for ever how stupid the Romantics can be. Ordered by an Italian nobleman, the painting shows Aristotle as a Venetian aristocrat, as a perfect courtier: with a wide white shirt, a large black hat and especially carrying a heavy golden chain.
In short, clothed as Castiglione, Aretino, Titian and Rubens… Rembrandt shows here his intimate knowledge of the species nature of Plato’s enemies of the Republic, that oligarchy to whom Aristotelianism became a quasi-religion.
With great irony, the canvas completely mocks knowledge derived from the « blind » submittal to sense perception. Here Rembrandt seems to join Erasmus of Rotterdam saying « experience is the school of fools! ».
Equipped with empty eyes, incapable of perception, Aristotle is groping with an uncertain hand Homer’s head of which he was supposedly a knowledgeable commentator. Homer, the Greek poet who turned blind, stares worriedly to Aristotle with the open eyes of mind.
That inversion of the respective roles of Aristotle and Homer is dramatized by situating the source enlightening the scene as a tangent behind the bust of the poet.
Light reflections illuminating Aristotle’s hat underneath make appear the ironical « ghost image » of donkey ears, the conventional attribute widely used since the Renaissance to designate the stubbornness of scholastic Aristotelianism.
To this Aristotelian blindness, Rembrandt, whose own father became blind, opposes the other clear-sightedness of Simeon, as seen in his last painting, found on Rembrandt’s easel after his death.
All during his life, Simeon had wished to see the Christ with his own eyes. But, growing old, that hope quitted him with along with his sight. As he did every day, Simeon went one day to the temple. There, Maria asked him to keep her child in his arms. Suddenly, an infinite joy
overwhelmed Simeon, who, without seeing Christ with his mortal eyes, saw him much more clearly with his mind than all the healthy seers. Rembrandt wanted us to reflect on that conviction: don’t believe what you see, but act coherently with God’s design and you might see him. On Simeon’s hands, a series of dashes of paint suggest some kind of crystal ball, an image which only « appears » when our minds dares to see it, underlining Simeon’s prophetic nature.
Jesus Christ healing the sick
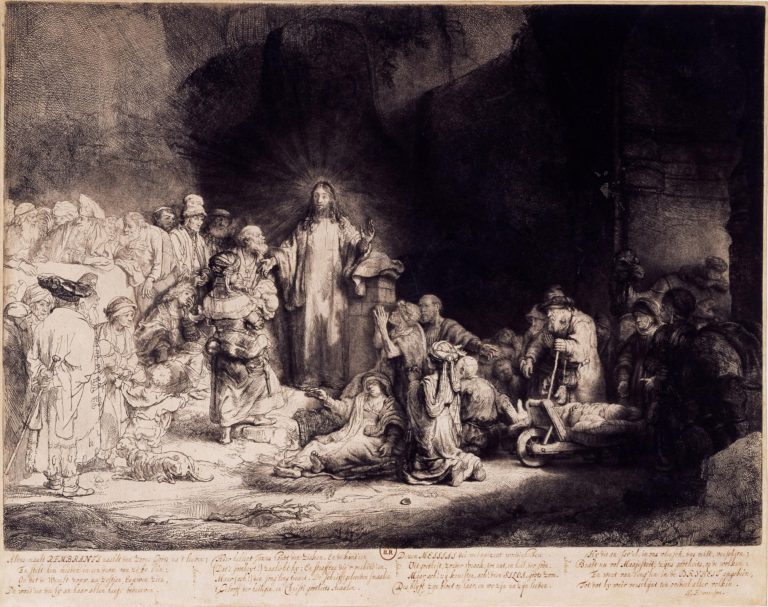

