Étiquette : Vitruvius
Erasmus’ dream: the Leuven Three Language College


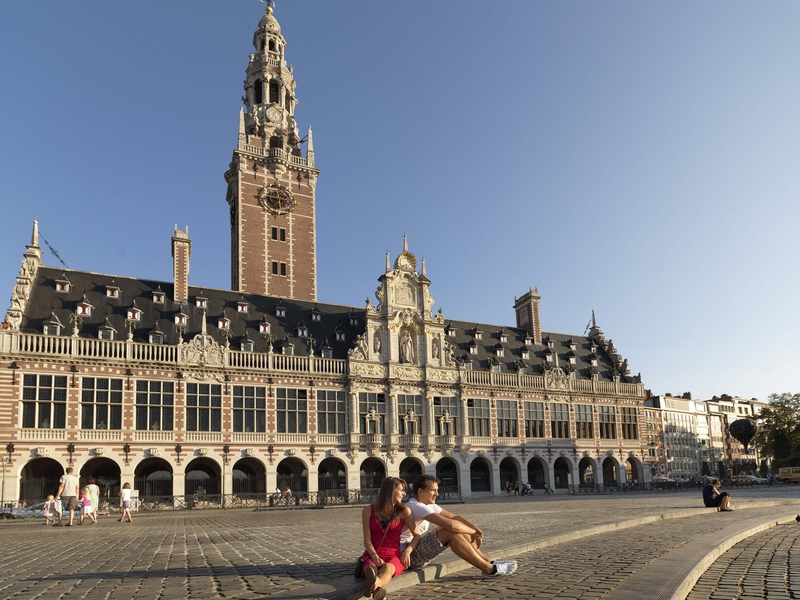
In autumn 2017, a major exhibit organized at the University library of Leuven and later in Arlon, also in Belgium, attracted many people. Showing many historical documents, the primary intent of the event was to honor the activities of the famous Three Language College (Collegium Trilingue), founded in 1517 by the efforts of the Christian Humanist Erasmus of Rotterdam (1467-1536) and his allies. Though modest in size and scope, Erasmus’ initiative stands out as one of the cradles of European civilization, as you will discover here.

Revolutionary political figures, such as William the Silent (1533-1584), organizer of the Revolt of the Netherlands against the Habsburg tyranny, humanist poets and writers such as Thomas More, François Rabelais, Miguel Cervantes and William Shakespeare, all of them, recognized their intellectual debt to the great Erasmus of Rotterdam, his exemplary fight, his humor and his great pedagogical project.
For the occasion, the Leuven publishing house Peeters has taken through its presses several nice catalogues and essays, published in Flemish, French as well as English, bringing together the contributions of many specialists under the wise (and passionate) guidance of Pr Jan Papy, a professor of Latin literature of the Renaissance at the Leuven University, with the assistance of a “three language team” of Latinists which took a fresh look at close to all the relevant and inclusively some new documents scattered over various archives.
“The Leuven Collegium Trilingue: an appealing story of courageous vision and an unseen international success. Thanks to the legacy of Hieronymus Busleyden, counselor at the Great Council in Mechelen, Erasmus launched the foundation of a new college where international experts would teach Latin, Greek and Hebrew for free, and where bursaries would live together with their professors”, reads the back cover of one of the books.

For the researchers, the issue was not necessarily to track down every detail of this institution but rather to answer the key question: “What was the ‘magical recipe’ which attracted rapidly to Leuven between three and six hundred students from all over Europe?”
Erasmus’ initiative was unprecedented. Having an institution, teaching publicly Latin and, on top, for free, Greek and Hebrew, two languages considered “heretic” by the Vatican, was already tantamount to starting a revolution.
Was it that entirely new? Not really. As early as the beginning of the XIVth century, for the Italian humanists in contact with Greek erudites in exile in Venice, the rigorous study of Greek, Hebraic and Latin sources as well as the Fathers and the New Testament, was the method chosen by the humanists to free mankind from the Aristotelian worldview suffocating Christianity and returning to the ideals, beauty and spirit of the “Primitive Church”.
For Erasmus, as for his inspirer, the Italian humanist Lorenzo Valla (1403-1457), the « Philosophy of Christ » (agapic love), has to come first and opens the road to end the internal divisions of Christianity and to uproot the evil practices of greed (indulgences, simony) and religious superstition (cult of relics) infecting the Church from the top to the bottom, and especially the mendicant orders.
To succeed, Erasmus sets out to clarify the meaning of the Holy Writings by comparing the originals written in Greek, Hebrew and Latin, often polluted following a thousand years of clumsy translations, incompetent copying and scholastic commentaries.
Brothers of the Common Life



My own research allows me to recall that Erasmus was a true disciple of the Sisters and Brothers of the Common Life of Deventer in the Netherlands, a hotbed of humanism in Northern Europe. The towering figures that founded this lay teaching order are Geert Groote (1340-1384), Florent Radewijns (1350-1400) and Wessel Gansfort (1420-1489), all three said to be fluent in precisely these three languages.
The religious faith of this current, also known as the “Modern Devotion”, centered on interiority, as beautifully expressed in the little book of Thomas a Kempis (1380-1471), the Imitation of Christ. This most read book after the Bible, underlines the importance for the believer to conform one owns life to that of Christ who gave his life for mankind.
Rudolph Agricola
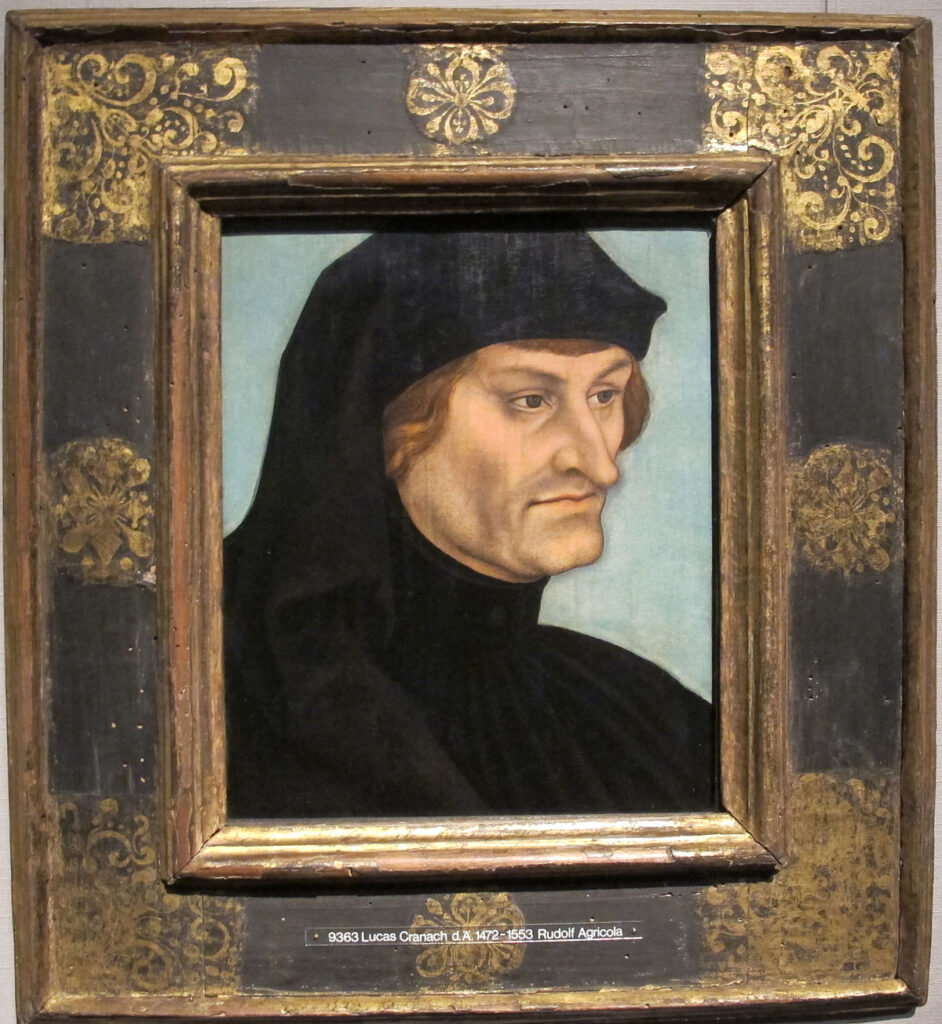

Hence, in 1475, Erasmus father, fluent in Greek and influenced by famous Italian humanists, sends his son to the chapter of the Brothers of the Common Life in Deventer, at that time under the direction of Alexander Hegius (1433-1499), himself a pupil of the famous Rudolph Agricola (1442-1485) which Erasmus had the chance to listen to and which he calls a “divine intellect”.
Follower of the cardinal-philosopher Nicolas of Cusa (1401-1464), enthusiastic advocate of the Italian Renaissance and the Good Letters, Agricola would tease his students by saying:
“Be cautious in respect to all that you learned so far. Reject everything! Start from the standpoint you will have to un-learn everything, except that what is based on your sovereign authority, or on the basis of decrees by superior authors, you have been capable of re-appropriating yourself”.
Erasmus, with the foundation of the Collegium Trilingue will carry this ambition at a level unreached before. To do so, Erasmus and his friend apply a new pedagogy. Hence, instead of learning by heart medieval commentaries, pupils are called to formulate their proper judgment and take inspiration of the great thinkers of the Classical period, especially “Saint Socrates”. Latin, a language that degenerated during the Roman Empire, will be purified from barbarisms.
With this approach, for pupils, reading a major text in its original language is only the start. An explorative work is required: one has to know the history and the motivations of the author, his epoch, the history of the laws of his country, its geography, cosmography, all considered to be indispensable instruments to put each text in its specific literary and historical context and allowing reading, beyond the words, the intention of their author.

This “modern” approach (questioning, critical study of sources, etc.) of the Collegium Trilingue, after having demonstrated its efficiency by clarifying the message of the Gospel, will rapidly travel over Europe and reach many other domains of knowledge, notably scientific issues! By uplifting young talents, out of the small and sleepy world of scholastic certitudes, this institution rapidly grew into a hotbed for creative minds.
For the ignorant reader who often considers Erasmus as some kind of comical writer praising madness which lost it after an endless theological dispute with Martin Luther, such a statement might come as a surprise.
Scientific Renaissance

While Belgium’s contributions to science, under Emperor Charles Vth, are broadly recognized and respected, few are those understanding the connection uniting Erasmus with a mathematician as Gemma Frisius and his pupil and friend Gerard Mercator, an anatomist such as Andreas Vesalius or a botanist such as Rembert Dodonaeus.
Hence, as already thoroughly documented in 2011 by Professor Jan Papy in a remarkable article, the scientific renaissance which bloomed in the Netherlands and Belgium in the early XVIth century, could not have taken place if it were for the “linguistic revolution” provoked by the Collegium Trilingue.
Because, beyond the mastery of their vernacular languages (French and Dutch), hundreds of youth, by studying Greek, Latin and Hebrew, suddenly got access to all the scientific treasures of Greek Philosophy and the best authors in those newly discovered languages.

At last, they could read Plato in the text, but also Anaxagoras, Heraclites, Thales of Millet, Eudoxus of Cnidus, Pythagoras, Eratosthenes, Archimedes, Galen, Vitruvius, Pliny the elder, Euclid and Ptolemy whose work they will master and eventually correct.
As the books published by Peeters account in great detail, during the first century of its existence, the Collegium Trilingue had a rough time confronting political uproar and religious strife. Heavy critique came especially form the “traditionalists”, a handful of theologians for which the Greeks were nothing but schismatics and the Jews the assassins of Christ and esoterics.
The opposition was such that Erasmus himself never could teach at the Collegium and, while keeping in close contact, decided to settle in Basel, Switzerland, in 1521.
Despite all of this, the Erasmian revolution conquered Europe overnight and a major part of the humanists of that period were trained or influenced by this institution. From abroad, hundreds of pupils arrived to follow classes given by professors of international reputation.
27 European universities integrated pupils of the Collegium in their teaching staff: among them stood Jena, Wittenberg, Cologne, Douai, Bologna, Avignon, Franeker, Ingolstadt, Marburg, etc.
Teachers at the Collegium were secured a decent income so that they weren’t obliged to give private lectures to secure a living and could offer public classes for free. As was the common practice of the Brothers of the Common Life in Deventer, a system of bursa allowed talented though poor students, including many orphans, to have access to higher learning. “Something not necessarily unusual those days, says Pr Jan Papy, and done for the sake of the soul of the founder (of the Collegium, reference to Busleyden)”.

