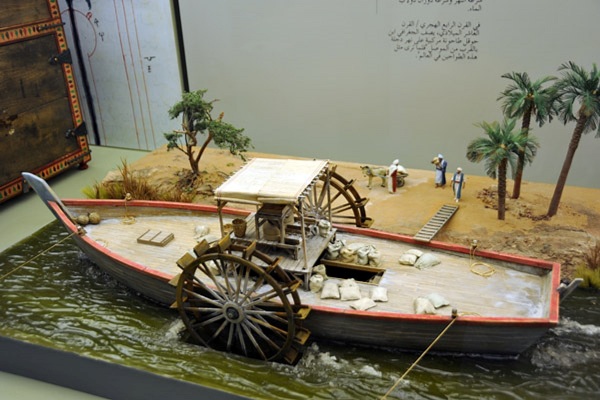
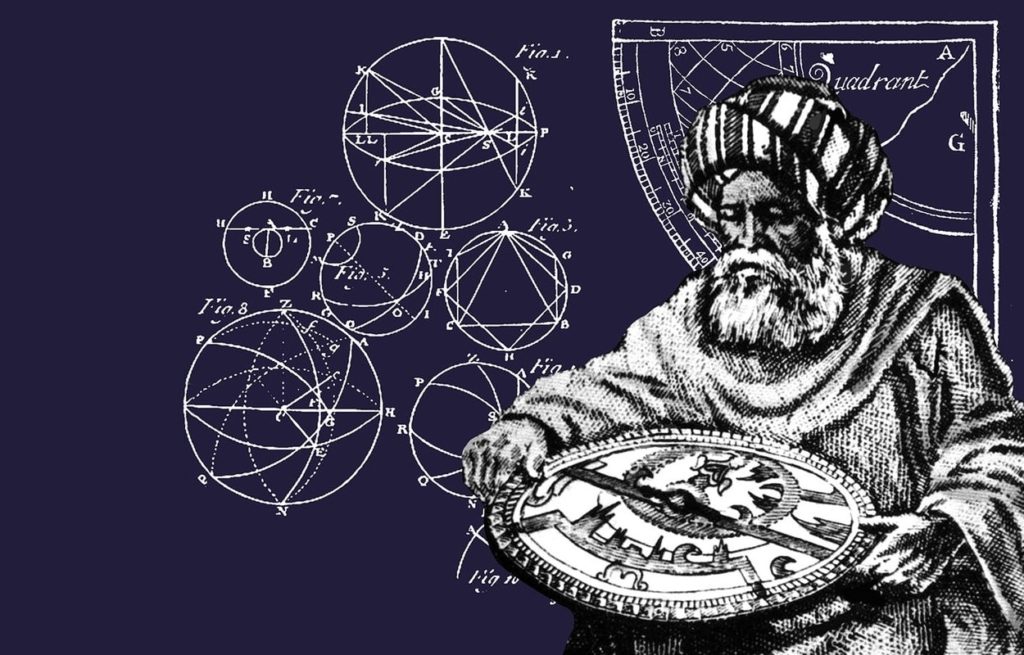
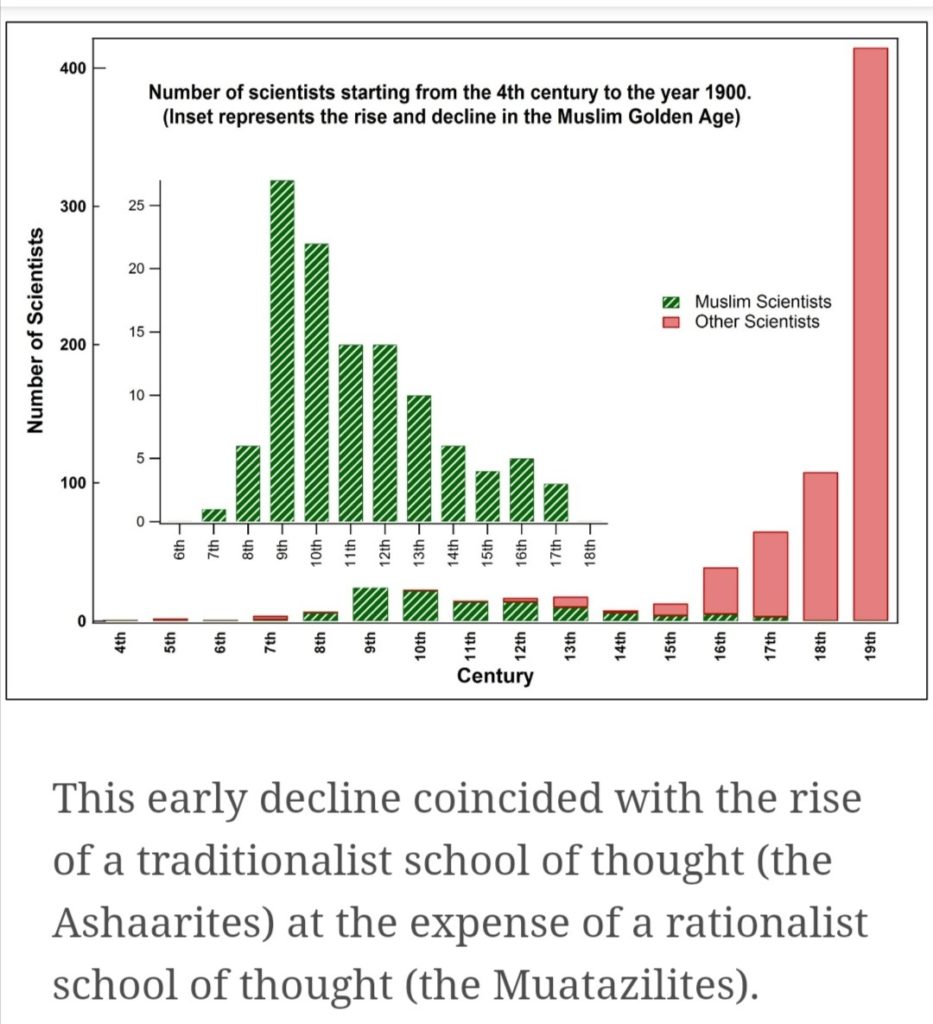
Étiquette : slavery
Shakespeare’s lesson in Economics

Cet article en FR

by Karel Vereycken
As early as 1913, the very year that a handful of major Anglo-American banks set up the Federal Reserve to prevent that any form of national bank in the US fixes the rules for money and credit, Henry Farnam 1 , an economist at Yale University, noted that « if one examines the dramas of Shakespeare, one will notice that quite often in his plays the action turns entirely or partly on economic questions. »
The comedy The Merchant of Venice (circa 1596) is undoubtedly the most striking example. While the plot of the story is generally well known, the deeper meaning of this play, which can be read on different levels, is often overlooked. The sequence of events (the story itself) is one, what they reveal (the principles) is another.
The narrative
To help out his protégé Bassanio and enable him to engage with his beloved Portia, a Catholic Venetian merchant and shipowner named Antonio borrows money from a Jewish moneylender, Shylock.
Shylock hates Antonio, the very archetype of the hypocritical Christian, because the latter treats him with contempt. Antonio, on the other hand, hates Shylock because he is Jewish and because he is a usurer: he lends at interest.
Shakespeare makes us understand that the prosperity of Venice is based on the mutual hatred fueled by the oligarchs between Jews and Christians, according to the famous principle of « Divide and rule. » 2
Double-dealing
The Venetian oligarchy never lacked imagination in circumventing the standards it imposed on its adversaries.
Indeed, among both Jews and Christians, financial usury is condemned and even punished. Interest, which is simply defined as the remuneration of a creditor by his debtor for having lent him capital, is a very ancient concept that probably dates back to the Sumerians and is also found in other ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians or the Romans.
Now, let us recall here that Judaism, which is the first of the Abrahamic religions, clearly prohibits lending at interest. We encounter numerous passages that condemn interest in the Torah, such as the book of Exodus 22:25-27, Leviticus 25:36-37 and Deuteronomy 23:20-21.
However, this prohibition only applies to loans within the Jewish community. In Deuteronomy 23:20-21, it is stated that
« When you lend money, food, or anything else to a fellow countryman, you shall not charge him interest. You may charge interest when you lend to a foreigner, but you shall not lend at interest to your fellow countrymen. »
Initially, the same rule applied among Christians. It was not until the First Council of Nicaea (in 325) that lending at interest was prohibited. At the time, many churches were held by lineages of priests , just as nearby castles were controlled by lineages of lords, the two often being related. While its condemnation had been relatively mild in Christianity before then, interest became a serious sin and was heavily punished from the 1200s onwards.
The exploitation of Jews
Italy has been home to Jews since ancient times. They were dependent on popes, princes, or merchant republics. Rome, Sicily, and the Kingdom of Naples had large communities, and popes sometimes hired Jewish doctors. In the 13th century, some cities granted Jewish bankers, with papal license, a monopoly on pawnbroking.
Venice welcomed Jews but forbade them from practicing any profession other than lending for interest. Initially, the Jews publicly enriched themselves in Venice, drawing the ire of the rest of the population.
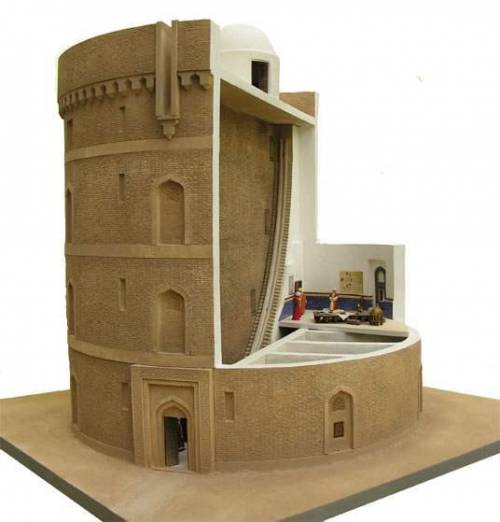
To « protect » the Jews, the Doge of Venice created the first ghetto (a Venetian word), offering, it must be said, the most unsanitary district of the lagoon to these Jews whom he detested while cherishing the financing they provided for Venetian colonial expeditions and the slave trade that « Catholic » Venice practiced without any qualms.
The Merchant of Venice
This is the essence of the Venetian system that Shakespeare unmasks in his comedy The Merchant of Venice . 3
So, when Antonio goes to ask Shylock for a loan of 3000 ducats for a period of three months, he first tells him:
« Shylock, I normally don’t lend or borrow money with interest, but in order to help my needy friend, I’ll break my custom. » 4
Shylock then replies:
« Sir Antonio, many times you have criticized me about my money and habit of charging interest in the Rialto. I have endured it all with patience and a shrug, because we Jews are known for our ability to endure. You say I believe in the wrong religion, call me a cut-throat dog, and spit on my Jewish clothing, all because I use my own money to make profit. And now it appears that you need my help. Okay, then!
You come to me and you say, « Shylock, I need money. » You tell me this! You who spat on my beard and kicked me as you’d kick a stray dog away from your threshold! You ask for money. What should I say to you? Shouldn’t I say, « Does a dog have money? Is it possible for a dog to lend you three thousand ducats? » Or should I get bend to my knees and with bated breath humbly whisper, « Fair sir, you spat on me last Wednesday; you spurned me then; another time you called me a dog—and for all this courtesy you’ve shown me, I will gladly lend you this much money? » 5
To which Antonio retorts:
« I am likely to call you such names again, spit on you again, and spurn you, too. If you decide to lend this money, don’t do it as if we are your friends. After all, when have friends ever charged each other interest? Lend me the money as your enemy and if I break my part of the agreement you can more happily punish me. » 6

Offended, Shylock replies:
« Why, look at your temper! I would be friends with you and have your affection, forget about how you have shamed me, lend you what you need and take no interest—but you won’t listen to me! I’m giving you a kind offer. » 7
Shylock, to escape from the mutual hatred, offers to lend him (according to the Jewish and Christian rule), as a friend, without interest.
But the « good » Catholic Antonio refuses to become friends with the Jew. He asserts that in business, one should not have friends , and demands that he lend to him as an enemy because it is easier to sanction in case of non-compliance with the contract.
As Churchill said, an empire has no friends, only interests. This principle would later be theorized by Nazi crown jurist Carl Schmidt to become the rule of today’s oligarchy: to exist, one needs an enemy, and if you lack one, hurry up to invent one!
The Venitian’s double game
As we can see, Shakespeare points out the hypocrisy of this Venetian system which bases its prosperity on a « win-win » policy, not between friends, but as a cynical game between concurring mafias.
Let us recall here that, although it was regularly at war with the Turks, Venice also created a ghetto for Turkish merchants and even a « Foundation », that is to say a functional trade representation in the city.

If a Venetian ambassador was reproached for this trade with the Ottomans which threatened the West, he would reply: « As merchants, we cannot live without them. »
The Ottomans sold wheat, spices, raw silk, cotton, and ash (essential for glassmaking) to the Venetians, while Venice supplied them with finished products such as soap, paper, textiles, and… weapons. Although this was explicitly forbidden by the Pope, countries as France, England, the Low Countries, but especially Venice, Genoa, and Florence sold firearms and gunpowder to the Levant and the Turks. 8
Venice supplied the Turks with cannons and military engineers with its left hand, while renting ships at high prices to Christians who wanted to fight them with its right hand. Added to this was the rivalry with Genoa, which had allied itself with the Palaeologus dynasty but which the Ottomans defeated in favor of the Venetians.
In 1452, a year before the fall of Constantinople, the Hungarian engineer and founder Urban (or Orban), a specialist in large bombards, entered the service of the Ottomans. These cannons, he entrusted to the Sultan, were so powerful that they would bring down « the walls of Babylon. » We know what happened next in 1453.

When the Franks wanted to hire ships in Venice to go on crusade, they lacked money.
No problem: Venice finds the right arrangement. To pay for the ships’ rental, the Franks are invited to make a small detour along the route and begin the crusade by liberating Constantinople, which Venice wants to retake from the Ottomans. And it works! Venice increases its trading posts and military bases in Constantinople to expand its financial and commercial empire.
A Pound of Flesh
Faced with Antonio’s foolish and arrogant response, Shylock pushes his logic to the point of absurdity and, jokingly, suggests that if his debtor does not repay his debt on time, he would have the right to take a pound of flesh from him.
This can be seen as a literal and wacky interpretation of what was written on the « bonds » or « receipts of debt » of the time. Antonio, who is convinced that his ships will return to Venice in time to provide him with enough to repay Shylock, accepts the terms of the contract, almost laughing at their surreal nature.
This is where Shakespeare poses a fundamental question and offers us a beautiful lesson in economics, in the form of a tragic and paradoxical metaphor. In most ancient civilizations, failure to repay a debt could lead you to slavery, cost you your life, or send you to prison for the rest of your life. From monetary slavery, we thus moved on to physical slavery. 9
Later, for example, we find in the archives of the Antwerp courts the text of a trial in 1567 concerning an obligation between Coenraerd Schetz and Jan Spierinck:
« I, Jan Spierinck, confess and declare with my own hand that I owe the honorable Lord Coenraerdt Schetz the sum of four hundred Flemish pounds, and this on the basis of the equal sum that I have received from him to my satisfaction. I promise to pay in full the said Lord Coenraerdt Schetz or the bearer of this present, on the fourth day of the next month of August without any delay, by pledging myself and all my property now and in the future. In the year 1565, on the 11th of June. »
You read that right: « by pledging myself. » Taken literally, the debtor pledges his person as surety to his creditor. Let us also recall that in France, imprisonment for private debts was instituted by a royal ordinance of Philip the Fair in March 1303. Apart from two periods of abolition, from 1793 to 1797 and in 1848, the imprisonment of debtors persisted in France until its abolition in 1867.
During the Renaissance, the Christian humanism of Petrarch, Erasmus, Rabelais, and Thomas More combined Socrates’ notion of justice with that of love for others, and a new principle emerged: the life of each individual is sacred and has a value immeasurably greater than any financial debt.
It is a questioning of this principle that turns Shakespeare’s comedy into a drama. Little by little, the spectator learns that Antonio’s ships have all been swept away by storms and other misfortunes. He therefore does not have the necessary means to repay his debt in time.
The Merchant of Venice must therefore accept that Shylock takes a pound of flesh from him as stipulated in the debt title he signed… a financial claim duely validated by a notary and the laws of the Venetian Republic.

To save Antonio’s life, his friends then offer the lender double the initial sum borrowed, but Shylock, driven by a sense of revenge, will not listen, angry moreover at the fact that his daughter has left his house with a young Christian merchant, taking with her a tidy sum of ducats and family jewels.
Shylock viciously responds to the Doge’s request to show mercy, saying that he is asking for nothing more… than the application of the law. He also reminds the Venetians that they are in no position to give moral lessons, because in Venice one can « buy » people:
« What judgment shall I dread, doing no wrong? You have among you many a purchased slave, Which—like your asses and your dogs and mules— You use in abject and in slavish parts. Because you bought them. Shall I say to you, “Let them be free! Marry them to your heirs! Why sweat they under burdens? Let their beds Be made as soft as yours and let their palates Be seasoned with such viands”? You will answer, “The slaves are ours.” So do I answer you. The pound of flesh which I demand of him Is dearly bought. ‘Tis mine and I will have it. If you deny me, fie upon your law— There is no force in the decrees of Venice. 105 I stand for judgment. Answer, shall I have it? » 10
To this, the impotent Doge offers no counterargument. He himself must obey the laws of the city. The only thing he has the right to do is to allow a doctor of law who has examined the case to deliver his expert opinion.
Turnaround of the situation
Here Shakespeare introduces Portia, who, disguised as a law doctor and acting in the name of a higher principle, love for humanity and good, will succeed in turning the tide. 11
Having acknowledged the validity of Shylock’s claim, she turns the tables with the kind of audacity we lack today. Regarding the claim, she notes an important detail concerning the implementation of the sanction:
« Hold on a second. There’s something else. This agreement doesn’t give you any drop of blood. The literal words are « a pound of flesh. » So take what is yours, take your pound of flesh, but if in cutting it off you shed one drop of Christian blood, your lands and goods will be confiscated by the state of Venice by the city’s laws. » 12

This is another beautiful lesson Shakespeare teaches us. How many excellent laws are worthless simply because their authors didn’t bother to specify their implementation? Do you know the laws that allow you to defend yourself against the injustices the system inflicts on you? Because if the devil is in the details, the good Lord is sometimes not far away. It’s up to you to go and find him.
Shakespeare reminds us that economics is not limited to law and mathematics. Every economic choice remains a societal choice. In reality, only « political economy » should be taught in our universities and theaters.
Presenting the science of economics and finance as an « objective » reality and not as a reality of human choices is the best proof that we are subject to propaganda.
In conclusion, let us emphasize that unlike Christopher Marlowe‘s play, The Jew of Malta (circa 1589), the main actor in Shakespeare’s play is not the evil Jew Shylock (as claimed by anti-Semites who performed distorted versions of the play during the dark periods of our history), but rather the very Catholic merchant of Venice who, as we have seen, uses the Jews for his own interests. Let us recall that in the Jewish ghetto of Venice, the Jews were only allowed to deal with finance but nothing else…
Finally, in The Merchant of Venice , Shakespeare unmasks the workings of a mad and criminal finance which knows how to use formal interpretations of law (the appearance of justice) to satisfy its greed (true injustice).
NOTES:
- Henry Farnam, Shakespeare as an economist, p. 437, Yale Publishing Association, New Haven; ↩︎
- See Sinan Guven, The Conflict Between Interest and Abrahamic Religions , HEConomist, the student newspaper; ↩︎
- All the following quotes from Shakespeare’s The Merchant of Venice are taken from the website Litcharts; ↩︎
- Act 1, Scene 3; ↩︎
- Act 1, Scene 3; ↩︎
- Act 1, Scene 3; ↩︎
- Act 1, Scene 3; ↩︎
- Salim Aydoz, Artillery Trade of the Ottoman Empire, Muslim Heritage website, Sept. 2006; ↩︎
- A case in point is the history of Haiti. See Invade Haiti, Wall Street urged, New York Times, 2022. ↩︎
- Act 4, Scene 1; ↩︎
- The principle of a « Promethean » woman intervening disguised as a man for the good of humanity will be, with the person of Leonore, at the center of Fidelio, Beethoven’s unique opera; ↩︎
- Act 4, Scene 1; ↩︎
The ancient practice of debt cancellation

This article in RUSSIAN (pdf)
Cet article en FRANCAIS (en ligne)

While anyone with a modicum of rationality knows that a huge proportion of the world’s debts are absolutely unpayable, it’s a fact that today any debt cancellation, however odious or illegitimate, remains taboo.
By Karel Vereycken, December 2020.
Debt repayment is presented by heads of state and government, central banks, the IMF and the mainstream press as imperative, inevitable, indisputable, compulsory. Citizens have elected their governments, so they must resign themselves to paying the debt. For not to pay is more than violating a symbol: it is to exclude oneself from civilization, and to renounce in advance any new credit that is granted only to « good payers ». What counts is not the effectiveness of the act, but the expression of one’s « good faith », i.e. one’s willingness to submit to the strongest. The only possible discussion is how to modulate the distribution of the necessary sacrifices.
It seems that the ultra-liberal, monetarist model that has been surreptitiously imposed on us is that of the Roman Empire: zero debt for states and cities, and no debt forgiveness for citizens!
In his treatise on Duties (De officiis), written in 44-43, Cicero, who had just quelled a revolt by people demanding a debt remission, justifies the radical nature of his policy towards indebtedness:

« What does the establishment of new debt accounts [i.e., remission] mean, if not that you buy land with my money, that you have this land, and that I don’t have my money? That’s why we have to make sure there are no debts, which can harm the state. There are many ways of avoiding it, but if there are debts, not in such a way that the rich lose their property and the debtors acquire the property of others. Indeed, nothing maintains the State more strongly than good faith (fides), which cannot exist if there is no need to pay one’s debts. Never has anyone acted more forcefully to avoid paying their debts than under my Consulate. It was attempted by men of all kinds and ranks, with weapons in hand, and by setting up camps. But I resisted them in such a way that this entire evil was eliminated from the State. »
What has been carefully concealed is that another human practice has also existed: moratoria, partial and even generalized debt cancellations have taken place repeatedly throughout history and were carried out according to different contexts.
Often, proclamations of generalized debt cancellation were the initiative of self-preservation-minded rulers, aware that the only way to avoid complete social breakdown was to declare a « washing of the shelves » – those on which consumer debts were inscribed – cancelling them to start afresh.
The American anthropologist David Graeber, in Debt, the first 5000 years (2011), pointed out that the first word we have for « freedom » in any human language is Sumerian amargi, meaning freed from debt and, by extension, freedom in general, the literal meaning being « return to the mother » insofar as, once debts were cancelled, all debt slaves could return home.
Debt cancellations were sometimes the result of bitter social struggles, wars and crises. What is certain is that debt has never been a detail of history.
David Graeber sums it up:
« For millennia, the struggle between rich and poor has largely taken the form of conflicts between creditors and debtors – disputes over the justice or injustice of interest payments, peonage, amnesty, property seizure, restitution to the creditor, confiscation of sheep, seizure of vineyards and the sale of the debtor’s children as slaves. And over the last 5,000 years, with remarkable regularity, popular insurrections have begun in the same way: with the ritual destruction of debt registers – tablets, papyri, ledgers or other media specific to a particular time and place. (After which, the rebels generally attacked cadastres and tax registers.) »
And as the great ancient scholar Moses Finley was fond of saying,
« All revolutionary movements have had the same program: cancellation of debts and redistribution of land. »
Let us now examine some historical precedents for voluntary debt forgiveness.
Debt cancellation in Mesopotamia
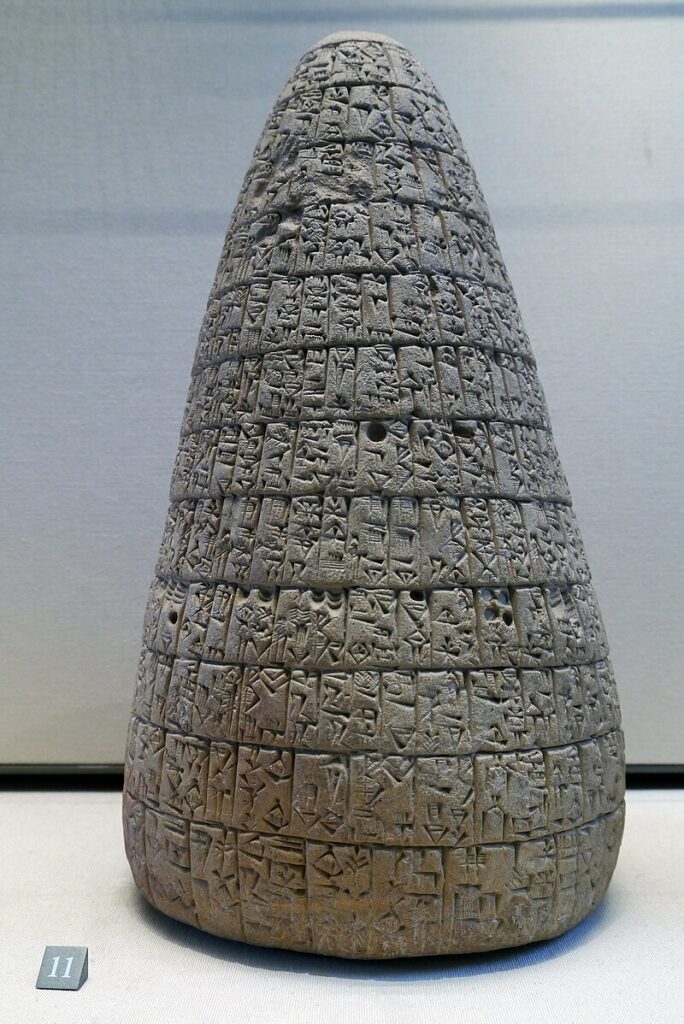

The earliest known debt cancellation was proclaimed in Mesopotemia by Entemena of Lagash c. 2400 BCE.
One of his successors, Urukagina, who was the last ruler of the 1st Dynasty of Lagash, is known for his code of rules that includes debt cancelation.
Urukagina’s code is the first recorded example of government reform, seeking to achieve a higher level of freedom and equality by limiting the power of priesthood and a usurous land-owner oligarchy. Usury and seizure of property for debt payment were outlawed. « The widow and the orphan were no longer at the mercy of the powerful man ».
Similar measures were enacted by later Sumerian, Babylonian and Assyrian rulers of Mesopotamia, where they were known as « freedom decrees » (ama-gi in Sumerian).
This same theme exists in an ancient bilingual Hittite–Hurrian text entitled « The Song of Debt Release ».
The reign of Hammurabi, King of Babylon (located in present-day Iraq), began in 1792 BC and lasted 42 years.
The inscriptions preserved on a 2-meter-high stele in the Louvre are known as the « Hammurabi Code ». It was placed in a public square in Babylon. If it is a long, very severe code of justice, prescribing the application of the law of retaliation (« an eye for an eye, a tooth for a tooth »), its epilogue nevertheless proclaims that « the powerful cannot oppress the weak, justice must protect the widow and the orphan (…) in order to render justice to the oppressed ».

Hammurabi, like the other rulers of the Mesopotamian city-states, repeatedly proclaimed a general cancellation of citizens’ debts to public authorities, their high officials and dignitaries.
Thanks to the deciphering of numerous documents written in cuneiform, historians have found indisputable evidence of four general debt cancellations during Hammurabi’s reign (at the beginning of his reign in 1792, in 1780, in 1771 and in 1762 BC).
Babylonian society was predominantly agricultural. The temple and palace, and the scribes and craftsmen they employed, depended for their sustenance on a vast peasantry from whom land, tools and livestock were rented.
In exchange, each farmer had to offer part of his production as rent. However, when climatic hazards or epidemics made normal production impossible, producers went into debt.
The inability of peasants to repay debts could also lead to their enslavement (family members could also be enslaved for debt).
The Hammurabi Code obviously wanted to change this. Article 48 of the Code of Laws states:
« Whoever owes a loan, and a storm buries the grain, or the harvest fails, or the grain does not grow for lack of water, need not give any grain to the creditor that year, he wipes the tablet of the debt in the water and pays no interest for that year. »
This ideal of justice is notably supported by the terms kittum, « justice as the guarantor of public order », and « justice as the restoration of equity. » It was asserted in particular during the « edicts of grace » (designated by the term mîsharum), a general remission of public and private debts in the kingdom (including the release of people working for another person to repay a debt).
Thus, to preserve the social order, Hammurabi and the ruling power, acting in their own interests and in the interests of society’s future, periodically agreed to cancel all debts and restore the rights of peasants, in order to save the threatened old order in times of crisis, or as a kind of reset at the beginning of a sovereign’s reign.
Proclamations of general debt cancellation are not confined to the reign of Hammurabi; they began long before him and continued afterwards. There is evidence of debt cancellations as far back as 2400 BC, six centuries before Hammurabi’s reign, in the city of Lagash (Sumer); the most recent date back to 1400 BC in Nuzi.
In all, historians have accurately identified some thirty general debt cancellations in Mesopotamia between 2400 and 1400 BC.
These proclamations of debt cancellation were the occasion for great festivities, usually during the annual spring festival. Under the Hammurabi dynasty, the tradition of destroying the tablets on which debts were written was established.
In fact, the public authorities kept precise accounts of debts on tablets kept in the temple. Hammurabi died in 1749 BC after a 42-year reign. His successor, Samsuiluna, cancelled all debts to the state and decreed the destruction of all debt tablets except those relating to commercial debts.
When Ammisaduqa, the last ruler of the Hammurabi dynasty, acceded to the throne in 1646 BC, the general cancellation of debts he proclaimed was very detailed. The aim was clearly to prevent certain creditors from taking advantage of certain families. The annulment decree stipulates that official creditors and tax collectors who have expelled peasants must compensate them and return their property, on pain of execution.
After 1400 BC, no deeds of debt cancellation have been found, as the tradition has been lost. Land was taken over by large private landowners, and debt slavery returned.
In Egypt
In Ancient Egypt interest-bearing debt did not exist for most of its history. When it started spreading in the Late Period, the rulers of Egypt regulated it and a number of debt remissions are known to have occurred during the Ptolemaic era, including the one whose proclamation was inscribed on the Rosetta Stone.
Now on display at the British Museum in London, the « Rosetta Stone » was discovered on July 15, 1799 at el-Rashid (Rosetta) by one of Napoleon’s soldiers during the Egyptian campaign. It contains the same text written in hieroglyphs, demotic (Egyptian cursive script) and Greek, giving Jean-François Champollion (1790-1832) the key to the passage from one language to another.
This was a decree issued by Pharaoh Ptolemy V on March 27, 196 BC, announcing an amnesty for debtors and prisoners. The Greek Ptolemy dynasty that ruled Egypt institutionalized the regular cancellation of debts.
It was perpetuating known practices, since Greek texts mention that Pharaoh Bakenranef, who ruled Lower Egypt from c. 725 to 720 BC, had promulgated a decree abolishing debt slavery and condemning debt imprisonment.