Rembrandt’s anti-Aristotelian philosophy is also explicitly manifest in an engraving known as Christ healing the sick, an exceptionally large etching on which he worked passionately over a six year period. In order to « sculpt » the ambiguous image of the Christ, son of both God and mankind, Rembrandt executed six oil portraits featuring young rabbi’s of Amsterdam. But it was Leonardo’s fresco, the Last Supper, which Rembrandt extensively studied as shown by drawings done after reproductions, that seems to have been his starting point.
Scientific analysis of his still existing copperplate indicate that the Christ’s hands were originally drawn as an exact imitation of Leonardo’s « Last Supper » fresco.
Completely different from the kind of « spotlight theatrics » that go from Caravagio to Hitchcock, the work reminds the description of the myth of the cavern in Plato’s Republic. But here stands the Christ blessing the sick.
Transfigured, and akin to the prisoners in Beethoven’s opera Fidelio, the sick people walk from right to left towards Christ. Encountering the light transforms them into philosophers!
One generally identifies easily, amidst others, Homer and Aristotle (who’s turning his head away from Christ), but also Erasmus and Saint-Peter, which according to some possesses here the traits of Socrates.
The etching brings together in a single instant eternal several sequences of Chapter XIX of Saint Mathew:
“Let the little children come to me, and do not hinder them, for the kingdom of heaven belongs to such as these.”
In a powerful gesture, Christ brushes aside even the best of all wise wisdom to make his love the priority, where Peter desperately tries to prevent the children from being presented to Jesus.
Sitting close to him we observe the image of an undecided young wealthy man plunged in profound doubts, since he desired eternal life but hesitated to sell his possessions and give it all to the poor.
When he left, Jesus commented that it was certainly easier for a camel to get through the eye of a needle, than for a rich man to enter the his kingdom.
Above simple earthly space situated in clock-ticking time, the action takes place in « the time of all times », an instantaneous eternity where human minds are measured with universality, some kind of « last judgment » of divine and philosophical consciousness.
The healing of the sick souls and bodies is the central breaking point which articulates the two universes, the one of sin and suffering, with the one of the good and happiness. Christ’s love, metaphorized as light, heals the « sick » and makes philosopher-kings out of them. They appear nearly as apostles and figure exactly on the same level as the apostles of Leonardo‘s milan fresco The last Supper. Brought out of darkness into the light, they become themselves sources of light capable of illuminating many others.
That « light of Agapè » is the single philosophical basis of Rembrandt’s revolution in the techniques of oil-painting: in stead of starting drawing and paint on a white gesso underground or lightly colored under-paint (the so-called priming, eventually adding imprimatura), all the later works are painted on a dark, even black under-paint!
The « modern » thick impasto, possible through the use of Venetian turpentine and the integration of bee wax, are revived by Rembrandt from the ancient « encaustic » techniques described by Pliny the Elder. They were employed by the School of Sycione three hundred years before Christ and gave us Alexander the Great‘s court painter Apelles, and the Fayoum mommy paintings in Alexandria, Egypt (*17).
Building the color-scale inversely permitted Rembrandt to reduce his late palette to only six colors and made him into a « sculptor of light ». His indirect pupil, Johannes Vermeer, systemized Rembrandt’s revolutionary discovery (*18).
Deprived of much earthly glory during their lives, Rembrandt and Comenius were immediately scrapped from official history by the oligarchic monsters that survived them. But their lives represent important victories for humanity. Their political, philosophical, esthetical and pedagogical battles against the oligarchy and its « valets » as Rubens, makes them eternal.
They are and will remain inexhaustible sources of inspiration for today’s and tomorrows combat.
NOTES:
- Karel Vereycken, « Rembrandt, bâtisseur de nation« , Nouvelle Solidarité, June 1985.
- The treatises of Westphalia (Munster and Osnabruck) of 1648, and the ensuing separate peace accords between France and the Netherlands with Spain, finally shred into pieces every political, philosophical and juridical argument serving as basis of the notion of empire, and by doing so put an end to Habsburg’s imperial fantasy, the « Thirty years war ». As some had outlined before, notably French King Henry IV’s great advisor Sully in his concept of « Grand Design », making the sovereign nation-state the highest authority for international law was, and remains today, the only safe road to guaranty durable peace. Empires, by definition, mean nothing but perpetual wars. If you want perpetual war, create an empire! Hence, through this revolution, small countries obtained the same rights as those held by large ones and the notions of big= strong, and small=weak, went out of the window. The Hobbesian idea that « might makes right » was abolished and replaced by mutual cooperation as the sole basis of international relations between sovereign nation-states. Hence, tiny Republics, as Switzerland or the Netherlands,the latter at war with Spain for nearly eighty years, finally obtained peace and international recognition. Second, and that’s undoubtedly the most revolutionary part of the agreements, mutual pardon became the core of the peace accords. For example paragraph II stipulated explicitly « that there shall be on the one side and the other a perpetual Oblivion, Amnesty or Pardon of all that has been committed since the beginning of these Troubles, in what place, or what manner soever the Hostilitys have been practis’d, in such a manner, that no body, under any pretext whatsoever, shall practice any Acts of Hostility, entertain any Enmity, or cause any Trouble to each other; » (translation: Foreign Office, London). Moreover, several paragraphs (XIII, XXXV, XXXVII, etc.) stipulate (with some exceptions) that there will be a general debt forgiveness concerning financial obligations susceptible of maintaining a dynamic of perpetual vengeance. In reality, the Peace of Westphalia was the birth of new political order, based on the creation of a new international economic and monetary system necessary to build peace on the ruins of the bankrupt imperial order.
- Footnote, p. 77 in Comenius by Olivier Cauly, Editions du Félin, Paris, 1995.
- Brochure dealing with that painting published by the Nationalmuseum of Stockholm.
- To put to an end to the politically motivated financial harassment which was organized by the family of his deceased wife, Saskia van Uylenburgh, Rembrandt submits on July 14, 1656 to the Dutch High Court a cessio bonorum (Cessation of goods to the profit of the creditors), accepting the sale of his goods. In 1660, Rembrandt abandons the official management of his art trading society to his wife Hendrickje Stoffels and his son Titus.
- p. 105, Henriette L.T.de Beaufort, in Rembrandt, HDT Willinck & Zoon, Harlem, 1957.
- p. 358, Samuel Hartlib and Universal Reformation, Cambridge University Press, 1994.
- p. 12-13, Bob van den Bogaert, in « Goethe & Rembrandt », Amsterdam University Press, Amsterdam 1999.
- p. 25, Marcelle Denis in Comenius, pédagogies & pédagogues, Presse Universitaire de France, 1994.
- Constantijn Huygens (1596-1687), was an exceptional precocious erudite. Politician, scientist, moralist, music composer, he played the violin at the age of six, wrote poems in Dutch, Latin, French, Spanish, English and Greek. His satire, « ‘t Kostelick Mal » (expensive folly), opposed to the « Profijtelijk Vermaak » (profitable amusement) makes great fun of courtly manners and the then rampant beaumondism. His son, Christiaan Huygens was a brilliant scientist and collaborator of Leibniz at the Paris Academy of sciences.
- One has to outline shortly here that contrary to the rule of the Greek canon of proportions (height of man = seven heads and a half), the Romans, as Leonardo seems to observe sourly in his drawing reworking Vitrivius, increase the body size up to eight and sometimes many more heads. It was the Greek canon established after the « Doryphore » of Polycletius, which settled the matter much earlier after many Egyptian inquiries on these matters. Leonardo, who wasn’t a fool, realized Vitruvius proportions (8 heads) are wrong, as can be seen by the two belly-buttons appearing in the famous man bounded by square and circle. Hence, the proportional « reduction » of the head was an easy trick to create the illusion of a stronger, more powerful musculature. That image of a biological man displaying « small head, big muscles » supposedly stood as the ultimate expression of Roman heroism. Foreknowledge of this arrangement permits the viewer to identify accurately what philosophy the painter is adhering to: Greek humanist or Roman oligarch? That Rubens chose Rome rather than Athens, leaves no doubt, as proven by his love for Seneca.
- « The holy Council states that it isn’t permitted to anybody, in any place or church, to install or let be installed an unusual image, unless it has been approved so by the bishop »; « finally any indecency shall be avoided, of that sort that the images will not be painted or possess ornaments of provoking beauty… » P. 1575-77, t. II-2, in G. Alberigo, « The ecumenical Councils », quoted by Alain Taton (p. 132) in « The Council of Trent », editions du CERF, Paris, 2000.
- p. 172, Simon Schama, in his magnificent Rembrandt’s eyes, Knopf, New York, 1999.
- For a more elaborate description of the tulip-bubble, Simon Schama, p. 471, « L’embarras de richesses, La culture hollandaise au Siècle d’Or », Gallimard, Paris, 1991.
- p. 117, Otto Sperling, Christian IV’s doctor, quoted by Marie-Anne Lescouret in her biography Pierre-Paul Rubens, J.C. Lattès, Paris, 1990.
- « Love your enemies », sermon of Martin Luther King, November 17, 1957, Dexter Avenue Baptist Church, Montgomery, Alabama. Quoted in Martin Luther King, Minuit, quelqu’un frappe à la porte, p.63, Bayard, Paris 1990.
- p. 87-88, Karel Vereycken, in The gaze from beyond, Fidelio, Vol. VIII, n°2, summer 1999.
- Johannes Vermeer of Delft was a close friend of Karel Fabritius, the most outstanding pupil of Rembrandt, who died at the age of thirty-four when the powderkeg of Delft exploded. Vermeer became the executor of his last will, a role generally reserved for the closest friend or relative. Anthonie van Leeuwenhoek, the inventor of the microscope and Leibniz correspondent, will become in turn the executor of Vermeer’s last will. That filiation does nothing more than prove the constant cross-fertilization of the artistic and scientific milieu. The Dutch « intimist » school, of which Vermeer is the most accomplished representative, is the most explicit expression of a « metaphysical » transcendence, transposed for political reasons, from the domain of religion, into the beauty of daily life scenes.
SELECTED BIBLIOGRAPHY:
- Baudiquey, Paul, Le retour du prodigue, Editions Mame, 1995, Paris.
- Bély, Lucien, L’Europe des Traités de Westphalie, esprit de la diplomatie et diplomatie de l’esprit, Presses Universitaires de France, Paris, 2000.
- Callot, Jacques, etchings, Dover, New York, 1974.
- Castiglione, Baldassare, Le Livre du Courtisan, GF-Flammarion, 1991.
- Cauly, Olvier, Comenius, Editions du Félin, Paris, 1995.
- Clark, Kenneth, An introduction to Rembrandt, Readers Union, Devon, 1978.
- Comenius, La Grande Didactique, Editions Klincksieck, Paris, 1992.
- Denis, Marcelle, Comenius, Presses Universitaires de France, Paris 1994.
- Descargues, Pierre, Rembrandt, JC Lattès, 1990.
- Goethe Rembrandt, Tekeningen uit Weimar, Amsterdam University Press, 1999.
- Grimberg, Carl, Histoire Universelle, Marabout Université, Verviers, 1964.
- Haak, B., Rembrandt, zijn leven, zijn werk, zijn tijd, De Centaur, Amsterdam.
- Hobbes, Thomas, Le Citoyen ou les fondements de la politique, Garnier Flammarion, Paris, 1982.
- Jerlerup, Törbjorn, Sweden und der Westphalische Friede, Neue Solidarität, mai 2000.
- King, Martin Luther, Minuit, quelqu’un frappe à la porte, Bayard, Paris, 2000.
- Komensky, Jan Amos, Le labyrinthe du monde et le paradis du cœur, Desclée, Paris, 1991.
- Lescourret, Marie Anne, Pierre-Paul Rubens, JC Lattès, Paris, 1990.
- Marienfeld Barbara, Johann Amos Comenius : Die Kunst, alle Menschen alles zu lehren. Neue Solidarität.
- Rembrandt and his pupils, Nationalmuseum, Stockholm, 1993.
- Sénèque, Entretiens, Editions Bouquins, Paris, 1993.
- Schama Simon, Rembrandt’s Eyes, Knopf, New York 1999.
- Schama, Simon, L’embarras de richesses, La culture hollandaise au Siècle d’Or, Gallimard, 1991.
- Schiller, Friedrich, traduction de Regnier, Vol. 6, Histoire de la Guerre de Trente ans, Paris, 1860.
- Sutton, Peter C., Le Siècle de Rubens, Mercatorfonds, Albin Michel, Paris, 1994.
- Tallon, Alain, Le Concile de Trente, CERF, Paris, 2000.
- Tümpel, Christian, Rembrandt, Fonds Mercator-Albin Michel, 1986.
- Van Lil, Kira, La peinture du XVIIème siècle aux Pays-Bas, en Allemagne et en Angleterre, dans l’art du Baroque, Editions Köneman, 1998, Cologne.
Erasmus’ dream: the Leuven Three Language College