While visiting Leuven and contemplating the worn-out steps of the spiral staircase (wentelsteen), one of the last remains of the building that had a hard time resisting the assaults of time and ignorance, one can easily imagine those young minds jumping down the stairs with enthusiasm going from the dormitory to the classroom. Looking at the old shopping list of the school’s kitchen one can conclude the food was excellent with lots of meat, poultry but also vegetables and fruits, and sometimes wine from Beaune in Burgundy, especially when Erasmus came for a visit! While over the years, of course, the quality of the learning transmitted, would vary in accordance with the excellence of its teachers, the Collegium Trilingue, whose activity would last till the French revolution, gave its imprint in history by giving birth to what some have called the “Little Renaissance” of the first half of the XVIth century.
In France, the Sorbonne University reacted with fear and in 1523, the study of Greek was outlawed in France.

François Rabelais, at that time a monk in Vendée, saw his books confiscated by the prior of his monastery and deserts his order. Later, as a doctor, he translated the medical writings of the Greek scientist Galen from Greek into French. Rabelais’s letter to Erasmus shows the highest possible respect and intellectual debt to Erasmus.
In 1530, Marguerite de Navarre, sister of King Francis, and reader and admirer of Erasmus, at war with the Sorbonne, convinced her brother to allow Guillaume Budé, a friend of Erasmus, to create the “Collège des Lecteurs Royaux” (ancestor of the Collège de France) on the model of the Collegium Trilingue. And to protect its teachers, many coming directly from Leuven, they got the title of “advisors” of the King. The Collège taught Latin, Hebrew and Greek, and rapidly added Arab, Syriac, medicine, botany and philosophy to its curriculum.
Dirk Martens

Also celebrated for the occasion, Dirk Martens (1446-1534), rightly considered as one of the first humanists to introduce printing in the Southern Netherlands.
Born in Aalst in a respected family, the young Dirk got his training at the local convent of the Hermits of Saint William. Eager to know the world and to study, Dirk went abroad. In Venice, at that time a cosmopolite center harboring many Greek erudite in exile, Dirk made his first steps into the art of printing at the workshop of Gerardus de Lisa, a Flemish musician who set up a small printing shop in Treviso, close to Venice.
Back in Aalst, together with his partner John of Westphalia, Martens printed in 1473 the first book in the country with a movable type printing press, a treatise of Dionysius the Carthusian (1401-1471), a friend and collaborator of cardinal-philosopher Nicolas of Cusa, as well as the spiritual advisor of Philip the Good, the Duke of Burgundy and thought to be the occasional « theological » advisor of the latter’s court painter, Jan Van Eyck.
If the oldest printed book known to us is a Chinese Buddhist writing dating from 868, the first movable printing types, made first out of wood and then out of hardened porcelain and metal, came from China and Korea in 1234.

The history of two lovers, a poem written by Aeneas Piccolomini before he became the humanist Pope Pius II, was another early production of Marten’s print shop in Aalst.
Proud to have introduced this new technique allowing a vast increase in the spreading of good and virtuous ideas, Martens wrote in one of the prefaces: “This book was printed by me, Dirk Martens of Aalst, the one who offered the Flemish people all the know-how of Venice”.
After some years in Spain, Martens returned to Aalst and started producing breviaries, psalm books and other liturgical texts. While technically elaborate, the business never reached significant commercial success.
Martens then moved to Antwerp, at that time one of the main ports and cross-roads of trade and culture. Several other Flemish humanists born in Aalst played eminent roles in that city and animate its intellectual and cultural life. Among these:
—Cornelis De Schrijver (1482-1558), the secretary of the City of Aalst, better known under his latin name Scribonius and later as Cornelius Grapheus. Writer, translator, poet, musician and friend of Erasmus, he was accused of heresy and hardly escaped from being burned at the stake.
—Pieter Gillis (1486-1533), known as Petrus Aegidius. Pupil of Martens, he worked as a corrector in his company before becoming Antwerp’s chief town clerk. Friend of Erasmus and Thomas More, he appears with Erasmus in the double portrait painted by another friend of both, Quinten Metsys (1466-1530).
—Pieter Coecke van Aelst (1502-1550), editor, painter and scenographer. After a trip to Italy, he set up a workshop in Antwerp. Pieter will produce patrons for tapestries, translated with the help of his wife the works of the Roman architect Vitruvius into Dutch and trained the young Flemish painter Bruegel the Elder who will marry his daughter.
Invention of pocket books
In Antwerp, Martens became part of this milieu and his workshop became a meeting place for painters, musicians, scientists, poets and writers. With the Collegium Trilingue, Martens opens a second shop, this time in Leuven to work with Erasmus. In order to provide adequate books to the Collegium, Martens proudly became, in the footsteps of the Venetian Printer Aldo Manuce, one of the first printers to concentrate on in-octavo 8° (22 x 12 cm), i.e. “pocket” size books affordable by all and which students could take home !
For the specialists of the Erasmus house of Anderlecht, close to Brussels,
“Martens innovated in nearly all domains. As well as in terms of printing types as lay-out. He was the first to introduce Italics, Greek and Hebrew letter types. He also generalized the use of ‘New Roman’ letter type so familiar today. During the first thirty years of the XVIth century, he also operated the revolution in lay-out (chapters and paragraphs) that gave birth to the modern book as we know it today. All this progress, he achieved in close cooperation with Erasmus”.
Thomas More’s Utopia

In 1516, it was Dirk Martens who printed the first edition of Thomas More’s Utopia. Among the hundreds of editions he printed mostly alone, 61 books and writings of Erasmus, notably In Praise of Folly. He also produced More’s edition of the roman satirist Lucian and Columbus’ account of the discovery of the new world. In 1423, Martens printed the complete works of Homer, quite a challenge!
In 1520, a papal bull of Leo X condemned the errors of Martin Luther and ordered the confiscation of his writings to be burned in public in front of the clergy and the people.
For Erasmus, burning books didn’t automatically erased their their content from the minds of the people. “One starts by burning books, one finishes by burning people” Erasmus warned years before Heinrich Heine said that “There, were one burns books, one ends up burning people”.
Printers and friends of Erasmus, especially in France, died on the stake opening the doors for the religious wars that will ravage Europe for the century to come.
What Erasmus feared above all, is that with the Vatican’s brutal war against Luther, it is the entire cultural renaissance and the learning of languages that got threatened with extinction.
In July 1521, confronted with the book burning, the German painter and engraver Albrecht Dürer, who made his living with bible illustrations, left Antwerp with his wife to return to his native Nuremberg.
Thirty years later, in 1552, the great cartographer Gerardus Mercator, a brilliant pupil of the Collegium Trilingue, for having called into question the views of Aristotle, went into exile and settled in Duisbourg, Germany.
In 1521, at the request of his friends who feared for his life, Erasmus left Leuven for Basel and settled in the workshop of another humanist, the Swiss printer Johann Froben.
In 1530, with a foreword of Erasmus, Froben published Georgius Agricola’s inventory of mining techniques, De Re Metallica, a key book that vastly contributed to the industrial revolution of Saxen, Switzerland, Germany and the whole of Europe.
Conclusion
If certain Catholic historians try to downplay the hostility of their Church towards Erasmus, the fact remains that between 1559 and 1900, the full works of Erasmus were on the “Index Vaticanus” and therefore “forbidden readings” for Catholics.
If Thomas More, whom Erasmus considered as his twin brother, was canonized by Pius XI in 1935 and recognized as the patron saint of the political leaders, Erasmus himself was never rehabilitated.
Interrogated by this author in a letter, the Pope Francis returned a polite but evasive answer.
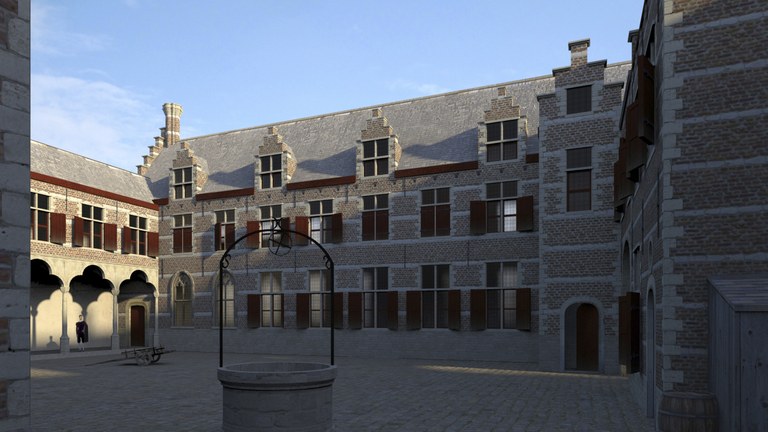

Let’s rebuild the Collegium Trilingue !
With the exception of the staircase, only a few stones remain of the historical building housing the Collegium Trilingue. In 1909, the University of Louvain planned to buy up and rebuild the site but the First World War changed priorities. Before becoming social housing, part of the building was used as a factory. As a result, today, there is no overwhelming charm. However, seeing the historical value of the site, we cannot but fully support a full reconstruction plan of the building and its immediate environment.
It would make the historical center of Leuven so much nicer, so much more attractive and very much more loyal to its own history. On top, such a reconstruction wouldn’t cost much and might interest private investors. The images in 3 dimensions produced for the Leuven exhibit show a nice Flemish Renaissance building, much in the style of the marvels constructed by architect Rombout II Keldermans.
Every period has the right to honestly “re-write” its own history, without falsifications, according to its own vision of the future.
It has to be noted here that the world famous “Rubenshuis” in Antwerp, is not at all the original building, but a scrupulous reconstruction of the late 1930s.
Avicenna and Ghiberti’s role in the invention of perspective during the Renaissance

By Karel Vereycken, Paris, France.
Same article in FR, même article en FR.
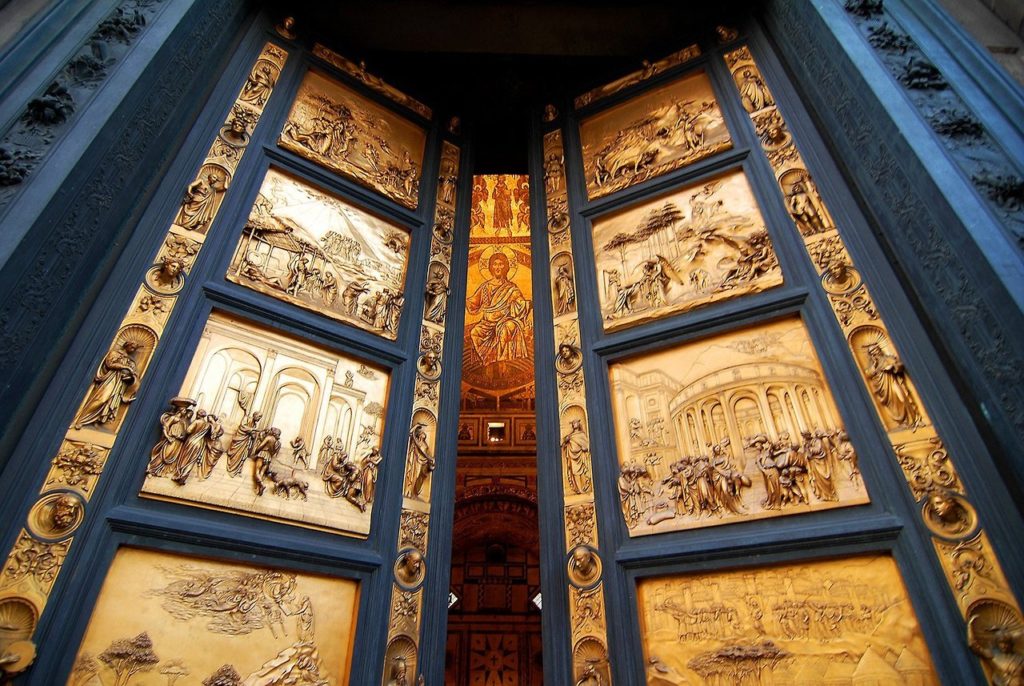

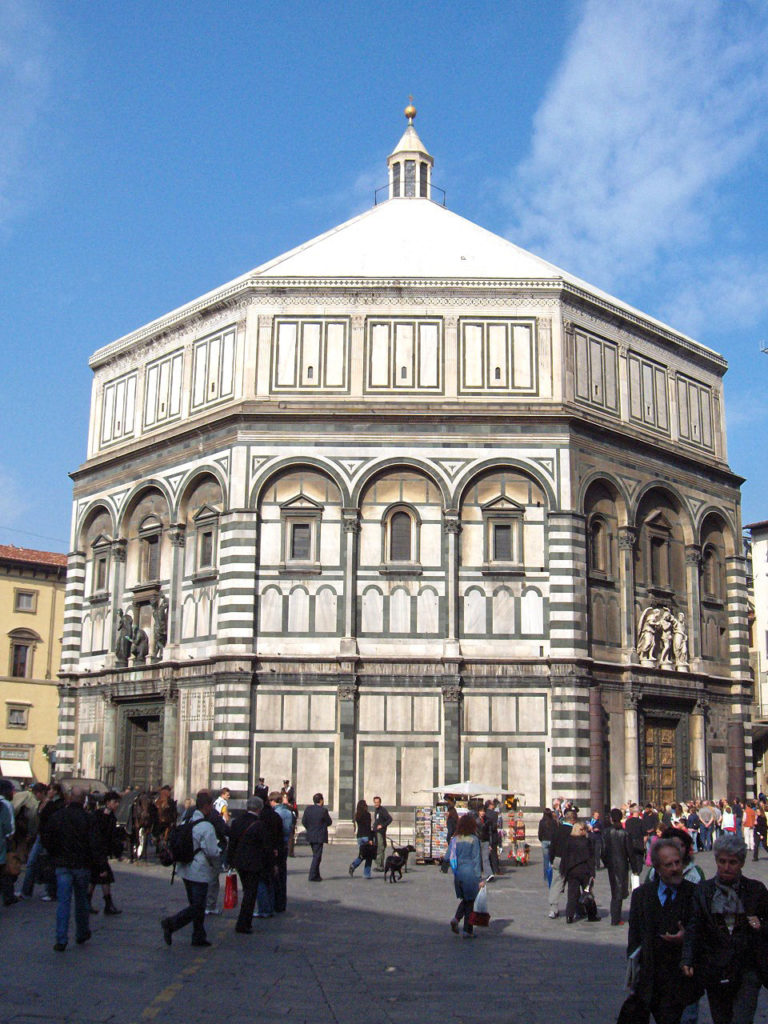
No visitor to Florence can miss the gilded bronze reliefs decorating the Porta del Paradiso (Gates of Paradise), the main gate of the Baptistery of Florence right in front of the Cathedral of Santa Maria del Fiore surmounted by Filippo Brunelleschi’s splendid cupola.