TRANSCRIPTION OF THE PHARAOH’S DECREE
ON THE ROSETTA STONE:
Assembled the Chief Priests and Prophets there and those who enter the inner temple to worship the gods, and the Fanbearers and Sacred Scribes and all the other priests of the temples of the earth who have come to meet the king at Memphis, for the feast of the Assumption of PTOLEMEE, THE LIVING FOREVER, THE BELOVED OF PTAH, THE GOD EPIPHANES EUCHARISTOS, the successor of his father, All assembled in the temple of Memphis on this day when it was declared:
“that King PTOLEMEE, THE LIVING FOREVER, THE BELOVED OF PTAH, THE GOD EPIPHANES EUCHARISTOS, the son of King Ptolemy and Queen Arsinoe, the Philopator Gods, both benefactors of the temple and those who dwell therein, as well as their subjects, being a god from a god and the goddess loves Horus the son of Isis and Osiris who avenged his father Osiris by being favorably disposed towards the gods, delivered to the revenues of the temples silver and corn and undertook much expenditure for the prosperity of Egypt, and the maintenance of the temples, and was generous to all out of his own resources ;
“and exempted them from some of the revenues and taxes levied in Egypt and alleviated others so that his people and all others could be in prosperity during his reign ;
“and that he cleared the debts to the crown for many Egyptians and for the rest of the kingdom; ”
The existence of this decree therefore confirms that the practice had existed for many centuries.
The Greek historian Diodorus Siculus (Ist Century BC) provides the following rationale for abolishing the debt bondage by Pharaoh Bakenranef:
« For it would be absurd… that a soldier, at the moment perhaps when he was setting forth to fight for his fatherland, should be haled to prison by his creditor for an unpaid loan, and that the greed of private citizens should in this way endanger the safety of all »
As one can see here, one of the very pragmatic reasons for debt cancellation was that the Pharaoh wanted to have a peasantry capable of producing enough food and, if need be, able to take part in military campaigns. For both of these reasons, it was important to ensure that peasants were not expelled from their lands under the thumb of creditors.
In another part of the region, the Assyrian emperors of the 1st millennium BC also adopted the tradition of debt cancellation.
In Greece: Solon of Athens

In Greece, the Athenian lawmaker Solon (c. 638 BC–558 BC), in order to rectify the widespread serfdom and slavery that had run rampant by the 6th century BCE, introduced a set of laws nown as the Seisachtheia introducing debt relief.
Before Solon, according to the account of the Constitution of the Athenians attributed to Aristotle, debtors unable to repay their creditors would surrender their land to them, then becoming hektemoroi, i.e. serfs who cultivated what used to be their own land and gave one sixth of produce to their creditors. However, should the debt exceed the perceived value of debtor’s total assets, then the debtor and his family would become the creditor’s slaves as well. The same would result if a man defaulted on a debt whose collateral was the debtor’s personal freedom. The fight for debt relief and the fight to abolish slavery were in practice identical.
Solon’s seisachtheia laws immediately cancelled all outstanding debts, retroactively emancipated all previously enslaved debtors, reinstated all confiscated serf property to the hektemoroi, and forbade the use of personal freedom as collateral in all future debts. The laws instituted a ceiling to maximum property size – regardless of the legality of its acquisition (i.e. by marriage), meant to prevent excessive accumulation of land by powerful families.
In the Torah and Old Testament
Social justice, particularly in the form of forgiving debts that shackle the poor to the rich, is a leitmotif in the history of Judaism. It was practiced in Jerusalem in the 5th century BC.
The writing of the Torah was completed at this time. Deuteronomy, 15 states:

The Year for Canceling Debts
15 At the end of every seven years you must cancel debts.
2 This is how it is to be done: Every creditor shall cancel any loan they have made to a fellow Israelite. They shall not require payment from anyone among their own people, because the Lord’s time for canceling debts has been proclaimed.
3 You may require payment from a foreigner, but you must cancel any debt your fellow Israelite owes you.
4 However, there need be no poor people among you, for in the land the Lord your God is giving you to possess as your inheritance, he will richly bless you,
5 if only you fully obey the Lord your God and are careful to follow all these commands I am giving you today.
6 For the Lord your God will bless you as he has promised, and you will lend to many nations but will borrow from none. You will rule over many nations but none will rule over you.
7 If anyone is poor among your fellow Israelites in any of the towns of the land the Lord your God is giving you, do not be hardhearted or tightfisted toward them.
8 Rather, be openhanded and freely lend them whatever they need.
9 Be careful not to harbor this wicked thought: “The seventh year, the year for canceling debts, is near,” so that you do not show ill will toward the needy among your fellow Israelites and give them nothing. They may then appeal to the Lord against you, and you will be found guilty of sin.
10 Give generously to them and do so without a grudging heart; then because of this the Lord your God will bless you in all your work and in everything you put your hand to.
11 There will always be poor people in the land. Therefore I command you to be openhanded toward your fellow Israelites who are poor and needy in your land.
Thus, the Israelites were obliged to free Hebrew slaves who had sold themselves to them for debt, and to offer them some of the produce of their small livestock, their fields and their wine presses, so that they would not return home empty-handed.
As the law is too rarely applied, Leviticus reaffirms it by modulating it:
The Year of Jubilee
8 “‘Count off seven sabbath years—seven times seven years—so that the seven sabbath years amount to a period of forty-nine years.
9 Then have the trumpet sounded everywhere on the tenth day of the seventh month; on the Day of Atonement sound the trumpet throughout your land.
10 Consecrate the fiftieth year and proclaim liberty throughout the land to all its inhabitants. It shall be a jubilee for you; each of you is to return to your family property and to your own clan.
11 The fiftieth year shall be a jubilee for you; do not sow and do not reap what grows of itself or harvest the untended vines.
12 For it is a jubilee and is to be holy for you; eat only what is taken directly from the fields.
13 “‘In this Year of Jubilee everyone is to return to their own property.
14 “‘If you sell land to any of your own people or buy land from them, do not take advantage of each other.
15 You are to buy from your own people on the basis of the number of years since the Jubilee. And they are to sell to you on the basis of the number of years left for harvesting crops.
16 When the years are many, you are to increase the price, and when the years are few, you are to decrease the price, because what is really being sold to you is the number of crops.
17 Do not take advantage of each other, but fear your God. I am the Lord your God.

Today, some will tell you that under these conditions, a year before the jubilee date, credit would necessarily be scarce and expensive, and that debt would thus find its limit!
This is a mistake, because to ensure that the law is followed, the codes describe in detail how purchases and sales of goods between private individuals must be carried out according to the number of years elapsed since the previous jubilee (i.e., the number of years remaining before the goods must be returned to their previous owner).
Another passage, this time from the prophet Jeremiah, vividly illustrates the scope of the law on the remission of debts.

Faced with the advance of enemy armies towards Jerusalem in 587 B.C., Jeremiah supports, in God’s name, the undertaking of King Zedekiah (then ruler of the Kingdom of Judea), who demands the immediate release of all those enslaved for debt from the powerful forces of his kingdom (Jer. 34:8-17).
Jeremiah forcefully recalls the ancient demand for the freeing of slaves… which the king, in fact, needs to patriotically reunite the social classes before the battle, and give himself sufficient troops free of all servile obligations!

A passage in the Book of (the prophet) Nehemiah (447 BC), the governor of Persian Judea under Artaxerxes I of Persia (465–424 BC), influenced by the ancient Mesopotamian tradition, also proclaims the cancellation of debts owed by indebted Jews to their rich compatriots.
The social situation Nehemiah discovered in Judea was appalling. To remedy the problem, Nehemiah placed the law of debt relief within a religious framework, the Covenant with Yahweh. From then on, it was God himself who commanded the forgiveness of debts and the liberation of slaves and their land, for the land belonged to God alone.
Nehemiah Helps the Poor
« Now the men and their wives raised a great outcry against their fellow Jews.
2 Some were saying, “We and our sons and daughters are numerous; in order for us to eat and stay alive, we must get grain.”
3 Others were saying, “We are mortgaging our fields, our vineyards and our homes to get grain during the famine.”
4 Still others were saying, “We have had to borrow money to pay the king’s tax on our fields and vineyards.
5 Although we are of the same flesh and blood as our fellow Jews and though our children are as good as theirs, yet we have to subject our sons and daughters to slavery. Some of our daughters have already been enslaved, but we are powerless, because our fields and our vineyards belong to others.”
6 When I heard their outcry and these charges, I was very angry.
7 I pondered them in my mind and then accused the nobles and officials. I told them, “You are charging your own people interest!” So I called together a large meeting to deal with them
8 and said: “As far as possible, we have bought back our fellow Jews who were sold to the Gentiles. Now you are selling your own people, only for them to be sold back to us!” They kept quiet, because they could find nothing to say.
9 So I continued, “What you are doing is not right. Shouldn’t you walk in the fear of our God to avoid the reproach of our Gentile enemies?
10 I and my brothers and my men are also lending the people money and grain. But let us stop charging interest!
11 Give back to them immediately their fields, vineyards, olive groves and houses, and also the money you are charging them—one percent of the money, grain, new wine and olive oil.”
12 “We will give it back,” they said. “And we will not demand anything more from them. We will do as you say.”
If we add to these passages the countless verses forbidding the lending of interest to fellow human beings and the taking of property as collateral, we get an idea of what the Israelites in the land of Canaan had put in place to try and maintain a certain social equilibrium.
Alas, in the first century AD, debt forgiveness and the freeing of slaves from debt were swept away from all Near Eastern cultures, including Judea.
The social situation there had deteriorated to such an extent that Rabbi Hillel was able to issue a decree requiring debtors to sign away their right to debt forgiveness.
In the Bible and New Testament
What happened to debt forgiveness in the New Testament?
While the Acts of the Apostles and the writings of the Fathers of the Church sometimes express a great docility, Jesus’ position on the forgiveness of debts, as reported repeatedly and most forcefully in Luke’s Gospel, chapter 4:16-21, appears to be marked by a revolutionary prophetic breath.
Luke places the passage at the beginning of Jesus’ public life. He makes it a key to everything that follows.
16 Jesus went to Nazareth, where he had been brought up, and on the Sabbath day he went into the synagogue, as was his custom. He stood up to read,
17 and the scroll of the prophet Isaiah was handed to him. Unrolling it, he found the place where it is written:
18 “The Spirit of the Lord is on me,
because he has anointed me
to proclaim good news to the poor.
He has sent me to proclaim freedom for the prisoners
and recovery of sight for the blind,
to set the oppressed free,
19 to proclaim the year of the Lord’s favor.”
20 Then he rolled up the scroll, gave it back to the attendant and sat down. The eyes of everyone in the synagogue were fastened on him.
21 He began by saying to them, “Today this scripture is fulfilled in your hearing.”

Let’s not forget that the « year of the Lord’s favor (Jubilee Year) » to which he called, demanded at once rest for the land, forgiveness of debts and the liberation of slaves.
In the midst of the slave-owning Roman Empire, which fiercely rejected the concept of debt forgiveness, Jesus’ declaration could only be seen as a declaration of war on the ruling system.
Before he was arrested, Jesus made a highly symbolic material gesture: he forcefully overturned the tables of the money-changers in the Jerusalem temple. For the Jewish high priests and the Roman authorities, this was too much.
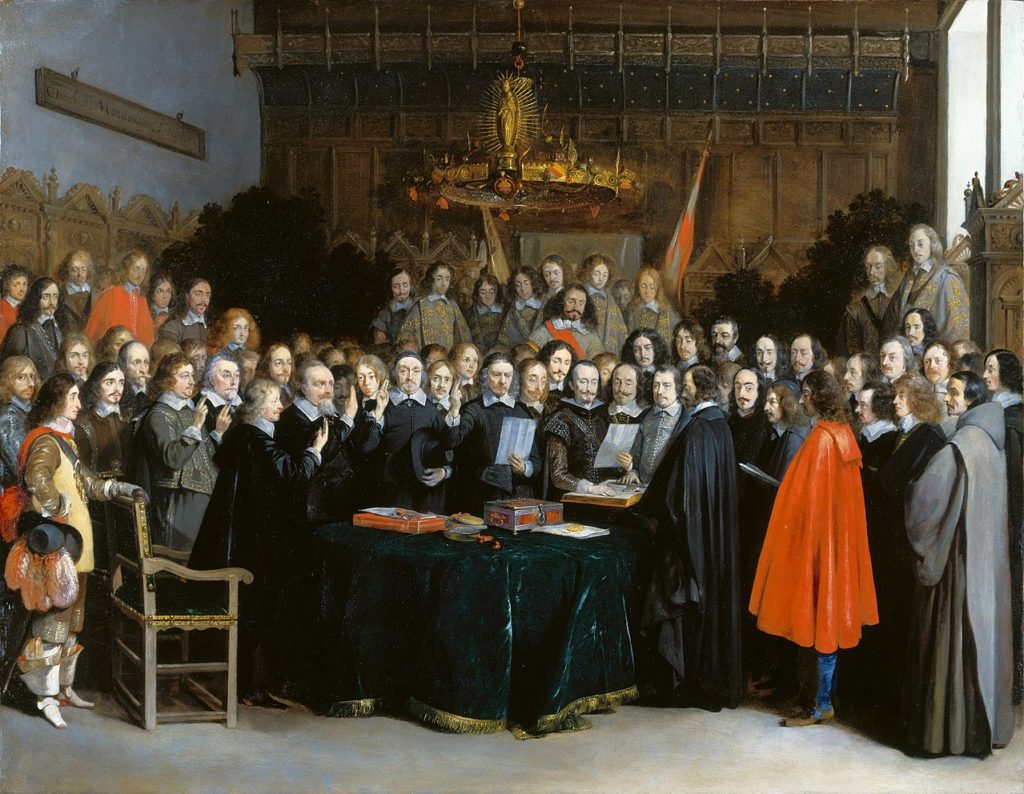
Peace of Westphalia of 1648
In 1648, after five years of negotiations, led by the French diplomat Abel Servien on the instructions of Cardinal Mazarin, the “Peace of Westphalia” was signed, putting an end to the Thirty Years’ War (1618-1648).
Long before the UN Charter, 1648 made national sovereignty, mutual respect and the principle of non-interference the foundations of international law.
But there was more. As we have documented, the peace deal also included the cancelation of debts that had become the very reason for continuing the war.
Unpayable, unsustainable and illegitimate debts, interests, bonds, annuities and financial claims, explicitly identified as fueling a dynamic of perpetual war, were examined, sorted out and reorganized, most often through the cancellation of debts (articles 13 and 35, 37, 38 and 39), through moratoria or debt rescheduling according to specific timetables (article 69).
Article 40 concludes that debt cancellations will apply in most cases, “and yet the Sums of Money, which during the War have been exacted bona fide, and with a good intent, by way of Contributions, to prevent greater Evils by the Contributors, are not comprehended herein. » (Implying that these debts would have to be honored.)
Finally, looking to the future, for Commerce to be “reestablished”, the treaty abolished many tolls and customs established by “private” authorities for they were obstacles to the exchange of physical goods and know-how and hence to mutual development. (Art. 69 and 70).
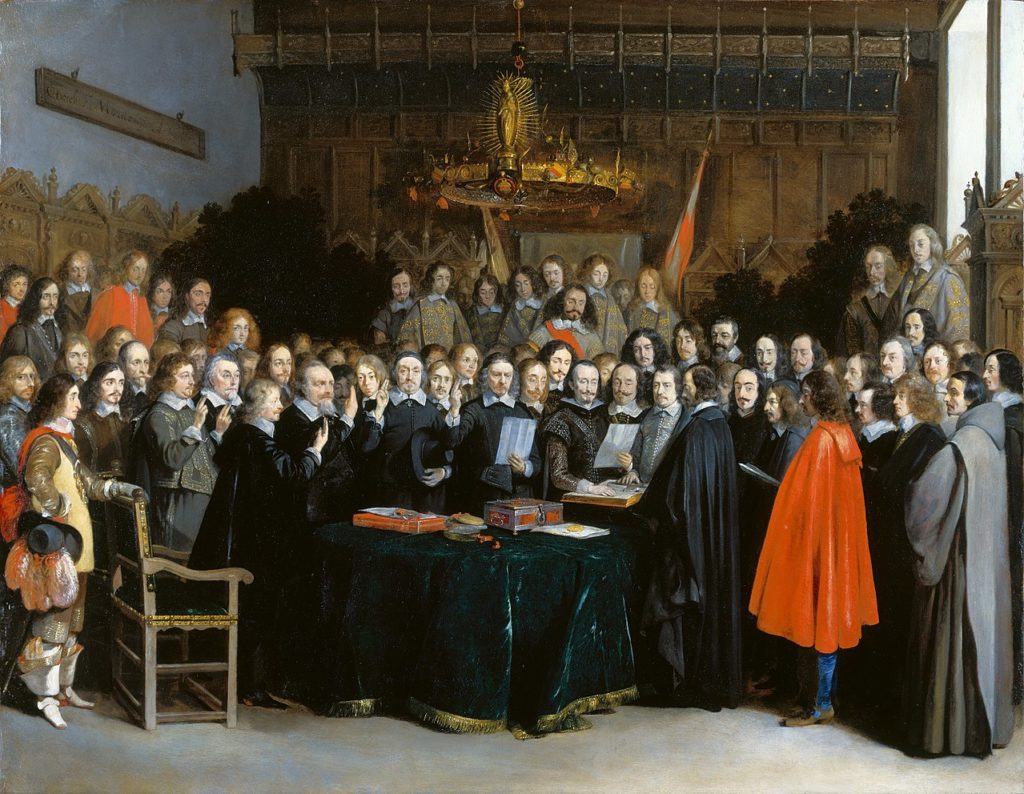

TREATY OF WESTPHALIA (1648)
Art. 13:
“Reciprocally, the Elector of Bavaria renounces entirely for himself and his Heirs and Successors the Debt of Thirteen Millions, as also all his Pretensions in Upper Austria; and shall deliver to his Imperial Majesty immediately after the Publication of the Peace, all Acts and Arrests obtain’d for that end, in order to be made void and null.”
Art. 35:
“That the Annual Pension of the Lower Marquisate, payable to the Upper Marquisate, according to former Custom, shall by virtue of the present Treaty be entirely taken away and annihilated; and that for the future nothing shall be pretended or demanded on that account, either for the time past or to come.”
In the United States
It is poorly known that in the United States, on three separate occasions, governments have successfully repudiated public debts owed to private bankers?
First, in the 1830s, four States repudiated their debts – Mississippi, Arkansas, Florida and Michigan. The creditors were mainly British.
The Russian born Alexander Nahum Sack (1890-1955), a professor of Russian law specialized in international financial legislation, wrote in this regard: “One of the main reasons justifying these repudiations was the squandering of the sums borrowed: they were usually borrowed to establish banks or build railways; but the banks failed and the railway lines were never built. These questionable operations were often the result of agreements between crooked members of the government and dishonest creditors.” (Les effets des transformations des États sur leurs dettes publiques et autres obligations financières : traité juridique et financier, Recueil Sirey, Paris, 1927, p. 158).
Second, and more importantly, following the American Civil War (1861-1865), the US Federal government summoned the Confederate States to repudiate the debts they had contracted in order to carry on the war.
In an article titled « The Rebel Debt », the New York Times, on Nov. 9, 1865, wrote the following:
« The debts of the Confederate Government, contracted for the purposes of war, and for all other purposes, were swept away when the Confederacy fell. All its currency, bills, bonds, treasury notes, and « promises to pay » of every kind, became worthless to the holders, even though those holders had given for them real property or services of a positive value. After the fall of Richmond, hundred-dollar bills, based on the faith and credit of the Confederacy, were sold for a nickel cent a piece, and thousand-dollar notes were exchanged evenly for three-cent shinplasters. There is little if any talk in any part of the South about assuming any part of this debt. Its magnitude is appalling, and the States of the South did not become responsible for it in their individual capacity. On its face it was declared to be payable upon the establishment of the independence of the Southern Confederacy — thus linking its fortunes with that of the rebel government; and it was but logical that the Confederacy’s credit should cease to have a value when the Confederacy itself ceased to have an existence. »
The creditors had purchased securities issued by European bankers on behalf of the Confederate States, mainly in London and Paris. Among the creditors was the German Banque Erlanger of Paris and its London subsidiary. The risk was remunerated by an interest rate of 7% per annum, relatively high for the period.
The Civil War debt held by individual Confederate states (South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas) at the end of the war has been estimated at close to $67 million. Even larger, the debt of the Confederate States of America, which was reported to be $1.4 billion on October 1, 1864. And, if one adds in compensation for freed slaves (which was a rumored demand of Southerners), valued at $1.75 billion in 1860, the total bill the South might have presented to the North amounted to $3.2 billion.

And the The New York Times continued:
« But there has appeared in many of the States, and still appears in some of them, a strong party desirous of assuming the payment of the debts contracted by the various States individually, in aid of rebellion, and while members of the Confederacy.
« It is the repudiation of these which has been effected in Mississippi, Alabama, North Carolina, and, as appears by this morning’s telegrams, also in Georgia, at the suggestion of the President; and it is the failure to repudiate this debt by South Carolina, which has disappointed the intelligent supporters of the President’s policy of reconstruction. This debt has been the subject of earnest debate in the Georgia State Convention now in session at Milledgeville; and it was in reference to this debate that the President (Andrew Johnson, who became president after Lincoln’s assassination in April 1865) sent a dispatch to the Provisional Governor of Georgia, in which was pointedly and vigorously set forth the course that ought to be followed by the convention.
« He remarked: ‘The people of Georgia should not hesitate one single moment in repudiating every single dollar of debt created for the purpose of aiding the rebellion against the Government of the United States. It will not do to levy and collect taxes from a State and people that are loyal and in the Union to pay a debt that was created to aid in taking them out and subverting the Constitution of the United States. I do not believe the great mass of the people of the State of Georgia, when left uninfluenced, will ever submit to the payment of a debt which was the main cause of bringing on their past and present suffering, the result of the rebellion. Those who invested their capital in the creation of this debt must meet their fate, and take it as one of the inevitable results of the rebellion, though it may seem hard to them. It should at once be made known, at home and abroad, that no debt contracted for the purpose of dissolving the Union can or ever will be paid by taxes levied on the people for such purpose.’
« There was nothing in the Constitution preventing the United States from repudiating its own debt. Numerous individual states had done this in the past. In the 1840s, and within the memory of many, a number of states had defaulted on or totally repudiated their debts because of the stresses brought on by the panic of 1837. Now, twenty years later, after a civil war, why should not the United States follow their example and wipe the slate clean?«
In 1868, following the Civil War, Congress submitted to the states three amendments as part of its Reconstruction program to guarantee equal civil and legal rights to Black citizens.
The Fourteenth Amendment to the US Constitution, among its provisions, grants citizenship to “All persons born or naturalized in the United States,” thereby granting citizenship to formerly enslaved people.
And relevant for our discussion, section four of the 14th amendment stipulates that while the debt of the Union are considered legitimate and should be honored, those of the Confederacy are what one could call an « odious debt » and shouldn’t be paid.
“The validity of the public debt of the United States, authorized by law, including debts incurred for payment of pensions and bounties for services in suppressing insurrection or rebellion [by the Union], shall not be questioned. But neither the United States nor any State shall assume or pay any debt or obligation incurred in aid of insurrection or rebellion against the United States, or any claim for the loss or emancipation of any slave; but all such debts, obligations and claims shall be held illegal and void.«
As a result, the bondholders of Confederate debt were never repaid due to the repudiation decreed by the Federal government and the application of Section 4 of the 14th Amendment to the Constitution, since loans had served to finance the rebellion of the Southern States. It was the purpose of the loans, and above all the fact that they had been contracted by rebel forces, that was cited as justification. The reality was that imposing debt repayment would prevent any successful reconstruction policy, considered far more important.
Finally, a third wave of repudiations took place in the USA after 1877, when eight Southern States (Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, North Carolina, South Carolina and Tennessee) repudiated their debts on the grounds that the bonds issued during the period between the end of the American Civil War and 1877 had been used for illicit loans to corrupt politicians (including former slaves) who were supported by the Northern States. This repudiation was decided by (racist) government officials (often members of the Democrat party) who had returned to power in the South after the withdrawal of the federal troops who occupied the South until 1877.
During the Cold War
In the United States, Eisenhower was elected in November 1952.
His Secretary of State, John Foster Dulles, otherwise an evil man, noted that, despite the Marshall Plan, Europe, still burdened by a mountain of debt dating from before the First World War and the Treaty of Versailles, was unable to regain momentum.
So much so that it is in danger of turning to the USSR!
Action was called for. In 1953, under the leadership of German banker Hermann Abs, a former Deutsche Bank executive, a major conference was organized in London.
It was decided to write off 66% of Germany’s 30 billion marks in debt.
It was wisely agreed that annual repayments of German debt should never exceed 5% of export earnings. Those wishing to have their debts repaid by Germany should instead buy its exports, enabling it to honor its debts.
In other words, nothing like the madness recently imposed on Greece to « save » the euro!
Although this was done in the name of geopolitical principles, i.e. « in favor of some » but « against others », once again, it was in the name of a better future, i.e. a Europe capable of being the showcase of capitalism in the face of Moscow, that we were able to shed the weight of the past.
« Mutual tuition »: historical curiosity or promise of a better future?


By Karel Vereycken, July 2023, PARIS.
1. Introduction
2. Learning and teaching at the same time, a precious joy
3. Precedents:
A. In India
B. In France
4. Gaspard Monge’s brigades
5. Andrew Bell
6. Joseph Lancaster
7. Mutual Tuition, how it works
A. The class room
B. Teachers and monitors
C. A day at a mutual school
D. Progress according to each pupil’s knowledge
E. Tools
F. Command
8. Bellists vs. Lancasterians
9. France adopting Mutual Tuition
10. Lazare Carnot takes the helm
11. Mutual tuition and choral music
12. The rue Saint-Jean-de-Beauvais pilot project
13. Jomard, Choron, Francœur and elementary knowledge
14. Going Nationwide
15. Critique
16. Mechanistic drift?
17. Death of mutual tuition in France
18. Conclusion
19. Short list of books and texts consulted
« Answer, my friends: it must be sweet for you
To have as your only mentors children like yourselves;
Their age, their mood, their pleasures are your own;
And these victors of one day, tomorrow vanquished by others,
Are, in turn, adorned with modest ribbons,
Your equals in your games, your masters on the benches.
Mute, eyes fixed on your happy emulators,
You are not distracted by the fear of ferulas;
Never an avenging whip, frightening your spirits,
Makes you forget what they taught you;
I listen badly to a fool who wants me to fear him,
And I know much better what a friend teaches me. »
Victor Hugo, Discours sur les avantages de l’Enseignement mutuel, 1817.
1. Introduction
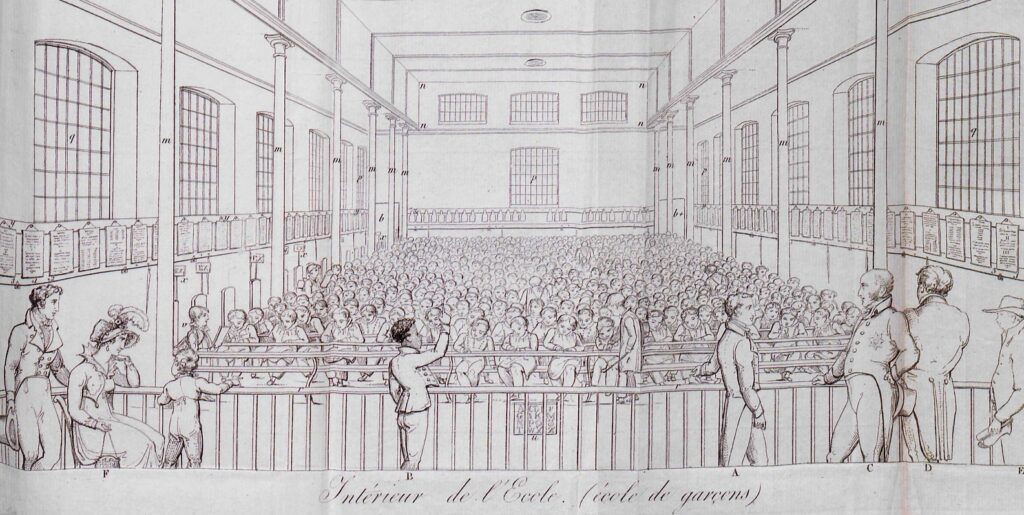

Teaching reading and writing to 1,000 children in the same room, without a teacher, without school books, without paper and ink, is clearly impossible. And yet, it has been imagined and put into practice with great success!
Shh! we mustn’t talk about it, because it could give some people ideas, and not just in emerging countries!
That such a challenge could be taken up could only worry the oligarchy and its servants, who since the dawn of time have been mandated to train an « elite » (the high priests of knowledge, « experts » and other know-it-alls) who reproduce in a vacuum at the top, while ensuring that the great mass of people below are educated just enough to be able to deliver parcels, pay their taxes, abide by the rules defined by the top, and above all, not make (too) much of a mess.
And yet, as Hippolyte Carnot, Minister of Public Instruction in the Second Republic, understood long before us, without a republican education – in other words, without genuine citizen training from kindergarten onwards – universal suffrage often becomes a tragic farce capable of producing monsters.
In the early 19th century, « mutual tuition », (sometimes referred to as the English Monitorial System, also known as Madras System or Lancasterian System), spread like wildfire across Europe and then the rest of the world including the United States of America.
If the teacher addresses a single pupil, it’s the individual mode (as in the case of the preceptor); if he addresses an entire class, it’s the simultaneous mode; if he instructs some children to teach others, it’s the mutual mode. The combination of simultaneous and mutual modes is called mixed mode.
Mutual tuition quickly fell victim to personal quarrels and ideological, political and religious issues. In France, it was seen as an aggression by religious congregations who practiced « simultaneous teaching », codified as early as 1684 by Jean-Baptiste de La Salle : classes by age, division by level, fixed and individual places, strict discipline, repetitive and simultaneous work supervised by an inflexible master.
With the formation of small groups where pupils teach each other and move around the classroom, mutual teaching immediately gave rise, rather foolishly, to the fear of an ass-over-head world straight out of a Hieronymus Bosch painting. What kind of world are we in if the pupil teaches the teacher? the child the parent? the faithful the priest? the citizen the government ! Without a clear leader, aren’t we lost ?
In 1824, Pope Leo XII (not to be confused with the benevolent Leo XIII), the « Pope of the Holy Alliance », a fierce supporter of order and suspect of a vast Protestant plot against the Vatican, forbade such teaching, believing it to « weaken the authority » of both teachers and political and religious authorities.
In France, where in the years following the 1830 revolution over 2,000 mutual schools existed, mainly in towns, in competition with denominational schools, François Guizot, Louis-Philippe’s minister and initially a promoter of broad public education, had them closed down.
2. Learning and teaching at the same time,
a precious joy

Today, « tutoring » is enjoying a revival in the context of school and vocational training. It is a process of « assistance by more experienced subjects to less experienced subjects, likely to enrich the latter’s acquisitions ».
Tutoring between children, in particular between children of different ages, is encouraged from nursery school right through to university, with the institutionalization of methodological tutoring at undergraduate level. Since the 1980s, elementary and secondary schools in France and abroad have seen the development of numerous tutoring experiments.
In reality, tutoring is no more than the pale heir to the mutual tuition system developed in England and then France in the 19th century.
Hence, the future of humanity depends on an exclusively human faculty: the discovery of new universal physical principles, often totally beyond the limits of our sensory apparatus, enabling Man to increase his capacity to transform the universe to qualitatively improve his lot and that of his environment. A discovery is never the result of the sum or average of opinions, but of an individual, perfectly sovereign act. Are we able to organize our society so that this « sacred » creative principle is cherished, respected and cultivated in any newborn child?
Because, without the socialization of this discovery, it will be useless. The history of mankind is therefore, by its very nature, the history of « mutual tuition ».