In autumn 2017, a major exhibit organized at the University library of Leuven and later in Arlon, also in Belgium, attracted many people. Showing many historical documents, the primary intent of the event was to honor the activities of the famous Three Language College (Collegium Trilingue), founded in 1517 by the efforts of the Christian Humanist Erasmus of Rotterdam (1467-1536) and his allies. Though modest in size and scope, Erasmus’ initiative stands out as one of the cradles of European civilization, as you will discover here.

Revolutionary political figures, such as William the Silent (1533-1584), organizer of the Revolt of the Netherlands against the Habsburg tyranny, humanist poets and writers such as Thomas More, François Rabelais, Miguel Cervantes and William Shakespeare, all of them, recognized their intellectual debt to the great Erasmus of Rotterdam, his exemplary fight, his humor and his great pedagogical project.
For the occasion, the Leuven publishing house Peeters has taken through its presses several nice catalogues and essays, published in Flemish, French as well as English, bringing together the contributions of many specialists under the wise (and passionate) guidance of Pr Jan Papy, a professor of Latin literature of the Renaissance at the Leuven University, with the assistance of a “three language team” of Latinists which took a fresh look at close to all the relevant and inclusively some new documents scattered over various archives.
“The Leuven Collegium Trilingue: an appealing story of courageous vision and an unseen international success. Thanks to the legacy of Hieronymus Busleyden, counselor at the Great Council in Mechelen, Erasmus launched the foundation of a new college where international experts would teach Latin, Greek and Hebrew for free, and where bursaries would live together with their professors”, reads the back cover of one of the books.

For the researchers, the issue was not necessarily to track down every detail of this institution but rather to answer the key question: “What was the ‘magical recipe’ which attracted rapidly to Leuven between three and six hundred students from all over Europe?”
Erasmus’ initiative was unprecedented. Having an institution, teaching publicly Latin and, on top, for free, Greek and Hebrew, two languages considered “heretic” by the Vatican, was already tantamount to starting a revolution.
Was it that entirely new? Not really. As early as the beginning of the XIVth century, for the Italian humanists in contact with Greek erudites in exile in Venice, the rigorous study of Greek, Hebraic and Latin sources as well as the Fathers and the New Testament, was the method chosen by the humanists to free mankind from the Aristotelian worldview suffocating Christianity and returning to the ideals, beauty and spirit of the “Primitive Church”.
For Erasmus, as for his inspirer, the Italian humanist Lorenzo Valla (1403-1457), the « Philosophy of Christ » (agapic love), has to come first and opens the road to end the internal divisions of Christianity and to uproot the evil practices of greed (indulgences, simony) and religious superstition (cult of relics) infecting the Church from the top to the bottom, and especially the mendicant orders.
To succeed, Erasmus sets out to clarify the meaning of the Holy Writings by comparing the originals written in Greek, Hebrew and Latin, often polluted following a thousand years of clumsy translations, incompetent copying and scholastic commentaries.
Brothers of the Common Life