In this article, Karel Vereycken sheds new light on the contribution of Arab science and Ghiberti’s crucial role in giving birth to the Renaissance.

Historical context
The Baptistery, erected on what most Florentines thought to be the site of a Roman temple dedicated to the Roman God of Mars, is one of the oldest buildings in the city, constructed between 1059 and 1128 in the Florentine Romanesque style. The Italian poet Dante Alighieri and many other notable Renaissance figures, including members of the Medici family, were baptized in this baptistery.
During the Renaissance, in Florence, corporations and guilds competed for the leading role in design and construction of great projects with illustrious artistic creations.
While the Arte dei Lana (corporation of wool producers) financed the Works (Opera) of the Duomo and the construction of its cupola, the Arte dei Mercantoni di Calimala (the guild of merchants dealing in buying foreign cloth for finishing and export), took care of the Baptistery and financed the embellishment of its doors.
The Gates of Paradise
The Baptistry, an octagonal building, has four entrances (East, West, North and South) of which only three (South, North and East) have sets of artistically important bronze doors with relief sculptures. Three dates are key : 1329, 1401 and 1424.
- In 1329, the Calimala Guild, on Giotto‘s recommendation, ordered Andrea Pisano (1290-1348) to decorate a first set of doors (initialy installed as the East doors, i.e. seen when one leaves the Cathedral, but today South). These consist of 28 quatrefoil (clover-shaped) panels, with the 20 top panels depicting scenes from the life of St. John the Baptist (the patron of the edifice). The 8 lower panels depict the eight virtues of hope, faith, charity, humility, fortitude, temperance, justice, and prudence, praised by Plato in his Republic and represented during the XVIth century by the Flemish humanist painter and reader of Petrarch, Peter Brueghel the Elder. Construction took 8 years, from 1330 till 1338.
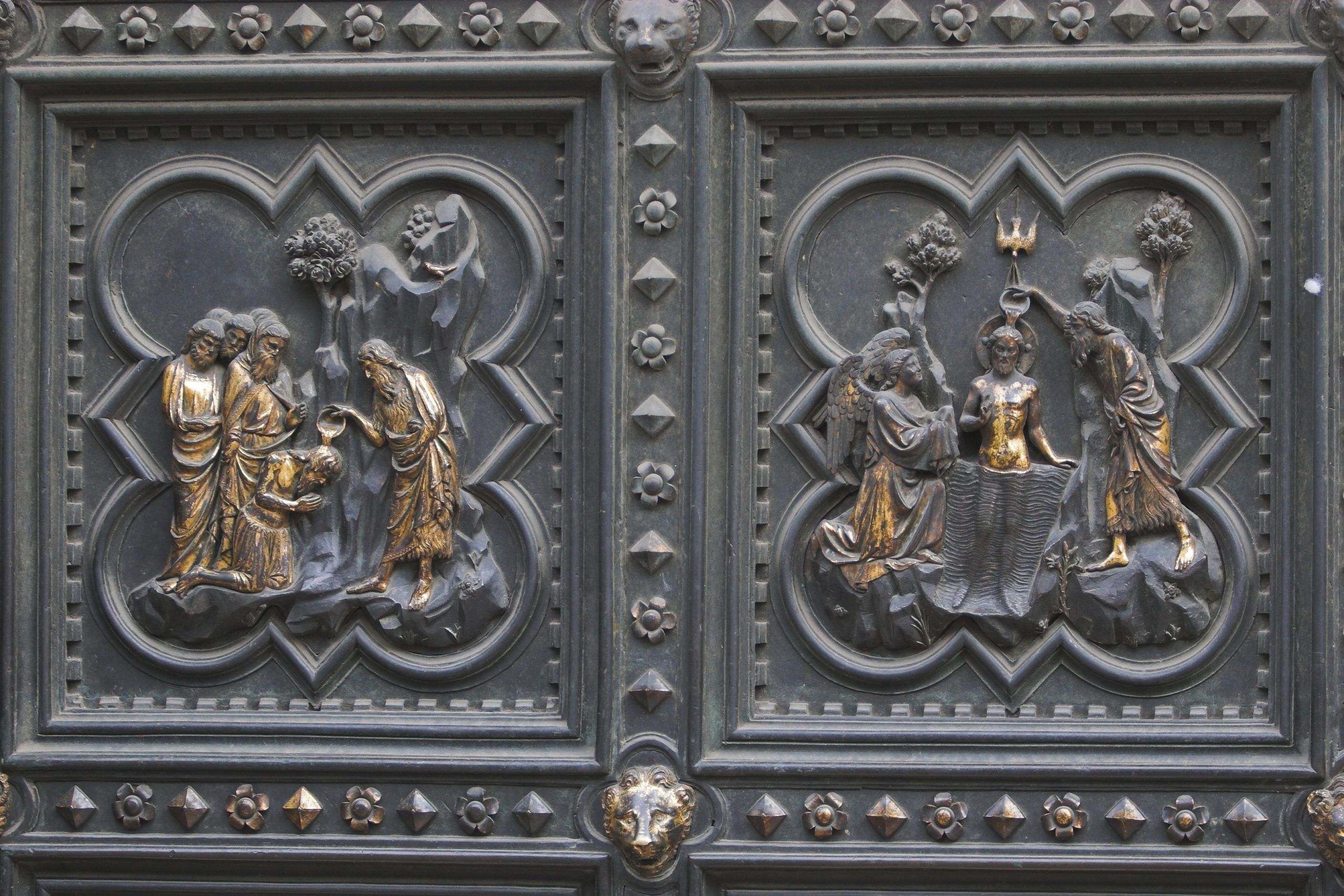

- In 1401, after having narrowly won the competition with Brunelleschi, the 23 year old and inexperienced young goldsmith Lorenzo Ghiberti (1378-1455), is commissioned by the Calima Guild to decorate the doors which are today the North Gate. Ghiberti cast the bronze high reliefs using a method known as lost-wax casting, a technique that he had to reinvent entirely since it was lost since the fall of the Roman Empire. One of the reasons Ghiberti won the contest, was that his technique was so advanced that it required 20 % less (7 kg per panel) bronze than that of his competitors, bronze being a dense material far more costly than marble. His technique, applied to the entire decoration of the North Gate, as compared to his competitors, would save some estimated 100 kg of bronze. And since in 1401, with the plague regularly hitting Florence, economic conditions were poor, even the wealthy Calimala took into account the total costs of the program.
The bronze doors are comprised of 28 panels, with 20 panels depicting the life of Christ from the New Testament. The 8 lower panels show the four Evangelists and the Church Fathers Saint Ambrose, Saint Jerome, Saint Gregory, and Saint Augustine. The construction took 24 years.


- In 1424, Ghiberti, at age 46, was given—unusually, with no competition—the task of also creating the East Gate. Only in 1452 did Ghiberti, then seventy-four years old, install the last bronze panels, since construction lasted this time 27 years! According to Giorgio Vasari (1511-1574), Michelangelo Buonarroti (1475-1564) later judged them « so beautiful they would grace the entrance to Paradise ».
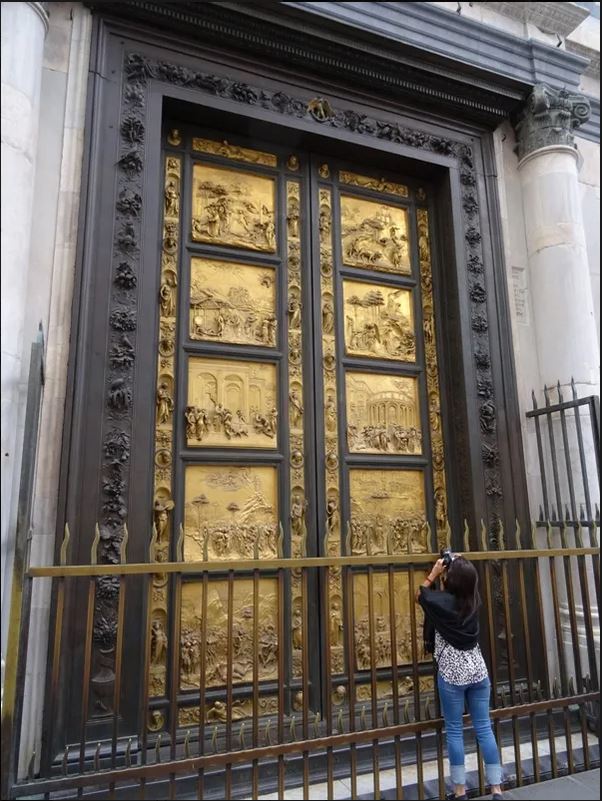

Over two generations, a bevy of well paid assistants and pupils were trained by Ghiberti, including exceptional artists, such as Luca della Robbia, Donatello, Michelozzo, Benozzo Gozzoli, Bernardo Cennini, Paolo Uccello, Andrea del Verrocchio and Ghiberti’s sons, Vittore and Tommaso. And over time, the seventeen-foot-tall, three-ton bronze doors became an icon of the Renaissance, one of the most famous works of art in the world.
In 1880, the French sculptor Auguste Rodin was inspired by it for his own Gates of Hell on which he worked for 38 year
Revolution
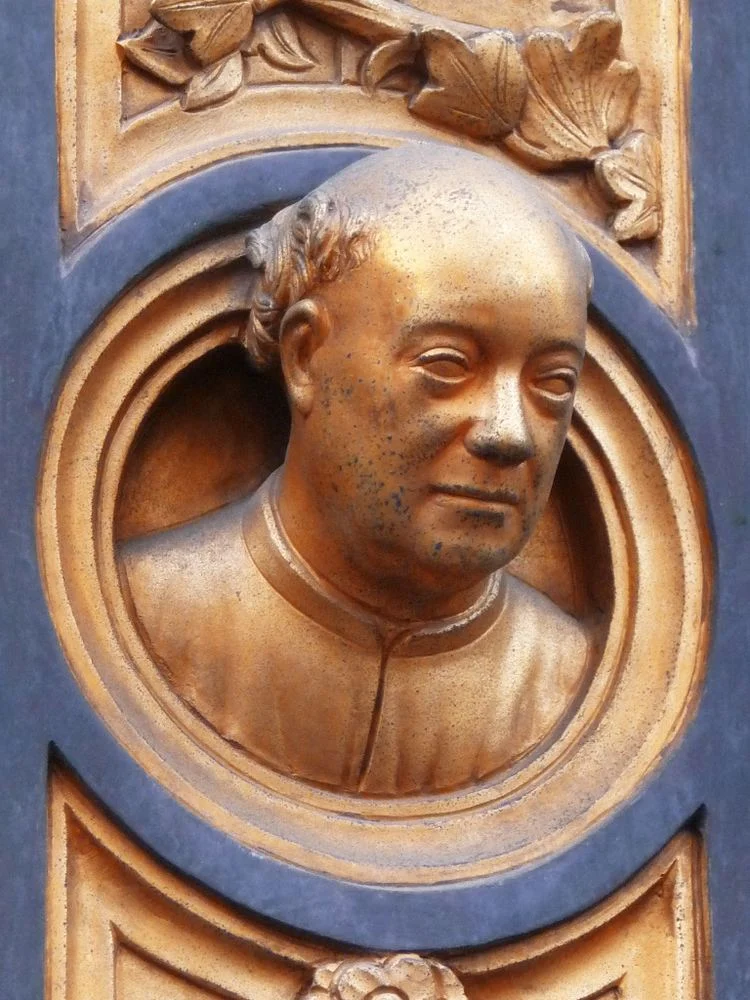