Is not the greatest pleasure of those who have just made a discovery – and this is natural for children – to share, with a view to a shared future, not only what he or she has just discovered, but the joy and beauty that every scientific breakthrough represents? And when those who discover teach and those that teach, discover, the pleasure is immense. So let’s give our professional teachers the time they need to make discoveries, for the quality of their teaching will be enhanced!
Precedents:
A. In India
In 1623, the Italian explorer Pietro Della Valle (1586-1652), after a trip to « Industan » (India), in a letter dispatched from Ikkeri (a town in south-west India), reports having seen boys teaching each other how to read and write using singing :

« In order to inculcate it perfectly in their memory, to repeat the previous lessons that had been prescribed to them, lest they forget them, one of them would sing in a certain musical tone a line from the lesson, such as two and two make four. After all, it’s easy to learn a song.
« While he sang this part of the lesson to learn it better, he wrote it down at the same time, not with a pen, nor on paper. But to spare him and not spoil it unnecessarily, they marked the characters with their fingers on the same floor where they were sitting in a circle, which they had covered for this purpose with very loose sand. After the first of these children had written in this way while singing, the others sang and wrote the same thing all together
« (…) When I asked them who (…) corrected them when they missed, given that they were all schoolboys, they answered me very reasonably, that it was impossible that a single difficulty should stop them all, four at the same time, without being able to overcome it and that for the subject they always practiced together so that if one missed, the others would be his teachers.«
In Della Valla‘s report, we can already identify some of the basic principles of mutual tuition, notably the simultaneous learning of reading and writing, the use of sand for writing exercises to avoid wasting paper, which is scarce and very expensive, a group lesson given by a teacher, followed by work in sub-groups in which pupils learn to self-regulate, and finally, an integration of knowledge which, thanks to the use of song, will facilitate memorization.
B. In France

In Lyon, the priest Charles Démia, was one of the precursors of mutual tuition, which he put into practice in the « petites écoles » for poor children he founded and theorized as early as 1688. According to the Nouveau dictionnaire de pédagogie et de l’instruction primaire:
« Démia introduced what later came to be known as mutual tuition into the classroom: he recommended that a certain number of officers be chosen from among the most capable and studious pupils, some of whom, under the name of intendants and decurions, would be responsible for supervision, while the others would have to have the master’s lessons repeated, correct pupils when they made mistakes, guide the hesitant hand of ‘young writers’, etc. » In order to make simultaneous teaching possible, Démia’s idea of ‘mutual teaching’ was based on the principle of ‘teaching to one another’. To make simultaneous teaching possible, the author of the regulations divides the school into eight classes, to be taught in turn by the master; each of these classes can be subdivided into bands ».
In Paris, as early as 1747, mutual education was practiced with great success in a school of over 300 pupils, established by M. Herbault, at the Hospice de la Pitié, in favor of the children of the poor. Unfortunately, the experiment did not survive its founder.
In 1772, the ingenious charity of Chevalier Paulet conceived and carried out the project of applying a similar method to the education of a large number of children, left without support in society by the death of their parents.
4. Gaspard Monge’s « brigades »

Finally, as recounted in his biography of Gaspard Monge by his most brilliant pupil, the astronomer François Arago (1786-1853), himself a close friend of Alexander von Humboldt, it was at the École Polytechnique that Monge perfected his own system of mutual tuition and tutoring.
Finding it unacceptable to have to wait three years for the first engineers to graduate from the Ecole Polytechnique, Monge decided to speed up student training by organizing « revolutionary courses », an accelerated training program lasting three months for those in charge of teaching to the others. To achieve this, he perfected the concept of « chefs de brigades », a technique he had already successfully tested at the Mézières engineering school.


François Arago:
« The brigade leaders, always working with small groups of students in separate rooms, were to have the extremely important task of ironing out difficulties as they arose. Never had a more skilful combination been devised to remove any excuse for mediocrity or laziness.
« This creation belonged to Monge. At Mézières, where the engineering students were divided into two groups of ten, and where, in fact, our colleague acted for some time as permanent brigade leader for both divisions, the presence in the classrooms of a person who was always in a position to overcome objections had produced results that were too fortunate for this former repetiteur, in drafting the developments attached to Fourcroy’s report, not to try to endow the new school with the same advantages.
« Monge did more; he wanted the 23 sections of 16 students each, of which the three divisions were to be composed, to have their brigade leader, as in ordinary times, following the revolutionary lessons, and at the opening of the courses of the three degrees. In a word, he wanted the School, at its beginning, to function as if it had already been in existence for three years.
« Here’s how our colleague achieved this seemingly unattainable goal. It was decided that 25 students, chosen by competitive examination from among the 50 candidates who had received the best marks from the admission examiners, would become brigade leaders of three divisions of the school, after receiving special instruction separately. In the mornings, the 50 young people, like all their classmates, attended revolutionary classes; in the evenings, they were brought together at the Hôtel Pommeuse, near the Palais-Bourbon, and various teachers prepared them for the functions they were destined to perform. Monge presided over this scientific initiation with infinite kindness, ardor and zeal. The memory of his lessons remains indelible in the minds of all those who benefited from them.
Arago then quotes Edme Augustin Sylvain Brissot (1786-1819), son of the famous abolitionist, , one of the 50 students, who reported : « It was there that we began to get to know Monge, this man so kind to youth, so devoted to the propagation of science. Almost always in our midst, he followed lessons in geometry, analysis and physics with private discussions where we found even more to gain. He became a friend to each and every one of the students at the Ecole provisoire, joining in the efforts he was constantly provoking, and applauding, with all the vivacity of his character, the successes of our young minds ».
While mutual teaching is fully practiced, the total dedication of a master as devoted as Monge completes what otherwise becomes nothing more than a « system ».
5. Andrew Bell

It was a Scotsman, the Anglican clergyman Andrew Bell (1753-1832), who claimed the paternity of mutual tuition, which he theorized and practiced in India, at the head of the Egmore Military Asylum for Orphans (Eastern India), an institution created in 1789 to educate and instruct the orphans and destitute sons of the European officers and soldiers of the Madras army.
After 7 years there, Bell returned to London and, in 1797, wrote a report to the East India Company (his employer in Madras) on the incredible benefits of his invention.
Russian physician, naturalist and inventor Iosif Khristianovich (Joseph) Hamel (1788-1862), a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, was commissioned by Alexander I, Emperor of Russia, to write a full report on this new type of education, which was then being discussed throughout Europe.

In Der Gegenseitige Unterricht (1818), he reports what Bell wrote in one of his writings: « It happened at this time, that one morning as I was taking my usual walk, I passed a school of young Malabar children, and saw them busy writing on the ground. The idea immediately occurred to me that perhaps the children at my school could be taught the letters of the alphabet by tracing on the sand. I immediately went home and ordered the teacher of the last class to carry out what I had just arranged. Fortunately, the order was very poorly received; for if the master had complied to my satisfaction, it is possible that all further development would have been stopped, and with it the very principle of mutual education… »
Mutual education was coldly received in England, but eventually won over Samuel Nichols, one of the school leaders at St. Botolph’s Aldgate, London’s oldest Anglican Protestant parish. Bell’s precepts were implemented with great success, and his method was taken up by Dr. Briggs when he opened an industrial school in Liverpool.



6. Joseph Lancaster

In England, it was Joseph Lancaster (1778-1838), a twenty-year-old London schoolteacher, who seized upon the new way of teaching, perfected it and generalized it on a large scale. (See text of his 1810 booklet)
In 1798, he opened an elementary school for poor children in Borough Road, one of London’s poorest suburbs. Education was not yet totally free, but it was 40% cheaper than other schools in the capital. Lacking money, Lancaster did everything in his power to drive down the costs of what was becoming a veritable « system »: use of sand and slate instead of ink and paper (Erasmus of Rotterdam reported in 1528 that in his day, people wrote with a kind of awl on tables covered in fine dust); boards reproducing the pages of school books hung on the walls to avoid having to buy books; auxiliary teachers replaced by pupils to avoid paying salaries; increase in the number of pupils per class.

By 1804, his school had 700 pupils, and twelve months later, a thousand. Lancaster, getting deeper and deeper into debt, opened a school for 200 girls. To escape his creditors, Lancaster left London in 1806, and on his return was jailed for debt. Two of his friends, dentist Joseph Foxe and straw hat maker William Corston, repaid his debt and founded with him « The Society for the Promotion of the Lancasterian System for the Education of the Poor ».
Other Quakers stepped in with support, notably abolitionist William Wilberforce (1759-1833), whom the french sculptor David d’Angers depicted alongside Condorcet and Abbé Grégoire on his famous monument commemorating Gutenberg in Strasbourg.
From there, as Joseph Hamel recounts in his 1818 report, the new approach spread to the four corners of the world: England, Scotland, France, Prussia, Russia, Italy, Spain, Denmark, Sweden, Poland and Switzerland, not forgetting Senegal and several South American nations such as Brazil and Argentina and of course, the United States of America. Mutual Tuition was adopted as the official pedagogy in New York City (1805), Albany (1810), Georgetown (1811), Washington D.C. (1812), Philadelphia (1817), Boston (1824) and Baltimore (1829), and the Pennsylvania legislature considered statewide adoption.

7. Mutual tuition, how does that works ?
The fundamental principle of « mutual tuition », particularly relevant to elementary school, is reciprocity of instruction between pupils, with the more able serving as teacher to the less able. From the outset, everyone progresses gradually, regardless of the number of pupils.
Bell and Lancaster, and their French disciples, postulated: the diversity of faculties, the inequality of progress, the rhythms of comprehension and acquisition. This led them to divide the school into different classes according to subjects and children’s level of knowledge, with age playing no part in this classification. Schoolchildren thus brought together take part in the same exercises. Their study program is identical in content and methods.
If the number of pupils in a division is too high in a particular subject – reading or arithmetic, for example – sub-groups are formed, which progress in parallel, while the teaching methods and materials remain identical.
So what does a school under the new system look like?
A. The classroom
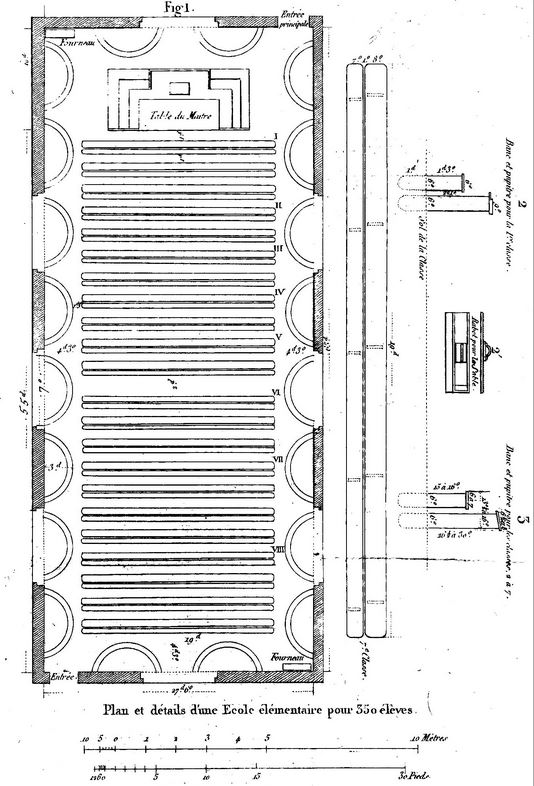
Whatever the number of pupils – around a 100 in French villages, close to a 1000 in the Lancaster school in London, 200 in Parisian schools – they are grouped together in one single rectangular room with no partitions.
Jomard, who was extraordinarily active and prolific in the early years of the mutual education system, set desirable standards for class sizes ranging from 70 to 1,000 pupils.
For 350 pupils, for example, he indicated the need for a room 18 m long by 9 m wide (graphic).
In England and the French countryside, a barn was often used for the new school. In France, a large number of religious buildings have been disused since the revolutionary period, and meet the required standards perfectly. Many mutual schools were built in these buildings.
B. « Masters » and « monitors »

The mutual method divided responsibility for teaching between the « master » and students designated as « monitors », considered « the linchpin of the method ».
As Bally reminded us as early as 1819: « The basis of mutual teaching rests on the instruction communicated by the strongest pupils to those who are weaker. This principle, which is the merit of this method, required a very special organization to create a reasonable hierarchy, which could contribute in the most effective way to the success of all. »
Each day, in a dedicated « classroom » reserved for instructors, the master imparts knowledge and provides his assistants with technical advice on the proper application of the method. During the course of the day, he remains in charge of the 8th class, and as such is responsible for conducting their exercises. He conducts periodic, monthly or occasional examinations in the classes, and may decide to change classes. Finally, it is he who, at the final stage, distributes punishments and rewards.
C. A day at a mutual school
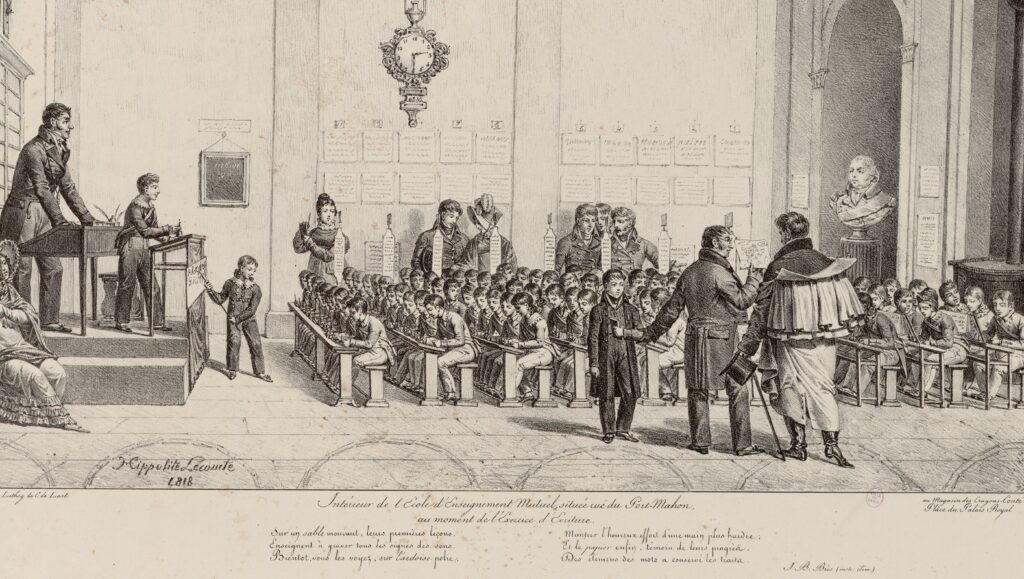

Thus, on a platform, the teacher’s desk with a large drawer where money, reward tickets, registers, writing templates, whistles and children’s notebooks are kept.
Behind the teacher, next to the clock – an essential instrument for organizing teaching life – is a blackboard on which are written sentences and writing models.
At the foot of the platform, benches are attached across the desks, of different sizes, in the middle of the room. The first tables, which are not inclined, have sand on which small children trace signs, while the other tables have slates; on the last of these there are lead inkwells and paper, and chopsticks to indicate words or letters to be read.
At the end of each table are « dictation tables » and telegraphic signals indicating the lesson’s moments, such as « COR » for « correction » or « EX » for « examination of work ». Semicircular table models were then proposed to facilitate the work of the instructors.
D. Progress according to each person’s knowledge
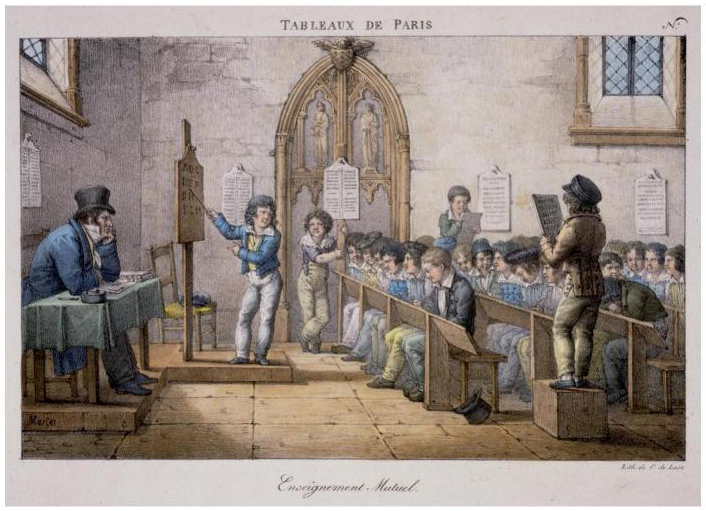

Initially, the mutual school program was limited to the 3 fundamental disciplines of reading, writing and arithmetic, and to the teaching of religion. Geography, grammar, writing, singing and linear drawing were soon added. The instrumental disciplines (music) are taught together, rather than in succession, as is customary in other schools. Pupil groupings are flexible, mobile and differentiated, depending on the nature of the subjects studied and the activities practised in the discipline.
Each subject matter taught in mutual schools is based on a precise, codified curriculum. This program is divided into 8 hierarchical levels, which must be covered in succession. Each degree is called a « class », and this is how we speak of the 8 classes of writing or arithmetic.
The term « class » refers only to acquisitions and knowledge, the 1st class being that of beginners and the 8th that of the completion of the school curriculum. The pace of learning and acquisition varies from student to student and from subject to subject.
Thus, after six months’ attendance, pupil « X » may find himself in 4th class reading, 5th class writing and 2nd class arithmetic. As we said, class assignment is decided on the basis of knowledge level, not age.
But this initial allocation is accompanied, within each class and in each subject, by the constitution of restricted groups established according to the activities to be practiced. In arithmetic, for example, written work is done on the slate. This takes place seated on benches reserved for this purpose, with a maximum of 16 to 18 students per bench, according to the standards established by Jomard.
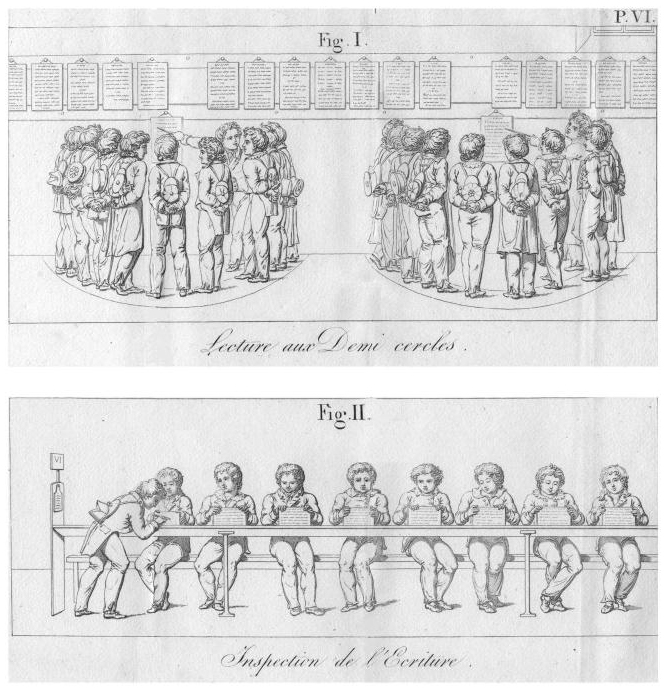
Oral exercises, in reading or arithmetic, or with the aid of a blackboard, arithmetic or linear drawing, are done standing up, in groups of no more than 9, with pupils standing side by side, forming a semi-circle. Hence the name given to this kind of activity: « circle work ».
So, in a mutual school with 36 students in 3rd arithmetic class, bench work will be done in two groups with two monitors, and blackboard exercises with 4 groups and 4 monitors. Class sizes can therefore vary from school to school and throughout the year, the only limitation being the size of the premises.

D. Tools
Low costs are one of the preoccupations of the new teaching method. Furniture was therefore very basic.
- Benches and desks are made of ordinary planks, fastened with heavy nails. The benches have no backrests: a superfluous luxury!
- The platform is clearly elevated: about 0.65 m. Several steps lead up to the teacher’s desk. The master reigns over the children’s community as much by his material position as by his personal ascendancy.
- The clock is noted as « indispensable », as teaching and maneuvers are strictly timed.
- Half-circles, also known as reading circles, give mutual schools a typical and original appearance. These are usually semi-circular iron hangers that can be raised or lowered at will. Sometimes, the materialization is simply applied to the floor: grooves, large nails or arched strips.
- Blackboards were systematically used for linear drawing and arithmetic. They are 1 m long and 0.70 m wide, with a movable meter at the top. They are placed inside each semicircle.
- Telegraphs. When work takes place at the tables, such as writing, signals are used to link and communicate between the general monitor and the individual monitors: these are the telegraphs. A planchette, attached to the upper end of a round stick 1.70 m high, is installed at the first table of each class, thanks to two holes drilled at the top and bottom of the desk. On one side is the class number (1 to 8); on the other, EX (examen), replaced around 1830 by COR (correction). These telegraphs are portable. They could be moved if the number of students increased or decreased. In this way, the master and the general monitor have the exact composition of each class and the number of tables occupied by each. As soon as an exercise is completed, the class monitor turns the telegraph and presents the EX side to the desk. All monitors do the same. The general monitor gives the order to proceed with inspection and any corrections. Once these have been completed, the class number is presented again. And the exercises resume. Next to the telegraphs are the occasional board stands.
- Monitor rods. These are used to indicate on tables the letters or words to be read, the details of operations to be carried out, and the lines to be reproduced. In rural schools, these are generally only available thanks to the good will and ingenuity of the teachers, who obtain them from nearby woods.
- Sand (for writing) and then slates are constantly used in all subjects. This was an essential innovation in the mutual mode, as other schools did not use them.
- Boards instead of books. The first reason is financial, as a single board is sufficient for up to nine pupils. But the pedagogical reasons are no less important. The format makes them easy to read and store. The concern for presentation and highlighting certain characters is accompanied by a different layout from that of the textbooks.
- Books are reserved for the eighth grade, as are nibs, ink and paper.
- Registers, currently in use, ensure sound management of the schools. One in particular deserves special mention: « Le grand livre de l’école » (the school’s ledger), which is first and foremost a registration book. It records the child’s surname, first name and age, as well as the parents’ occupation and address. The teacher enters the precise date of entry and exit of each child, in each class, including music and linear drawing.
E. Communication
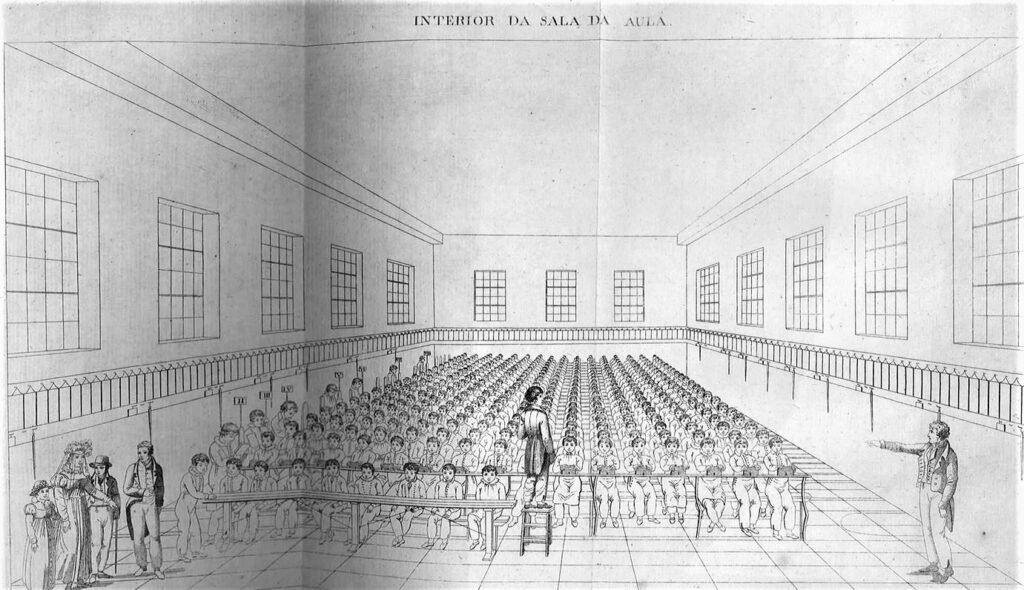
To ensure that dozens or hundreds of pupils are led and developed correctly, and to avoid wasting time, those in charge of mutual education have planned precise, rapid, immediately comprehensible orders:
- The voice is rarely used. Injunctions transmitted in this way are generally addressed to the instructors, sometimes to a specific class;
- The bell attracts attention. It precedes information or a movement to be executed;
- The whistle has a dual function. It is used to intervene in the general order of the school, « to impose silence », for example, and to signal the start or end of certain exercises during the lesson, « to have the pupils say by heart, to spell, to stop reading ». Only the teacher is authorized to use them.
- As for hand signals, they have been used extensively. Intended to evoke the act or movement to be accomplished, they attract the eye and should bring calm to the community.
« Bellists » versus « Lancasterians »
While the two schools, Bell’s and Lancaster’s, were very close to each other in terms of content, methods and organization, they clashed violently over the role and place of religious education. All other program-related differences are a matter of taste, habit or local circumstance.
As Sylvian Tinembert and Edward Pahud point out in « Une innovation pédagogique, le cas de l’enseignement mutuel au XIXe siècle » (Editions Livreo-Alphil, 2019), Lancaster, as a follower of the dissident Quaker movement,
« recognized Christianity but professed that belief belonged to the professional sphere and that each person was free in his or her convictions. He also advocates egalitarianism, tolerance and the idea that, in this country, there is such a variety of religions and sects that it is impossible to teach all doctrines. Consequently, it is necessary to remain neutral, to limit teaching to the reading of the Bible, avoiding any interpretation, and to leave fundamental religious instruction to the various churches, ensuring that pupils follow the services and teachings of the denomination to which they belong ».
Nevertheless, Bellists and Lancasterians had their differences. For the Lancasterians, Bell had invented nothing and was merely describing what he had seen in India. For the Bellists, furious that Lancaster found a positive response from certain members of the Royal family, Lancaster was portrayed as the devil, an « enemy » of the official Anglican religion, who admitted children of all origins and denominations to his schools !
9. France adopting mutuel tuition



In London, the Lancaster association was joined by a number of high-ranking personalities, both English and foreign. These included Geneva physicist Marc Auguste Pictet de Rochemont (1752-1825), French paleontologist Georges Cuvier (1769-1832) and his compatriots, agronomist Charles Philibert de Lasteyrie (1759-1849) and Lancaster’s future translator into French, archaeologist Alexandre de Laborde (1773-1842).
After the peace of 1814, many countries – notably England, Prussia, France and Russia – bled dry by the Napoleonic wars, which had resulted in the loss of thousands of young teachers and qualified executives on the battlefields, made education their top priority, not least to keep up with the industrial revolution that was coming to shake them to their foundations.
Added to this is the fact that the number of orphans in Europe has become a major problem for all states, especially as the coffers are empty. To keep street children occupied, schools were needed, many of them to be built with very little money and many teachers… nonexistent. Learning of the resounding success of mutual education, several Frenchmen travelled to England to discover the new method.
Laborde brought back his « Plan d’éducation pour les enfants pauvres, d’après les deux méthodes (du docteur Bell et de M. Lancaster) », and Lasteyrie his « Nouveau système d’éducation pour les écoles primaires ». In 1815, the Duc de la Rochefoucauld-Liancourt (1747-1827) published his book on Joseph Lancaster’s « Système anglais d’instruction ».

Since 1802, Paris had been home to the « Société d’encouragement pour l’industrie nationale », whose Secretary General was linguist Joseph-Marie de Gérando (1772-1842), and of whom Laborde was a founder together with Jean-Antoine Chaptal (1752-1832). Unsurprisingly, Gérando had been raised by the Oratorians and was initially destined for the Church.
On March 1, 1815, Lasteyrie, Laborde and Gérando proposed to the Société d’Encouragement the creation of a new association whose purpose would be « to gather and spread enlightenment likely to provide the lower classes of the people with the kind of intellectual and moral education most suited to their needs ».