My own research allows me to recall that Erasmus was a true disciple of the Sisters and Brothers of the Common Life of Deventer in the Netherlands, a hotbed of humanism in Northern Europe. The towering figures that founded this lay teaching order are Geert Groote (1340-1384), Florent Radewijns (1350-1400) and Wessel Gansfort (1420-1489), all three said to be fluent in precisely these three languages.
The religious faith of this current, also known as the “Modern Devotion”, centered on interiority, as beautifully expressed in the little book of Thomas a Kempis (1380-1471), the Imitation of Christ. This most read book after the Bible, underlines the importance for the believer to conform one owns life to that of Christ who gave his life for mankind.
Rudolph Agricola
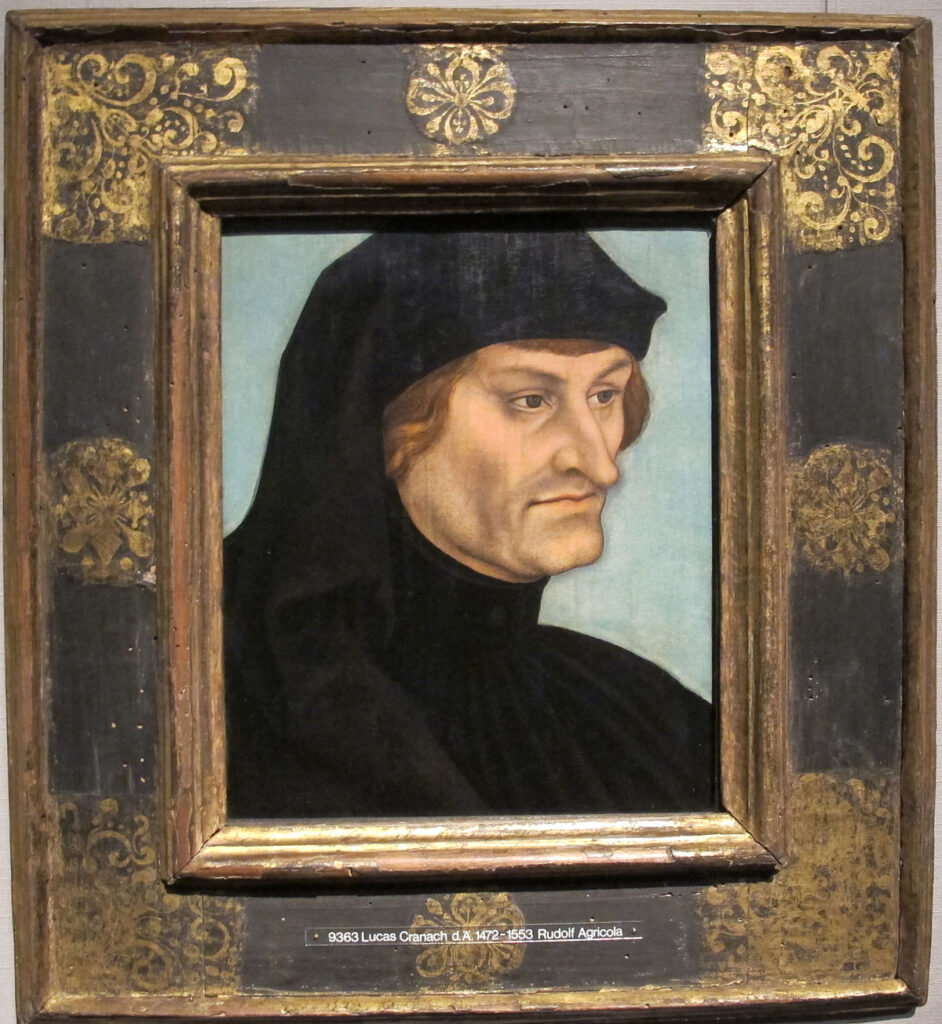

Hence, in 1475, Erasmus father, fluent in Greek and influenced by famous Italian humanists, sends his son to the chapter of the Brothers of the Common Life in Deventer, at that time under the direction of Alexander Hegius (1433-1499), himself a pupil of the famous Rudolph Agricola (1442-1485) which Erasmus had the chance to listen to and which he calls a “divine intellect”.
Follower of the cardinal-philosopher Nicolas of Cusa (1401-1464), enthusiastic advocate of the Italian Renaissance and the Good Letters, Agricola would tease his students by saying:
“Be cautious in respect to all that you learned so far. Reject everything! Start from the standpoint you will have to un-learn everything, except that what is based on your sovereign authority, or on the basis of decrees by superior authors, you have been capable of re-appropriating yourself”.
Erasmus, with the foundation of the Collegium Trilingue will carry this ambition at a level unreached before. To do so, Erasmus and his friend apply a new pedagogy. Hence, instead of learning by heart medieval commentaries, pupils are called to formulate their proper judgment and take inspiration of the great thinkers of the Classical period, especially “Saint Socrates”. Latin, a language that degenerated during the Roman Empire, will be purified from barbarisms.
With this approach, for pupils, reading a major text in its original language is only the start. An explorative work is required: one has to know the history and the motivations of the author, his epoch, the history of the laws of his country, its geography, cosmography, all considered to be indispensable instruments to put each text in its specific literary and historical context and allowing reading, beyond the words, the intention of their author.

This “modern” approach (questioning, critical study of sources, etc.) of the Collegium Trilingue, after having demonstrated its efficiency by clarifying the message of the Gospel, will rapidly travel over Europe and reach many other domains of knowledge, notably scientific issues! By uplifting young talents, out of the small and sleepy world of scholastic certitudes, this institution rapidly grew into a hotbed for creative minds.
For the ignorant reader who often considers Erasmus as some kind of comical writer praising madness which lost it after an endless theological dispute with Martin Luther, such a statement might come as a surprise.
Scientific Renaissance

While Belgium’s contributions to science, under Emperor Charles Vth, are broadly recognized and respected, few are those understanding the connection uniting Erasmus with a mathematician as Gemma Frisius and his pupil and friend Gerard Mercator, an anatomist such as Andreas Vesalius or a botanist such as Rembert Dodonaeus.
Hence, as already thoroughly documented in 2011 by Professor Jan Papy in a remarkable article, the scientific renaissance which bloomed in the Netherlands and Belgium in the early XVIth century, could not have taken place if it were for the “linguistic revolution” provoked by the Collegium Trilingue.
Because, beyond the mastery of their vernacular languages (French and Dutch), hundreds of youth, by studying Greek, Latin and Hebrew, suddenly got access to all the scientific treasures of Greek Philosophy and the best authors in those newly discovered languages.

At last, they could read Plato in the text, but also Anaxagoras, Heraclites, Thales of Millet, Eudoxus of Cnidus, Pythagoras, Eratosthenes, Archimedes, Galen, Vitruvius, Pliny the elder, Euclid and Ptolemy whose work they will master and eventually correct.
As the books published by Peeters account in great detail, during the first century of its existence, the Collegium Trilingue had a rough time confronting political uproar and religious strife. Heavy critique came especially form the “traditionalists”, a handful of theologians for which the Greeks were nothing but schismatics and the Jews the assassins of Christ and esoterics.
The opposition was such that Erasmus himself never could teach at the Collegium and, while keeping in close contact, decided to settle in Basel, Switzerland, in 1521.
Despite all of this, the Erasmian revolution conquered Europe overnight and a major part of the humanists of that period were trained or influenced by this institution. From abroad, hundreds of pupils arrived to follow classes given by professors of international reputation.
27 European universities integrated pupils of the Collegium in their teaching staff: among them stood Jena, Wittenberg, Cologne, Douai, Bologna, Avignon, Franeker, Ingolstadt, Marburg, etc.
Teachers at the Collegium were secured a decent income so that they weren’t obliged to give private lectures to secure a living and could offer public classes for free. As was the common practice of the Brothers of the Common Life in Deventer, a system of bursa allowed talented though poor students, including many orphans, to have access to higher learning. “Something not necessarily unusual those days, says Pr Jan Papy, and done for the sake of the soul of the founder (of the Collegium, reference to Busleyden)”.