Of utmost interest for our discussion here is the dramatic shift in conception and design of the bronze relief sculptures that occurred between the North and the East Gates, because it reflects how bot the artist as well as his patrons used the occasion to share with the broader public their newest ideas, inventions and exciting discoveries.
The themes of the North Gate of 1401 were inspired by scenes from the New Testament, except for the panel made by Ghiberti, « The Sacrifice of Isaac », which had won him the selection competition the same year. To complete the ensemble, it was therefore only logical that the East Gate of 1424 would take up the themes of the Old Testament.
Originally, it was the scholar and former chancellor of Florence Leonardo Bruni (1369-1444) who planned an iconography quite similar to the two previous doors. But, after heated discussions, his proposal was rejected for something radically new. Instead of realizing 28 panels, it was decided, for aesthetic reasons, to reduce the number of panels to only 10 much larger square reliefs, between borders containing statuettes in niches and medallions with busts.
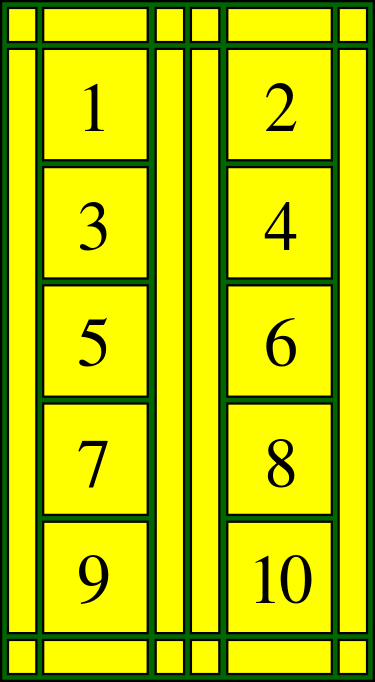
Hence, since each of the 10 chapters of the Old Testament contains several events, the total number of scenes illustrated, within the 10 panels has risen to 37 and all appear in perspective :
- Adam and Eve (The Creation of Man)
- Cain and Abel (Jalousie is the origin of Sin)
- Noah (God’s punishment)
- Abraham and Isaac (God is just)
- Jacob and Esau
- Joseph
- Moses
- Joshua
- David (Good commandor)
- Solomon and the Queen of Sheba
The general theme is that of salvation based on Latin and Greek patristic tradition. Very shocking for the time, Ghiberti places in the center of the first panel the creation of Eve, that of Adam appearing at the bottom left.
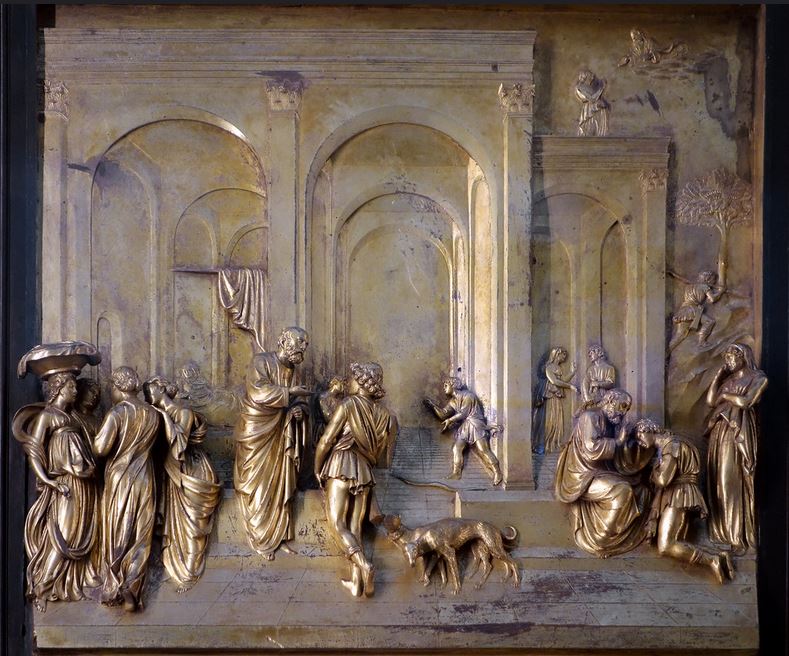
After the first three panels, focusing on the theme of sin, Ghiberti began to highlight more clearly the role of God the Savior and the foreshadowing of Christ’s coming. Subsequent panels are easier to understand. One example is the panel with Isaac, Jacob and Esau where the figures are merged with the surrounding landscape so that the eye is led toward the main scene represented in the top right.
Many of the sources for these scenes were written in ancient Greek, and since knowledge of Greek at that time was not so common, it appears that Ghiberti’s “theological advisor” was Ambrogio Traversari (1386-1439), with whom he had many exchanges.
Traversari was a close friend of Nicolas of Cusa (1401-1464), a protector of Piero della Francesca (1412-1492) and a key organizer of the Ecumenical Council of Florence of 1438-1439, which attempted to put an end to the schism separating the Church of the East from that of the West.
Perspective
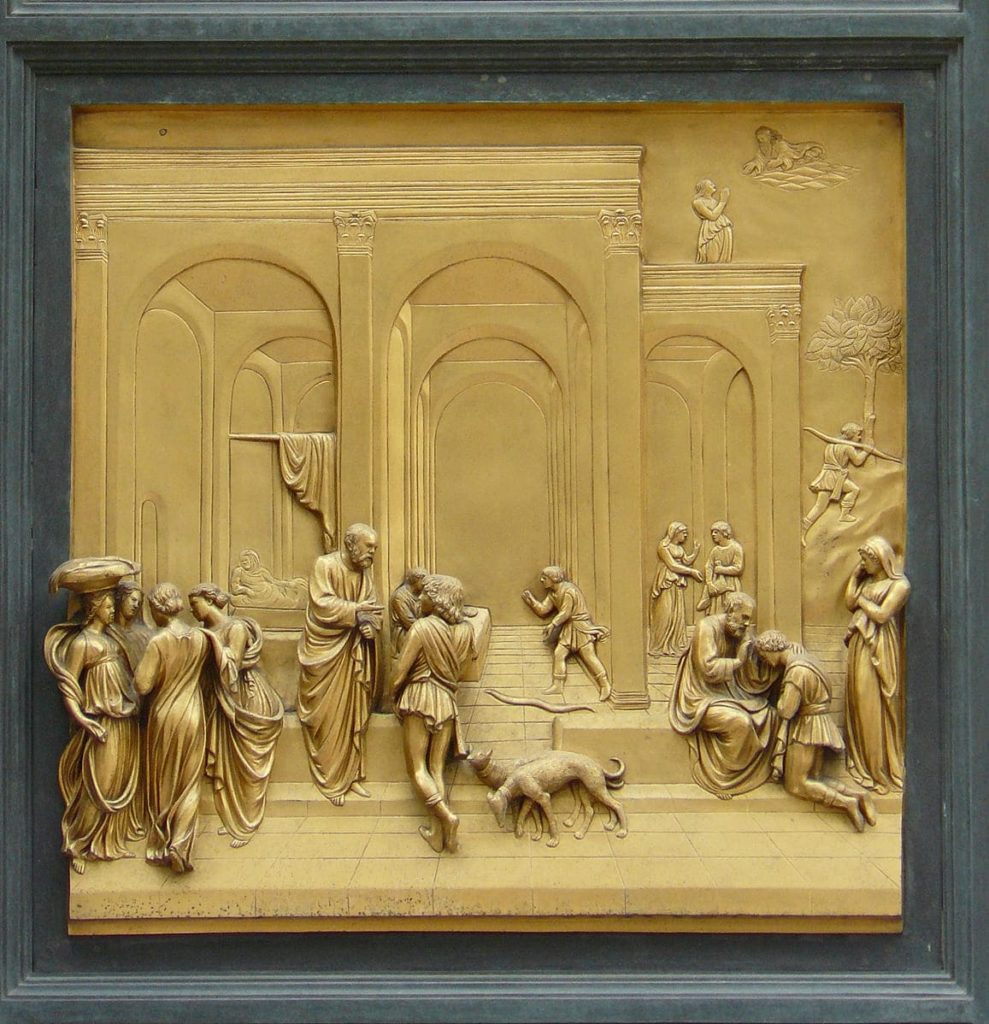
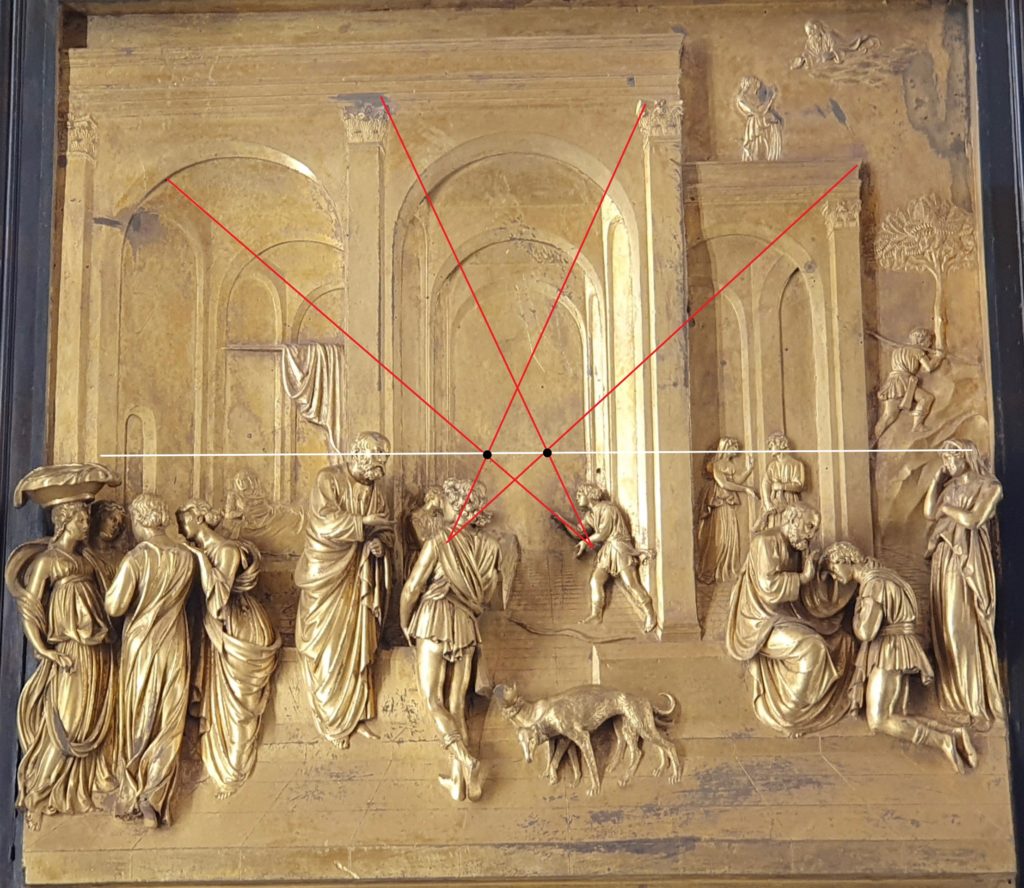