In his report presented to the Société d’Encouragement on March 20, 1815, Gérando proposed that the newly-appointed Minister of the Interior, Lazare Carnot (During les Cents-Jour, i.e. between March 20-June 22, 1815), be asked to promote « the adoption of procedures likely to regenerate primary education in France », i.e. the system of mutual tuition.
Political and social interests were not the only ones at stake. The French economy, too, was much to benefit from the development of education. « What can we expect, » said Carnot in 1815, « if the man who drives the plough is as stupid as the horses that pull it?«
Gérando also proposed the creation of an association dedicated specifically to its propagation, underlining the advantages of the new approach: economic advantage first, since it involves « employing the children themselves, in relation to each other, as teaching aids », and that a single teacher is sufficient for 1,000 pupils; educational advantage second, since it is possible « to teach, in two years, everything that children of inferior conditions need to know, and much more than they learn today by much longer processes »; a moral and social advantage, insofar as children « are imbued from an early age with a sense of duty, a feeling that will one day guarantee their obedience to the law and their respect for the social order ».
The engineer-geographer and polytechnician Edeme-François Jomard (1777-1862), for whom the education of the people is an obligation of society towards itself, said nothing else: « How can we demand that unfortunate people, devoid of all enlightenment, know the social pact and submit to it? Or how can we, without being foolish, count on their invariable and blind submission?«
The Société d’Encouragement then validated the conclusions of its report by subscribing the sum of 500 francs in favor of the new association, and by deciding that, in addition to its moral influence, it would place at the latter’s disposal the various means of execution that might belong to it.
10. Lazare Carnot at the helm

Following the Concordat between Napoleon and the Vatican, the Emperor issued a decree on education on August 15, 1808, requiring schools to follow the « principles of the Catholic Church ».
The Frères des Ecoles Chrétiennes (Institute of the Brothers of the Christian Schools), unconditional advocates of the « simultaneous education » theorized by their founder Jean-Baptiste de La Salle (1651-1719), were to take charge of all primary education and train teachers.
Disbanded during the Revolution, the Brothers resumed their functions in 1810. Encouraged to develop to counter the influence of the Jesuits, authorized in 1816 to return to France, they rapidly expanded throughout France.
But the educational situation was pitiful. This is what senior French officials constantly say when they visit the territories annexed by the Empire, notably North Germany and Holland. The comparison with France makes them blush with shame.
In 1810, the naturalist Georges Cuvier wrote in his report:
« We would be hard pressed to convey the effect produced on us by the first elementary school we entered in Holland. Children, teachers, premises, methods, teaching, everything is in perfect order (…) Several prefects have assured us that we would not find a single young boy in their department today who did not know how to read and write. »
Faced with such a contrast, which was not to the conqueror’s advantage, the Imperial University, like ancient Rome, set out to teach the conquered country. In his decree of November 15, 1811, the Emperor decided:
« The council of our Imperial University will present us with a report on the part of the system established in Holland for primary instruction that would be applicable to the other departments of our Empire. »
The Emperor abdicated on April 4, 1814, before any decision had been taken to regenerate the French « petites écoles ». At least the Imperial University’s reports had exposed their misery and drawn public attention to them.
Appointed Minister of the Interior, and therefore in charge of Education during the Cents-Jours, Lazare Carnot, a co-founder of the Ecole Polytechnique, was completely convinced of the potential excellence of « mutual education ».
On April 10, 1815, he set up a Council for Industry and Charity, at whose first meeting he himself presented Gérando‘s report;
On April 27, 1815, he submitted a report to the Emperor in which he stated:
« There are 2 million children in France clamoring for primary education, and of these 2 million, some receive a very imperfect education, while others are completely deprived« .
He then recommended mutual education, whose « purpose is to give primary education the greatest degree of simplicity, rapidity and economy, while also giving it the degree of perfection suitable for the lower classes of society, and also by bringing into it everything that can give rise to and maintain in the hearts of children a sense of duty, justice, honor and respect for the established order ».
Minutes later, Lazare Carnot had the French Emperor sign the following decree:
« Article 1. – Our Minister of the Interior will call upon those persons who deserve to be consulted on the best methods of primary education. He will examine these methods, and decide on and direct the testing of those he deems to be preferable.
« Art. 2 – A primary education test school will be opened in Paris, organized in such a way as to be able to serve as a model and to become a normal school for training primary school teachers.
« Art. 3 – Once satisfactory results have been obtained from the trial school, our Minister of the Interior will propose the appropriate measures to ensure that all departments can rapidly benefit from the new methods that will have been adopted.«
For Carnot, contrary to those in the business of Philanthropy, there were not any longer poor or rich children. All citizens of the Republic required and had to be offered the best education available on Earth.
The advisory board set up by Carnot included his friends Laborde, Jomard, Abbé Gaultier, then Lasteyrie and Gérando, i.e. the very promoters or first founders of the Société en formation.
Thus, on June 17, 1815 (the eve of the defeat at Waterloo), the Société pour l’instruction élémentaire (SIE) was born, still under the impetus of Carnot, determined to win the war for education. The SIE’s first general meeting was held on the premises of the Société d’Encouragement. At its head were several protagonists of the ministerial commission: Jomard became one of the secretaries of the new society, alongside Gérando (president), Lasteyrie (vice-president) and Laborde (general secretary).
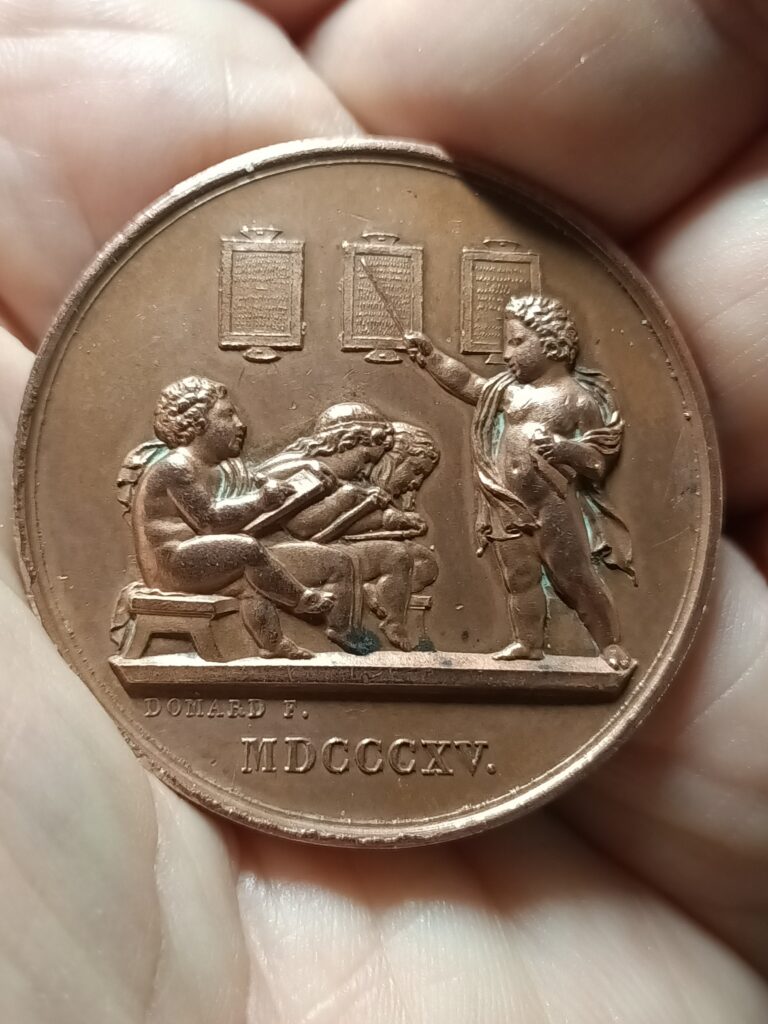


for whom Mutual Tuition was the core of their commitment to primary education.
Before the ordinance of 1816, the number of children attending « petites écoles » was 165,000 throughout France, and by the end of 1820 it had risen to 1,123,000. Almost a factor of 10!
Lazare Carnot clearly wanted to perpetuate the offensive he had launched during the Hundred Days to propagate mutual education throughout the country and, in so doing, to rapidly develop the education of all the children of the Patrie.
After its creation, subscriptions for the SIE poured in, and before long 150 names were added to those of the founders to promote and organize mutual education in France. One of these subscribers was Lazare Carnot.
In its first year of existence, the SIE attracted almost 700 members, initially teachers from the École Polytechnique (Ampère, Berthollet, Chaptal, Guyton de Morveau, Hachette, Mérimée, Thénard), and then some 30 alumni, around half of them from the first graduating class (1794) of the École Polytechnique. Among the latter were a fellow student of Jomard‘s at the geographers’ school, Louis-Benjamin Francœur, professor of higher algebra at the Paris Faculty of Science, comrades from the Egyptian campaign, and Chabrol de Volvic, prefect of the Seine since 1812.
All had but one hope: that Monge’s genial methods of brigades and mutual tuition, which had been diminished and banned once Napoleon turned Polytechnique into a mere military school under the direction of mathematician Pierre-Simon Laplace (1749-1827), could benefit the greatest number and organize a national recovery.
Based in Paris, the SIE extended its operations to the provinces, where it encouraged the founding of subsidiary companies, to which it offered « to send them teachers, to provide them with any information they might need, to give them paintings and books at cost price… ».

The SIE was also interested in education girls (art. 10). It set up a committee of ladies to look after them: president, Baroness de Gérando; vice-president, Countess de Laborde.
Beyond women, the movement spread to uneducated adults, so numerous at the time. On May 1, 1816, the Society set up a commission for the establishment of adult schools. It was also concerned with barracks, which were to be turned into military schools; prisons, especially children’s prisons; and the colored inhabitants of the colonies, who were to be regenerated by the development of education.
Finally, the members of the Society, attributing a human and general value to their mission, dreamed of founding branches abroad. In November 1818, Laborde called for the creation of a special committee to do so.
Last but not least, the Society did not limit its activities to simply creating schools, but also organized inspections and examinations. It published works (on the mutual tuition method, elementary books on reading, grammar and arithmetic). It distributed awards to the best teachers and instructors.

Following the promulgation of the ordinance of July 29, 1818 authorizing Caisse d’Epargne societies (Saving Banks associations), it asked teachers to entrust part of their salaries to these funds to ensure their retirement; setting an example, it deposited funds with the Caisse for the teachers of the schools it had set up.
Today, the SIE, whose head office is a specially-built building at 6, rue du Fouarre in the 5th arrondissement of Paris, remains the oldest and largest secular primary education association in France.
11. The rue Saint-Jean-de-Beauvais pilot program

As said before, after his trip to England, Jomard, whose portrait appears in a medaillon on the façade of the SIE, also embraced the new system.
In his « reflections on the state of English industry », he wrote, after expressing his enthusiasm for various inventions observed across the Channel: « There is, however, something even more extraordinary: these are schools without teachers: nothing, however, is more real. We now know that there are thousands of children taught without a teacher, and at no cost to their families or the State: an admirable method that will soon spread to France.«
A graduate of the Ecole Polytechnique, and an exceptionnal scientist who went with Monge to Egypt, Jomard was the ideal man to oversee the material organization of the test school, in particular by arranging for furniture to be made and teaching aids to be printed in accordance with English principles. Jomard also supervised the training of a small nucleus of students – around 20 – as « monitors » before the opening of the school proper in September 1815, planned for 350 students: a modality reminiscent of the « chefs de brigade » of the first graduating class of the École polytechnique.
However, the members of the SIE soon realized that they needed to train trainers. The English therefore welcomed several Frenchmen to train them in mutual teaching. A pastor from the Cévennes, François Martin (1793-1837), after training as a « monitor » in England, was called in by Lasteyrie to run the first mutual school, which opened its doors on June 13, 1815, on rue Saint-Jean-de-Beauvais in Paris, close to Place Maubert. This was the model school that would enable other mutual schools to be opened, thanks to the training of competent « monitors ». The school was soon unable to keep up with demand from hundreds of communes, which were considering sending one of their own to be trained in the new method.
Pastor Paul-Emile Frossard, also trained by the English, took charge of a Parisian school on rue Popincourt, while Bellot ran another. In July, Martin submitted his report. The model class takes in some 15 students destined to become monitors and principals of elementary schools with up to 350 children. Martin reports that in six weeks, they read, write, calculate and « know how to execute the movements that form the gymnastic part of the new education system ».
12. Mutual tuition and music
As Christine Bierre amply documents in her article « La musique et formation du citoyen à l’ère de la Révolution française » (1990):

« It was at this school on rue Saint-Jean-de-Beauvais, under the direction of a Commission comprising Gérando, Jomard, Lasteyrie, Laborde and Abbé Gaultier, that the application of mutual teaching to the learning of solfeggio and singing was tested for the first time. Alexandre Choron (1771-1834), who since 1814 had opened two music schools for boys and girls, was also a member of the Commission. Not surprisingly, it was on the initiative of Baron de Gérando that the idea of introducing singing into primary education was adopted. When Monsieur le baron de Gérando proposed the introduction of elementary singing in primary schools’, says Jomard in a report presented to the Board of Directors of the Société pour l’Enseignement mutuel, ‘you were all struck by the correctness of the views developed by our colleague (…) It showed the happy influence that such a practice could have, and the real connection that exists between the proper use of song and the perfecting of morals, the ultimate goal of instruction and of all our efforts. Not only was the application of mutual instruction to music revolutionary in itself, but what was equally revolutionary was the fact that children were learning to read and write, almost as intensively. Children studied singing, for four to five hours a week! »
In fact, it was Lazare Carnot himself who wanted to introduce music into the mutual education schools. To this end, he met several times with musician Alexandre Choron (1771-1834), who brought together a number of children and had them perform in his presence several pieces learned in very few lessons. Carnot also was acquinted with Guillaume-Louis Bocquillon, known as Wilhem (1781-1842) for ten years. He saw the possibility of using him to introduce singing into schools, and together they visited the one on rue Saint-Jean-de-Beauvais, a free pilot school for mutual education in Paris open to three hundred children.
Michael Werner‘s recent article, « Musique et pacification sociale, missions fondatrices de l’éducation musicale (1795-1860) », echoes and confirms the groundbreaking research initiated by Christine Bierre in 1990.

Excerpt:
« One of the fields in which the results of mutualist pedagogy are clearly visible is musical education. Several players played a decisive role here, and deserve a brief mention.
The first is Guillaume-Louis Bocquillon, known as Wilhem (1781-1842). The son of an officer and himself from a military background, he then devoted himself to musical composition and teaching, particularly at the Lycée Napoléon (later Collège Henri-IV). His friend Pierre Jean de Béranger put him in touch with Joseph-Marie de Gérando and François Jomard, the leading lights of the SIE. Through them, he learned about mutual teaching and immediately understood the benefits of this method for musical education. In 1818, the Paris municipality allowed him to set up a first experiment at the elementary school on rue Saint-Jean-de-Beauvais. Wilhem developed a method, the necessary teaching materials (in the form of charts) and instructed the chosen student monitors. The results were, according to Jomard, spectacular. At the end of a few months’ instruction, the pupils had not only acquired the basic notions of solfeggio and musical notation, chromatic scales, intervals and measures, but were also performing collective songs in several voices (Jomard 1842: 228 ff)
This success led the SIE to propose to the Prefect and Minister of the Interior that music be introduced into the teaching of elementary schools in the city of Paris, a move officially endorsed in 1820. Wilhem himself was appointed full professor of music teaching in Paris, and music classes were introduced in many of the city’s schools, before spreading to the départements and regions. At the same time, the municipality opened two teacher-training colleges to train future singing teachers.
The second early player in the debate was the composer Alexandre Choron (1771-1834). A member, like Jomard and Francœur, of the first graduating class of the École polytechnique (1795), composer and friend of André Grétry, he had been concerned since 1805 about the decline of choral singing following the abolition of the master classes. An opponent of the Conservatoire, whose academicism and lack of interest in the teaching of choral singing he criticized, in 1812 he was entrusted by the Ministry with a mission to « reorganize the choir and the choirmasters of the churches of France ». He developed a teaching method known as the « concertante method », but also remained committed to the social vocation of choral music. Choron was also one of the founding members of the SIE in 1815, a sign of his commitment to educational issues. During the Restoration, he turned more to religious songs, which he considered to be the historical heart of choral practice. (…) Finally, with the king’s support, he founded the Institution royale de musique classique et religieuse, successfully competing with the Conservatoire in the teaching of vocal art.
For the general public, he arranged for oratorios, requiems and cantatas to be performed by singers from his school in a number of spacious churches, thus ensuring a new presence for sacred music on the Parisian stage. For some of these concerts, he sometimes mobilized student singers from elementary and poor schools, whom he never ceased to follow throughout his career. »
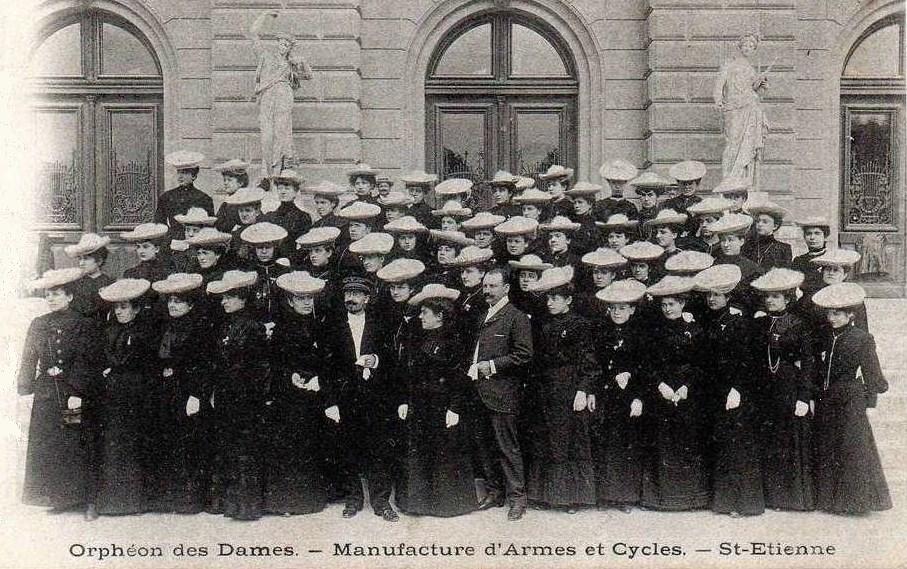
« (…) What fostered this expansion of music education for young people and the working classes from 1820 onwards was a political will shared by a broad spectrum of leaders and stakeholders. The liberals who formed the core of the SIE continued to adhere to the emancipatory mission of education set out by the Convention. By focusing on both the inner formation of the soul and the blossoming of a collective conscience, music – and singing in particular – became a prime field for popular education. Liberals therefore emphasized the moral benefits of music. Thus, in his proposal to introduce singing into elementary school, Gérando remarks:
‘Those of us who have visited Germany have been surprised to see how much simple music plays a part in popular entertainment and family pleasures, even in the poorest conditions, and have observed how salutary its influence is on morals. And Joseph d’Ortigue states lapidary: ‘A people that sings is a happy people, and therefore a moral people. This emphasis on the social benefits of musical activity fits in well with the idea of ‘universal education’, inherited from the Enlightenment and the foundation of the pedagogies of Lancaster in England or Johann Heinrich Pestalozzi in Switzerland.' »
After a trial run at the St-Jean-de-Beauvais school in 1819, singing quickly spread to all the mutual schools. Wilhem was both the creator and the architect of the development of this teaching method, which soon spread to adult and apprentice classes. Periodic meetings of children initiated into vocal music were organized. Thus was born the first French post-school organization: the Orphéon, which, after Wilhem, counted Charles Gounod and Jules Pasdeloup among its directors.
In an 1842 speech to the SIE, Hippolyte Carnot asserted that Wilhem had « elevated music to the rank of a civic institution », and that the « ennoblement » of the individual soul was to be achieved in the new collective order of the reunited nation.
13. Jomard, Choron, Francoeur and « elementary » knowledge
Renaud d’Enfert‘s comprehensive article, published on the website of the Société de la bibliothèque et de l’histoire de l’Ecole polytechique (SABIX), completes the picture with a close-up on the work of Jomard and Francoeur, whose portraits are featured in a medallion on the façade of the SIE headquarters on rue du Fouarre in Paris.
Right from the start of the Second Restoration, the SEI received the backing and support of the Prefect of the Seine, Gaspard de Chabrol de Volvic (1773-1843). In the summer of 1815, the latter appointed Jomard, a linguist in contact with the Humboldt brothers who had been part of the short-lived commission under Carnot and who had protected him during the Hundred Days, « head of the office of public instruction and arts », a position he held until 1823.
In a decree dated November 3, 1815, Volvic, in order to take « the necessary measures to extend the benefits of instruction to all poor families domiciled within the prefecture » and to develop « the new system of elementary instruction » throughout the Seine department, created an eleven-person committee « to extend the benefits of free education to the Seine department », and included all the influential members of the SIE (Jomard, Gérando, Laborde, Doudeauville, Lasteyrie, Gaultier, etc.). ).
In this role, Jomard was responsible for finding sites for new schools. These rapidly multiplied in and around the capital: in 1818, he counted 18 free and 32 fee-paying mutual schools covering all of the capital’s arrondissements, as well as 13 schools in the arrondissements of Sceaux and Saint-Denis. From this work, he drew up his « Abrégé des écoles élémentaires » (1816), a sort of practical guide in which he compiled everything a cityen decided to set up a mutual school needed to know about material organization.
On the pedagogical front, Jomard was the author, in 1816, of a reading method produced in collaboration with the composer and musician Alexandre Choron, who had published a method for learning to read and write as early as 1802, and Abbé Gaultier, a pedagogue who had developed a teaching method under the name of « jeux instructifs » and had traveled to London to study English methods.

Designed for the new elementary school on rue Saint-Jean-de-Beauvais, where Choron was appointed music teacher, it breaks with the traditional spelling method.
Instead of saying « b-o-n = bon », she uses the musical sounds of the language to say « b-on = bon ». In 1821-1822, Jomard also published « Arithmétique élémentaire » (Elementary Arithmetic), designed to remedy the weaknesses of Lancaster’s arithmetic method, which he accused of « making children contract a simple, routine and mechanical habit » instead of serving « to fortify their attention and train them in reasoning ». In the meantime, he and Francœur and Lasteyrie had set up a « calligraphy commission » at the SIE, to develop the principles that would guide the teaching of writing in mutual schools, a writing style intended to be « national », to replace the English models.

For his part, Louis-Benjamin Francoeur (1773-1849) provides, according to Jomard, « a long series of luminous reports on treatises on arithmetic, weights and measures, singing and musical art, drawing and geometry, which it would take far too long to relate or quote ». Filling a gap, in 1819 Francœur published « Le dessin linéaire » (Linear Drawing), a drawing method based on freehand drawing of geometric figures, which broke with traditional, academically inspired ways of teaching and learning drawing.
For Jomard and Francoeur, the idea behind « mutuel tuition » was to broaden the range of subjects taught in primary schools beyond the traditional « reading, writing and arithmetic »: in addition to drawing, also singing, gymnastics, geography and grammar now made their appearance in elementary school.
Linear drawing was nonetheless seen as an elementary skill in its own right, on a par with reading, writing and arithmetic.
Presenting Francœur‘s method to the Société d’Encouragement, Jomard declared:
« The usefulness that industry may one day derive from it is so great and so visible, that it would be superfluous to insist on it. It is not without reason that this result has been considered as precious for the people, as the knowledge of reading and writing ».
Finally, for Jomard, the widespread teaching of reading, writing, arithmetic, linear drawing and singing is the prerequisite for the scientific education of the people:
« In recent times, we have rightly insisted on the usefulness of teaching the elements of the physical and mathematical sciences to the working class. On this depends the advancement of industry and agriculture, which, despite all their progress, are still backward in many respects. It is only through the possession of these elementary notions that workers will perfect their processes, their means, their instruments and their products, and will be able to become skilful foremen and good workshop managers. But how can this be achieved when the mass of the population is still so ignorant?
How, without the art of reading and writing, could they not understand a single word of the chemical and mechanical arts, but only feel their advantage and consent to engage in arduous studies? What’s this! Fifteen million Frenchmen and more perhaps, do not know how to do the first two rules of arithmetic, and we would flatter ourselves to propagate among them the first principles of mechanics and geometry! The basis of this improvement is obviously primary education made more general or even universal ».
14. Nationwide

The results of mutual education are spectacular and rapid, both in terms of learning time and the quality of skills acquired. Whereas in the Lasalle Brothers’ schools it took 4 years to learn to read, this time was reduced to a year and a half in the mutuel establishments!
The enthusiastic French of 1815, with their vivid imagination, saw in this teaching system a veritable panacea. It had undeniable advantages. First of all, it was economical, requiring few teachers and enabling a considerable number of children to be taught at low cost. It is estimated that 4,000 to 5,000 fr. a year were sufficient to maintain a school of 1,000 children: 4 fr. per pupil! Education would never have been so cheap. It also ensured rapid development of primary education, since the shortage of teachers was no longer a limiting factor. With figures to back it up, it was calculated that it would only take a dozen years to extend the benefits of primary education to the whole of France!
To these indisputable advantages, the travelers of 1815 added qualitative arguments. They considered the teaching of instructors superior to that of masters: « He does not know his lesson better than the master, » wrote Laborde, « but he knows it differently ». The child instructor (monitor) takes pleasure in communicating his newly acquired knowledge to his classmates, doing his job « with as much charm as a preceptor finds it disgusting » (Laborde).
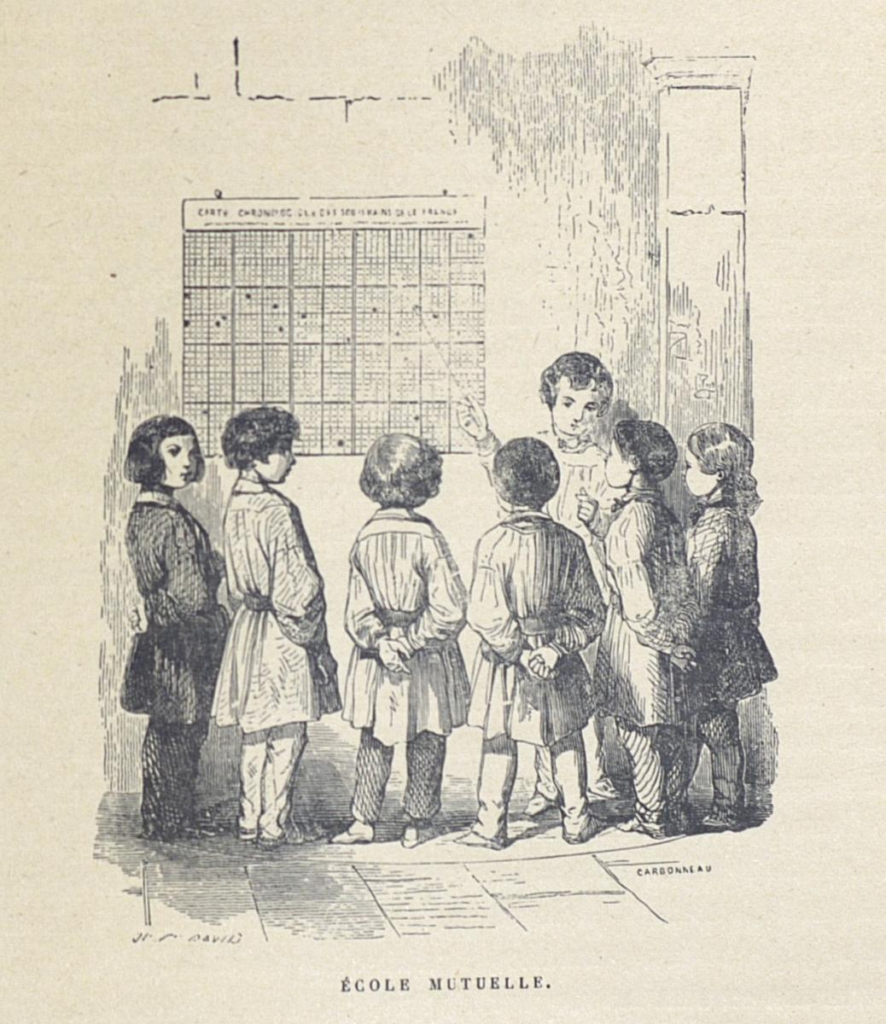

On the other hand, being a child himself, he knows better than the teacher the difficulties of the task, the pitfalls of the lesson, over which he has just stumbled. He will therefore lead his classmates more slowly, more surely, and be a better guide for them.
But teaching won’t be the only thing to benefit from the mutual system; school discipline and morals will also benefit. The child, submissive to his classmate, will obey him more readily than the teacher, since the young instructor owes his superiority solely to his own merit. Finally, the child, with his classmate who knows him well because he lives with him, will not have, as with the teacher, the resource of lying to hide his intimate thoughts or faults: and dissimulation, the social scourge that was learned from the school benches, will thus disappear from mutual establishments.
And Laborde concluded his apology for the method : in the new schools, « work is for them a game, science a struggle, authority a reward ».
The benefits of this teaching were not to be confined to the school: children returning home would in turn exert a happy influence on their parents, becoming « missionaries » of both morality and truth in their families.
Gontard wrote in 1956:
« And let no evil spirits say that these are the daydreams and utopias of idealists! There is irrefutable proof of the value of this method. Look at Scotland. At the end of the 17th century, it was a land of beggary and misery, living without law, without religion, without morals, men drinking, women blaspheming, all fighting. In 1815, thanks to the magic wand of the mutual school, Scotland became a paradise. « It is not uncommon in Scotland to find a shepherd reading Virgil… but it is almost unheard of to meet a malefactor there, »
Laborde agrees.
« Let’s develop the method in France and, by 1850, it will be a land of prosperity and happiness, from which immorality, fanaticism, revolutions and social unrest, all sons and daughters of ignorance, will be banished. »
In 1818, Joseph Hamel, in his report to the Emperor of Russia, notes:
« The method of mutual education has been introduced throughout France with a rapidity and success far greater than could reasonably be expected, and in less than three years more than 400 schools have already been founded. There is every reason to hope that, in the not-too-distant future, more than 2 million children who were still in complete ignorance will be able to receive the benefits of a free education, sufficient for their future vocation.«
Right from the start, with Carnot and a generation of brilliant scientist coming out of Polytechnique, France was giving leadership !

Amiens and the Somme department
Interesting in that regard, the following account of the adoption of mutual tuition methods in Amiens and the Somme department.
« On May 15, 1817, after much mistrust and hesitation, the Amiens town council founded a society to encourage elementary education in the department. More than ennobling the pupils’ souls, for the rector, it was a question of ‘giving the children of these workers an elementary education, [to prepare them] not only for the habit of order and subordination that is acquired in the mutual education schools and which they carry over to the workshops, but also to put them in a position to serve more usefully inside the factories, how to study the industrial processes whose preservation and improvement are so essential to national prosperity' ».
For the Rector, speed of acquisition was a guarantee of success for the new method compared to the « simultaneous method »:
« That a primary education which takes children away for whole years from work necessary for the family’s subsistence becomes for the poor a very onerous burden; but that experience teaches the father of a family that a few months will suffice to procure for his children an advantage which he has regretted so many times in the course of life not to have been able to enjoy himself, we must hope that he will not sway to make a slight sacrifice in order to obtain an important result ».

These are mainly boys’ schools. There are a few girls’ schools and evening classes for adults. They mainly catered for the children of small craftsmen: dyers, octroi clerks, innkeepers, foremen, tailors, millers, dressmakers, coopers, dressmakers, locksmiths, butchers, spinners, ironers, laborers, car loaders, carpenters, booksellers, lamplighters, cutlers, bookbinders and so on.
At its peak, in 1821, mutual education in the Somme department included not one but 25 schools, 4 of them for girls (for a fee): 4 out of 10 were located in towns. In 1833, there were 16 more. The network shrank considerably thereafter, but did not disappear altogether. The last two schools in Amiens closed their doors involuntarily in 1879, and the one in Abbeville in 1880: until then, it played an important role in preparing candidates for examinations.
The Amiens Model School – the first provincial model school – prepares future teachers for the practice of mutual education. It was founded on May 26, 1817. It welcomed over 200 pupils. By 1818, 6 teachers from the Somme had graduated. Most of the teachers from the Aisne, Oise and Pas-de-Calais departments spent some time there before taking up their duties.
In 1831, when the Prefect created the Ecole normale de garçons, it was called the « Ecole normale primaire d’enseignement mutuel ». At first, it served as a training school: student teachers were required to visit the school once a week to observe and practice the mutual teaching method.



After the government reshuffles of 1817-1818, several SIE members were appointed to important ministries: Mathieu Molé (1778-1838) to the Navy, Laurent Gouvion-Saint-Cyr (1764-1830) to the War, Elie Decazes (1780-1860) above all to the Interior, the ministry on which primary education depended. Government support became systematic.
The Minister of the Interior supported the SIE de Paris and its subsidiaries with grants for school foundations and maintenance. He invited the prefects to contribute in any way they could to the development of the method. Prefects took the initiative in setting up local companies, and lobbied local assemblies for subsidies.
A growing number of General and Municipal Councils voted to set up mutual schools. Once a school had been founded, the local authorities (prefect and mayor) visited it and presided over the prize-giving ceremony. For its part, on July 22, 1817, the Commission d’Instruction Publique, which since 1815 had replaced the Grand Master of the University, decided to establish a model mutual-education school in the chief towns of France’s twelve Academies, as a breeding ground for future teachers. Other ministers, each in their own sphere, supported the method.
Molé, in charge of the colonies, founded mutual tuition schools in Senegal.
In 1818, Gouvion-Saint-Cyr established a full-fledged « Ecole normale militaire d’enseignement mutuel » in the caserne Babylone of Paris. Each regiment in Paris and the provinces was required to send one officer and one non-commissioned officer, who would return after a few months’ training to teach the troops the benefits of primary education.
In 1817-1818, mutual tuition triumphed. An irresistible enthusiasm carried France towards it. The network of schools continued to expand. From term to term, more and more reports arrived in Paris from the provinces, counting schools and their pupils.
It was a song of victory that Jomard could sing at the SIE meeting in January 1819. Of the 81 départements in France, only 5 had no mutual school; the other 76 had 687 schools, attended by over 40,000 pupils. There were also 105 regimental schools, 5 adult schools, 4 prison schools and 2 or 3 schools in Senegal.