While visiting Leuven and contemplating the worn-out steps of the spiral staircase (wentelsteen), one of the last remains of the building that had a hard time resisting the assaults of time and ignorance, one can easily imagine those young minds jumping down the stairs with enthusiasm going from the dormitory to the classroom. Looking at the old shopping list of the school’s kitchen one can conclude the food was excellent with lots of meat, poultry but also vegetables and fruits, and sometimes wine from Beaune in Burgundy, especially when Erasmus came for a visit! While over the years, of course, the quality of the learning transmitted, would vary in accordance with the excellence of its teachers, the Collegium Trilingue, whose activity would last till the French revolution, gave its imprint in history by giving birth to what some have called the “Little Renaissance” of the first half of the XVIth century.
In France, the Sorbonne University reacted with fear and in 1523, the study of Greek was outlawed in France.

François Rabelais, at that time a monk in Vendée, saw his books confiscated by the prior of his monastery and deserts his order. Later, as a doctor, he translated the medical writings of the Greek scientist Galen from Greek into French. Rabelais’s letter to Erasmus shows the highest possible respect and intellectual debt to Erasmus.
In 1530, Marguerite de Navarre, sister of King Francis, and reader and admirer of Erasmus, at war with the Sorbonne, convinced her brother to allow Guillaume Budé, a friend of Erasmus, to create the “Collège des Lecteurs Royaux” (ancestor of the Collège de France) on the model of the Collegium Trilingue. And to protect its teachers, many coming directly from Leuven, they got the title of “advisors” of the King. The Collège taught Latin, Hebrew and Greek, and rapidly added Arab, Syriac, medicine, botany and philosophy to its curriculum.
Dirk Martens

Also celebrated for the occasion, Dirk Martens (1446-1534), rightly considered as one of the first humanists to introduce printing in the Southern Netherlands.
Born in Aalst in a respected family, the young Dirk got his training at the local convent of the Hermits of Saint William. Eager to know the world and to study, Dirk went abroad. In Venice, at that time a cosmopolite center harboring many Greek erudite in exile, Dirk made his first steps into the art of printing at the workshop of Gerardus de Lisa, a Flemish musician who set up a small printing shop in Treviso, close to Venice.
Back in Aalst, together with his partner John of Westphalia, Martens printed in 1473 the first book in the country with a movable type printing press, a treatise of Dionysius the Carthusian (1401-1471), a friend and collaborator of cardinal-philosopher Nicolas of Cusa, as well as the spiritual advisor of Philip the Good, the Duke of Burgundy and thought to be the occasional « theological » advisor of the latter’s court painter, Jan Van Eyck.
If the oldest printed book known to us is a Chinese Buddhist writing dating from 868, the first movable printing types, made first out of wood and then out of hardened porcelain and metal, came from China and Korea in 1234.

The history of two lovers, a poem written by Aeneas Piccolomini before he became the humanist Pope Pius II, was another early production of Marten’s print shop in Aalst.
Proud to have introduced this new technique allowing a vast increase in the spreading of good and virtuous ideas, Martens wrote in one of the prefaces: “This book was printed by me, Dirk Martens of Aalst, the one who offered the Flemish people all the know-how of Venice”.
After some years in Spain, Martens returned to Aalst and started producing breviaries, psalm books and other liturgical texts. While technically elaborate, the business never reached significant commercial success.
Martens then moved to Antwerp, at that time one of the main ports and cross-roads of trade and culture. Several other Flemish humanists born in Aalst played eminent roles in that city and animate its intellectual and cultural life. Among these:
—Cornelis De Schrijver (1482-1558), the secretary of the City of Aalst, better known under his latin name Scribonius and later as Cornelius Grapheus. Writer, translator, poet, musician and friend of Erasmus, he was accused of heresy and hardly escaped from being burned at the stake.
—Pieter Gillis (1486-1533), known as Petrus Aegidius. Pupil of Martens, he worked as a corrector in his company before becoming Antwerp’s chief town clerk. Friend of Erasmus and Thomas More, he appears with Erasmus in the double portrait painted by another friend of both, Quinten Metsys (1466-1530).
—Pieter Coecke van Aelst (1502-1550), editor, painter and scenographer. After a trip to Italy, he set up a workshop in Antwerp. Pieter will produce patrons for tapestries, translated with the help of his wife the works of the Roman architect Vitruvius into Dutch and trained the young Flemish painter Bruegel the Elder who will marry his daughter.
Invention of pocket books
In Antwerp, Martens became part of this milieu and his workshop became a meeting place for painters, musicians, scientists, poets and writers. With the Collegium Trilingue, Martens opens a second shop, this time in Leuven to work with Erasmus. In order to provide adequate books to the Collegium, Martens proudly became, in the footsteps of the Venetian Printer Aldo Manuce, one of the first printers to concentrate on in-octavo 8° (22 x 12 cm), i.e. “pocket” size books affordable by all and which students could take home !
For the specialists of the Erasmus house of Anderlecht, close to Brussels,
“Martens innovated in nearly all domains. As well as in terms of printing types as lay-out. He was the first to introduce Italics, Greek and Hebrew letter types. He also generalized the use of ‘New Roman’ letter type so familiar today. During the first thirty years of the XVIth century, he also operated the revolution in lay-out (chapters and paragraphs) that gave birth to the modern book as we know it today. All this progress, he achieved in close cooperation with Erasmus”.
Thomas More’s Utopia

In 1516, it was Dirk Martens who printed the first edition of Thomas More’s Utopia. Among the hundreds of editions he printed mostly alone, 61 books and writings of Erasmus, notably In Praise of Folly. He also produced More’s edition of the roman satirist Lucian and Columbus’ account of the discovery of the new world. In 1423, Martens printed the complete works of Homer, quite a challenge!
In 1520, a papal bull of Leo X condemned the errors of Martin Luther and ordered the confiscation of his writings to be burned in public in front of the clergy and the people.
For Erasmus, burning books didn’t automatically erased their their content from the minds of the people. “One starts by burning books, one finishes by burning people” Erasmus warned years before Heinrich Heine said that “There, were one burns books, one ends up burning people”.
Printers and friends of Erasmus, especially in France, died on the stake opening the doors for the religious wars that will ravage Europe for the century to come.
What Erasmus feared above all, is that with the Vatican’s brutal war against Luther, it is the entire cultural renaissance and the learning of languages that got threatened with extinction.
In July 1521, confronted with the book burning, the German painter and engraver Albrecht Dürer, who made his living with bible illustrations, left Antwerp with his wife to return to his native Nuremberg.
Thirty years later, in 1552, the great cartographer Gerardus Mercator, a brilliant pupil of the Collegium Trilingue, for having called into question the views of Aristotle, went into exile and settled in Duisbourg, Germany.
In 1521, at the request of his friends who feared for his life, Erasmus left Leuven for Basel and settled in the workshop of another humanist, the Swiss printer Johann Froben.
In 1530, with a foreword of Erasmus, Froben published Georgius Agricola’s inventory of mining techniques, De Re Metallica, a key book that vastly contributed to the industrial revolution of Saxen, Switzerland, Germany and the whole of Europe.
Conclusion
If certain Catholic historians try to downplay the hostility of their Church towards Erasmus, the fact remains that between 1559 and 1900, the full works of Erasmus were on the “Index Vaticanus” and therefore “forbidden readings” for Catholics.
If Thomas More, whom Erasmus considered as his twin brother, was canonized by Pius XI in 1935 and recognized as the patron saint of the political leaders, Erasmus himself was never rehabilitated.
Interrogated by this author in a letter, the Pope Francis returned a polite but evasive answer.