The bronze reliefs, known for their vivid illusion of deep space in relief, are one of the revolutionary events that epitomize the Renaissance. In the foreground are figures in high relief, which gradually become less protruding thereby exploiting the full illusionistic potential of the stiacciato technique later brought to its high point by Donatello. Using this form of “inbetweenness”, they integrate in one single image, what appears both as a painting, a low relief as well as a high relief. Or maybe one has to look at it another way: these are flat images traveling gradually from a surface into the full three dimensions of life, just as Ghiberti, in one of the first self-portraits of art history, reaches his head out of a bronze medal to look down on the viewers. The artist desired much more than perspective, he wanted breathing space!
This new approach will influence Leonardo Da Vinci (1452-1517). As art historian Daniel Arasse points out :
(…) It was in connection with the practice of Florentine bas-relief, that of Ghiberti at the Gate of Paradise (…) that Leonardo invented his way of painting. As Manuscript G (folio 23b) would much later state, ‘the field on which an object is painted is a capital thing in painting. (…) The painter’s aim is to make his figures appear to stand out from the field’ – and not, one might add, to base his art on the alleged transparency of that same field. It is by the science of shadow and light that the painter can obtain an effect of emergence from the field, an effect of relief, and not by that of the linear perspective.
Donatello
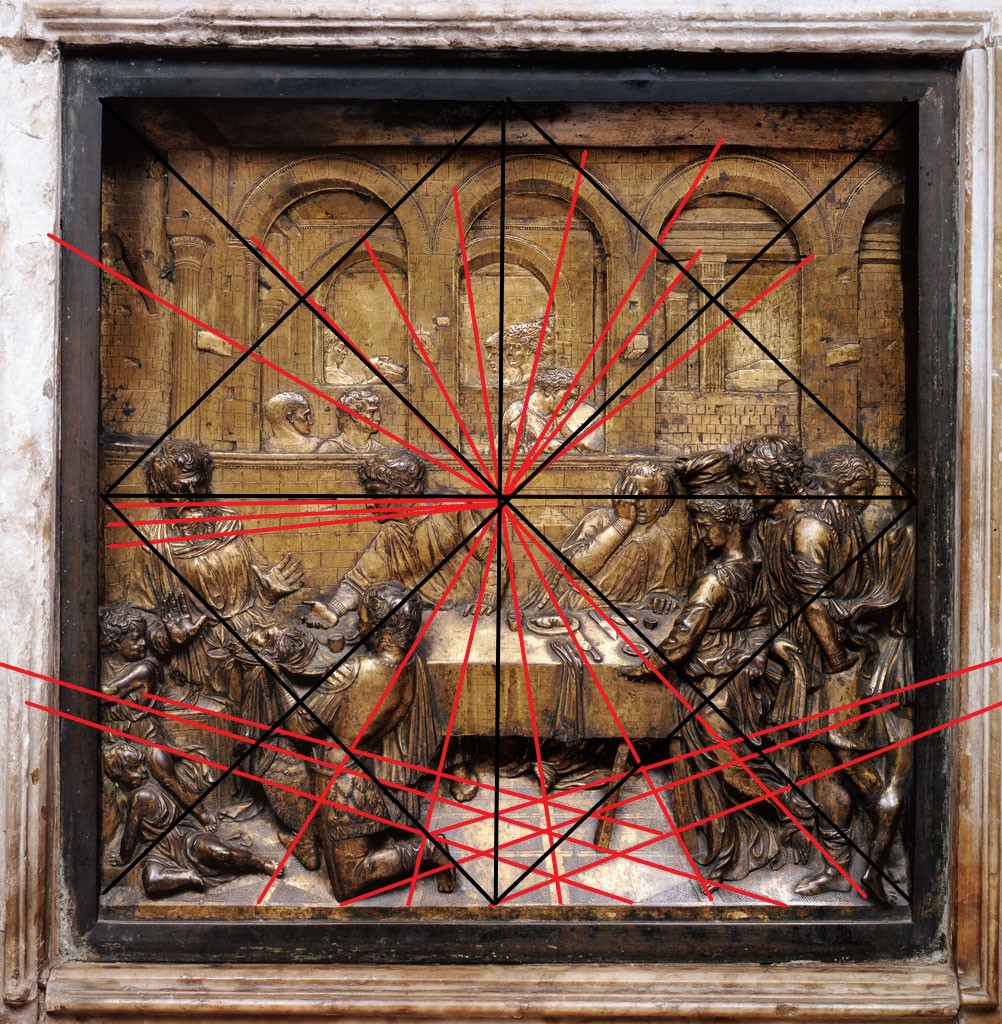

At the beginning of the 15th century, several theoretical approaches existed and eventuall contradicted each other. Around 1423-1427, the talentful sculptor Donatello, a young collaborator of Ghiberti, created his Herod’s Banquet, a bas-relief in the stiacciato technique for the baptismal font of the Siena Baptistery.
In this work, the sculptor deploys a harmonious perspective with a single central vanishing point. Around the same time, in Florence, the painter Massacchio (1401-1428) used a similar construction in his fresco The Trinity.
As we will see, Ghiberti, starting from the anatomy of the eye, opposed such an abstract approach in his works as well as in his writings and explored, as early as 1401, other geometrical models, called « binocular ». (see below).
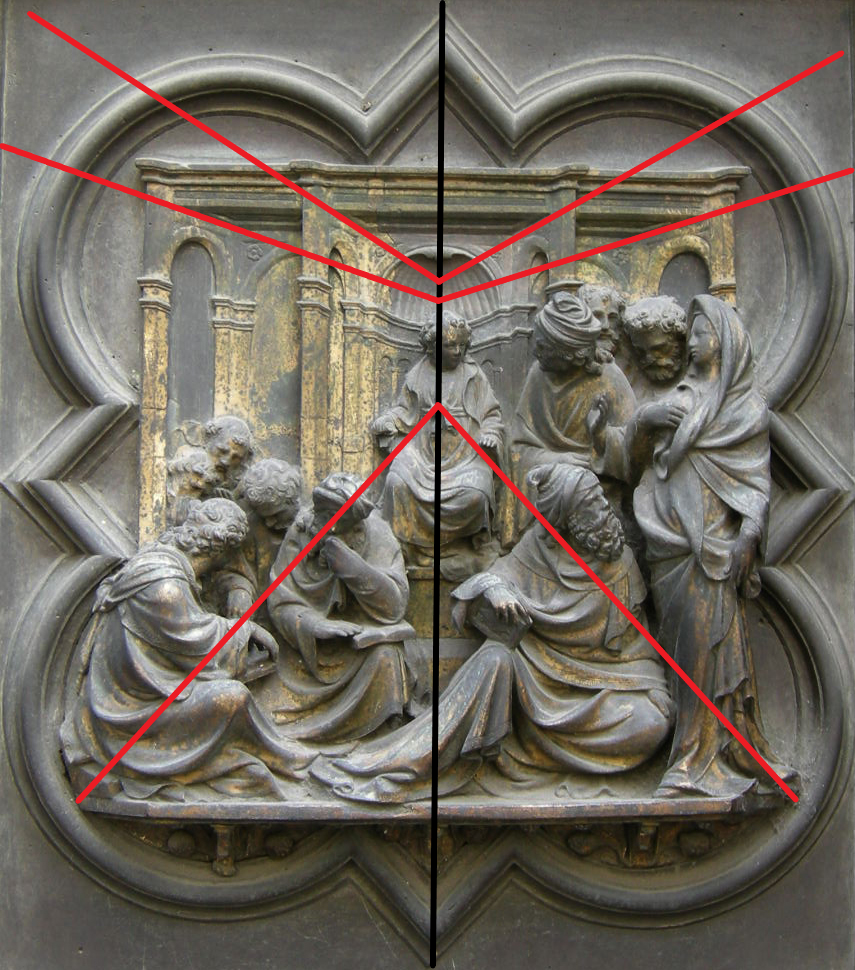

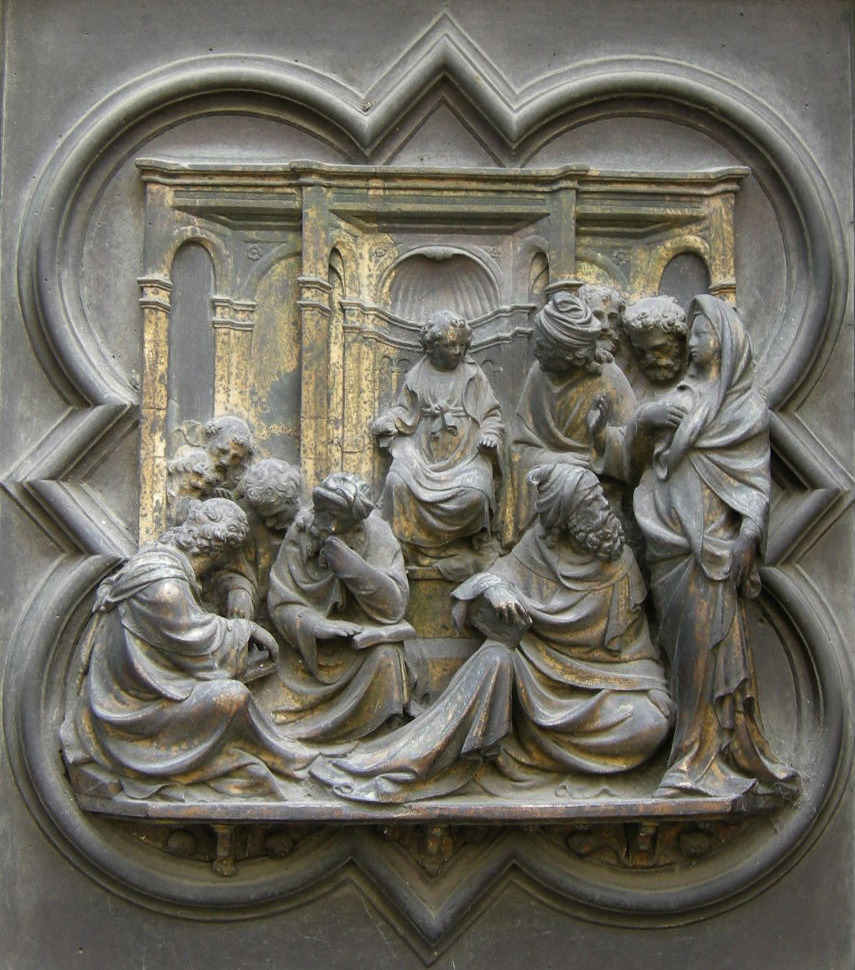
Christ among the Doctors, Ghiberti, before 1424.
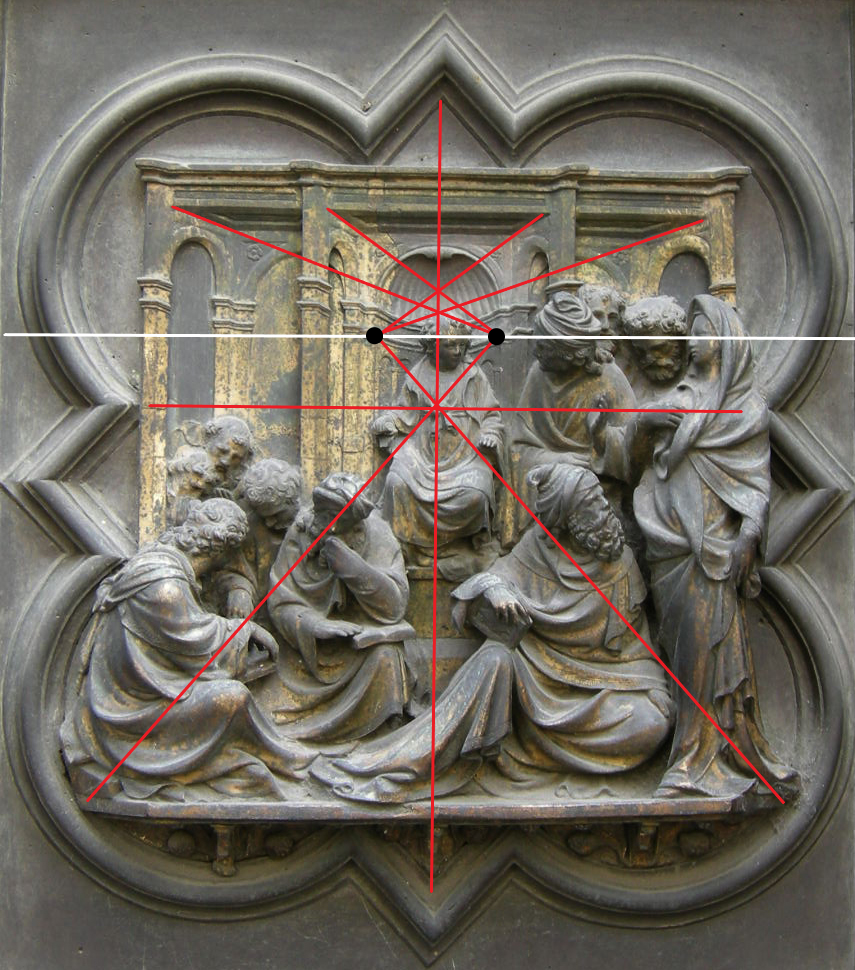
Christ among the Doctors, Ghiberti, before 1424.
Then, as far as our knowledge reaches, in 1407, Brunelleschi had conducted several experiments on this question, most likely based on the ideas presented by another friend of Cusa, the Italian astronomer Paolo dal Pozzo Toscanelli (1397-1482), in the latter’s now lost treaty Della Prospettiva. What we do know is that Brunelleschi sought above all to demonstrate that all perspective is an optical illusion.
Finally, it was in 1435, that the humanist architect Leon Baptista Alberti (1406-1472), in his treatise Della Pictura, attempted, on the basis of Donatello’s approach, to theorize single vanishing point perspective as a representation of a harmonious and unified three-dimensional space on a flat surface. Noteworthy but frustrating for us today is the fact that Alberti’s treatise doesn’t contain any illustrations.
However, Leonardo, who read and studied Ghiberti’s writings on, would use the latter’s arguments to indicate the limits and even demonstrate the dysfunctionality of Alberti’s “perfect” perspective construction especially when one goes beyond a 30 degres angle.
In the Codex Madrid, II, 15 v. da Vinci realizes that « as such, the perspective offered by a rectilinear wall is false unless it is corrected (…) ».
Perspectiva artificialis versus perspectiva naturalis