Exemplifying what was becoming a new Promethean paradigm of scientific optimism, on December 15, 1821, at a meeting at Paris City Hall, the Geographical Society was founded by 217 leading figures, including some of the greatest scientists of the day, such as Jomard, Champollion, Cuvier, Chaptal, Denon, Fourier, Gay Lussac, Berthollet, von Humboldt and Chateaubriand. Other illustrious members include Jean-Baptiste Charcot, Dumont d’Urville, Élisée Reclus and Jules Verne.
The collection and study of geographical data from many continents enabled certain members, such as Gustave Eiffel and Ferdinand de Lesseps, to propose major infrastructure projects, notably the Suez and Panama Canals.
15. Criticism
The first criticisms of mutual education came not from its failure, but from its success. The first « risk » was that the children, having learned too effectively and too quickly (2 to 3 times faster !), would return « to the streets » too soon, not yet being old enough to go to work!
Children weren’t « locked up » at school long enough, and so mutual education disturbed the existing social order. In 1818, the General Council of Calvados heard:
« The greatest service to be rendered to society would perhaps be to devise a method that would make instruction for the lower and indigent classes of society more difficult and time-consuming »…
The second « risk » was that, by continuing to use mutual education, these newly-educated people, mostly from the poorer classes, would become too intelligent, too « enlightened », and begin to express political or social demands, in particular that everyone should have the same rights as the better-off social classes.
Imagine the mess if the social order were challenged! French urban planner and sociologist Anne Querrien notes that, in fact, most of the organizers of the labor movement at the time came from the mutual school, where they had of course learned to read, write and count, but also to trust themselves and their comrades. The mutual school encouraged its pupils to think, and in particular to reflect on the organization of society, a society that assigned them a destiny of submission and obedience.
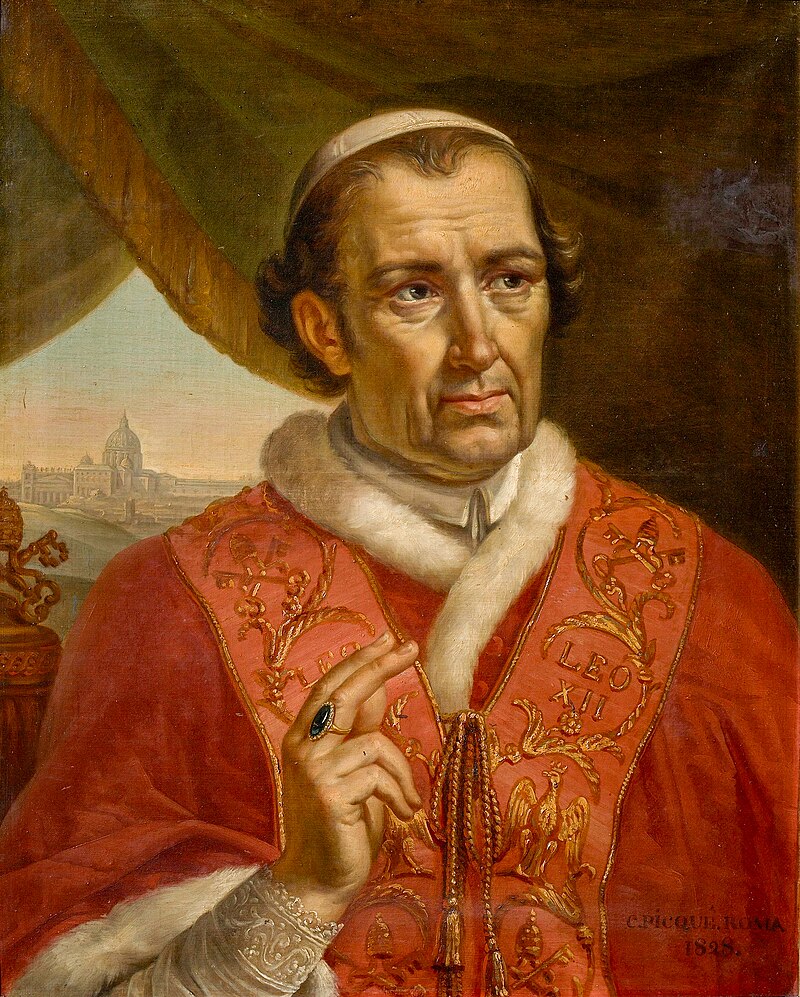



The influential theologian and politician Félicité Robert de Lamennais (1782-1854) said it loud and clearly :
« Lancaster-style schools are the craze of the day. All the authorities in this country, and especially the Prefect, are infatuated beyond expression. Hatred for priests has a lot to do with this mania. The fact is that everything good about this method has been practiced for over a century by the Brothers of the Christian Schools; the rest is pure charlatanism. There is talk of teaching children to read and write in four months: in the first place, this would be a great misfortune, for what can be done with such well-educated children, whose age would not yet allow them to work? Secondly, nothing could be further from the truth than these marvellous results. »
If one has « to decide between the instruction of Abbé de La Salle and that of Lancaster, the question is quite simple; it’s a question of choosing between society and anarchy ».
His brother, the vicar Jean-Marie de la Mennais (1780-1860), took the lead in what can only be described as a political witch-hunt. He said:
« Mutual education was introduced into France by Protestants during the disastrous Hundred Days. M. Carnot was then Minister of the Interior; under his auspices, the Société d’Encouragement, established to propagate this method, held its first meeting on May 16, 1815 ».
He struggled to prove that « the Lancastrian method is defective in its procedures, dangerous for religion and morals in its results » and in a brochure, De l’Enseignement mutuel, published in 1819 in Saint-Brieuc, Brittany, he vigorously attacked this teaching method.
It’s true that questioning authority and the established order is inherent to mutual education. The « simultaneous » method is based on the premise that to pass on knowledge, you need to be qualified (to be the teacher). Conversely, in the mutual school, the teacher is no longer the repository of knowledge, as each student can enlighten his or her classmates.
Another concern for the elites was that, with this method, children are merely instructed, not « educated », and no Christian moral education is imparted.
Last but not least, mutual teaching required fewer supervisors, given the pupils’ role as creators, transmitters and bearers of knowledge. Some may have feared for their jobs…

In 1818, in his report to the Emperor of Russia, Joseph Hamel told the mutualists’ main opponents, the « Brothers of the Christian Schools », that they were almost entirely unaware of what they were denouncing. Hamel also points out that there are 40,000 communes to be provided with elementary school, and that the number of Brothers‘ schools « does not amount to more than one hundred in the kingdom… ».
On the negative side, what is striking, when examining the incriminations, is that one thing is said in the morning and its opposite in the afternoon. In the morning, it’s said that mutual education blurs minds by diluting the authority of teachers; in the afternoon, it’s asserted that it overly « militarizes » education through a totally hierarchical command structure!
On the question of « morality », Lazare Carnot would never have endorsed an education that ruined the Christian spirit, let alone the notion of legitimate authority, while vigorously combating those that lacked it, such as the Monarchy of divine right or the Consulate for life imposed by Napoleon. In the same way, in the morning, the mutualist system was accused of failing to transmit Christian « morals »; in the afternoon, it was seen as a Protestant plot…
And yet, the national impulse in favor of « the fatherland » and future generations has succeeded in uniting personalities from all political and religious backgrounds in a single effort.
Cuvier (Protestant) and Gérando (Catholic), both fervent republicans and promoters of the mutual mode, as well as the Inspector General of the University, Ambroise Rendu (1778-1860, Catholic), even took part in drafting the ordinance of February 29, 1816, promulgated by Louis XVIII and the Minister of the Interior, de Vaublanc (1756-1845).
Following massive pressure from the congregations, mutualist teachers Martin, Frossard and Bellot, all Protestants, were forced to leave their school headships. Martin went on to be very useful in other European countries, notably Brussels, where in 1820 he organized a mutual school at Les Minimes.
16. Mechanistic drift?
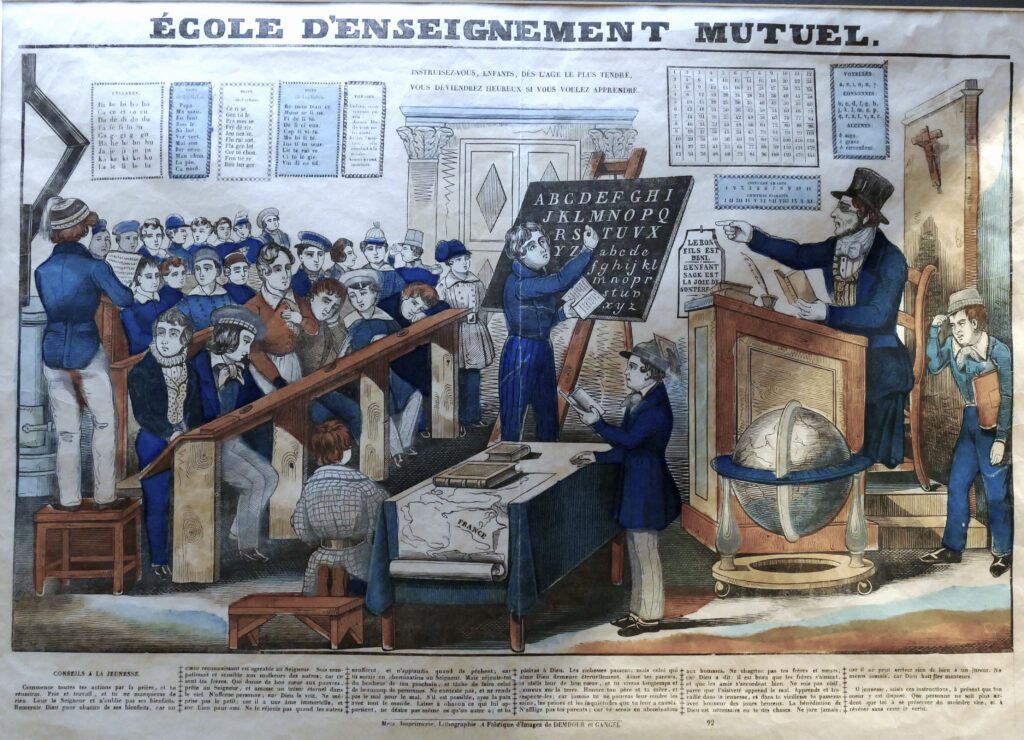

Without grasping the state of mind and enthusiasm that young polytechnicians might have had for the blossoming of an industrial culture and the wonders of machinismo, the defenders of a feudal France see only a « fundamentally mechanistic vision », when Jomard compares the mutual method to a machine, with its cogs and springs, of which the teacher is a mere operator:
« Once the school has been establisehd out and equipped with all the furniture it needs, all that remains to be done is to introduce the pupils and the teacher, and then to set in motion all the springs of this kind of mechanism, by means of the new practices ».
While Victor Hugo evoked a « happy swarm », Laborde was accused of a « mechanistic » drift when he compared the buzzing activity of pupils in English mutual schools to the noise of machines in cotton mills.
Communication, argued critiques, is « entirely mechanical and hierarchical ». It flows « only from the master or general instructor to the instructors and pupils, not in the other direction. It’s a means of action, not a means of exchange.«
Let’s face it, any pedagogical approach, no matter which one, set up as a system and postulating that it’s « enough » to apply mechanically to a human being, can be horrifying. It’s easy, then, to accuse the mutual school of all the ills from which those who accused them suffered, perhaps even more so.
At the mutual school, corporal punishment is banned. It was a courageous decision that Octave Greard was quick to point out:
« It is one of the claims of the founders of the mutual schools to public recognition that they outlawed the corporal punishments, ferulas and whips, which were still in use, and we cannot be too grateful to them for having sought to replace in the hearts of pupils the feeling of fear with the feeling of honor, or, as M. de Laborde used to say, the feeling of well-administered shame ».
Knowing the immense happiness of the thousands of children who quickly gained access to a minimum of public instruction and experienced the indescribable joy of educating their peers, one can only suspect the pen of jealous congregations behind this poem falsely lamenting the misfortune of the poor little ones:
« This system, it is said, born of Anglomania,
Contrasts horribly with our genius.
There, everything is mechanism and our sad children
Seem like a machine, in the middle of their benches;
Their absurd discipline, and no doubt fatal,
Governs even the steps, the attitude or the gesture:
Today, we can prophesy the fate
Of this automaton people thus moved by spring ».
17. Death of Mutual Tuition in France
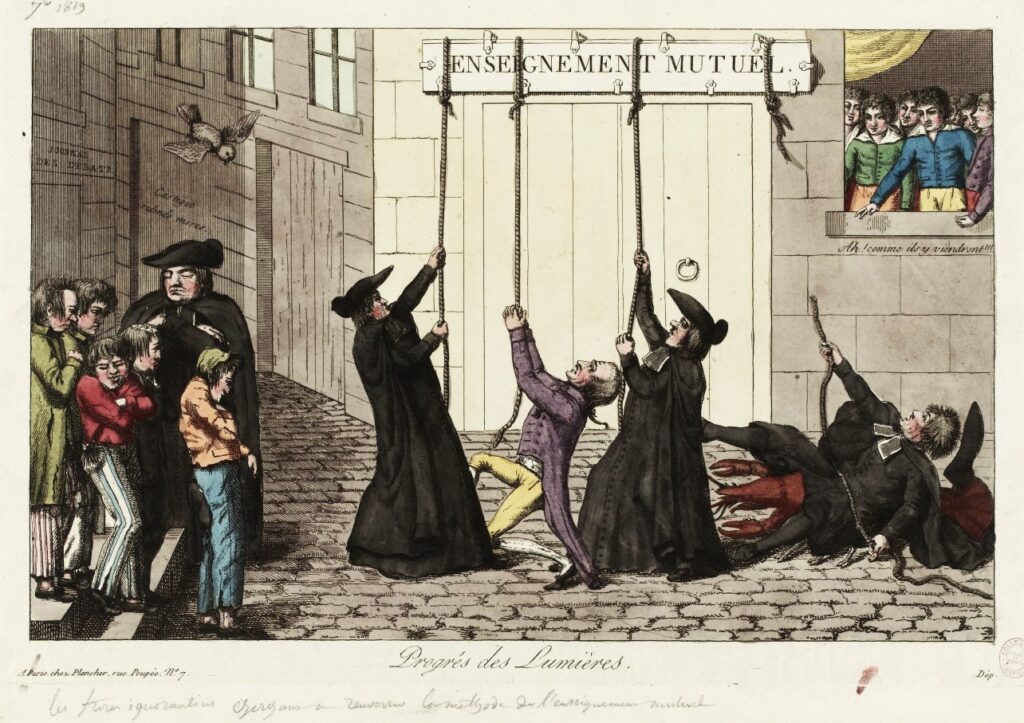

In 1815, after Waterloo, King Louis XVIII, who had fled, returned on July 8, 1815. Unlike his brother, the future Charles X, leader of the ultra-royalists, was fully aware that the history of the Revolution could not be erased. He realized that France could no longer be a country of « subjects », and that it had become a Nation. Hence the « Constitutional Charter » he promulgated, which had the force of a constitution. In the same spirit, in view of the popularity of mutual education, he granted it favors (subsidies, creation of model schools, protection from the Ministry of the Interior).
Mutual education soon lost its protectors, as the ministerial commission created by the decree of April 27 did not survive Napoleon’s fall in June 1815.
By the autumn of 1816, criticism was pouring in from the Congregationalists. The Grand Chaplain of France, Cardinal de Talleyrand-Périgord, Archbishop of Reims (John Baptist de La Salle’s birthplace…), for his part, addressed the King to express the alarm of Catholics.
By 1820, the SIE already had a network of 1,500 mutual schools, grouping together more than 170,000 pupils thanks to an audacious collective pedagogy. However, mutualism came under fire from the ultras, who considered it too liberal, too favorable to children’s autonomy and incapable of « raising youth in religious and monarchical sentiments ».
The child who leaves this school, they say, « is a learned parrot, without religious ideas, without moral values, more dangerous than the ignorant for the political and social order, since instruction has developed new needs in him, always ready to engage in new scenes of revolution or dechristianization. Ah, Carnot, the regicidal conventionalist and patron of mutual education, knew what he was up to when he introduced it into France with the decree of 1815! »
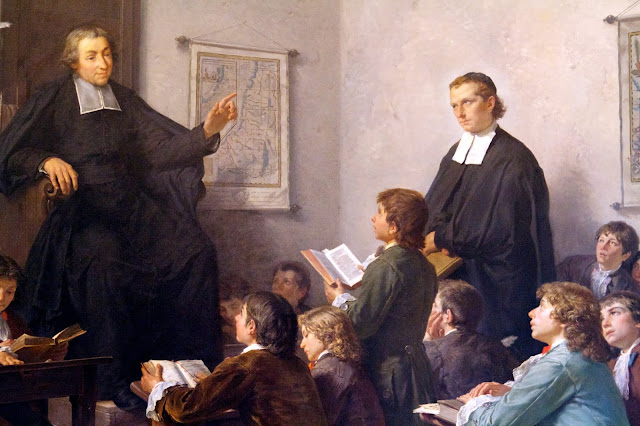

As said earlier, in France, mutual tuition was seen as an aggression by the religious congregations who practiced « simultaneous teaching », codified as early as 1684 by Jean-Baptiste de La Salle (1651-1719) for Institute of the Brothers of the Christian Schools (Latin : Fratres Scholarum Christianarum; French Frères des Écoles Chrétiennes; Italian: Fratelli delle Scuole Cristiane, abbreviated FSC) : classes by age, division by level, fixed and individual places, strict discipline, repetitive and simultaneous work supervised by an inflexible master.
And the merits of the FSC’s schools and « simultaneous teaching », confirmed by centuries of experience, were considered in total opposition to those of mutual education, the « mania of the moment », and considered the work of « charlatans » speculating on primary education.
A fierce supporter of order and suspecting a vast Protestant plot against the Vatican, Pope Leo XII, the « Pope of the Holy Alliance », decided in Quod Divina Sapientia, his papal bull of August 28, 1824 (art. XXVII, 299), that « public schools of mutual instruction will be suppressed and abolished in all the Papal States. The bishops will prosecute those who continue to use this teaching method or who attempt to introduce it into their dioceses ».
In anticipation of the Papal Bull, the Ordinance of April 1824 placed mutual education in France under the strict supervision of the traditional Church, which took over the entire educational question. In August, just after Leo XII’s bull, a Ministry of « Ecclesiastical Affairs and Public Instruction » was created, a name that reflected the Church’s return to business. The accession of Charles X only exacerbated this situation. The Church of the time loved the Enlightenment, but above all it loved candlelight…
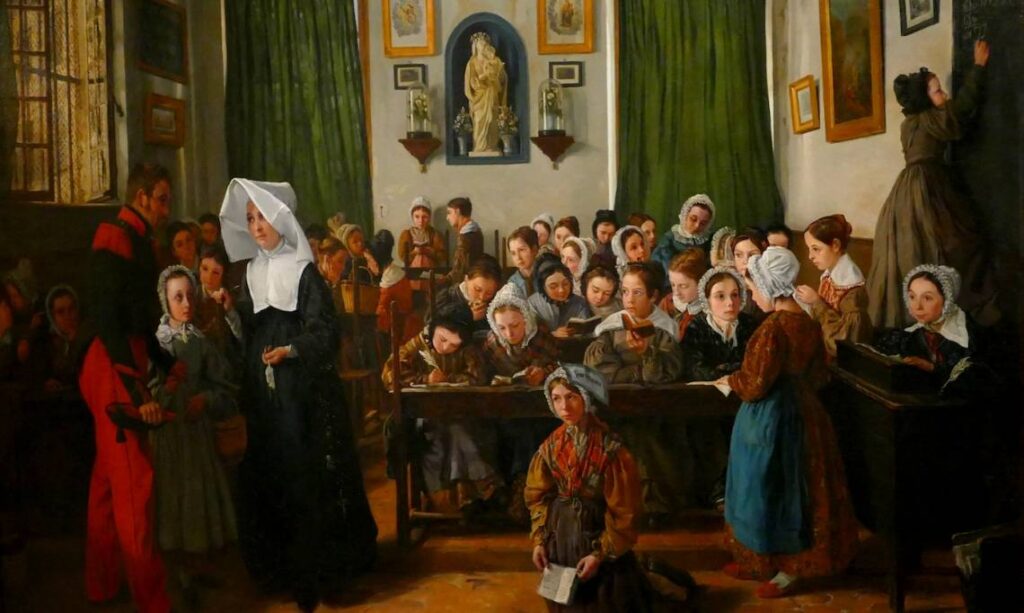

From then on, the schooling situation took a dramatic turn for the worse.
In 1828, of the 39,381 communes :
- around 24,000 had boys’ schools, catering for 1,070,000 children ;
- no more than 430,000 girls attended elementary school;
- 15,381 communes have no boys’ schools ;
- and perhaps 20,000 without girls’ schools;
- 1,680,000 boys and 2,320,000 girls attend no school at all, making a total of 4 million.
Despite an upturn between 1828 and 1829, mutuellism was rejected, its schools closed one after the other (their number fell by three-quarters compared to 1820), although the electoral weight of the ultras diminished from election to election. However, the people’s educators resisted.
In the years following the 1830 revolution, over 2,000 mutual schools were still in operation, mainly in towns, in competition with the denominational schools promoted by the regime. Officially, the mutual school was not a guarantor of morality, and was said to be « industrial » and inhumane.

Then came the famous « Guizot moment ». Although he had initially campaigned for the development of mutual education within the SIE, François Guizot (1787-1874), Louis-Philippe’s Minister of Public Instruction from 1832 onwards, gave mutual education the coup de grâce in France by having the « simultaneous » method endorsed as the only official teaching method.
Schools adopting mutual tuition were no longer subsidized, nor did they receive any support from the government or the Church. Faced with material difficulties, the majority of pupils mostly admitted free of charge had now to pay a fee. Many parents in need withdrew their children and sent them to the newly opened Brother of the Christian Schools, who had become free of charge…
The Church slanders, casts doubt on the morality of the teachers, tried to keep the children of Catholic families away from the « devil’s school », persecutes and threatens to keep them away from catechism and communion in order to break mutual tuition. Most of the teachers using that method felt obliged to bandon it and embrace the official « simultanous » method. With no more pupils, no more teachers, mutual schools gradually disappeared.
It was Guizot who put the final nail in the coffin of mutual tuition, creating the École normale des instituteurs in 1867 to train the future teachers of Jules Ferry’s school in the simultaneous method still the norm today.
The young Hippolyte Carnot also joined the SIE in order to reconnect, post mortem, with his father. In 1847, when he became Minister of Public Instruction under the Second Republic, he attempted to revive the mutual education cherished by his father Lazare Carnot, but although his work was great, his enemies were many and his term of office very short.
18. Conclusion

Education is in deep crisis. Everything that was largely accomplished by Lazare Carnot and his son Hippolyte has been systematically destroyed by the new church of our time: the financial, transhumanist and decadent oligarchy, having led the world to the brink of collapse, still determined to save its privileges by organizing the physical and moral ruin of humanity.
To rebuild an education worthy of the name, we are convinced that mutual education, provided it is adapted to our times, is an extremely promising avenue. Several African countries, currently lacking sufficient resources, are already taking inspiration from it.
Mutual tuition is not a relic of the past, but an experiment to be renewed to open the gates of the futur. For the Global South, still plagued by post-colonial exploitation, war and epidemics, education of this kind is the way to go: efficient, rapid and cheap but also humanizing and joyfull, it is the way to go.
It’s a message that Vincent Faillet, a young french teacher with a doctorate in education and training in the Paris region, who is reviving this method, cleary expresses in this video:
19. Short list of works consulted
- François Arago, Biography of Gaspard Monge, read at the Académie des Sciences, 1846.
- Joseph Hamel, L’enseignement mutuel, 1818, Paris.
- John Franklin Reigart, The Lancastrian System of Instruction in the schools of New York City, Teachers College, Columbia University, 1916.
- Sylviane Tinembart, Edward Pahud, Une innovation pédagogique, le cas de l’enseignement mutuel au XIXe siècle. Editions Livreo-Alphil, 2019, Neuchâtel, Switzerland;
- Bruno Poucet, Petite histoire de l’enseignement mutuel : l’exemple du département de la Somme, Carrefours de l’éducation, N° 27, 2009/1, pages 7 to 18;
- Michel Chalopin, L’enseignement mutuel en Bretagne, Presses Universitaires de Rennes, 2011;
- Claire Giordanengo, La grande vogue de l’enseignement mutuel, Hypotheses, Bibliothèque Diderot de Lyon;
- M. Gontard, Un aspect des luttes de partis en France au début de la Restauration : la question de l’enseignement mutuel, Revue d’Histoire du XIXe siècle – 1849, Année 1953, pp. 48-63.
- Dell Upton, Lancasterian Schools, Republican Citizenship, and the Spatial Imagination in Early Nineteenth-Century America, Journal of the Society of Architectural Historians, Vol. 55, No. 3 (Sep., 1996), pp. 238-253,University of California Press;
- Alexis de Garaudé, Manuel de l’enseignement mutuel et populaire de la musique, 1854;
- Anne Querrien, L’école mutuelle – Une pédagogie trop efficace?, Les Empêcheurs De Penser En Rond, 2005.
- René Girard, Carnot et l’éducation populaire pendant les Cents Jours, 1907, Paris.
- Michael Werner, Musique et pacification sociale, missions fondatrices de l’éducation musicale (1795-1860) « , Gradhiva (N° 31/2020);
- Rémi Dalisson, Hippolyte Carnot – 1801-1888, La liberté, l’école et la République, CNRS, Paris, 2019;
- Renaud d’Enfert, Jomard, Francœur et les autres… Des polytechniciens engagés dans le développement de l’instruction élémentaire (1815-1850), Bulletin de la Société des amis de la Bibliothèque et de l’Histoire de l’École polytechnique (SABIX), 2014.
Hippolyte Carnot, father of modern republican education


Table of contents
- Introduction
- In the storm
- From charity to universal schooling
- Malebranche and the Oratorians
- The Revolution of the Mind
- The Committee of Public Instruction (1791)
- Condorcet and the « American Party
- The « Condorcet » Plan
- The battle under the Convention (1792-1795)
- Lazare Carnot under Les Cent-Jours (The Hundred Days)
- Carrying on the torch
- Lazare Carnot’s exile
- Hippolyte with Abbé Grégoire
- Like Schiller, patriot and citizen of the world
- The Revolution of 1830
- Minister of Public Instruction under the Second Republic
- Hippolyte’s Carnot’s reforms
A. Nursery school
B. Primary school
C. Explanatory memorandum to the School Act of June 1848
D. Teachers to enlighten the rural world
E. Secondary education
F. High Commission for Scientific and Literary Studies
G. A School of Administration
H. Lifelong education for all
I. People’s libraries
J. Fine arts, hygiene and gymnastics on the program
K. Citizen Concord - Conclusion
- Appendix: works by Hippolyte Carnot
- Short list of books and articles consulted.
« The tree you are planting is as young as the Republic itself (…) It will spread its branches over you, just as the Republic will spread over France the benefits of Popular Instruction.
« Hippolyte Carnot, Memorial (1848), dossier 13.



1. Introduction
Hippolyte Carnot (1801-1888) had neither the glory of his father Lazare Carnot (1753-1823), the « Organizer of Victory » of Year II, nor the renown of his brother, the inventor of thermodynamics Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832), nor the tragic fate of his son, François Sadi Carnot (1837-1887), President of the Republic assassinated by an anarchist in Lyon.
History retains almost exclusively his magnificent « Memories on Lazare Carnot by his son », in which he recounts the actions, ideas and life of his father, the « great Carnot », scientific mind, poet, fervent republican and Minister of War.
Hippolyte remains little-known, despite the fact that his long life (87 years), slightly longer than Victor Hugo‘s (83 years), spans almost an entire century (1801-1888), and that his work and influence are considerable.
As is amply demonstrated by « Hippolyte Carnot et le ministère de l’Instruction publique de la IIe République » (PUF, 1948), written by his son, the physician Paul Carnot (1867-1957), he was much more than a mere observer or commentator on events.
2. In the storm
The 19th century was a period of profound change. The flame of hope kindled by the American and French Revolutions, the ideal of liberty, fraternity and emancipation of individuals, peoples and sovereign states alike, proved unquenchable, and was affirmed and extended throughout the 19th century. The long march towards a new paradigm was fraught with pitfalls. Changes took place slowly, against a backdrop of brutal crises and violent ruptures.

During his lifetime, Hippolyte Carnot (1801-1888) was directly or indirectly involved in :
Two Empires:
1803-1814: First Empire under Napoleon Bonaparte
1852-1870: Second Empire under Napoléon III
Three Monarchies:
1814-1815: First Restoration under Louis XVIII
1815-1830: Second Restoration under Charles X
1830-1848: July Monarchy under Louis-Philippe, Duc d’Orléans.
Two Republics:
1848-1852: Second Republic
1870: Third Republic
Three Revolutions expressing popular republican fervor:
1830 (Trois Glorieuses) ;
1848 (uprisings) ;
1871 (Commune).
In an ever-changing environment, through revolutions, coups d’état, monarchies, empires or republics, wars and trials, the man who was (too) briefly Minister of Public Instruction in 1848, a friend of Victor Hugo and Jules Ferry, Hippolyte was a nation builder and an inspiration.
Philosopher and journalist, memoirist and minister, Freemason and believer, political exile and member of parliament, senator and member of the Académie, he took part in all the battles for public and private freedoms, laid the foundations for teacher training and free, compulsory schooling, including kindergarten, created the forerunner of the ENA and defended the most advanced causes (schooling for girls, universal suffrage, the fight against slavery and the abolition of the death penalty).
Rémi Dalisson, in a fascinating and richly documented biography entitled « Hippolyte Carnot 1801-1888. La liberté, l’école et la République », published by the French CNRS in 2011, with supporting evidence, points out that « the vulgate of Jules Ferry as the inventor of the republican and secular school has been widely debunked ».

Given that Hippolyte‘s name, let alone his work, is nowhere to be found on the Ministry’s website, the author laments that « few people, including those at the Ministry of Education, pay tribute to the role and personality of Hippolyte Carnot« .
The anthologies of founding texts and speeches of the republican school, which have proliferated in recent years, systematically forget him.
« It is therefore an injustice and an oversight that we are repairing by tracing the life and work of Hippolyte Carnot, which go far beyond his educational projects and achievements. Through his stature, his training, his career, his ideas, his writings and his battles, this man of many talents will enable us to retrace the history of the construction of the school and therefore of society in the 19th century (…) And as this question refers to the political, social, even economic and cultural question of the nation, and as the minister was involved in all the philosophical battles of his century (…) it is largely the history of a century that will be evoked (…) ».
The full text of this magnificent biography is available free of charge on the Internet, and we have drawn heavily on it to write this text.
3. From charity to universal schooling
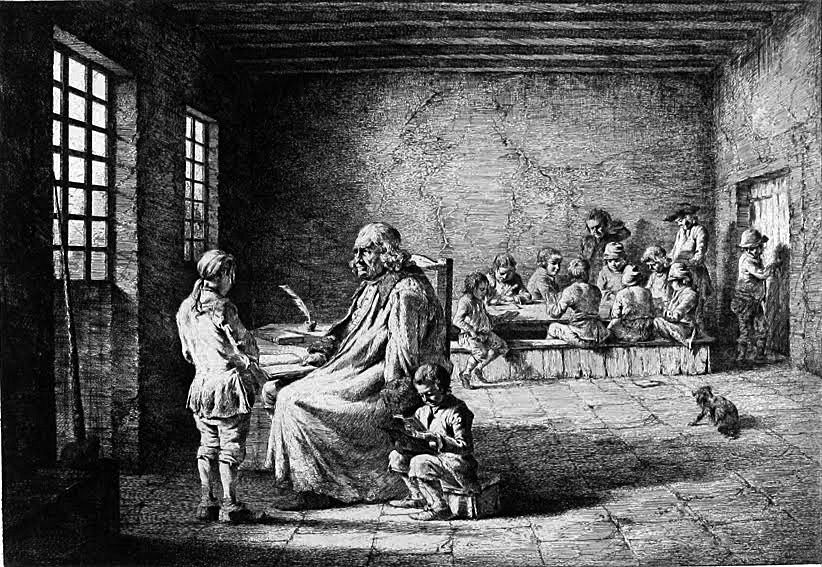

In order to fully appreciate the fundamental contribution of Lazare Carnot‘s ideas, and of their initial implementation by his son Hippolyte, a brief history of schooling in our country is in order.
Educating a handful of more or less talented children? We knew how to do it, especially since the tasty advice of the great Renaissance pedagogues (Vittorino da Feltre, Alexandre Hegius, Erasmus of Rotterdam, Juan Luis Vivès, Comenius, etc.). But organizing compulsory, secular and free education for an entire nation, boys and girls alike, remained an enormous challenge.
And as the following chronology shows, the road to universal schooling was strewn with many pitfalls.
In France, from the 16th century onwards, the royal state entrusted the Catholic Church (Jesuits, Oratorians and Brothers of the Christian Schools) with the task of educating state officials and the children of the nobility: only wealthy families could afford to pay a tutor for their own children, while the others, often described as « not suited to study », remained essentially illiterate.