Let’s rebuild the Collegium Trilingue !
With the exception of the staircase, only a few stones remain of the historical building housing the Collegium Trilingue. In 1909, the University of Louvain planned to buy up and rebuild the site but the First World War changed priorities. Before becoming social housing, part of the building was used as a factory. As a result, today, there is no overwhelming charm. However, seeing the historical value of the site, we cannot but fully support a full reconstruction plan of the building and its immediate environment.
It would make the historical center of Leuven so much nicer, so much more attractive and very much more loyal to its own history. On top, such a reconstruction wouldn’t cost much and might interest private investors. The images in 3 dimensions produced for the Leuven exhibit show a nice Flemish Renaissance building, much in the style of the marvels constructed by architect Rombout II Keldermans.
Every period has the right to honestly “re-write” its own history, without falsifications, according to its own vision of the future.
It has to be noted here that the world famous “Rubenshuis” in Antwerp, is not at all the original building, but a scrupulous reconstruction of the late 1930s.
Le « rêve d’Erasme », le Collège des Trois Langues de Louvain


REVUE DE LIVRE :
Le Collège des Trois Langues de Louvain (1517-1797)
Erasme, les pratiques pédagogiques humanistes et le nouvel institut des langues.
Sous la direction de Jan Papy, avec les contributions de Gert Gielis, Pierre Swiggers, Xander Feys & Dirk Sacré, Raf Van Rooy & Toon Van Hal, Pierre Van Hecke.
Edition Peeters, Louvain 2018.
230 pages, 60 €.
__________________________________________________________________

En Belgique, il y a un an, dans la vieille ville universitaire de Louvain, et ensuite à Arlon, une exposition très intéressante a échappé à notre attention.
Réunissant des documents historiques, gravures et manuscrits de la bibliothèque universitaire ainsi que de nombreuses pièces de l’étranger, du 19 octobre 2017 au 18 janvier 2018, l’évènement a voulu, à l’occasion du 500e anniversaire de sa fondation, retracer l’origine et mettre à honneur l’activité du fameux « Collège Trilingue » érigé en 1517 grâce aux efforts du grand humaniste chrétien Erasme de Rotterdam (1467-1536).
Quand on parle de civilisation européenne, c’est bien cette institution, bien que peu connue et de taille modeste, qui en fut l’un des artisans majeurs.
Car tout comme Guillaume le Taciturne (1533-1584), l’organisateur de la révolte des Pays-Bas contre la tyrannie habsbourgeoise, les visionnaires More, Rabelais, Cervantès et Shakespeare s’inspireront de son combat exemplaire, de sa verve et de son grand projet pédagogique.

L’occasion pour les Editions Peeters de Louvain de consacrer à cet anniversaire un beau catalogue et plusieurs recueils, publiés aussi bien en néerlandais, en français, qu’en anglais, réunissant les contributions de plusieurs spécialistes sous l’œil avisé (et passionné) de Jan Papy, professeur de littérature latine de la Renaissance à l’Université de la ville, appuyé d’une « équipe trilingue louvainiste » qui n’a pas épargné ses efforts pour relire attentivement toutes les publications ayant trait au sujet et explorer des sources nouvelles dans diverses archives d’Europe.
L’histoire de cet établissement humaniste en est une non seulement d’une remarquable visée scientifique et pédagogique, mais aussi d’efforts obstinés, voire de combats courageux, couronnés d’un succès international sans précédent. Mettant à profit le legs de Jérôme de Busleyden (1470-1517), conseiller au Grand Conseil de Malines, décédé en août 1517, Érasme s’attela aussitôt à la création d’un collège où des savants de renommée internationale prodigueraient un enseignement public et gratuit du latin, du grec et de l’hébreu. Dans ce collège ‘trilingue’, étudiants-boursiers et professeurs vivaient ensemble.
peut-on lire sur la jaquette du catalogue de plus de 200 pages.
Pour les chercheurs, il ne s’agissait pas de retracer de façon exhaustive l’histoire de cette entreprise mais de répondre à la question :
Quelle fut la ‘recette magique’ qui a permis d’attirer aussi rapidement à Louvain entre trois et six cents étudiants venant de partout en Europe ?

En tout cas, la chose est inédite, car, à l’époque, rien que le fait d’enseigner et en plus gratuitement, le grec et l’hébreu —considéré par le Vatican comme hérétique— est déjà révolutionnaire. Et ceci, bien que, dès le XIVe siècle, initié par les humanistes italiens au contact des érudits grecs exilés en Italie, l’examen des sources grecques, hébraïques et latines et la comparaison rigoureuse des grands textes aussi bien des pères de l’Eglise que de l’Evangile, est la voie choisie par les humanistes pour libérer l’humanité de la chape de plomb aristotélicienne qui étouffe la Chrétienté et de faire renaître l’idéal, la beauté et le souffle de l’église primitive.
Pour Erasme, comme l’avait fait avant lui Lorenzo Valla (1403-1457), en promouvant ce qu’il appelle « la philosophie du Christ », il s’agit d’unir la chrétienté en mettant fin aux divisions internes résultant de la cupidité (les indulgences, la simonie, etc.) et des pratiques de superstition religieuse (culte des reliques) qui infectent l’Eglise de haut en bas, en particulier les ordres mendiants.
Pour y arriver, Erasme désire reprendre l’Evangile à sa source, c’est-à-dire comparer les textes d’origine en grec, en latin et en hébreux, souvent inconnus ou sinon entièrement pollués par plus de mille ans de copiages et de commentaires scolastiques.
Frères de la Vie Commune

Mes recherches propres me permettent de rappeler qu’Erasme est un disciple des Sœurs et Frères de la Vie commune de Deventer au Pays-Bas. Les figures fondatrices et emblématiques de cet ordre laïc et enseignant sont Geert Groote (1340-1384), Florent Radewijns (1350-1400) et Wessel Gansfort (1420-1489) dont on croit savoir qu’ils maitrisaient précisément ces trois langues.
Le piétisme de ce courant dit de la « Dévotion Moderne », centré sur l’intériorité, s’articule à merveille dans le petit livre de Thomas a Kempis (1380-1471), L’imitation de Jésus Christ. Celui-ci souligne l’exemple personnel à suivre de la passion du Christ tel que nous l’enseigne l’Evangile, message qu’Erasme reprendra.