Alberti’s “perspectiva artificialis” is nothing but an abstraction, necessary and useful to represent a rational organization of space. Without this abstraction, it is fairly impossible to define with mathematical precision the relationships between the appearance of objects and the receding of their various proportions on a flat screen: width, height and depth.
From the moment that a given image on a flat screen was thought about as the intersection of a plane cutting a cone or pyramid, a method emerged for what was mistakenly considered as an “objective” representation of “real” three dimensional space, though it is nothing but an “anamorphosis”, i.e. a tromp-l’oeil or visual illusion.
What has to be underscored, is that this construction does away with the physical reality of human existence since it is based on an abstract construct pretending:
- that man is a single eyed cyclops;
- that vision emanates from one single point, the apex of the visual pyramid;
- that the eye is immobile;
- that the image is projected on a flat screen rather than on a curved retina.
Slanders and gossip
The crucial role of Ghiberti, an artist which “Ghiberti expert” Richard Krautheimer mistakenly presents as a follower of Alberti’s perspectiva artificialis, has been either ignored or downplayed.
Ghiberti’s unique manuscript, the three volumes of the Commentarii, which include his autobiography and which established him as the first modern historian of the fine arts, is not even fully translated into English or French and was only published in Italian in 1998.
Today, because of his attention to minute detail and figures « sculpted » with wavy and elegant lines, as well as the variety of plants and animals depicted, Ghiberti is generally presented as “Gothic-minded”, and therefore “not really” a Renaissance artist!
Giorgio Vasari, often acting as the paid PR man of the Medici clan, slanders Ghiberti by saying he wrote « a work in the vernacular in which he treated many different topics but arranged them in such a fashion that little can be gained from reading it. »
Admittedly, tension among humanists, was not uncommon. Self-educated craftsmen, such as Ghiberti and Brunelleschi on the one side, and heirs of wealthy wool merchants, such as Niccoli on the other side, came from entirely different worlds. For example, according to a story told by Guarino Veronese in 1413, Niccoli greeted Filippo Brunelleschi haughtily: « O philosopher without books, » to which Filippo replied with his legendary irony: « O books without philosopher ».
For sure, the Commentarii, are not written according to the rhetorical rules of those days. Written at the end of Ghiberti’s life, they may have simply been dictated to a poorly trained clerk who made dozens of spelling errors.
The humanists

The Commentarii does reveal a highly educated author and a thinker having profound knowledge of many classical Greek and Arab thinkers. Ghiberti was not just some brilliant handcraft artisan but a typical “Renaissance man”.
In dialogue with Bruni, Traversari and the “manuscript hunter” Niccolo Niccoli, Ghiberti, who couldn’t read Greek but definitely knew Latin, was clearly familiar with the rediscovery of Greek and Arab science, a task undertaken by Boccaccio’s and Salutati’s “San Spirito Circle” whose guests (including Bruni, Traversari, Cusa, Niccoli, Cosimo di Medici, etc.) later would convene every week at the Santa Maria degli Angeli convent. Ghiberti exchanges moreover with Giovanni Aurispa, a collaborator of Traversari who brought back from Byzantium, years before Bessarion, the whole of Plato’s works to the West.
Amy R. Bloch, in her well researched study Lorenzo Ghiberti’s Gates of Paradise, Humanism, History, and Artistic Philosophy in the Italian Renaissance (2016), writes that « Traverari and Niccoli can be tied directly to the origins of the project for the Gates and were clearly interested in sculptural commissions being planned for the Baptistery. On June 21, 1424, after the Calima requested from Bruni his program for the doors, Traversari wrote to Niccoli acknowledging, in only general terms, Niccoli’s ideas for the stories to be included and mentioning, without evident disapproval, that the guild had instead turned to Bruni for advice. »
Palla Strozzi
Ghiberti’s patron, sometimes advisor, and close associate was Palla Strozzi (1372-1462), who, besides being the the richest man in Florence with a gross taxable assets of 162,925 florins in 1427, including 54 farms, 30 houses, a banking firm with a capital of 45,000 florins, and communal bonds, was also a politician, a writer, a philosopher and a philologist whose library contained close to 370 volumes in 1462.
Just as Traversari and Bruni, Strozzi learned Latin and studied Greek under the direction of the Byzantine scholar Manuel Chrysoloras, invited to Florence by Salutati.
Ghiberti’s close relationship with Strozzi, writes Bloch, « gave him access to his manuscripts and, as importantly, to Strozzi’s knowledge of them. »
But there was more. « The relationship between Ghiberti and Palla Strozzi was so close that, when Palla went to Venice in 1424 as one of two Florentine ambassadors charged with negociating an alliance with the Venetians, Ghiberti accompanied him in his retinue. »
Strozzi was known as a real humanist, always looking to preserve peace while strongly opposing oligarchical rule, both in Florence as in Venice.
In fact it was Palla Strozzi, not Cosimo de’ Medici, who first set in motion plans for the first public library in Florence, and he intended for the sacristy of Santa Trinita to serve as its entryway. While Palla’s library was never realized due to the dramatic political conflict knows as the Albizzi Coup that led to his exile in 1434, Cosimo who got a free hand to rule over Florence, would make the library project his own.
A bold statement
Ghiberti begins the Commentarii with a bold and daring statement for a Christian man in a Christian world, about how the art of antiquity came to be lost:
The Christian faith was victorious in the time of Emperor Constantine and Pope Sylvester. Idolatry was persecuted to such an extent that all the statues and pictures of such nobility, antiquity an perfection were destroyed and broken in to pieces. And with the statues and pictures, the theoretical writings, the commentaries, the drawing and the rules for teaching such eminent and noble arts were destroyed.
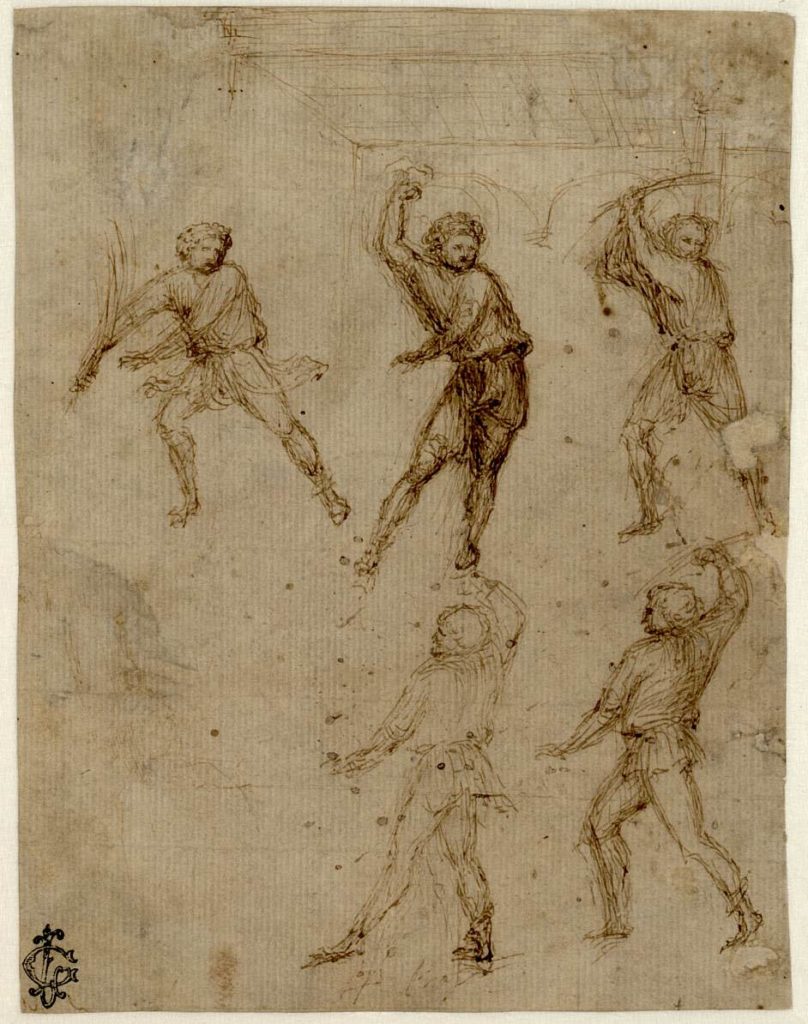



Ghiberti understood the importance of multidisciplinarity for artists. According to him, “sculpture and painting are sciences of several disciplines nourished by different teachings”.
In book I of his Commentarii, Ghiberti gives a list of the 10 liberal arts that the sculptor and the painter should master : philosophy, history, grammar, arithmic, astronomy, geometry, perspective, theory of drawing, anatomy and medecine and underlines that the necessity for an artist to assist at anatomical dissections.
As Amy Bloch underscores, while working on the Gates, in the intense process of visualizing the stories of God’s formation of the world and its living inhabitants, Ghiberti’s engagement « stimulated in him an interest in exploring all types of creativity — not only that of God, but also that of nature and of humans — and led him to present in the opening panel of the Gates of Paradise (The creation of Adam and Eve) a grand vision of the emergence of divine, natural, and artistic creation. »

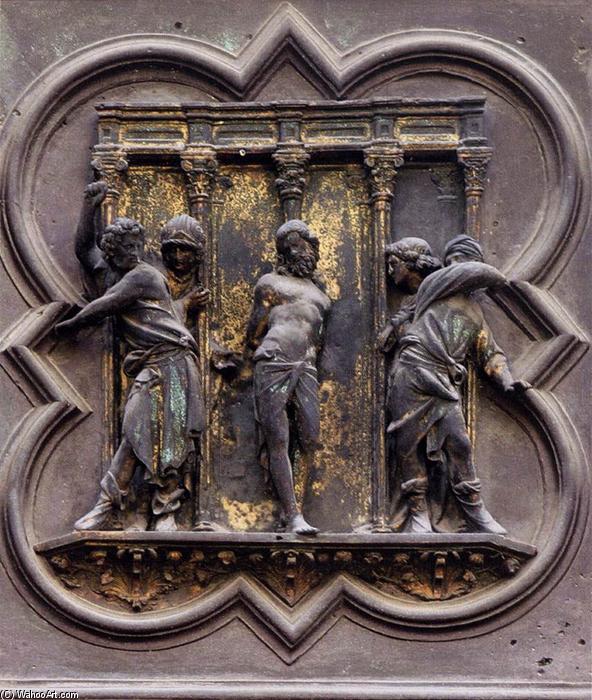
The inclusion of details evoking God’s craftmanship, says Bloch, « recalls similes that liken God, as the maker of the world, to an architect, or, in his role as creator of Adam, to a sculptor or painter. Teh comparison, which ultimately derives from the architect-demiurge who creates the world in Plato’s Timaeus, appears commonly in medieval Jewish and Christian exegesis. »
Philo of Alexandria wrote that man was modeled « as by a potter » and Ambrose metaphorically called God a « craftsman (artifex) and a painter (pictor) ». Consequently, if man is « the image of God » as says Augustine and the model of the « homo faber – man producer of things », then, according to Salutati, « human affairs have a similarity to divine ones ».
The power of vision and the composition of the Eye
Concerning vision, Ghiberti writes:
I, O most excellent reader, did not have to obey to money, but gave myself to the study of art, which since my childhood I have always pursued with great zeal and devotion. In order to master the basic principles I have sought to investigate the way nature functions in art; and in order that I might be able to approach her, how images come to the eye, how the power of vision functions, how visual [images] come, and in what way the theory of sculpture and painting should be established.
Now, any serious scholar, having worked through Leonardo’s Notebooks, who then reads Ghiberti’s I Commentarii, immediately realizes that most of Da Vinci’s writings were basically comments and contributions about things said or answers to issues raised by Ghiberti, especially respecting the nature of light and optics in general. Leonardo’s creative mindset was a direct outgrowth of Ghiberti’s challenging world outlook.