In the 17th century, holy men, moved by the great misery of the children of the people, founded teaching orders to take in orphans and abandoned children free of charge. Their teaching was primarily religious, but they also provided them with food, basic education and basic writing and arithmetic skills. In the 18th century, women’s congregations took in poor girls in the same way.
Whatever his real motives, in 1698, following the revocation of the Edict of Nantes in 1685, Louis XIV ordered every village community or parish to open a school, whose teacher had to be a Catholic priest. This was the first time the state considered providing education for rural children.
Literacy figures at the end of the Ancien Régime show the scope and limits of the work accomplished. At that time, an estimated 37% of French people were literate enough to sign their marriage certificate, compared with 21% a century earlier. Female education progressed slowly, with around a quarter of women literate, many of them only in very basic terms. There were major disparities between town and country.
4. Malebranche and the Oratorians

Among the congregations, the Oratorians have been the exception since 1660, under the influence of the philosopher and theologian Nicolas Malebranche (1638-1715), who became its director. Breaking away from the Aristotelianism of the Jesuits and the dualism advocated by René Descartes, Malebranche, who had become an honorary member of the Académie des Sciences, was to be won over to the optimistic vision of the great German scientist Wilhelm Gottfried Leibniz through a sustained exchange of letters. Reconciling science and faith, on the metaphysical level his god is a wise and reasonable God, always respecting his essence and the laws of order he generates. His perfection lies above all in his function as legislator, identified with wisdom or reason, rather than arbitrary power.
Two examples demonstrate the excellence of their teaching: Gaspard Monge and Lazare Carnot, two great scientific minds and future co-founders of the Ecole Polytechnique. Convinced that the political, economic and industrial future of the Republic depended on it, they led the fight to ensure that the best possible education was available to all, not just the privileged few of whom they were a part.


The son of a Savoyard merchant, Gaspard Monge (1746-1818) studied at the Collège des Oratoriens in his native Beaune. From the age of 17, he taught mathematics at the Oratoriens de Lyon, then in 1771, mathematics and physics at the École de Génie established in Mézières. That same year, he came into contact with the physicist Jean Le Rond d’Alembert (1717-1783) and corresponded with the mathematician Nicolas de Condorcet (1743-1794), who encouraged him to submit four dissertations, one in each of the fields of mathematics he was studying at the time. It wasn’t long before his talents as a geometrician came to the fore: at the Ecole de Génie, he invented « Descriptive Geometry », which became part of the school’s curriculum and was essential to the industrial revolution just around the corner…
As for the future General Lazare Carnot (1753-1823), son of a Burgundian notary, after studying at the Oratoriens d’Autun (1762), he too entered the École du Génie de Mézières (1771), where he was taught by Gaspard Monge.
5. The Revolution of the Mind (1789)
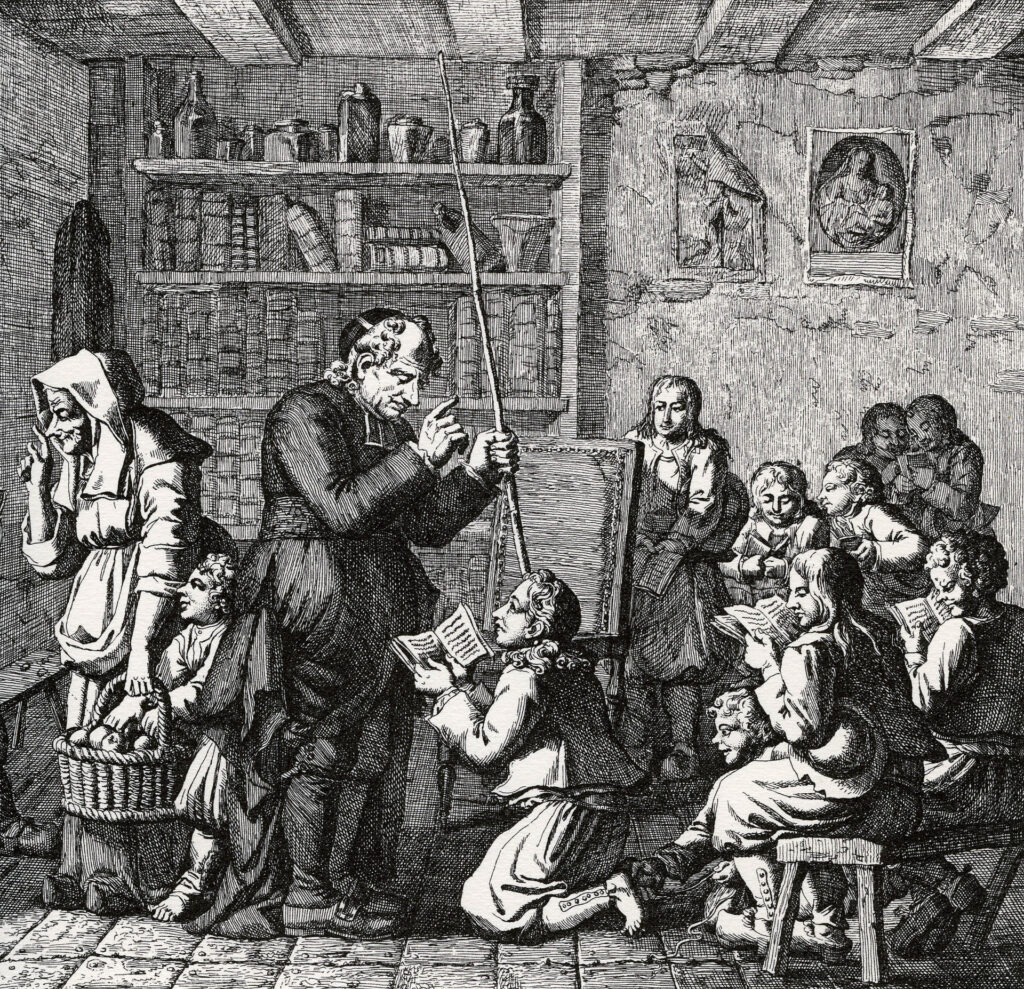

In 1789, the Revolution turned the situation upside down. On February 13, 1790, all religious corporations and congregations were abolished by decree, and religious were ordered to swear an oath to the revolution. The all-powerful Church was totally challenged, and the few education that existed collapsed.

In a break with the Ancien Régime, the Constitution of 1791 asserted that « public instruction common to all citizens shall be created and organized. » A report and draft law were presented by Talleyrand (1754-1838) on September 10, 1791.
His Rapport sur l’Instruction publique, drafted in reality with contributions from some of the greatest scientists of the time (Condorcet, Lagrange, Monge, Lavoisier, La Harpe), represented a real break with the way education had been conceived under the Ancien Régime. It poses the question of public education in new terms, both in terms of principle (public education is presented as a political, social and moral necessity, and therefore as something the State must guarantee to its citizens) and in terms of form.
The plan encompassed the entire national education system, which was organized on four levels and whose establishments were distributed across the country according to administrative divisions. It laid the foundations for free education for all, including girls (separate schools and curricula), and specified that « the first elements of the French language, both spoken and written, will be taught ». In 1794, the jurist Bertrand Barère de Vieuzac (1755-1841) specified: « We will teach French to populations that speak Bas-Breton, German, Italian or Basque, in order to put them in a position to understand republican laws, and to attach them to the cause of the Revolution. » Due to lack of time, the bill was not passed.
In the bill, Talleyrand proposed the creation of an elementary school in each municipality. The Constituent Assembly had just established the territorial organization that is still in place today. The decree of December 14, 1789 had just created 44,000 municipalities (on the territory of the former « parishes »), which became « communes » in 1793. The law of December 22, 1789 created the départements, and the decree of February 26, 1790 set their number at 83.
6. The « Committee of Public Instruction » (1791)
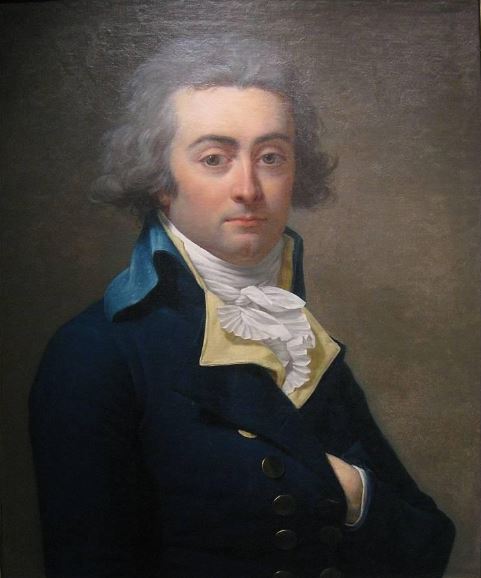

A month after Talleyrand’s report, on October 14, 1791, the National Legislative Assembly created its first « Committee of Public Instruction », of which the mathematician and philosopher Nicolas de Condorcet (1743-1794) was elected president and lawyer Emmanuel de Pastoret vice-president. The other members were future general Lazare Carnot, deputy Jean Debry, mathematician Louis Arbogast and politician Gilbert Romme.
Condorcet also presided over one of the three sections, dealing with the general organization of public education. On March 5, 1792, he was appointed rapporteur for the draft decree on the general organization of public education that the committee was to present to the Assembly.
Educated at the age of 11 at the Jesuit college in Reims, he was sent to the Collège de Navarre in Paris at the age of 15. Throughout his life, he retained painful memories of this primarily religious education, which he criticized for its brutality and humiliating methods. His indignation led him to imagine a totally different approach. In 1791, in La Bibliothèque de l’homme public (The Public Man’s Library), he published five memoirs on public education, constituting a veritable plan.
They formed the basis of the project he drafted for the Legislative Assembly, and were approved by the Committee of Public Instruction on April 18 and presented to the National Assembly on April 20 and 21, 1792.
7. Condorcet and the « American Party »

A hagiographer of the physiocrat Anne Robert Jacques Turgot (1727-1781), while criticizing the sectarianism of the « economists », Condorcet, in terms of economics, largely shared his Physiocratic worldview, notably the establishment of a tax on agricultural income alone, considered to be the nation’s sole source of wealth, with industry seen as a « sterile » category of the national economy (see my article dealing with Karl Marx’s errors).
For the Physiocrats, great defenders of the land rent that made them fat, the enemy to be fought was the centralized, dirigiste and mercantile state that Jean-Baptise Colbert, following in Sully’s footsteps, had begun to set up.
This did not prevent Condorcet, more courageous than many of his generation, from taking center stage in openly supporting the American Revolution in its fight for dignity and emancipation against the horrors of the British Empire: slavery, the death penalty, human and women’s rights.



Although a friend of Voltaire, Condorcet wrote a vibrant eulogy of Benjamin Franklin. A friend of the influential English pamphleteer Thomas Paine, in 1786 he published « De l’influence de la Révolution d’Amérique sur l’Europe », dedicated to La Fayette. In this vibrant plea for democracy and freedom of the press, Condorcet considers that American Independence could serve as a model for a new political world. Along with Paine and du Chastellet, Condorcet contributed anonymously to an intermittent publication, Le Républicain, which promoted republican ideas. At the time, there were only a few states in the world known as republics (the Swiss cantons, Venice and the United Provinces, among others). Condorcet later had an argument with the second President of the United States, John Adams, whose encyclopedists scorned his proposal for a bicameral parliament.
Condorcet also made friends with the American president Thomas Jefferson, who promoted and published Condorcet’s writings in favor of the physiocrat Turgot in order to make them known in America. On July 31, 1788, Jefferson wrote to James Madison: « I am also sending you two little pamphlets by the Marquis de Condorcet, in which is the most judicious judgment I have ever seen on the great questions which are agitating this nation at this moment ». These were « Lettres d’un Citoyen des États-Unis à un Français et des Sentiments d’un Républicain ».

While in Paris, Jefferson frequented Mme de Condorcet’s cosmopolitan salon. Before returning to America, he received his closest friends one last time at his home, the Hôtel de Langeac: Condorcet, La Rochefoucauld, Lafayette and key organizer, Governor Morris.
After Jefferson’s return to America, Condorcet continued his dialogue with the American Secretary of State in Washington. On May 3, 1791, he sent him a copy of the report on the choice of a unit of measurement, presented by Borda, Lagrange, Laplace, Monge and himself to the Académie des Sciences on March 19, and subsequently submitted to the Assemblée nationale on the 26th. Indeed, it was a matter of common interest: on July 4, 1790, Jefferson had presented his Report on Weights and Measures to the American Congress, a copy of which he had sent to Condorcet. It was the same faith in progress that encouraged both men to support the idea of a universal, decimal system of measurement.
In a letter, Jefferson informed Condorcet of the work of a black American mathematician and astronomer, Benjamin Banneker, author of an almanac, of which he had sent him a copy. In his « Réflexions sur l’esclavage des nègres » (Reflections on Negro Slavery), Condorcet, though a staunch abolitionis, had expressed himself in favor of a gradual abolition of slavery, in the same way as Jefferson did in his « Notes on the State of Virginia ».
Jefferson oscillated in his positions, attributing the inferiority of blacks sometimes to natural causes, sometimes to the effects of slavery, while Condorcet – in agreement with Franklin – had always been convinced of the natural equality of all men.
In reality, the very man who became the third president of the United States owned over 600 slaves during his adult life. He freed two slaves during his lifetime, and five more were freed after his death, including two of his children from his relationship with his slave Sally Hemings. After his death, the remaining slaves were sold to pay off the debts of his estate.
Jefferson strongly opposed the « Federalists » like Alexander Hamilton, who promoted a strong federal state, Colbert-style economic dirigisme and mercantilism. Condorcet was to encourage Jefferson in his project of « agrarian democracy », the physiocratic vision of the great landowners that would become, until the arrival of Abraham Lincoln and his advisor Henry Carey, the ideology of the American Republican Party.
8. The « Condorcet » Plan
Progress of science and reason will lead to the happiness of societies and individuals, according to Condorcet. In Esquisse d’un tableau historique des progrès de l’esprit humain, he writes:
« Our hopes, concerning the future state of the human species, can be reduced to these three important points: the destruction of inequality between nations, the progress of equality within the same people; finally, the real perfection of man. »
Preferring « L’Instruction publique » to national education, he dreamed of an education totally independent of the State and free of dogmatism:
« Public authority cannot, even on any subject,
have the right to teach opinions as truths; it must not impose any belief. »
(Sur l’instruction publique, first memoir, 1791).
Outlining secular principles, for Condorcet, « the principles of morality taught in schools and institutes will be those which, founded on our natural feelings and on reason, belong equally to all men. »
At the National Assembly, he received massive applause when he declared :
« In these schools, the primary truths of social science will precede their applications. Neither the French Constitution nor even the Declaration of Rights will be presented to any class of citizens as tables descended from heaven, to be worshipped and believed. Their enthusiasm will not be based on the prejudices and habits of childhood; and they will be told: ‘This Declaration of Rights, which teaches you both what you owe to society and what you are entitled to demand of it, this Constitution which you must uphold at the expense of your life, are but the development of those simple principles, dictated by nature and reason, whose eternal truth you learned to recognize in your early years.
This Bill of Rights, which teaches you both what you owe to society and what you have the right to demand of it, this Constitution, which you must uphold at the cost of your life, is but the development of those simple principles, dictated by nature and reason, whose eternal truth you learned to recognize in your early years. As long as there are men who do not obey their reason alone, who receive their opinions from a foreign opinion, in vain will all chains have been broken, in vain will these command opinions be useful truths; the human race will no less remain divided into two classes, that of men who reason and that of men who believe, that of masters and that of slaves.' »
For those standing behind the Condorcet plan, the aim was to ensure the development of each individual’s abilities, and to strive for the perfection of humanity. His project proposed the creation of 5 categories of establishments:
- elementary school for civic and practical education ;
- secondary schools, with a focus on mathematics and science;
- institutions, providing training for primary and secondary school teachers in each département, and general education for pupils;
- lycées, training teachers and those « destined for professions in which great success can only be achieved through in-depth study of one or more sciences »;
- the Société nationale des sciences et des arts, whose mission was to manage schools, enrich cultural heritage and disseminate discoveries.
The plan was also characterized by the equality of ages and sexes in education, universal and free elementary education, and the freedom to open schools. Last but not least, religion was to be confined to the private sphere.
The project did not forget « the people », as weekly and monthly lectures for adults were intended to « continue education throughout life », an ambition taken up by Abbé Grégoire and Hippolyte Carnot.
As his son Paul Carnot recounts:
« In its short existence, the Constituent Assembly had only been able to pass on Talleyrand’s famous report to the Convention. After the no less famous reports by Condorcet and Lakanal, and the discussions of its Education Committee (almost as active as the Public Safety Committee), the Convention proclaimed the principles of compulsory, free and secular primary education, which are still ours today. The Declaration of the Rights of Man (art. XXII) proclaimed, with Robespierre, ‘Instruction is the need of all; society must favor, with all its power, the progress of public reason and put Instruction within the reach of all citizens’. »
Rarely were all parties in agreement on these points. The Girondins (Condorcet, Ducos) said, along with François Xavier Lanthenas (1754-1799), that « instruction is the State’s first debt to its citizens. »
On the subject of free education, Georges Danton said: « No one has the right not to educate his children. There is no real expense where there is a good use for the public interest. After bread, education is the first need of the people.
But the program of public education leading to the perfectibility of mankind thanks to reason, had not the chance to become a priority, as King Louis XVI, at the suggestion of General Dumouriez, went to the National Assembly to propose declaring war on Austria… Added to that, money for education wasn’t available.
Condorcet had to interrupt the lecture of his project. At the end of the afternoon of April 20, 1792, the Assembly adopted the declaration of war against the King of Bohemia and Hungary, unanimously minus seven votes. The following day, Condorcet completed the reading of his project. The Assembly decreed that the report be printed, but postponed discussion of it.
On May 24, Romme, on behalf of the Committee of Public Instruction, requested in vain that discussion of the report be placed on the agenda. Condorcet’s project, like Talleyrand’s report, did not have time to be debated, and was not adopted.
9. The battle under the « Convention » (1792-1795)

The protagonists of Year I (under the Convention) were hardly more decisive. A new Committee of Public Instruction was set up. It included Abbé Henri Grégoire, abolitionist and close friend of Lazare Carnot and later of his son Hippolyte, and Joseph Lakanal (1762-1845).
On December 12, 1792, Marie-Joseph de Chénier (1764-1811) read Lanthénas’s proposals, which echoed the ideas of Talleyrand and Condorcet. The discussions were fruitless, and the project was swept aside by Marat. Marat exclaimed that day:
« However brilliant the speeches we hear here on this subject may be, they must give way to more urgent interests. You are like a general who would amuse himself by planting and removing trees to feed starving soldiers. I ask that the assembly order the printing of these speeches, to attend to more important objects. »
The following year, Robespierre opted for a national education plan devised by Lepeltier de Saint-Fargeau (1760-1793). According to this plan, presented by Robespierre himself on July 13, 1793, education without a healthy dose of republican ideology would not suffice to regenerate the human race. It is therefore up to the State to inculcate a republican morality, by taking charge of the common education of children between the ages of 5 and 12.
On January 21, 1793, the King was beheaded. While Carnot, who only backed the decision to prevent any possible return to power of the Monarchy, Condorcet, who was opposed to the death penalty on principle, opposed it.
Debates on public education were delayed. It was not until the end of the year that compromise legislation on the organization of elementary school came into being, making education compulsory and free for all children aged six to eight, and establishing the freedom to all to open schools. The decree of December 19, 1793 stipulated that primary schools were the first level of instruction, teaching the knowledge strictly necessary for all citizens, and that those responsible for teaching in these schools would henceforth be called « instituteurs » (teachers). This decree was only partially implemented.
1794 saw a profusion of legislative texts on the subject including the decree of January 27, 1794 which imposed the use of the French language in all education.
On October 21, 1794, another decision organized the distribution of the first schools in the communes.
On October 30, at the instigation of Dominique Joseph Garat, Joseph Lakanal and the Comité d’Instruction Publique, the first « Ecole Normale » was created to train teachers. The law stipulated that « a teacher training college would be established in Paris, to which citizens from all parts of the Republic who were already educated in the useful sciences would be called, to learn the art of teaching under the most skilful teachers in all disciplines ». The school, planned for some 1,500 students, was set up in an amphitheatre at the Muséum national d’histoire naturelle, which was too small to accommodate the entire class. Although the school was soon closed, it nevertheless attracted a number of brilliant teachers, including the scientists Monge, Vandermonde, Daubenton and Berthollet.
On November 17, 1794, Lakanal had a law passed making education free, with the Republic providing salaries and housing for teachers, and authorizing the creation of private schools.

Also in 1794, Jacques-Élie Lamblardie, Gaspard Monge and Lazare Carnot, the institution’s founding fathers, were given the task of organizing a « Ecole centrale des travaux publics », renamed the « École Polytechnique » in 1795 by Claude Prieur de la Côte d’Or, not only to alleviate the shortage of engineers in post-Revolution France, but to create, by intensive training in projective geometry, a generation of scientific geniuses.
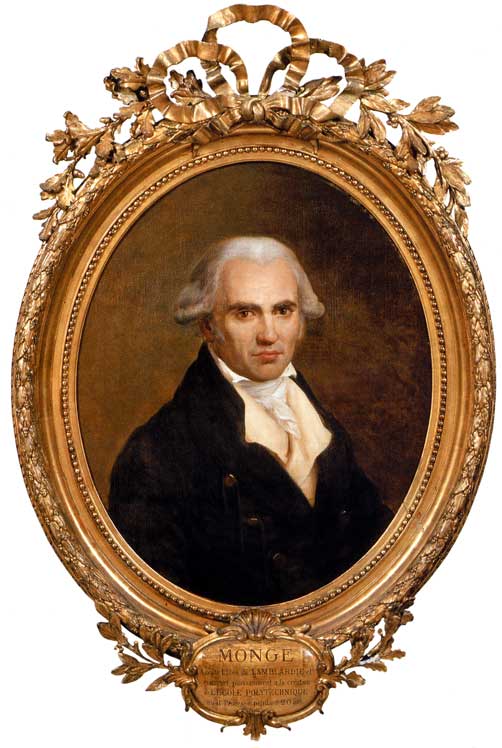



Unfortunately, in terms of universal schooling, the results in 1795 were disastrous: none of the decrees of 1794 had been implemented. Worse still, on October 25, 1795, a new law drafted by Pierre Daunou marked a step backwards: for lack of a budget, education was no longer free, teachers had to be paid by pupils (and their wealthy relatives), and the school curriculum was poor. This law remained in force until Napoleon’s texts on secondary and higher education in 1802. While it abandoned compulsory and free education, it did call for the creation of one elementary school per canton and secondary « central schools » in each département.
The new authorities set deadlines for municipalities to organize schools. They sent special envoys to see whether municipalities were taking the necessary steps to find and install a teacher.
In the towns and cities, the administration managed to recruit a certain number of candidate teachers, but in the countryside, the list often remained empty. In addition to the problem of recruitment, local authorities were faced with the problem of money, furniture, heating and books. Practising teachers complained about the shortage of pupils, as the republican school aroused mistrust. When the teacher ventured to replace the catechism and the Gospels with the Constitution and the Rights of Man, parents, encouraged by resistant priests, preferred to keep their children at home. The Comité d’Instruction Publique was inundated with questions, suggestions and requests.
On November 17, 1795, Lakanal had a new law passed by the Convention. Education remained free but not compulsory. It guaranteed a fixed salary and pension for teachers, and provided them with premises and housing. It authorized all citizens to set up private schools.
10. Lazare Carnot during the Cent-Jours (The Hundred Days)

On November 9, 1799, Bonaparte fomented a coup d’état and established the Consulate regime. As First Consul, he signed the Concordat with Pope Pius VII on July 16, 1801, abolishing the 1795 law separating Church and State.
Seizing the opportunity of the moment, and above all seeking to respond to immediate needs, the Minister of the Interior, the republican chemist and industrialist Jean-Antoine Chaptal (1756-1832), submitted to Bonaparte a project for the organization of secondary education, entrusted in particular to the Oratorians of Tournon. In 1800, he presented his « Rapport et projet de loi sur l’instruction publique » (Report and draft law on public education).
Recalled by the First Consul, Lazare Carnot was given the War portfolio, which he held until the conclusion of the Peace of Amiens in 1802, after the battles of Marengo and Hohenlinden.

An early revolutionary, but also a moderate and republican, he voted against the Consulate for life, then was the only speaker to vote against the Empire on May 1, 1804.
From then on, deprived of all political influence, he refocused on the Académie des Sciences. In 1814, he was entrusted with the defense of Antwerp, a city of which he became mayor: he held on for a long time, and only agreed to hand over the city on the orders of Louis XVIII.
But a few months later, the Emperor returned to power for the Hundred Days, from March to June 1815. It was at this point that Lazare, who had finally been threatened with arrest to the point of hiding out on rue du Parc-Royal, was appointed Minister of the Interior on March 22, 1815. And as this ministry included Public Instruction in its remit, he was able to launch the educational project that was so close to his heart.
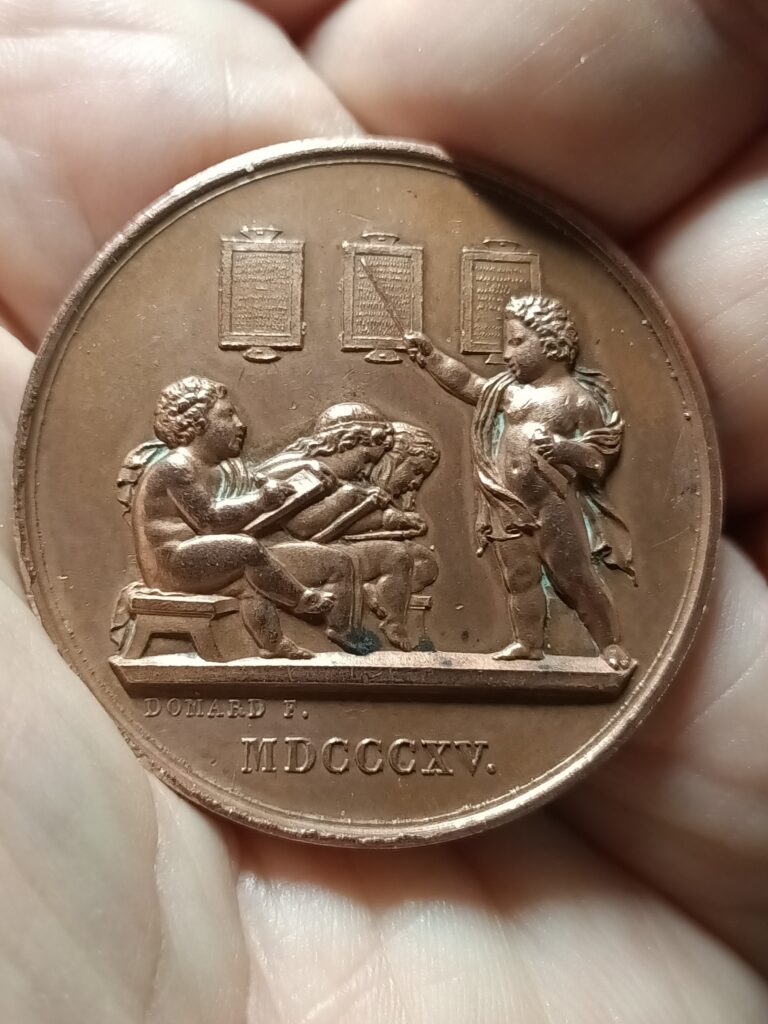



Three days after his installation at the Ministry, Lazare Carnot commissioned a study on education. It was inspired by the work of the « Société d’encouragement pour l’industrie nationale », headed by philanthropist Joseph Marie de Gérando, who had also been educated by the Oratorians in Lyon and was a proponent of Mutual Tuition.
Carnot and his faction then founded the « Société pour l’Instruction Elémentaire » (SIE) to promote this type of education. For Carnot and Grégoire, education and instruction should « elevate all individuals of the human species to the dignity of Man », educate as much as moralize, and spread love among men.

During the Hundred Days, Carnot had just enough time to prepare, in April 1815, a « comprehensive plan for popular education », followed by a decree and the creation of a Special Commission for Elementary Education, tasked with outlining prospects in this area, drawing inspiration from English and Dutch models.
Familiar with the « brigades » invented by Gaspard Monge at Polytechnique, where the best students supervised the others, Carnot was in favor of the system of mutual tuition in popular schools. For him, the issue was not alleviating the suffering of the poor or avoiding social chaos, but educating every citizen of the Republic, whatever his conditions, to have a functial Republic. After spreading to England and Switzerland, Carnot established mutual tuition in France. Convinced of the importance of music and linear drawing, he wanted pupils to be taught it.
With this in mind, he met several times with Alexandre-Étienne Choron (1771-1834), who had also been educated by the Oratorians, and brought together a number of children to perform several pieces learned in very few lessons. Carnot had also known the pedagogue Louis Bocquillon, known as Wilhem (1781-1832), for ten years. He also saw the possibility of introducing singing into schools, and together they visited the Mutual Tuition pilot project on rue Jean-de-Beauvais, which had opened in Paris to three hundred children. Starting from there, Wilhem created the mass musical movement known as « Orphéons ». (see article by Christine Bierre)
11. Hippolyte carries on the Torch
Lazare, a pupil of Gaspard Monde and a scientific mind of the highest order, had strong ideas about education that would shape the personalities of his sons, notably Hippolyte, the future Minister of Public Instruction in the Second Republic. For the two Carnots,
« all social institutions must aim at the physical, intellectual and moral improvement of the largest and poorest classes ».
More than « full heads », he aspired to turn his sons into « well-made heads », « to let us know the taste of good things rather than make us infallible about the meaning of words », in the words of his younger son. For Lazare, it was a matter of putting to the test in the family the educational principles he advocated for the nation.
Although he had little interest in « dead languages » and was more interested in living ones, Lazare introduced his children to Latin, which was once again a compulsory language in the imperial lycées created in May 1802. For the rest, while their father’s rich library introduced Sadi Carnot and his brother Hippolyte to the classics that were essential to the humanist culture on which secondary education was based, it also introduced them to other, more contemporary and innovative thinkers.
Among them, Hippolyte was interested in those who addressed educational issues, such as Rousseau, but also in more original philosophers like Saint-Simon (whose movement was attractive but became a cult after his lifetime), of whom Lazare Carnot said:
« Here is a man who is called extravagant, yet he has said more sensible things in his entire life than the wise men who scoff at him […]. But he is a very original, very bold mind whose ideas deserve the attention of philosophers and statesmen ». Evoking his father, Hippolyte would later say, « The lessons we received were all intended to make us, like the master who gave them, virtuous without effort, wise without system. »
Lazare Carnot sends Hippolyte to the Polytechnic Institution, 8 avenue de Neuilly. According to Dalisson,
« the young Carnot received a Spartan education where, while discipline did not exclude corporal punishment under the rule of ‘Inspecteurs généraux’, pedagogy was innovative. Pupils were divided into classes according to age, and teaching combined intellectual and physical education through programs that complemented their father’s education. Hippolyte thus perfected his reading, ancient and modern languages, literature, mathematics, physics and geometry, and acquired a taste for chronology, history, drawing, music, fencing and dance, proving himself an excellent student in every respect.«
12. Exile of Lazare Carnot

After Napoleon’s second abdication, Lazare Carnot joins the provisional government. Exiled at the time of the Restoration, he was banished as a regicide in 1816 and retired to Warsaw, then to Magdeburg, where he devoted the rest of his life to study and, above all, the education of his children.
Dalisson: « when he’s not at school, he (Hippolyte) serves as secretary to his father, who continues his education ». In Magdeburg, « one of Carnot’s consolations was to complete the education of his young son, whose studies he directed more especially towards historical questions and social economics ». So it was in Prussia that Hippolyte found his way, abandoning the « hard » sciences to devote himself to philosophy in general, and political and social philosophy in particular. There, education had a privileged status since Frederick II had made primary education compulsory in 1763, envisaged a form of free education (for poor families) and created gymnasiums for secondary education. Enough to inspire Carnot père and fils to imagine how France could catch up.
Better still, as Dalisson points out:
« Prussia remains a kingdom which, like France a few years earlier, carried out a « levée en masse » (mass recruitment) in 1813 to drive out the invader. The link between popular education and national sentiment, between education and the economy, between liberalism and national education, is an obvious one, and ties in with the Carnot family’s educational ideals. That’s why, at the [prussian] government’s request, Lazare set up an educational project to create a « vocational school » in this distant host country. With the help of Hippolyte, he set up a complete teaching system for agriculture and industry. Although we have no trace of the text, it undoubtedly influenced the young man as much for his Parisian and liberal years as for his future ministry ».
13. Hippolyte with Abbé Grégoire

Back in France, Hippolyte contacted his father’s old friends, notably Abbé Henri Grégoire. An emblematic figure in the fight for the emancipation of Jews and blacks, this « revolutionary bishop » called for the total abolition of privileges and advocated universal male suffrage.
In principle, Hippolyte approved. However, in practice, after observing the people’s infatuation with public executions, he discovers how easily a crowd can be led, even manipulated, by playing on irrationality, passion and impulses – all things that make the use of universal suffrage tricky, and can lead to dictatorship. He concludes that popular education must enlighten the people to bring them back to more fraternal and reasonable sentiments.
For Abbé Grégoire, as for Carnot père and fils, slavery must be abolished, nations must free themselves from Empires by recovering their sovereignty, and education must free citizens from ignorance, a set of subjects marvelously brought together in the iconography of the bas-reliefs on the base of the statue of Gutenberg in Strasbourg, a commemorative monument created by a friend of both Grégoire and Hippolyte, after Victor Hugo, the sculptor David d’Angers.
As a member of the Comité d’Instruction Publique, Henri Grégoire called for the generalization of the French language, as the Oratorians had done before him, and became the rapporteur for the abolition of the old academies and the creation of the Institut.
The opening of a whole series of « special schools », such as the Ecole polytechnique (1794) and the Institut des langues orientales (1795), the establishment of the Musée du Louvre (1793), the preliminary project for a Bibliothèque nationale (1790), the creation of the Bureau des Longitudes (1795), the introduction of new units of weights and measures, the metric and decimal systems, the extension of elementary schools to all communes and one of the jewels in the crown of this policy: the founding of the Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers (1794), owed much of their success to the boundless energy of Abbé Grégoire.
The aim was to transmit technical knowledge to two types of audience. On the one hand, the « grandes écoles », aimed at the country’s new elites, provided high-level education to train scientists and engineers (École polytechnique, Ponts et chaussées, etc.) or the future teachers of the new public education system with the École normale (1794); on the other hand, schools designed for middle management in factories, good workers and workshop managers: this was the case of the écoles d’arts et métiers, heirs to the vocational school imagined in 1780 in Liancourt (60) by the Duc de la Rochefoucauld-Liancourt.
Grégoire also established several major institutions that still exist today, including, in addition to those already mentioned, the Natural History Museum (1793), the Royal Garden of Medicinal Plants (1793) and the Museum of French Monuments (1795).