En 1475, le père d’Erasme, qui maîtrise le grec et aurait écouté des humanistes réputés en Italie, envoie son fils de neuf ans au chapitre des frères de Deventer, à l’époque dirigé par Alexandre Hegius (1433-1498), élève du célèbre Rudolphe Agricola (1442-1485), qu’Erasme a eu la possibilité d’écouter et qu’il appelle un « intellect divin ».
Disciple du cardinal-philosophe Nicolas de Cues (1401-1464), défenseur enthousiaste de la renaissance italienne et des belles lettres, Agricola a comme habitude de secouer ses élèves en leur lançant :
Soyez méfiant à l’égard de tout ce que vous avez appris jusqu’à ce jour. Rejetez tout ! Partez du point de vue qu’il faut tout désapprendre, sauf ce que, sur la base de votre autorité propre, ou sur la base du décret d’auteurs supérieurs, vous avez été capable de vous réapproprier.
Erasme reprend cet élan et, avec la fondation du Collège Trilingue, le portera à des hauteurs inédites. Pour ce faire, Erasme et ses amis appliqueront une nouvelle pédagogie.
Désormais, au lieu d’apprendre par cœur des commentaires médiévaux, les élèves doivent formuler leur propre jugement en s’inspirant des grands penseurs de l’antiquité classique, notamment « Saint Socrate », et ceci dans un latin purgé de ses barbarismes. Dans cette approche, lire un grand texte dans sa langue originale n’est que la base.
Vient ensuite tout un travail exploratoire : il faut connaître l’histoire et les motivations de l’auteur, son époque, l’histoire des lois de son pays, l’état de la science et du droit, la géographie, la cosmographie, comme des instruments indispensables pour situer les textes dans leur contexte littéraire et historique.

Cette approche « moderne » (questionnement, étude critique des sources, etc.) du Collège Trilingue, après avoir fait ses preuves en clarifiant le message de l’Evangile, se répand alors rapidement à travers toute l’Europe et surtout s’étend à toutes les matières, notamment scientifiques !
En sortant les jeunes talents du monde étroit et endormi des certitudes scolastiques, l’institution devient un formidable incubateur d’esprits créateurs.
Certes, cela peut étonner le lecteur français pour qui Erasme n’est qu’un littéraire comique qui se serait perdu dans une dispute théologique sans fin contre Luther. Si l’on admet généralement que sous Charles Quint, les Pays-Bas et l’actuelle Belgique ont apporté leurs contributions à la science, peu nombreux sont ceux qui comprennent le lien unissant Erasme avec la démarche d’un mathématicien tel que Gemma Frisius, d’un cartographe comme Gérard Mercator, d’un anatomiste comme André Vésale ou d’un botaniste comme Rembert Dodoens.
Or, comme l’avait déjà documenté en 2011 le professeur Jan Papy dans un article remarquable, en Belgique et aux Pays-Bas, la Renaissance scientifique de la première moitié du XVIe siècle, n’a été possible que grâce à la « révolution linguistique » provoquée par le Collège Trilingue.
Car, au-delà de leurs langues vernaculaires, c’est-à-dire le français et le néerlandais, des centaines de jeunes, étudiant le grec, le latin et l’hébreu, accèderont d’un coup, à toutes les richesses scientifiques de la philosophie grecque, des meilleurs auteurs latins, grecs et hébreux. Enfin, ils purent lire Platon dans le texte, mais aussi Anaxagore, Héraclite, Thalès, Eudoxe de Cnide, Pythagore, Ératosthène, Archimède, Galien, Vitruve, Pline, Euclide et Ptolémée dont ils reprennent les travaux pour les dépasser ensuite.

Comme le retracent en détail les œuvres publiées par les Editions Peeters, dans le premier siècle de son existence, le collège dut traverser des moments difficiles à une époque fortement marquée par des troubles politiques et religieux.
Le Collège Trilingue, près du Marché aux poissons, au centre de Louvain, a notamment dû affronter de nombreuses critiques et attaques de la part d’adversaires « traditionalistes », en particulier certains théologiens pour qui, en gros, les Grecs n’étaient que des schismatiques et les Juifs les assassins du Christ et des ésotériques. L’opposition fut telle qu’en 1521, Erasme quitte Louvain pour Bâle en Suisse, sans perdre contact avec l’institution.
En dépit de cela, la démarche érasmienne a d’emblée conquis toute l’Europe et tout ce qui comptait alors parmi les humanistes sortait de cette institution. De l’étranger, des centaines d’étudiants y accouraient pour suivre gratuitement les cours donnés par des professeurs de réputation internationale. 27 universités européennes ont nommé dans leur corps professoral d’anciens étudiants du Trilingue : Iéna, Wittenberg, Cologne, Douai, Bologne, Avignon, Franeker, Ingolstadt, Marburg, etc.

Comme à Deventer chez les Frères de la Vie Commune, un système de bourses permet à des élèves pauvres mais talentueux, notamment les orphelins, d’accéder aux études. « Une chose pas forcément inhabituelle à l’époque, précise Jan Papy, et entreprise pour le salut de l’âme du fondateur (du Collège, c’est-à-dire Jérôme Busleyden) ».
En contemplant les marches usées jusqu’à la corde de l’escalier tournant en pierre (Wentelsteen), l’un des rares vestiges du bâtiment d’alors qui a résisté à l’assaut du temps et du mépris, on imagine facilement les pas enthousiastes de tous ses jeunes élèves quittant leur dortoir situé à l’étage. Comme l’indiquent les registres des achats de la cuisine du Collège Trilingue, pour l’époque, la nourriture y est excellente, beaucoup de viande, de la volaille, mais également des fruits, des légumes, et parfois du vin de Beaune, notamment lorsque Erasme y est reçu.
Avec le temps, la qualité de son enseignement a forcément variée avec celle de ses enseignants, le Collège Trilingue, dont l’activité a perduré pendant longtemps après la mort d’Erasme, a imprimé sa marque sur l’histoire en engendrant ce qu’on qualifie parfois de « petite Renaissance » du XVIe siècle.
Erasme, Rabelais et la Sorbonne
Quitte à nous éloigner du contenu du catalogue, nous nous permettons d’examiner brièvement l’influence d’Erasme et du Collège Trilingue en France.
A Paris, chez les chiens de garde de la bienpensance, c’est la méfiance. La Sorbonne (franciscaine), alarmée par la publication d’Erasme sur le texte grec de L’Evangile de Saint Luc, fait interdire dès 1523 l’étude du grec en France. En Vendée, à Fontenay-le-Comte, les moines du couvent de Rabelais confisquent alors sans vergogne ses livres grecs ce qui incitera l’intéressé à déserter son ordre mais pas ses livres. Médecin, Rabelais traduit par la suite Galien du grec en français. Et, comme le démontre la lettre de Rabelais à Erasme, le premier tient le second en haute estime.
Dans son Gargantua (1534), esquissant les contours d’une Eglise du futur, Rabelais évoque le Collège Trilingue sous le nom d’abbaye de Thélème (Thélème = désir en grec, peut-être une référence à Désiré, prénom d’Erasme), un magnifique bâtiment hexagonal à six étages, digne des plus beaux châteaux de la Loire où l’on puisse retrouver, « les belles grandes librairies, en Grec, Latin, Hébrieu, François, Tuscan et Hespaignol, disparties par les divers estaiges selon langaiges », référence on ne peut plus claire au projet érasmien.