In Commentario 3, 6, which deals with optics, vision and perspective, Ghiberti, opposing those for whom vision can only be explained by a purely mathematical abstraction, writes that “In order that no doubt remains in the things that follow, it is necessary to consider the composition of the eye, because without this one cannot know anything about the way of seeing.” He then says, that those who write about perspective don’t take into account “the eye’s composition”, under the pretext that many authors would disagree.
Ghiberti regrets that despite the fact that many “natural philosophers” such as Thales, Democritus, Anaxagoras and Xenophanes have examined the subject along with others devoted to human health such as “Hippocrates, Galen and Avicenna”, there is still so much confusion.
Indeed, he says, “speaking about this matter is obscure and not understood, if one does not have recourse to the laws of nature, because more fully and more copiously they demonstrate this matter.”
Avicenna, Alhazen and Constantine
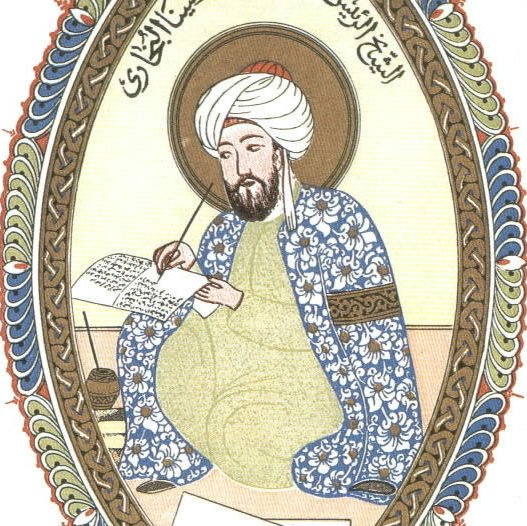


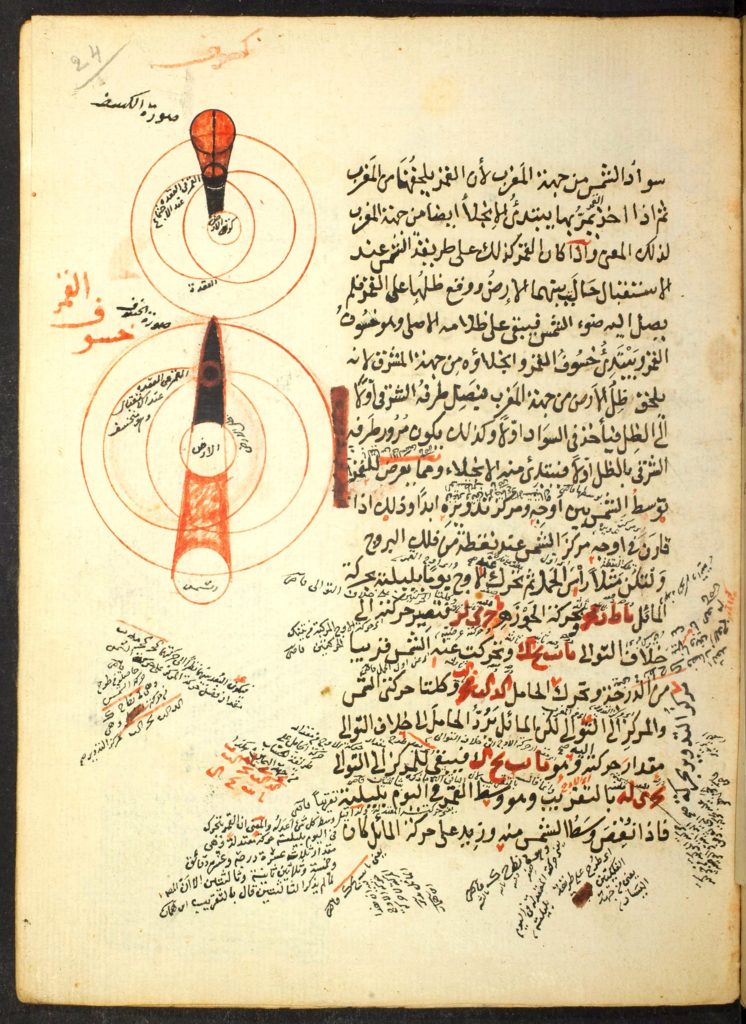
Therefore, says Ghiberti:
it is necessary to affirm some things that are not included in the perspective model, because it is very difficult to ascertain these things but I will try to clarify them. In order not to deal superficially with the principles that underlie all of this, I will deal with the composition of the eye according to the writings of three authors, Avicenna (Ibn Sina), in his books, Alhazen (Ibn al Haytham) in his first volume on perspective (Optics), and Constantine (the Latin name of the Arab scholar and physician Qusta ibn Luqa) in his ‘First book on the Eye’; for these authors suffice and deal with much certainty in these subjects that are of interest to us.
This is quite a statement! Here we have “the” leading, founding figure of the Italian and European Renaissance with its great contribution of perspective, saying that to get any idea about how vision functions, one has to study three Arab scientists: Ibn Sina, Ibn al Haytham and Qusta ibn Luqa ! Cultural Eurocentrism might be one reason why Ghiberti’s writings were kept in the dark.
Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen) made important contributions to opthalmology and improved upon earlier conceptions of the processes involved in vision and visual perception in his Treatise on Optics (1021), which is known in Europe as the Opticae Thesaurus. Following his work on the camera oscura (darkroom) he was also the first to imagine that the retina (a curved surface), and not the pupil (a point) could be involved in the process of image formation.
Avicenna, in the Canon of Medicine (ca. 1025), describes sight and uses the word retina (from the Latin word rete meaning network) to designate the organ of vision.
Later, in his Colliget (medical encyclopedia), Ibn Rushd (Averroes, 1126-1198) was the first to attribute to the retina the properties of a photoreceptor.
Avicenna’s writings on anatomy and medical science were translated and circulating in Europe since the XIIIth century, Alhazen’s treatise on optics, which Ghiberti quotes extensively, had just been translated into Italian under the title De li Aspecti.
It is now recognized that Andrea del Verrocchio, whose best known pupil was Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1517) was himself one of Ghiberti’s pupils. Unlike Ghiberti, who mastered Latin, neither Verrocchio nor Leonardo mastered a foreign language.
What is known is that while studying Ghiberti’s Commentarii, Leonardo had access in Italian to a series of original quotations from the Roman architect Vitruvius and from Arab scientists such as Avicenna, Alhazen, Averroes and from those European scientists who studied Arab optics, notably the Oxford Fransciscans Roger Bacon (1214-1294), John Pecham (1230-1292) and the Polish monk working in Padua, Erazmus Ciolek Witelo (1230-1275), known by his Latin name Vitellion.
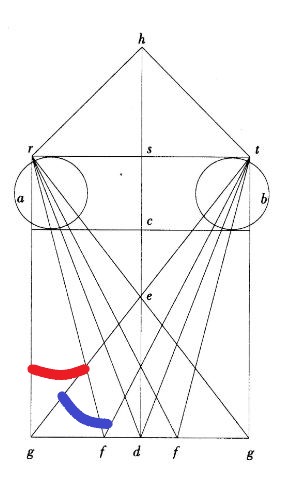
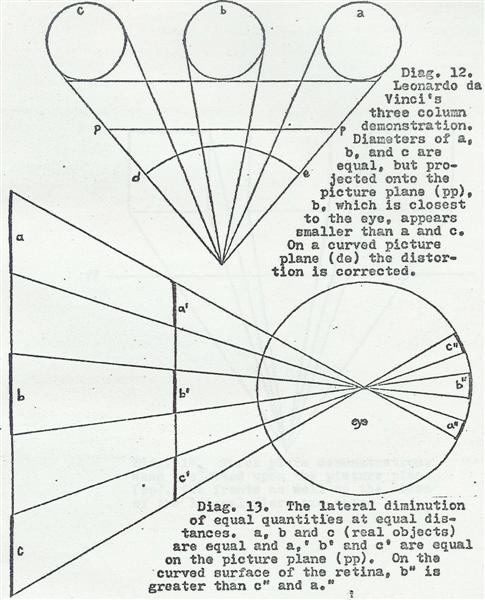
As stressed by Professor Dominque Raynaud, Vitellion introduces the principle of binocular vision for geometric considerations.
He gives a figure where we see the two eyes (a, b) receiving the images of points located at equal distance from the hd axis.
He explains that the images received by the eyes are different, since, taken from the same side, the angle grf (in red) is larger than the angle gtf (in blue). It is necessary that these two images are united at a certain point in one image (Diagram).
Where does this junction occur? Witelo says: « The two forms, which penetrate in two homologous points of the surface of the two eyes, arrive at the same point of the concavity of the common nerve, and are superimposed in this point to become one ».
The fusion of the images is thus a product of the internal mental and nervous activity.
The great astronomer Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) will use Alhazen’s and Witelo’s discoveries to develop his own contribution to optics and perspective. “Although up to now the [visual] image has been [understood as] a construct of reason,” Kepler observes in the fifth chapter of his Ad Vitellionem Paralipomena (1604), “henceforth the representations of objects should be considered as paintings that are actually projected on paper or some other screen.” Kepler was the first to observe that our retina captures an image in an inverted form before our brain turns it right side up.
Out of this Ghiberti, Uccello and also the Flemish painter Jan Van Eyck, in contact with the Italians, will construct as an alternative to one cyclopic single eye perspective revolutionary forms of “binocular” perspective while Leonardo and Louis XI’ court painter Jean Fouquet will attempt to develop curvilinear and spherical space representations.
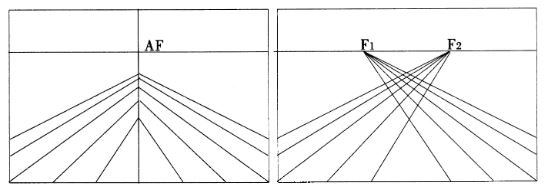
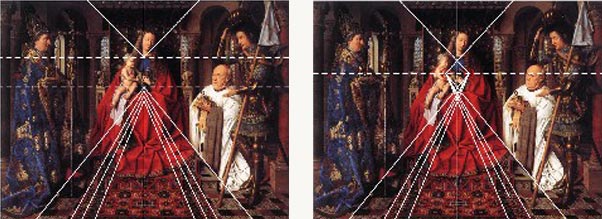


In China, eventually influenced by Arab optical science breakthrough’s, forms of non-linear perspective, that integrate the mobility of the eye, will also make their appearance during the Song Dynasty.
Light
Ghiberti will add another dimension to perspective: light. One major contribution of Alhazen was his affirmation, in his Book of Optics, that opaque objects struck with light become luminous bodies themselves and can radiate secondary light, a theory that Leonardo will exploit in his paintings, including in his portraits.
Already Ghiberti, in the way he treats the subject of Isaac, Jacob and Esau (Figure), gives us an astonishing demonstration of how one can exploit that physical principle theorized by Alhazen. The light reflected by the bronze panel, will strongly differ according to the angle of incidence of the arriving rays of light. Arriving either from the left of from the right side, in both cases, the Ghiberti’s bronze relief has been modeled in such a way that it magnificently strengthens the overall depth effect !


While the experts, especially the neo-Kantians such as Erwin Panofsky or Hans Belting, say that these artists were “primitives” because applying the “wrong” perspective model, they can’t grasp the fact that they were in reality exploring a far “higher domain” than the mere pure mathematical abstraction promoted by the Newton-Galileo cult that became the modern priesthood ruling over “science”.
Much more about all of this can and should be said. Today, the best way to pay off the European debt to “Arab” scientific contributions, is to reward not just the Arab world but all future generations with a better future by opening to them the “Gates of Paradise”.
See all of Ghiberti’s works at the WEB GALLERY OF ART
Short Biography
- Arasse, Daniel, Léonard de Vinci, Hazan, 2011;
- Avery, Charles, La sculpture florentine de la Renaissance, Livre de poche, 1996, Paris;
- Belting, Hans, Florence & Baghdad, Renaissance art and Arab science, Harvard University Press, 2011;
- Bloch, Amy R., Lorenzo Ghiberti’s Gates of Paradise; Humanism, History and Artistic Philosophy in the Italian Renaissance, Cambridge University Press, 2016, New York;
- Borso, Franco et Stefano, Uccello, Hazan, Paris, 2004 ;
- Butterfield, Andrew, Verrocchio, Sculptor and painter of Renaissance Florence, National Gallery, Princeton University Press, 2020 ;
- Butterfield, Andrew, Art and Innovation in Ghiberti’s Gates of Paradise, High Museum of Art, Yale University Press, 2007;
- Kepler, Johannes, Paralipomènes à Vitellion, 1604, Vrin, 1980, Paris;
- Krautheimer, Richard and Trude, Lorenzo Ghiberti, Princeton University Press, New Jersey, 1990;
- Martens, Maximiliaan, La révolution optique de Jan van Eyck, dans Van Eyck, Une révolution optique, Hannibal – MSK Gent, 2020.
- Pope-Hennessy, John, Donatello, Abbeville Press, 1993 ;
- Radke, Gary M., Lorenzo Ghiberti: Master Collaborator; The Gates of Paradise, Lorenzo Ghiberti’s Renaissance Masterpiece, High Museum of Atlanta and Yale University Press, 2007;
- Rashed, Roshi, Geometric Optics, in History of Arab Sciences, edited by Roshdi Rashed, Vol. 2, Mathematics and physics, Seuil, Paris, 1997.
- Raynaud, Dominique, L’hypothèse d’Oxford, essai sur les origines de la perspective, PUF, 1998, Paris.
- Raynaud, Dominique, Ibn al-Haytham on binocular vision: a precursor of physiological optics, Arabic Sciences and Philosophy, Cambridge University Press (CUP), 2003, 13, pp. 79-99.
- Raynaud, Dominique, Perspective curviligne et vision binoculaire. Sciences et techniques en perspective, Université de Nantes, Equipe de recherche: Sciences, Techniques, et Sociétés, 1998, 2 (1), pp.3-23.;
- Vereycken, Karel, interview with People’s Daily: Leonardo Da Vinci’s « Mona Lisa » resonates with time and space with traditional Chinese painting, 2019.
- Vereycken, Karel, Uccello, Donatello, Verrocchio and the art of military command, 2022.
- Vereycken, Karel, The Invention of Perspective, Fidelio, 1998.
- Vereycken, Karel, Van Eyck, un peintre flamand dans l’optique arabe, 1998.
- Vereycken, Karel, Mutazilism and Arab astronomy, two bright stars in our firmament, 2021.
- Walker, Paul Robert, The Feud That Sparked the Renaissance, How Brunelleschi and Ghiberti changed the World, HarperCollins, 2002.
On Leonardo da Vinci’s « Vitruvian Man »