Grégoire introduced the young Hippolyte to the Masonic lodge of which he was a member, Les Philadelphes. Inspired by Grégoire’s struggle, of which he would be the executor and about which he would publish a work towards the end of his life, Hippolyte, barely 23 years old, published « Gunima, an 18th-century African short story » (1824), a philosophical tale recounting the moral education of young Benjamin who, equipped with the principles of the Enlightenment, confronts his prejudices and the injustice of the slave and servitude regime of the so-called Hottentots of the Cape. Surprisingly modern, the story takes up the challenge of fraternity at a time when France was responding to Haiti’s demands for recognition.
True to the philosophy of Abbé Grégoire, he protested against the expulsion of Jews from Dresden, where they were forbidden to stay. Indignant, he tried to alert public opinion: since 1789, Jews have been French citizens like any others. He reaffirmed his faith in freedom of worship, which had enabled the emancipation of the Jews, and exclaimed:
« If we call a Jew someone who, from his mother’s womb, society condemns to the vilest slavery, who vegetates without rights in his homeland and serves as a breastplate for the insults of the rabble, to whom his actions deserve nothing (…) and who is relentlessly pursued by shame and contempt, then I am a Jew and always will be ».
14. Like Schiller, patriot and world citizen
From Dalisson‘s book:

« Carnot’s position is summed up at a celebration in homage to the French Revolution on March 19, 1838 in Paris. In the name of ‘holy equality, solidarity between all peoples and all races of men in a spirit of fraternity’, he toasted ‘the abolition of slavery, the cessation of this awful scandal of humanity’.
« From that day on, he collaborated regularly with Victor Schoelcher, a journalist, Freemason, close to the Saint-Simonians and member of the same societies as himself, whom he would meet again three years later in the government of the Republic, then in exile. Schoelcher had been confronted with slavery in Cuba as early as 1828 and also believed that their emancipation should be gradual, before changing his mind and becoming a supporter of immediate abolition.
« Freedom must also apply to peoples and therefore to nations, because ‘the principle of all sovereignty lies in the nation’. A son of 1789, educated during the struggles for national emancipation, a student steeped in Romanticism, passionate about the revolts of the fifties and thirties before being caught up in the « Spring of the Peoples », Carnot placed his trust in the freedom of nations: « Salvation will come from peoples uniting to overcome the common enemy, despotism. If liberated nations and peoples manage to get along and unite, they will even build ‘United Europe’.
« Throughout the century, he would support all national struggles, and hence national unity, against empires that oppressed minorities. For nationality ‘is the human right proclaimed in 1789, the right to group together according to one’s affinities of character, tradition, race and language, and is basically LIBERTY itself’.
Even after the 1870 war, he was convinced of a kind of « right of peoples to self-determination » in a Europe founded on the freedom of peoples.
In his writings on foreign policy, notes Dalisson, he regularly recalled Friedrich Schiller‘s maxim: « Man is created free, he is free, even if he is born in chains. (…) Do not tremble before the free man. This freedom of peoples and nations must even be based, horresco referens, on the necessary reconciliation between France and Germany, two neighboring peoples who have been separated by the vicissitudes of history, but who are « two friends who have been divided by long quarrels and who need to explain themselves ».
15. The 1830 Revolution

The Revolution of 1830, also known as the July Revolution or the « Three Glorious Days », took place in Paris on July 27-28-29, 1830. Parisians, at that time the foremost revolutianary citizenry, rose up against the reactionary policies of King Charles X’s government. One of them, was Hippolyte Carnot who had transgressed his legendary moderation, took a rifle and joined those on the barricades. The question immediately arose: « What should replace the king? » Many intended to restore the Republic.
On July 30, deputies and journalists in favor of the Duc d’Orléans put up posters recalling the « patriotic » past of the duke, a veteran of Valmy who claimed to be in line with the ideas of George Washington, and his commitment to the future: he would be « a citizen-king ».
Unconditionally, the representatives of the people (95 deputies present in Paris) proposed that the Duc d’Orléans be appointed Lieutenant-General of the kingdom.
On July 31, he accepted the position and went to Hôtel de Ville in Paris, the Republican headquarters. There, before a gathered crowd, he was embraced by La Fayette, both wrapped in the tricolor flag. Lafayette felt that a gradual transition to a republic could only be achieved through a constitutional monarchy. On August 9, the deputies amended the Charter of 1814 to become the constitutional « charter » of 1830, and the Duc d’Orléans was proclaimed « King of the French » under the name of Louis-Philippe I.

Hippolyte Carnot, always a moderate, believed in « representative democracy » and was elected three times as a deputy under the Monarchy of 1830. A spokesman of the opposition to the regime, he prepared for what was to come.
16. Minister of Public Instruction under the Second Republic (1848)

After an initial attempt to re-establish republican values, neutralized by Louis-Philippe’s « Coup d’état » in 1830, the uprisings of 1847-48 succeded in February 1848 with the formation, at Paris City Hall, of the « Provisional Government » led by several friends of Hippolyte Carnot, to establish the « Second Republic ».
The provisional government’s first measures were intended to break with the previous period. The death penalty was abolished in politics. Corporal punishment was abolished on March 12, and « contrainte par corps » (imprisonment for debt) on March 19.
On March 4, a commission was set up to resolve the problem of slavery in the French colonies. Under the aegis of the Minister of Colonies, the Republican astronomer François Arago, a close friend of Alexander von Humboldt, and whose Secretary of State was Victor Schoelcher, its work led to abolition on April 27.
In the political sphere, the changes were significant. Freedom of the press and of assembly were proclaimed on March 4. On March 5, the government instituted universal male suffrage, replacing the censal suffrage in force since 1815. In one fell swoop, the electorate rose from 250,000 to 9 million…
This democratic measure made the rural world, which accounted for three-quarters of the population, the master of political life for many decades to come. Elections for a Constituent Assembly are scheduled for April 9. Lafayette’s National Guard, previously reserved for notables and shopkeepers, was made accessible to all citizens.

The provisional government proposed appointing Hippolyte Carnot to the Ministry of War or the Interior; he declined the offer, but accepted the Ministry of Public Instruction (which Victor Hugo had just refused), to which was added the Ministry of Religious Affairs, which until then had been the responsibility of the Ministry of Justice. Carnot’s desire to see cults be part of public education was based not only on his lack of hostility to the Church, but also on his belief that a close alliance between the Republic and the lower clergy was the best guarantee of progress.
« I myself, » he wrote, « have religious sentiment too deeply engraved in my heart not to be and not to want those around me to be full of deference towards the ministers of all religions. » And again: « My constant efforts have been aimed at reattaching the lower clergy to the Republic. The minister of religion and the schoolmaster are, in my eyes, the columns on which the republican edifice must rest. »
17. Hippolyte Carnot’s reforms

En s’appuyant sur le degré d’instruction des Français à l’âge du mariage, cette carte met en
évidence une grande disparité entre les régions. Ainsi, le taux d’alphabétisation des
habitants du nord et de l’est est-il nettement supérieur à celui des habitants du sud et de
l’ouest. La France alphabétisée est celle des grandes villes, des campagnes riches et des
populations denses.
During his very short ministry, armed with an overall vision that had been carefully thought through and prepared in advance, he announced, sometimes several times a week, republican reforms of all the major areas of education, from early childhood through to adults, including teacher training, senior civil servants and all citizens. Declaring in his preparatory notes that « it is important that the various levels of the education system integrate into each other, leading directly from one to the other ».
A. Nursery schools
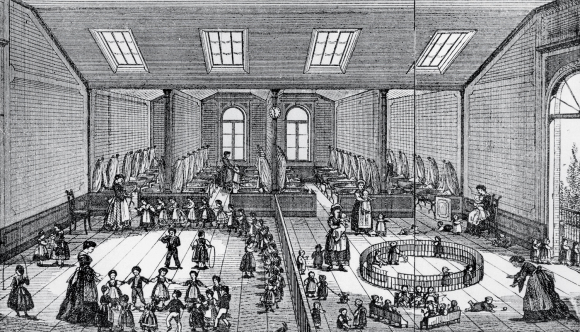
For Carnot, « salles d’asile » were little more than charitable establishments run by nuns. Little was done to educate infants. Their name, reminiscent of misery and almsgiving, was replaced on April 28 by « nursery school ». « The child should find there the education he cannot receive from his mother, i.e. the care of the body, the language of feeling, and those little exercises intended, not yet to furnish the intelligence, but only to open it up ».
In the minds of Jean Reynaud (Under-Secretary of State for Public Instruction) and Carnot, the asylum was neither a school of instruction, nor a place of refuge for children deprived of their parents. At the same time, a « normal nursery school » was set up in Paris, for pupils aged between twenty and forty.
B. Primary schools

As early as February 27, in a circular to the rectors, Carnot expressed his intention to improve the condition of primary school teachers: « The condition of primary school teachers is one of the main objects of my solicitude…. It is to them that the foundations of national education are entrusted. It is not only important to raise their status through a fair increase in their salaries; the dignity of their function must be enhanced in every way…. Instead of sticking to the education they have received in elementary school, they must be constantly encouraged to improve it… There is nothing to prevent those who are capable of doing so from rising to the highest echelons of our hierarchy. Their lot in terms of advancement cannot be inferior to that of soldiers; their merit is also entitled to conquer ranks… However, to ensure that all are encouraged to emulate each other in such a glorious way, intermediate positions must be guaranteed. This will naturally be achieved by extending the teaching of mathematics, physics, natural history and agriculture to higher elementary school. In the name of the Republic, primary school teachers will therefore be invited to prepare themselves for the recruitment of staff for these schools. This is one of the complements to the establishment of primary teacher training colleges. It is in the interest of the Republic that the doors of the university hierarchy should be opened as wide as possible to these popular magistrates ».
On June 30, the Minister therefore tackled primary education. Before him, the ordinance of February 29, 1816 had marked a turning point. It established a cantonal committee to oversee schools and, in article 14, obliged communes, without giving them the means to do so, to « ensure that the children who live there receive primary education, and that indigent children receive it free of charge ». In short, primary education was left entirely to the communes, which in turn, for lack of premises and resources, called on religious congregations.
The minister therefore proposed « to raise the status of teachers by transforming them from commune officials into state officials », to emancipate them from local potentates, parents and clerics. For « it is certainly necessary that the teacher be accepted in his commune, but if he depends too much on it, he is not considered enough. It is therefore important that he cannot be capriciously dismissed ». With this in mind, he abolished the « certificate of morality », which had tied schoolteachers to the Church and, incidentally, to the government.
In addition to the compulsory schooling (for both sexes and for communes of at least 300 inhabitants) and total free education already mentioned, he wanted to complete the curricula to form a « uniform core curriculum (…) designed to review everything and serve to determine vocations », prefiguring the school of Jules Ferry and going further than just reading, writing and arithmetic.
In addition to national history and geography, several of Carnot’s favorite subjects, singing, natural history and linear drawing – three subjects designed to develop and educate – there are several specific features to be found in the new texts. The first, which would be taken up again thirty years later, is a kind of civic instruction that the Minister describes as « the duties and rights of man and citizen, the development of feelings of liberty, equality and fraternity (…), the basis of a civic education for the republican education of the country ».
Hippolyte had been elected to the Constituent Assembly on April 23, 1848. When, on May 10, 1848, the « Executive Commission » (May 9 – June 28, 1848) replaced the « Provisional Government » (February 24 – May 9, 1848), he retained his portfolio; but the executive, « in order to strengthen the revolutionary element », appointed Jean Reynaud (1806-1863), a former Saint-Simonian like himself, also elected as a representative, as Under-Secretary of State: I knew the real moderation of his principles, » Carnot wrote; « he knew the firmness of mine, and together we laughed at the role they were trying to assign him« . Edouard Charton (1807-1890), also a former Saint-Simonian and now a member of the Assembly, resigned as Secretary General, but continued his good offices without an official title.
Among Carnot’s actions in this second period of his ministry, we should mention the tabling, on June 3, of a draft decree opening a credit of 995,000 francs, intended to increase, for the second half of 1848, the salaries of those primary schoolteachers whose fixed and contingent salaries remained below six hundred francs; and a second credit, of 105,000 francs, intended to assist, during 1848, female communal schoolteachers whose fixed and contingent salaries remained below four hundred francs (the decree was voted on July 7).
C. Explanatory memorandum to the June 1848 School Act
The drafting of the primary education law continued in a small committee, charged with coordinating the work prepared by the High Commission. It was completed in the course of June, but the submission of the draft, delayed by events, could only take place on June 30, 1848. The explanatory statement reads as follows:
« Citoyens représentants, the difference between the Republic and the monarchy should nowhere be more profoundly demonstrated, in the field of public education, than in what concerns elementary school. Since the free will of the citizens must henceforth give the country its direction, it is on the proper preparation of this will that the future salvation and happiness of France will depend.
« The purpose of primary education is thus clearly defined. It is no longer simply a matter of equipping children with the notions of reading, writing and grammar; the State’s duty is to ensure that all children are brought up to be truly worthy of the great name of citizen that awaits them. Primary education must therefore include everything necessary for the development of the human being and the citizen, as the current conditions of French civilization allow us to conceive them. At the same time as introducing a greater body of knowledge into this teaching, it must also contribute more directly to moral education, and particularly to the consecration of the great principle of fraternity that we have inscribed on our flags, and which it is essential to make penetrate and live everywhere in people’s hearts if it is to be truly immortal.
« It is here, citizens, that primary education joins religious education, which is not the responsibility of the schools, but to which we sincerely appeal, to whatever religion it relates, because there is no more solid and general basis for the love of men than that which is deduced from the love of God.
« The establishment of the Republic, in giving primary education this new tendency, also required, as natural consequences, two important measures, which are to make this education free and compulsory.
« We want it to be compulsory, because no citizen can be exempted, without damage to the public interest, from an intellectual culture recognized as necessary for the proper exercise of his personal participation in sovereignty.
« We want it to be free, because we want it to be compulsory, and because there should be no distinction between the children of the rich and those of the poor in the schools of the Republic.
« We ask you to proclaim the freedom of education, i.e. the right of every citizen to communicate to others what he knows, and the right of the father of a family to have his children brought up by the teacher of his choice. We consider the declaration of this right as one of the legitimate and sincere applications of the word of liberty that our Republic has enthusiastically thrown into the world (…). (…) It even seemed to us that it would not be the least of the means of raising the standards of public schools to allow private schools to flourish, on condition that in this career of emulation, the former did not lack any favorable chance (…) In a word, citizens, the idea according to which we have directed ourselves has been the continual union of the principle of authority with that of liberty. (…) It is in this conciliation between two equally respectable principles that the whole spirit of the law we have the honor of submitting to you consists. »
Source : Hippolyte Carnot, Bulletin des lois, 1848
D. Schoolteachers called to enlighten the countryside

On March 5, a decree set April 9 as the date for convening the electoral assemblies for the appointment, by universal suffrage, of the « Constituent Assembly », which would sit from May 4 to 26. These were the first elections since 1792 to be held by universal male suffrage.
By decision of the Second Republic, the number of voters, which rose to 9,395,035, was multiplied by 40 !
However, as we have said, while Hippolyte Carnot was theoretically in favor of universal suffrage, with the vast majority of French people uneducated, the expression of the vote was likely to lead to disaster. No part of primary education, he writes, « has been more neglected under previous governments than the training of children as citizens ». As a result, many of the voters who have just been invested with the right to vote by the decree of the provisional government are not, especially in the countryside, sufficiently educated in the interests of public affairs.
To try and enlighten these voters about their rights and freedoms, Carnot appealed to schoolteachers:
« Encourage those around you who are capable of such a task to compose short manuals for your schoolteachers, with questions and answers, on the rights and duties of citizens. See to it that these books reach the teachers in your jurisdiction, and that they become in their hands the text of profitable lessons. This is what is going to be done in Paris before my eyes; imitate it. Let our 36,000 primary schoolteachers rise to my call and immediately become the repairers of public education for the rural population. May my voice reach even our last villages! I beg them to do their part in founding the Republic. It’s not a question of defending it against the danger of its borders, as it was in the days of our fathers; it’s a question of defending it against ignorance and lies, and it’s up to them to do this. New men, that’s what France needs. A revolution must not only renew institutions, it must also renew men. You change your tools when you change your work. This is a fundamental principle of politics. But schoolteachers, in enlightening voters, must not only teach them to choose the representatives most capable of consolidating the democratic regime; they can do more: « Why shouldn’t our primary schoolteachers put themselves forward, not only to teach this principle, but to take their place among these new men? There are some, I have no doubt, who are worthy: let a generous ambition ignite in them; let them forget the obscurity of their condition; it was most humble under the monarchy; it becomes, under the Republic, most honorable and most respected (…) Let them come among us, in the name of these rural populations in whose bosom they were born, whose sufferings they know, whose misery they share only too much. Let them express within the legislature the needs, wishes and hopes of this element of the nation, so vital and so long neglected. Such is the new service which, in these revolutionary times, I claim from the zeal of Messieurs les instituteurs primaires. »
These were words the like of which France had not heard since Year II. They caused deep emotion; they put the flame in the heart of all that was young and generous in the primary teaching staff, at the same time as they produced the most lively irritation in the conservative camp. Furious, Léon Faucher wrote to a friend on March 7: « Read Carnot’s circular to the rectors. It’s a masterpiece of madness!«
The Minister’s call for textbooks on the rights and duties of the citizen was heard. In several académies, rectors had civic education catechisms written and published. In Paris, the historian Henri Martin published a Manuel de l’instituteur pour les élections; the philosopher Charles Renouvier published, under the auspices of the Minister, a Manuel républicain de l’homme et du citoyen: both works were sent to the rectors and distributed by them.
Their electoral efforts were not crowned with success. The elections finally held on April 23 gave a majority to the moderates (« camouflaged monarchists » and « moderate republicans »). The « advanced » Republicans, including Carnot, were clearly defeated. The new assembly met on May 4. It proclaimed the Republic and put an end to the existence of the provisional government. It elected an « Executive Commission » from which the most progressive elements of the provisional government were excluded.
E. Secondary Education
Then, on February 28, a circular outlined the program of the Minister and his collaborators, « unfolding the general principles of our undertaking », said Carnot. It read:
« It is necessary, in the interests of society, that a certain number of citizens should receive knowledge beyond that which is sufficient to ensure human development. The establishment of secondary education is the answer. The republican government intends to recruit these essential agents from the mass of the people. It is therefore necessary to ensure that the doors of secondary education are not closed to any of the elite students who perform in primary schools. All necessary measures will be taken in this respect. – It is only in the higher schools that the principle of specialization, cautiously prepared for in the others, should fully take shape. No one can be denied access to the lessons of these schools; but it is with a view to students worthy of serving the general interest that they must be instituted. Only the decision of examinations can confer full rights. »
F. School of Administration
A decree dated March 8, 1848 announced that a:
« School of Administration, intended for the recruitment of the various branches of administration hitherto lacking preparatory schools, will be established on a basis similar to that of the Ecole Polytechnique ».
For Carnot, the aim was to create a home capable of « radiating » the « republican light » throughout France, by promoting the philosophical values of human rights. It was not up to the private sector, but rather the State, to establish « a seedbed for public service » by training administrators who would devote themselves body and soul to the general interest. In the absence of sufficient subsidies, the school was set up in a dilapidated building, the former Collège du Plessis, and the Ministry provided the chairs; students were required to attend lectures at the Collège de France, which were then repeated and commented on by lecturers. The curriculum was eclectic: alongside vocational training, « a large part was devoted to scientific studies, but also to literary studies, which furnish the intellect and give it breadth ». Unlike today’s ENA, this school did not teach « management » and statistics, but architecture, drawing, art history and oriental religions. Caught up in the political turbulence, this school did not survive the minister who founded it, but it would go on to become a benchmark.
G. High Commission for Scientific and Literary Studies
In preparation for a new law on primary education, and to find solutions to the new issues that were arising, Carnot set up a High Commission for Scientific and Literary Studies, chaired by Jean Reynaud, and including « the most notable men and friends of progress in the sciences, letters, administration and, above all, teaching ». Among the 45 members of the Commission were songwriter Pierre-Jean de Béranger, Boussingault, Henri Martin, Poncelet, Edgar Quinet and Charles Renouvier.
H. Lifelong Education for all
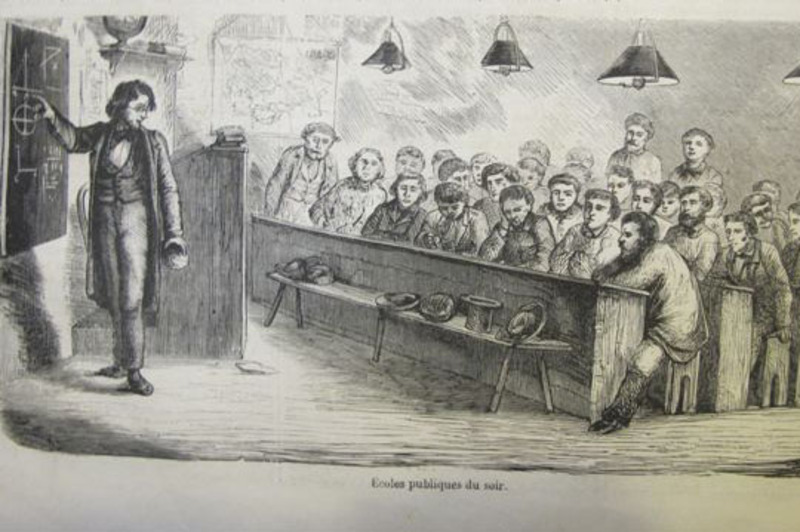

In terms of education, the situation in 1848 remained disastrous. Out of 300,000 conscripts, more than 112,000 could neither read nor write. Among the oldest, the proportion was even higher. Hence the decree of June 8, which instituted public evening readings in Paris, « intended to popularize knowledge of the masterpieces of our national literature ». These readings were to take place twice a week, « in various venues located, as far as possible, in the most populous districts of Paris ».
The Minister’s priority target is the peasants – two-thirds of the population – who have no association structures and are far from the towns and schools. It was they who had to be converted by reading, the key to education and emancipation, and brought into the schools:
« The teachers, now librarians, will read to them, aloud and intelligibly, and will be able to instruct them, interest them and (…) enthuse them about the political life of the country. Teachers, according to their availability, will provide general instruction in agricultural matters and readings in the schoolhouse or town hall, for civics and even literature. »
I. People’s Libraries

Based on the observation that « we lack reading books for the people as there are elsewhere », the Minister set up a vast public network of communal libraries of all sizes. He commissioned the publisher Paulin to assemble collections of the widest possible variety of books in every city district and rural canton, and make them available to the public free of charge. He also created a whole range of complementary establishments, such as special libraries near faculties, to make the most learned knowledge available to as many people as possible. Based on an idea by Jules Simon, he set out to create popular and rural libraries, which he renamed « circulating collections », with teachers who would « travel to small villages and bring to isolated children the instruction they could not find elsewhere ». The « missionary librarians » of these itinerant establishments would be « teacher-curators of the little people’s library », guiding the public, checking loans and reading on demand.
The creation of an official Service des lectures publiques du soir in the spring of 1848 should be seen in this bibliophile light. The aim was always the same: to give the best to the people. As Émile Deschanel explains:
« The Minister of the Republic wanted the sovereign people to have their own readers and teachers too. This service, as political as it is moral, is reminiscent of the sessions organized by philanthropists and Saint-Simonians, intended to replace cabarets and over-served balls. They would enable the worker (and later the peasant) tired « of daily toil to find a convenient asylum, a pleasure that would carry with it instruction, good advice and the familiarity of the great minds of our race ».
The aim was to popularize heritage texts and, if necessary, to comment on them in order to « nobly instruct listeners while amusing them », as the former Saint-Simonian Sainte-Beuve put it. The program of these readings must be varied to avoid fatigue. The great classics such as Corneille and Molière alternated with Michelet-style history, which had an obvious civic function, and comedies or songs such as those by Béranger.
The first Parisian screenings, attended by respectful workers and craftsmen, were a success « in an attentive silence where the slightest impressions were painted on faces ». The Minister noted amused reactions to the comedies, patriotic ones to the evocation of great battles such as Crécy, critical ones to the pompous style and bewildered ones to the Fables de la Fontaine. With this in mind, the Ministry envisaged the creation of a free Athénée based on the German and American models. The idea would be to bring together a handful of teachers in an amphitheater or former auditorium to offer free tuition, open to all and delivered by « pioneers in as yet unexplored fields » of science and technology.
J. Fine Arts, Hygiene and Gymnastics
In addition to « elements of national history and geography », he added French, public law and hygiene, not forgetting gymnastics to improve the health of the most disadvantaged. This was the adult version of what the new school and republican instruction would offer all French children. These courses should even bring art within everyone’s reach, through the promotion of heritage: « Is there a more powerful means of popular education? » he says, referring to art in general and the Beaux-Arts in particular.
In concrete terms, on March 29, the Minister and thirteen teachers founded the Association Philotechnique to provide workers with the professional and technical knowledge required for modern trades. The association agreed on courses in geometry, grammar, algebra, mechanics and drawing, to be given in the rooms of the Halle aux draps, and later at the École Turgot. Teachers from Parisian high schools are the first to be called on by the association to complete the training in history and law. The experiment began in early April, with 150 dyer-workers from the faubourg Saint-Marcel learning about science in the amphitheater of the pharmacy school. Vocational training soon spread to the provinces, including Orléans, before disappearing in the tumult of June.
Carnot wanted to go further, and envisaged « club-schools » based on the Scottish model of « Mechanic-institutions », i.e. lecture halls, libraries and permanent courses for workers in buildings adjoining factories. Keeping abreast of Braille’s work, he also took an interest in the deaf and blind, for whom he intended to multiply the number of specialized institutions under his ministry, rather than the Interior.
K. Citizen Concord
To crown this democratization, Carnot considered one of the Revolution’s most original methods: civic education through public festivals. At the end of February, he had already tested their civic virtues by taking part in the planting of a Tree of Liberty, a ritual practice in 1848, in the gardens of Saint-Nicolas in Paris. In this establishment specialized in the education of workers’ children, the ceremony was placed under the sign of the Three Colors. The clergyman blessed the tree, as is customary, in the presence of the mayor of the arrondissement. The Minister’s speech was edifying:
« The tree you are planting is as young as the Republic itself (…) It will spread its branches over you, just as the Republic will spread the benefits of popular education over France. (…) Good pupils become good citizens ».
The Minister of Education was also impressed by the « Fête de la Concorde » on March 21, between the Bastille and the Champ de Mars, with its parades, civic statuary, reviews of industrial works, hymns to the Republic and reformist enthusiasm. This civic pedagogy seemed effective to him, thanks to its symbolic representation of the regime and its « crowd of men obeying a common inspiration ».
18. Conclusion
By way of conclusion, here’s the end of that of Remi Dalisson, whose magnificent biography of Hippolyte Carnot we highly recommend:
« His practice is his legislative texts on instruction, including school curricula, as varied as they are innovative, like those of his School of Administration or the ‘nursery school’. They make Carnot the undisputed precursor of Jules Ferry and the educational and civic project of the Third Republic. His laws and decrees were designed (…) to emancipate children and turn them into active, critical citizens in a peaceful, moderate and socially fluid democracy, under the aegis of restored teachers, symbols of the new times.
« His practice was his fights and commitments, first and foremost in the opposition, to which he belonged for a long time. His early writings against the death penalty, his participation in the events of 1830, his role in the 1848 Assembly, his fight for teachers, for whom he spent lavishly, and his voluntary exile are all worthy of note. (…)
« In a century crushed by the memory of two world wars, by the erasure of the Republic under Vichy and then by decolonization and the fall of Communism, forgetting 1848 and its social and educational hopes speaks volumes about our mental structures and our memory. This kind of amnesia, which does not prevent the often anachronistic sacralization of the republican corpus, has consigned Hippolyte Carnot and the whole of the 19th century to a sad oblivion. The period no longer evokes much of anything, apart from the occasional spotlight. It has even been sacrificed in teaching, as if only the 20th century were worthy of study.
« At a time when the French educational model is being called into question, when the republican school is doubting its missions, when secularism is also being discussed and when teachers feel abandoned, it is more necessary than ever to understand the roots of an educational system intimately linked to the republican regime. To this end, at the dawn of the 21st century, a reappraisal of the life and work of Hippolyte Carnot, a staunch defender of freedom, schools, Clio and the Republic, can lay the foundations for renewed, civic-minded reflection on the school system.«
19. Appendix: list of works by Hippolyte Carnot
- Gunima, an 18th-century African short story (Paris, Barba, 1824).
- Le Gymnase, a collection of morals and literature (Paris, Balzac, 1828).
- Doctrine de Saint-Simon (Brussels, Hauman, 1831).
- Mémoires de Grégoire, Évêque constitutionnel de Blois (Paris, Dupont, 6 vols., 1837-1845).
- Quelques réflexions sur la domesticité (Paris, Henry, 1838).
- Rapport sur la législation qui règle dans quelques états d’Allemagne les conditions de travail des jeunes ouvriers (Paris, Imp. Royale, 1840).
- Mémoires de Barère de Vieuzac (avec David d’Angers) (Paris, Labitte, 4 volumes, 1842-1844).
- L’Allemagne avant l’invasion française (Fragments*, Paris, Revue indépendante, 1842).
- L’Allemagne pendant la Révolution (Fragments*, Paris, Revue indépendante, 1843).
- Les Esclaves noirs (Paris, Magasin pittoresque, 1844).
- De l’esclavage colonial (Paris, Revue indépendante, 1845).
- Les Radicaux et la Charte, (Paris, Pagnerre, 1847).
- Le Ministère de l’Instruction Publique et des Cultes, 24 février-5 juillet 1848 (Paris, Pagnerre, 1848).
- Éducation républicaine, (Paris, Prost, 2 vols., 1849).
- L’insurrection littéraire en Allemagne (Fragments*, Paris, Liberté de penser, 1848).
- Le Mémorial de 1848, (Paris, Revue indépendante, n.p. 1849).
- Doctrine saint simonienne (Paris, Librairie nouvelle, 1854).
- Mémoires sur Lazare Carnot par son fils (Paris, Pagnerre, 1861-63, reed. in 1893 and 1907, Hachette).
- Œuvres de Saint-Simon by Enfantin, preceded by two historical notes by H. Carnot (Paris, Dentu, 1865).
- La Révolution française, résumé historique (2 vols., Paris, Dubuisson et Pagnerre, 1867).
- L’Instruction populaire en France (Paris, Degorce-Cadot, 1869).
- Trois discours sur l’instruction publique, (Paris, Degorce-Cadot, 1869).
- Cours de l’association philotechnique pour l’instruction gratuite des adultes (Paris, Parent, 1872).
- Ce que serait un nouvel Empire (Paris, Société du patriote, Bibliothèque utile, 1874).
- Lazare Hoche, général républicain (Paris, Société du patriote, Bibliothèque utile, 1874).
- D’une École d’Administration (Versailles, Aubert, 1878);
- Henri Grégoire, évêque républicain (Paris, Libraire des publications populaires, 1882).
- La Révolution française (Paris, Boulanger, 1888).
- Les premiers échos de la Révolution française au-delà du Rhin (Paris, Picard, 1888).
20. Short list of books and articles consulted
- Rémi Dalisson, Hippolyte Carnot, la liberté, l’école et la République, CNRS Editions, Paris 2011.
- Paul Carnot, Hippolyte Carnot et le ministère de l’Instruction publique de la IIe République, PUF, Paris, 1948.
- Jacques Cheminade, Lazare Carnot, l’organisateur de la victoire.
- Jacques Cheminade, L’exemplarité de l’oeuvre d’Henri Grégoire et de Lazare Carnot, 2005.
- Jacques Cheminade, Dino di Paoli and Claude Albert, L’Ecole polytechnique et la science de l’éducation républicaine, Campaigner publications, 1980.
- Website: Le temps des instituteurs.
- Karel Vereycken, The statue of Gutenberg in Strasbourg, the republican fight of David d’Angers.
- José Manuel Menudo, Une apologie des physiocrates par Condorcet, Dixhuitième siècle N° 46, pp 657 to 672.
- Condorcet, De l’influence de la révolution d’Amérique sur l’Europe (excerpts).
- Manuel Albertone, Condorcet, Jefferson and America.
- Dorette Huggins, John Adams and his reflections on Condorcet.
- E. -T. Hamy, Correspondance d’Alexandre de Humboldt avec François Arago, 1907, Paris.
Uccello, Donatello, Verrocchio and the art of military command


Uccello, Donatello, Verrocchio and the art of military command. An inquiry into the key events and artistic achievements that created the Renaissance. By Karel Vereycken, Paris.
Prologue

If there is still a lot to say, write and learn about the great geniuses of the European Renaissance, it is also time to take an interest in those whom the historian Georgio Vasari condescendingly called « transitional figures ».
How can one measure the contributions of Pieter Bruegel the Elder without knowing Pieter Coecke van Aelst? How can we value Rembrandt’s work without knowing Pieter Lastman? How did Raphaelo Sanzio innovate in relation to his master Perugino?
In 2019, an exceptional exhibition on Andrea Del Verrocchio (1435-1488), at the National Gallery in Washington, D.C., highlighted his great achievements, truly inspiring outbursts of great beauty that his pupil Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519) would theorize and put to his greatest advantage.
The sfumato of Leonardo ? Verrochio is the pioneer, especially in the blurred features of portraits of women made with mixed techniques (pencil, chalk and gouache).