Contre la Sorbonne, en 1530, le Collège Trilingue d’Erasme servira explicitement de modèle pour la création, à l’instigation de Guillaume Budé (ami d’Erasme), du « Collège des lecteurs royaux » (devenu depuis le Collège de France) par François Ier, avec les encouragements de sa sœur Marguerite de Valois reine de Navarre (1492-1549) (grand-mère d’Henri IV), poétesse, femme de lettres et lectrice d’Erasme.
Dans le même élan, en 1539, Robert Estienne est nommé imprimeur du roi pour le latin et l’hébreu, et c’est à sa demande que François Ier fit graver par Claude Garamont une police complète de caractères grecs dits « Grecs du Roi ».
Pour les mettre à l’abri des foudres des sorbonagres et des sorbonicoles, François Ier déclare alors les lecteurs royaux conseillers du roi. A l’ouverture, il s’agit de chaires de lecture publique pour le grec, l’hébreu et les mathématiques mais d’autres chaires suivront dont le latin, l’arabe, le syriaque, la médecine, la botanique et la philosophie. Aujourd’hui, il aurait sans doute ajouté le chinois et le russe.
Ce qui n’empêche pas qu’à peine un an après sa publication, en 1532, Pantagruel, le conte philosophique de Rabelais déchaîne les foudres de la Sorbonne. Accusé d’obscénité, en sus d’apostasie, Rabelais s’en tire de justesse grâce à l’un de ses anciens condisciples, Jean du Bellay (1498-1560), diplomate et évêque de Paris, qui l’emmène à Rome à titre de médecin.
A son retour, les esprits calmés, la bienveillance de François Ier et de Marguerite de Navarre, lui permettent de retrouver son poste à l’Hôtel-Dieu de Lyon.
Si certains historiens de l’Eglise estiment qu’Erasme, à Louvain en particulier, a exagéré et parfois même suscité des réactions hostiles de la part de certains théologiens à son encontre, rappelons tout de même que lors du Concile de Trente (1545-1563), l’œuvre complète d’Erasme, taxée d’hérésie, fut interdite de lecture pour les catholiques et mise à l’Index Vaticanus en 1559 où elle restera jusqu’en 1900 !
Si Thomas More, en qui Erasme voyait son « frère jumeau », a été béatifié en 1886 par le pape Léon XIII, canonisé par Pie XI en 1935 et fait saint patron des responsables de gouvernement et des hommes politiques par Jean-Paul II en l’an 2000, pour Erasme, il va falloir attendre.
Interrogé en 2015 au sujet d’un geste éventuel de réhabilitation en faveur d’un chrétien qui a tant fait pour défendre le christianisme, sa Sainteté le pape François, dans sa réponse écrite, a vivement remercié l’auteur pour ses réflexions.
Reconstruisons le Collège Trilingue !


Dans le catalogue de l’exposition, le professeur Jan Papy retrace également le destin qu’ont connu les bâtiments qui abritaient jadis le Collège Trilingue.
Il mentionne notamment la tentative d’un des recteurs de l’Université Catholique de Louvain, de récupérer l’édifice en 1909, un projet qui échoua malheureusement à cause de la Première Guerre mondiale.
Le bâtiment est ensuite transformé en dépôt et en logements sociaux. « Dans la chapelle du Collège Trilingue, on fume alors le hareng et la salle de cours sert d’usine à glace… »
Aujourd’hui, à part l’escalier, rien n’évoque la splendeur historique de cette institution, ce qui fut forcément ressentie lors des commémorations de 2017.
Jan Papy regrette, bien que l’Université ait célébré les 500 ans avec « tout le faste académique requis », que l’ « on ne peut cependant s’empêcher d’éprouver des sentiments équivoques à la pensée que cette même Université n’a toujours pas pris à cœur le sort de cet institut qu’Erasme avait appelé de ses vœux et pour lequel il avait tant œuvré ».
Les restes du bâtiment, certes, dans leur état actuel, n’ont pas grande « valeur », du point de vue « objectif ». Ce n’est qu’en fonction de l’attention subjective que nous leur attribuons, qu’elles ont une valeur inestimable et précieuse comme témoignage ultime d’une partie de notre propre histoire.

A cela s’ajoute que reconstruire le bâtiment, dont il ne reste pas grand-chose, coûterait à peine quelque petits millions d’euros, c’est-à-dire pas grand-chose à l’aube des milliards d’euros que brassent nos banques centrales et nos marchés financiers. Des mécènes privés pourraient également s’y intéresser.

De notre point de vue, la reconstruction effective du Collège Trilingue dans sa forme originale, qui constitue en réalité une partie du cœur urbanistique de la ville de Louvain, serait une initiative souhaitable et incontestablement « un énorme plus » sur la carte de visite de la ville, de son Université, des Flandres, de la Belgique et de toute l’Europe. N’est-il pas un fait regrettable, alors que tous les jeunes connaissent les bourses Erasmus, que la plupart des gens ignorent les idées, l’œuvre et le rôle qu’a pu jouer un si grand humaniste ?
Des images en trois dimensions, réalisées dans la cadre de l’exposition sur la base des données historiques, permettent de visualiser un bel édifice, du même type que ceux construit par l’architecte Rombout II Keldermans à l’époque (Note), apte à remplir des missions multiples.

Enfin, chaque époque est en droit de « ré-écrire » l’histoire en fonction de sa vision de l’avenir sans pour autant la falsifier. Rappelons également, bien qu’on tende à l’oublier, que la Maison de Rubens (Rubenshuis) à Anvers, un Musée qui attire des milliers de visiteurs chaque année, n’est pas du tout le bâtiment d’origine ! Comme le reconnaît le site du Musée actuel :
La maison de Rubens reste sans doute inchangée jusqu’au milieu du 18e siècle, après quoi elle est entièrement transformée. Les façades sur la rue sont démolies et reconstruites selon le goût de l’époque. La demeure du XVIe siècle est aussi en grande partie remplacée par une bâtisse neuve. Le bâtiment est confisqué par les Français en 1798 et devient une prison pour les religieux condamnés au bannissement. La maison est rachetée par un particulier après l’époque napoléonienne. L’idée de faire de la maison un monument naît dans le courant du XIXe siècle. La Ville d’Anvers en fait l’acquisition en 1937. Les années suivantes seront mises à profit pour rendre autant que possible à la demeure son aspect à l’époque de Rubens. Le musée Maison Rubens ouvre ses portes en 1946. C’est la maison que vous visitez aujourd’hui.
L’annonce officielle d’une reconstruction du bâtiment pourrait éventuellement se faire le 18 octobre 2020, date anniversaire du jour où le Collège Trilingue ouvrait ses portes. Moi j’y serais !
Note: On pense à la Cour de Busleyden et le Palais de Marguerite d’Autriche à Malines ou à la Cour des marquis (Markiezenhof) de Bergen-op-Zoom
















































