By Karel Vereycken
Leonardo da Vinci’s « Viruvian Man ». Since we’re commemorating this year (2019) Leonardo Da Vinci, who died 500 years ago, many silly things are presented by fake scholars trying to make a real living.
Since I was introduced into the canon of proportions of the human body during my training as a professional painter and engraver, I want offer you some hints on how to look at what is called Da Vinci’s « Vitruvian man », a drawing currently on exhibit at the Da Vinci show at the Louvre in Paris.
Hence, as Leonardo underlines himself in his notebooks, adopting Cusanus wordings, it is only with the « eyes of the mind » that art becomes visible, because the « eyes of the flesh » are intrensically blind to it.
Canons of proportions
Europe, and Classical Greece, as everybody should know, emerged largely by absorbing several major discoveries accomplished much earlier by other civilizations. Much of it came from Asia, but African and especially Egypt, were key.
The very practice of mummification, a process which takes at least 60 days of work, made Egypt the key area of anatomical research.
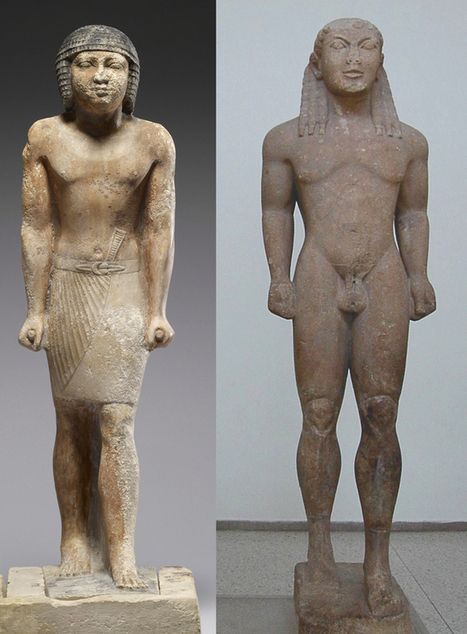

As demonstrated by early Egyptian sculpture, the exact size of the entire adult human body is 7,5 times the size of the head. The size of a newborn is only four heads, that of a seven year old, six heads and that of a 17 years old adolescent, 7 heads.
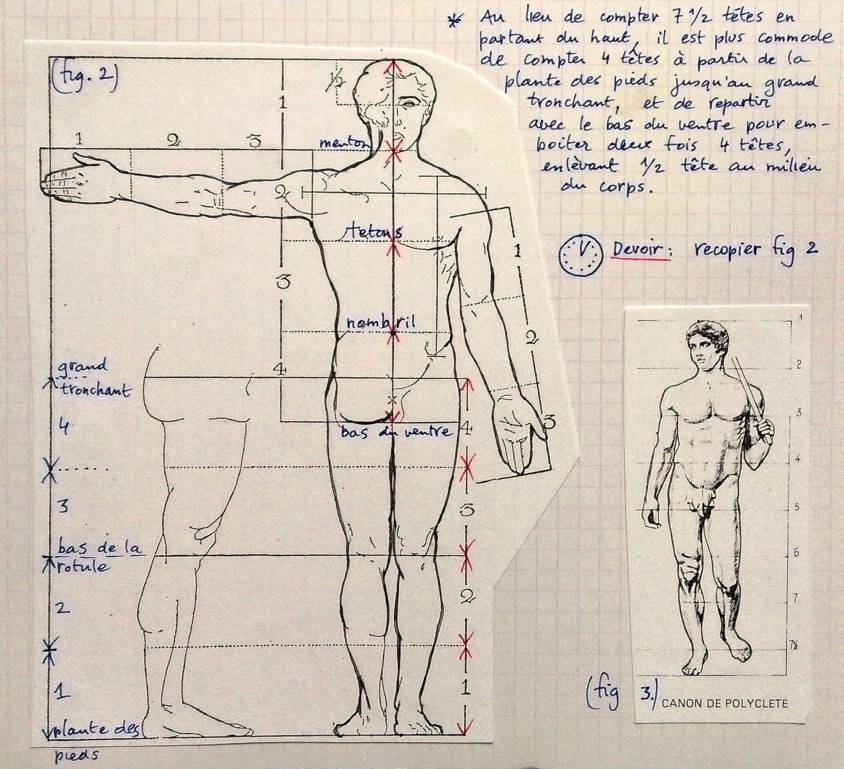
If one subdivides the overall 7.5 proportion, for an adult, from the top of the head till the lowest part of the torso, one measures four heads, one till the nipples, one till the belly button and a fourth one till the lowest part of the pubis. Going up from the sole till the middle of the pelvis, one measures 3.5 heads: 2 heads till the knee and 1.5 till the middle of the pelvis. That brings the total till 7.5 heads for the entire length of the adult human body and it is proportional in the sense that people with smaller heads also have small bodies.
Polikleitos versus Lysippus
In the Vth Century BC, the Greek sculptor Polikleitos’ spear bearer (The “Doryphoros”) of Naples National Archeological Museum applied this most beautiful canon of proportions, known as the “Polikleitos canon”.
During the Renaissance, the nostalgics of the Roman Empire preferred another Greek canon, that of Greek sculptor Lysippus (4th Century BC), formalized by the Roman author, architect and civil engineer, Vitrivius (1st century BC).
Vitruvius only transcribed the prevalent taste of his epoch. Roman sculptors, in order to give an athletic and heroic look to the Emperors which they were portraying, adopting the canon of Lysippus, could reduce the head of their models to only an eight of the total length of the body. The trick was that by reducing the relative size of the head, the body looked more preeminent and powerful, something most emperors, who were often physical failures, appreciated and secured their popularity. Even extreme cases of 12 to 15 heads of body length appeared. In short, Public relations ruled at the detriment of science and truth.
Today’s comic strip drawers chose proportions according to purpose:
–For real life, 7.5 or “normal canon”
–For a movie star, 8 heads, with the “idealistic canon”;
–For a fashion magazine: 8.5 heads;
–For a comic book hero: 9 heads for the “heroic canon”
Vitruvian man
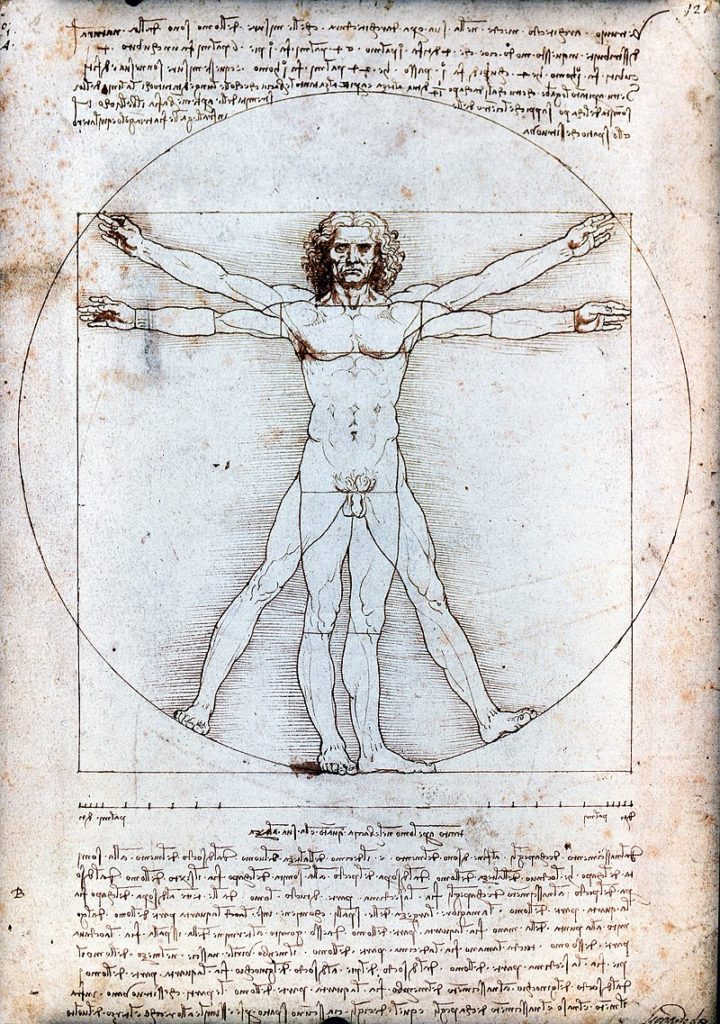
Text accompanying Leonardo DaVinci’s Vitruvian Man:
Vitruvius, the architect, says in his work on architecture that the measurements of the human body are distributed by Nature as follows that is that 4 fingers make 1 palm, and 4 palms make 1 foot, 6 palms make 1 cubit; 4 cubits make a man’s height. And 4 cubits make one pace and 24 palms make a man; and these measures he used in his buildings. If you open your legs so much as to decrease your height 1/14 and spread and raise your arms till your middle fingers touch the level of the top of your head you must know that the centre of the outspread limbs will be in the navel and the space between the legs will be an equilateral triangle.
The length of a man’s outspread arms is equal to his height.
From the roots of the hair to the bottom of the chin is the tenth of a man’s height; from the bottom of the chin to the top of his head is one eighth of his height; from the top of the breast to the top of his head will be one sixth of a man. From the top of the breast to the roots of the hair will be the seventh part of the whole man. From the nipples to the top of the head will be the fourth part of a man. The greatest width of the shoulders contains in itself the fourth part of the man. From the elbow to the tip of the hand will be the fifth part of a man; and from the elbow to the angle of the armpit will be the eighth part of the man. The whole hand will be the tenth part of the man; the beginning of the genitals marks the middle of the man. The foot is the seventh part of the man. From the sole of the foot to below the knee will be the fourth part of the man. From below the knee to the beginning of the genitals will be the fourth part of the man. The distance from the bottom of the chin to the nose and from the roots of the hair to the eyebrows is, in each case the same, and like the ear, a third of the face.
Of course, Da Vinci’s exploration of the Vitruvian man doesn’t mean he approves or disapproves the stated fakery in proportions.
Soul or muscle?
It should be known that in Italy, the pure Roman taste has become trendy again following the discovery in 1506 of the statue of the Laocoon on the site of Nero’s villa in Rome. From that moment, artist will feel obliged to increase the volume of the muscular masses in order to appear as working « in Antique style ».
Although Leonardo never openly criticized this trend, it is hard not to think of Michelangelo’s frescoes in the Sistine Chapel, when the artist, seeking to raise the spirit to unequalled philosophical heights, advised painters: « do not give all the muscles of the figures an exaggerated volume » and « if you act differently, it is more a sort of representation of a sack of nuts that you will have achieved than to that of a human figure » (Codex Madrid II, 128r).
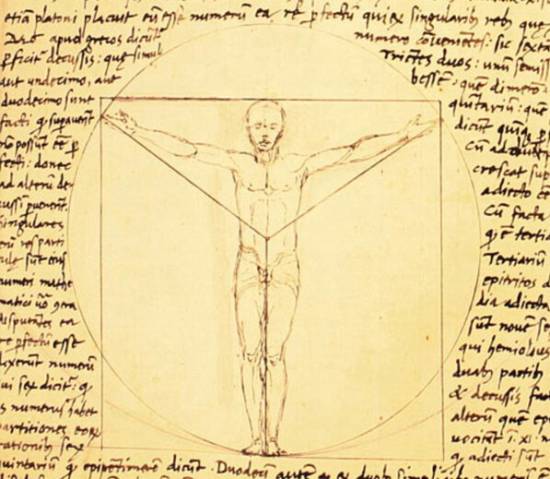

No doubt inspired by his friend, the architect Giacomo Andrea, in « The Vitruvian Man », Leonardo is above all interested by other harmonies: if a person extends his arms in a direction parallel to the ground, one obtains the same length as one’s entire height. This equality is inscribed by Leonardo in a square (symbol of the earthly realm). But if one stretches his arms and legs in a star shape, they are inscribed in a circle whose center is the navel. The location of the navel divides the body according to the golden ratio (in this example 5 heads out of a total of 8 heads, 5+3 being part of the Fibonnacci series: 1+2 = 3; 3+2 = 5; 5+3 = 8; 8+5 = 13; 13+8 = 21, etc.).
Leonardo clearly understood what the golden section really means: not a “magical” number in itself, but the reflexion of the dynamic of least action, the very principle uniting man (the square) with the creator and the universe (the circle).
So if you take a look, beware of what you see and especially what you don’t !