The joy of discovery
Leafing through the catalog of this exhibition, my joy got immense when I discovered (and to my knowledgne nobody else seems to have made this observation before me) that the enigmatic angel the viewer’s eye meets in Leonardo’s painting titled The Virgin on the Rocks (1483-1486) (Louvre, Paris), besides the movement of the body, is grosso modo a visual “quote” of the image of a terra cotta high relief (Louvre, Paris) attributed to Verrochio and “one of his assistants”, possibly even Leonardo himself, since the latter was training with the master as early as age seventeen ! The finesse of its execution and drapery also reminds us of the only known statue of Da Vinci, The Virgin with the laughing Child.


Many others made their beginnings in Verrocchio’s workshop, notably Lorenzo de Credi, Sandro Botticelli, Piero Perugino (Raphael’s teacher) and Domenico Ghirlandaio (Michelangelo’s teacher).
Coming out of the tradition of the great building sites launched in Florence by the great patron of the Renaissance, Cosimo de Medici for the realization of the doors of the Baptistery and the completion of the dome of Florence by Philippo Brunelleschi (1377-1446), Verrocchio conceived his studio as a true “polytechnic” school.
In Florence, for the artists, the orders flowed in. In order to be able to respond to all requests, Verrocchio, initially trained as a goldsmith, trained his students as craftsman-engineer-artists: drawing, calculation, interior decoration, sculpture, geology, anatomy, metal and woodworking, perspective, architecture, poetry, music and painting. A level of freedom and a demand for creativity that has unfortunately long since disappeared.
The Ghiberti legacy

In painting, Verrocchio is said to have begun with the painter Fra Filippo Lippi (1406-1469). As for the bronze casting trade, he would have been, like Donatello, Masolino, Michelozzo, Uccello and Pollaiuolo, one of the apprentices recruited by Lorenzo Ghiberti (1378-1455) whose workshop, starting from 1401, over forty years, will be in charge of casting the bronze bas-reliefs of two of the huge doors of the Baptistery of Florence.
Others suggest that Verrocchio was most likely trained by Michelozzo, the former companion of Ghiberti who said up shop with Donatello. As a teenager, Donatello had accompanied Brunelleschi on their joint expeditions to Rome to investigate the legacy of Greek and Roman art, and not only the architectural legacy.
In reality, Verrocchio only perpetuated and developed the model of Ghiberti’s « polytechnic » studio, where he learned the art. An excellent craftsman, Ghiberti was also goldsmith, art collector, musician and humanist scolar and historian.
His genius is to have understood the importance of multidisciplinarity for artists. According to him « sculpture and painting are sciences of several disciplines nourished by different teachings ».
The ten disciplines that he considered important to train artists are grammar, philosophy, history, followed by perspective, geometry, drawing, astronomy, arithmetic, medicine and anatomy.
You can discover, says Ghiberti, only when you managed to isolate the object of your research from interfering factors, and you can discover by detaching oneself from a dogmatic system;
as the nature of things want it, the sciences hidden under artifices are not constituted so that the men with narrow chests can judge them.
Anticipating the type of biomimicry that will characterize Leonardo thereafter, Ghiberti affirms that he sought:
to discover how nature functioned and how he could approach it to know how the objects come to the eye, how the sight functions and in which way one has to practice sculpture and painting.
Ghiberti, who was familiar with some of the leading members of the circle of humanists led by Salutati and Traversari, based his own reflexions on optics on the authority of ancient texts, especially Arabic. He wrote:
But in order not to repeat in a superficial and superfluous way the principles that found all opinions, I will treat the composition of the eye particularly according to the opinions of three authors, namely Avicenna [Ibn Sina], in his books, Alhazen [Ibn al Haytam], in the first book of his perspective, and Constantine [Qusta ibn Luqa] in the first book on the eye; for these authors are sufficient and treat with more certainty the things that interest us.
Deliberately ignored (but copied) by Vasari, Ghiberti’s Commentaries are a real manuel for artists, written by an artist. Most interestingly, it is by reading Ghiberti’s Commentaries that Leonardo da Vinci became familiar with important Arab contributions to science, in particular the outstanding work of Ibn al Haytam (Alhazen) whose treatise on optics had just been translated from Latin into Italian under the title De li Aspecti, and is quoted at length by Ghiberti in his Commentario Terzio. Author A. Mark Smith suggests that, through Ghiberti, Alhazen’s Book of Optics
may well have played a central role in the development of artificial perspective in early Renaissance Italian painting.

Ghiberti’s comments are not extensive. However, for the pupils of his pupil Verrocchio, such as Leonardo, who didn’t command any foreign language, Ghiberti’s book did make available in italian a series of original quotes from the roman architect Vitruvius, arab scientists such as Alhazen), Avicenna, Averroes and those european scientists having studied arab optics, notably the Oxford fransciscans Roger Bacon, John Pecham and the Polish monk working in Padua, Witelo.
Finally, in 1412, Ghiberti, while busy coordinating all the works on the Gates of the Baptistry, was also the first Renaissance sculptor to cast a life-size statue in bronze, his Saint John the Baptist, to decorate Orsanmichele, the house of the Corporations in Florence.
Lost wax casting
However, in order to cast bronzes of such a size, the artists, considering the price of metal, would use the technique known as “lost wax casting”.
This technique consists of first making a model in refractory clay (A), covered with a thickness of wax corresponding to the thickness of the bronze thought necessary.
The model is then covered with a thick layer of wet plaster (B) which, as it solidifies, forms an outer mold. Finally, the very hot molten bronze, pored into the mold it penetrates by rods (J) provided for this purpose, will replace the wax.
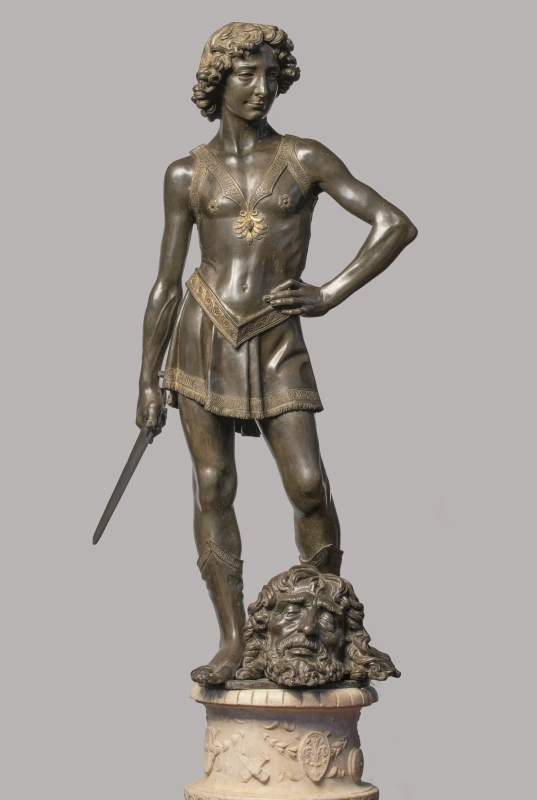

Finally, once the metal has solidified, the coating is broken. The details of the bronze (K) are then adjusted and polished (L) according to the artist’s choice.
This technique would become crucial for the manufacture of bells and cannons. While it was commonly used in Ifé in Africa in the 12th century for statuary, in Europe it was only during the Renaissance, with the orders received by Ghiberti and Donatello, that it was entirely reinvented.
In 1466, after the death of Donatello, it was Verrocchio’s turn to become the Medici’s sculptor in title for whom he produced a whole series of works, notably, after Donatello, his own David in bronze (Bargello National Museum, Florence).
If with this promotion his social ascendancy is certain, Verrocchio found himself facing the greatest challenge that any artist of the Renaissance could have imagined: how to equal or even surpass Donatello, an artist whose genius has never been praised enough?
Equestrian art
This being said, let us now approach the subject of the art of military command by comparing four equestrian monuments:
- Roman Emperor Marcus Aurelius on the Capitoline square in Rome (175 AD) ;
- Paolo Uccello’s fresco of John Hawkwood in the church of Santa Maria del Fiore in Florence (1436);
- Erasmo da Narni, known as “Gattamelata” (1446-1450), casted by Donatello in Padua.
- Bartolomeo Colleoni by Andrea del Verrocchio in Venice (1480-1488).
Equestrian statues appeared in Greece in the middle of the 6th century B.C. to honor the victorious riders in a race. From the Hellenistic period onward, they were reserved for the highest state figures, sovereigns, victorious generals and magistrates. In Rome, on the forum, they constituted a supreme honor, subject to the approval of the Senate. Apart from being bronze equestrian statues, each one is placed in a place where their troops fought.
While each statue is a reminder of the importance of military and political command, the way in which this responsibility is exercised is quite different.
Marcus Aurelius in Rome

Marcus Aurelius was born in Rome in 121 A.D., into a noble family of Spanish origin. He was the nephew of the emperor Hadrian. After the death of Marcus Aurelius’ father, Hadrian entrusted him to his successor Antonin. The latter adopts and gives him an excellent education. He was initiated early in philosophy by his master Diognetus.
Interested in the stoics, he adopted for a while their lifestyle, sleeping on the ground, wearing a rough tunic, before he was dissuaded by his mother.
He went to Athens in 175 A.D. and became a promotor of philosophy. He helps financially the philosophers and the rhetoricians by granting them a fixed salary. Concerned with pluralism, he supported the Platonic Academy, the Lyceum of Aristotle, the Garden of Epicurus and the Stoic Portico.
On the other hand, during his reign, persecutions against Christians were numerous. He saw them as troublemakers – since they refused to recognize the Roman gods, and as fanatics.

Erected in 175 A.D., the statue was entirely gilded. Its location in antiquity is unknown, but in the Middle Ages it stood in front of the Basilica of St. John Lateran, founded by Constantine, and the Lateran Palace, then the papal residence.
In 1538, Pope Paul III had the monument of Marcus Aurelius transferred to the Capitol, the seat of the city’s government. Michelangelo restored the statue and redesigned the square around it, one of the fanciest in Rome. It is undoubtedly the most famous equestrian statue, and above all the only one dating back to ancient Rome that has survived, the others having been melted down into coins or weapons…
If the statue survived, it is thanks to a misunderstanding: it was thought that it represented Constantine, the first Roman emperor to have converted to Christianity at the beginning of the 4th century, and it was out of the question to destroy the image of a Christian ruler.
Neither the date nor the circumstances of the commission are known.
But the presence of a defeated enemy under the right foreleg of the horse (attested by medieval testimonies and since lost), the emperor’s gesture and the shape of the saddle cloth, unusual in the Roman world, make us to belief that the statue commemorated Marcus Aurelius’ victories, perhaps on the occasion of his triumph in Rome in 176, or even after his death. Indeed, his reign (161-180) was marked by incessant wars to counter the incursions of Germanic or Eastern peoples on the borders of an Empire that was now threatened and on the defensive.
The horse, while not that large, but looking powerful, has been sculpted with great care and represented with realism. Its nostrils are strongly dilated, its lips pulled by the bit reveal its teeth and tongue.
One leg raised, he has just been stopped by his rider, who holds the reins with his left hand. Like him, the horse turns his head slightly to the right, a sign that the statue was made to be seen from that side. Part of his harness is preserved, but the reins have disappeared.
The size of the athletic rider nevertheless dominates that of a powerful horse that he rides without stirrups (accessories unknown to the Romans). He is dressed in a short tunic belted at the waist and a ceremonial cloak stapled on the right shoulder. It is a civil and not a military garment, adapted to a peaceful context. He is wearing leather shoes held together by intertwined straps.
The statue is striking for its size (424 cm high) and for the majesty it exudes. Without armor or weapons, eyes wide open and without emotion, the emperor raises his right arm. His authority derives above all from the function he embodies: he is the Emperor who protects his Empire and his people by punishing their enemies without mercy.
The fresco by Paolo Uccello

In 1436, at the request of Cosimo de’ Medici, the young Paolo Uccello was commissioned to paint a fresco depicting John Hawkwood (1323-1394), the son of an English tanner who had become a warlord during the Hundred Years’ War in France and whose name would be Italicized into Giovanno Acuto.
Serving the highest bidder, especially rival Italian cities, Hawkwood’s company of mercenaries was no slouch.
In Florence, although it may seem paradoxical, it was the humanist chancellor Coluccio Salutati (1331-1406) who put Hawkwood at the head of a regular army in the service of the Signoria.
This approach is not unlike that of Louis XI in France, who, in order to control the skinners and other cutthroats who were ravaging the nation, did not hesitate to discipline them by incorporating them into a standing army, the new royal army.
The humanists of the Renaissance, notably Leonardo Bruni (1370-1440) in his De Militia (1420), became aware of the curse of using mercenaries in conflicts and of the fact that only standing army, i.e. a permanent army formed of professionals and even better by citizens and maintained by a state or a city could guarantee a lasting peace.
Although Hawkwood faithfully protected the city for 18 years, his ugly “professionalism” as a mercenary was not unanimously accepted, to the point of inspiring the proverb “Inglese italianato è un diavolo Incarnato” (« An Italianized Englishman is a devil incarnate »).
Petrarch denounced him, Boccaccio tried in vain to mount a diplomatic offensive against him, St. Catherine of Sienna begged him to leave Italy, Chaucer met him and, no doubt, used him as a model for The Knight’s Tale (The Canterbury Tales).
All this will not prevent Cosimo, a member of the humanist conspiracy and a great patron of the arts, returning from exile, from wanting to honor him. But in the absence of the bronze equestrian statue (which had been promised to him…), Florence, will only offer him a fresco in the nave of Santa Maria del Fiore, that is to say under right under the cupola of the Duomo.

From the very beginning, Paolo Uccello’s fresco seems to have stirred quite a controversy. A preparatory drawing in the collections of Florence’s Uffizi Museum indicates the commander, more armed, taller, and, with his horse in a more military position. Uccello had originally depicted Hawkwood as « more threatening », with his baton raised and horse « at the ready ».
A recent ultraviolet study confirms the fact that the painter had originally depicted the condottiere armed from head to toe. In the final version, he wears a sleeveless jacket, the giornea, and a coat; only his legs and feet are protected by a piece of armor. The final version presents a less imposing rider, less warlike, more human and more individualized
In the dispute, it was not Uccello who was considered faulty, but his sponsors. Moreover, the painter was quickly given the task of redoing the fresco in a way deemed “more appropriate”.

Unfortunately, there is no record of the debates that must have raged among the officials of the church fabric (Opera Del Domo). What is certain is the fact that in the final version, visible today, the condottiere has been transformed from a warlord running a gang of mercenaries, into the image of philosopher-king whose only weapon is his commanding staff. At the bottom of the fresco, we can read in Latin: “Giovanno Acuto, British knight, who was in his time held as a very prudent general and very expert in military affairs.”
The position of the horse and the perspective of the sarcophagus have been changed from a simple profile to a di sotto in su view.
If this perspective is somewhat surrealistic and the pose of the horse, raising both legs on the same side, simply impossible, it remains a fact that Uccello’s fresco will set “the standards” of the ideal and impassive image of virtue and command that must embody the hero of the Renaissance: his goal is no longer to “win” a war (the objective of the mercenary), but to preserve the peace by preventing it (the objective of a philosopher-king or simply a wise head of state).
Paradigm shift
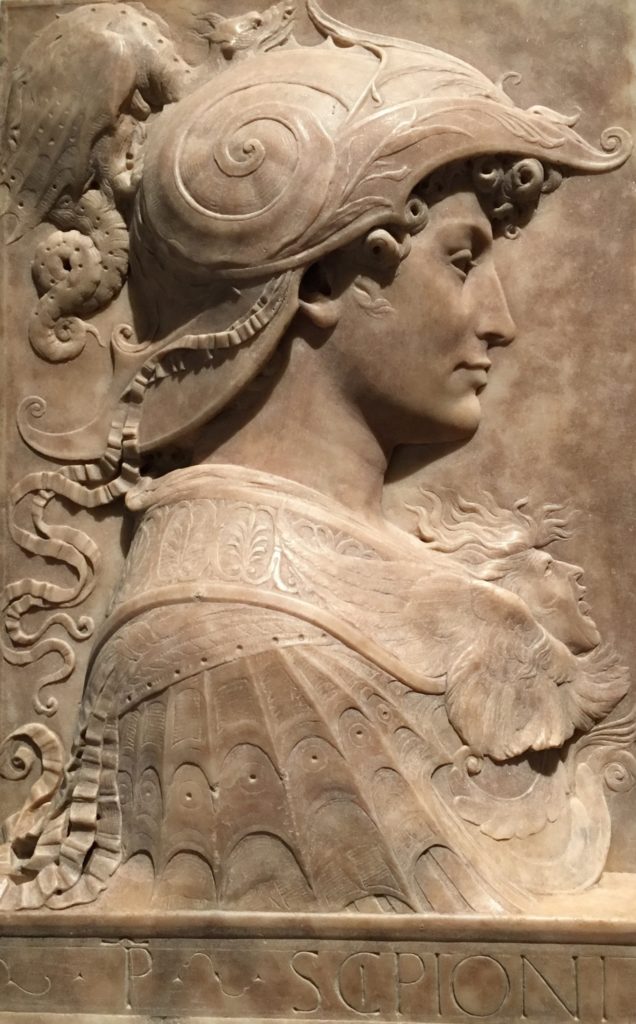



As such, one might say that Uccello’s fresco announces the “paradigm shift” marking the end of the age of perpetual feudal wars, to that of the Renaissance, that is to say to that of a necessary concord between sovereign nation-states whose security is indivisible, the security of one being the guarantee of the security of the other, a paradigm even more rigorously defined in 1648 at the Peace of Westphalia, when it made the agapic notion of the “advantage of the other” the basis of its success.
One historian suggests that the recommissioning of Uccello’s fresco was part of the « refurbishing » of the cathedral associated with its rededication as Santa Maria del Fiore by the humanist Pope Eugene IV in March 1436, determined to convince the Eastern and Western Churches to peacefully overcome their divisions and réunite as was attempted at the Council of Florence of 1437-1438 and for which the Duomo was central.
Interesting is the fact that Uccello’s fresco appeared at around the same time that Yolande d’Aragon and Jacques Coeur, who had his Italian connections, persuaded the French king Charles VII to put an end to the Hundred Years’ War by setting up a permanent, standing army.
In 1445, an ordinance was passed to discipline and rationalize the army in the form of cavalry units grouped into Compagnies d’Ordonnances, the first permanent army at the disposal, not of warlords or aristocrats, but of the King of France.
Donatello’s “Gattamelata” (1447-1453)

It was only some years later, in Padua, between 1447 and 1453, that Donatello would work on the statue of Erasmo da Narni (1370-1443), a Renaissance condottiere, i.e. the leader of a professional army in the service of the Republic of Venice, which at the time ruled the city of Padua. An important detail is that Erasmo was nicknamed “il Gattamelata”.
In French, « faire la chattemite » means to affect a false air of sweetness to deceive or seduce… Others explain that his nickname of “honeyed cat” comes from the fact that his mother was called Melania Gattelli or that he wore a crest (a helmet) in the shape of a honey-colored cat in battle…
The man was of humble origin, the son of a baker, born in Umbria around 1370. He learned to handle weapons from Ceccolo Broglio, lord of Assisi, and then, when he was in his thirties, from the captains of Braccio da Montone, who was known for recruiting the best fighters.
In 1427, Erasmo, who had the confidence of Cosimo de’ Medici, signed a seven-year contract with the humanist Pope Martin V, who wished to strengthen an army corps loyal to his cause with the aim of bringing to heel the lords of Emilia, Romagna and Umbria who were rebellious against papal authority.

He bought a huge suit of armor to reinforce his high stature. He was not an impetuous fighter, but a master of siege warfare, which forced him to take slow, thoughtful and progressive action. He spied on his prey for a long time before trapping it.
In 1432, he captured the fortress of Villafranca near Imola by cunning alone and without fighting. The following year he did the same to capture the fortified town of Castelfranco, thus sparing his soldiers and his treasure.
Those who were unable to grasp his tactics, accused him of being a coward for “running away” from the front-line, not realizing, that on a given moment, this was part of the tactics of his winning strategy.
He was a prudent captain, with a very well-mannered troop, and he was careful to maintain good relations with the magistrates of the towns that employed him. He obtained the rank of captain-general of the army of the Republic of Venice during the fourth war against the Duke of Milan in 1438 and died in Padua in 1443. Following his death, the Venetian Republic gave him full honors and Giacoma della Leonessa, his widow, commissioned a sculpture in honor of her late husband for 1650 ducats.
The statue, which represents the life-size condottiere, in antique-style armor and bareheaded, holding his commanding staff in his raised right hand, on his horse, was made by the lost-wax method. As early as 1447, Donatello made the models for the casting of the horse and the condottiere. The work progresses at full speed and the work is completed in 1453 and placed on its pedestal in the cemetery that adjoins the Basilica of Padua.

Brilliant for his cunning and guile, Gattamelata was a thoughtful and effective fighter in action, the type of leader recommended by Machiavelli in The Prince, and which appears in the sixteenth century by François Rabelais in his account of the “Picrocholine wars”.
Not the brute power of weapons, but the cunning and the intelligence will be the major qualities that Donatello will make appear powerfully in his work.
Contrary to Marcus Aurelius, it is not his social status that gives the commander his authority, but his intelligence and his creativity in the government of the city and the art of war. Donatello had an eye for detail. Looking at the horse, we see that it is a massive animal but far from static. It has a slow and determined gait, without any hesitation.
But that’s not all. A rigorous analysis shows that the proportions of the horse are of a “higher order” than those of the condottiere. Did Donatello make a mistake and make Erasmo too small and the horse too large? No, the sculptor made this choice to emphasize the value of Gattamelata who, thanks to his skills, is able to tame even wild and gigantic animals. In addition, the horse’s eyes show him as wild and untameable. Looking at him, one could say that it is impossible to ride him, but Gattamelata manages it with ease and without effort.
Because if you look at the reins in the hands of the protagonist, you will notice that he holds them in complete tranquility. This is another detail that highlights Erasmus’ powerful cunning and ingenuity.
Next, did you notice that one of the horse’s legs rests on a sphere? If this sphere (which could also be a cannonball, since Erasmus was a warrior) serves to give stability to Donatello’s composition as a whole, it also indicates how this animal of gigantic strength (symbolizing here warlike violence), once tamed and well used, allows the globe (the earthly kingdom) to be kept in balance.
Having told you about the horse, it is time to know more about the condottiere.
He has a proud and determined expression. The baton of command, which he holds in his hand, delicately touches the horse’s mane. The baton is not just a symbolic object; he may have received it in 1438 from the Republic of Venice.
Unlike Uccello’s fresco, Gattamelata is not dressed as a contemporary prince of commander, but as a figure beyond time embodying both the past, the present and the future. To capture this, Donatello, who takes care of every detail, has taken an ancient model and modernized it with incredible results. The details of the protagonist’s armor include purely classical motifs such as the head of Medusa, taken from Marcus Aurelius, in Greek mythology one of the three gorgons whose eyes had the power to petrify any mortal who crossed her gaze.
Although the helmet of Gattamelata would have allowed to identify him at eyesight, Donatello has discarded this option. With a helmet on his head, he would have been the symbol of a bloodthirsty warrior, rather than a cunning man. Even better, the absence of a helmet allows the artist to show us a fearless commander whose fixed gaze shows his determination. With the figure slightly bowed and legs extended, the sword in its scabbard placed at an angle, Donatello gives the illusion of an “imbalance” that reinforces in the viewer’s mind the idea that the horse is advancing with full strength.
Art historian John Pope-Hennessy is emphatic:
The fundamental differences between the Gattamelata and Marcus Aurelius are obvious. The (roman) emperor sits passively on his horse, legs dangling. In the fifteenth century, on the other hand, the art of riding implies the use of spurs. The impression of authority that emanates from the monument designed by Donatello comes from the total domination of the condottiere over his horse. (…) The soles of the feet are exactly parallel to the surface of the pedestal, as are the large six-pointed spurs, stretched to the middle of the animal’s flank.
As a result, Gattamelata is not a remake of the “classical Greek or Roman sculpture” of a hero with a sculpted physique, but a kind of new man who succeeds through reason. The fact that the statue has such a high pedestal also has its reason. Placed at such a height, the Gattamelata does not “share” our own space. It is in another dimension, eternal and out of time.
Verrocchio’s Colleoni
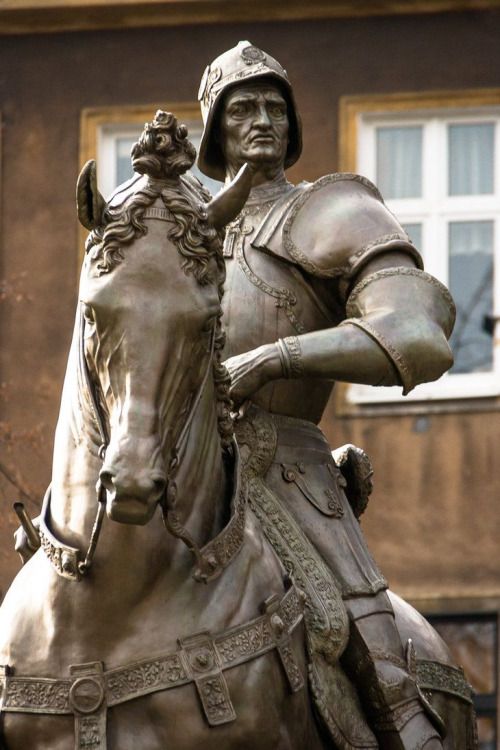

Some thirty years later, between 1480 and 1488, Andrea del Verrocchio, after a contest, was selected to make a large bronze equestrian statue of another Italian condottiere named Bartolomeo Colleoni (1400-1475).
A ruthless mercenary, working for a patron one day and his rival the next day, he served from 1454 the Republic of Venice with the title of general-in-chief (capitano generale). He died in 1475 leaving a will in which he bequeathed part of his fortune to Venice in exchange for the commitment to erect a bronze statue to his honor in St. Mark’s Square.
The Venetian Senate agreed to erect an equestrian monument to his memory, while charging the costs to the widow of the deceased…
In addition, the Senate refused to erect it in St. Mark’s Square, which was, along with St. Mark’s Basilica, at the heart of the city’s life. The Senate therefore decided to interpret the conditions set by Colleoni in his last will and testament without contradicting them, choosing to erect his statue in 1479, not in St. Mark’s Square, but in an area further from the city center in front of the Scuola San Marco, on the campo dei Santi Giovanni e Paolo.
Although Verrocchio had started working on the project since 1482, it remained unfinished at his death in 1488. And it is, not as Verrocchio wished, his heir Lorenzo di Credi who will cast the statue, but the Venetian Alessandro Leopardi (who lost the contest to Verrocchio), who will not hesitate to sign it!

If the horse is in conformity with the typology of the magnificent horses composing the quadriga overseeing the Basilica of Saint Mark of Venice (Greek statuary of the IVth century BC brought back by the crusaders from Constantinople to Venice in 1204) and of the horse of Marcus Aurelius, its musculature is more nervously underlined and traced. Objectively, this statue is ideally more proportionate. There is also more fine detail, a result of new pre-sculpture techniques, making the work captivating and realistic to look at.
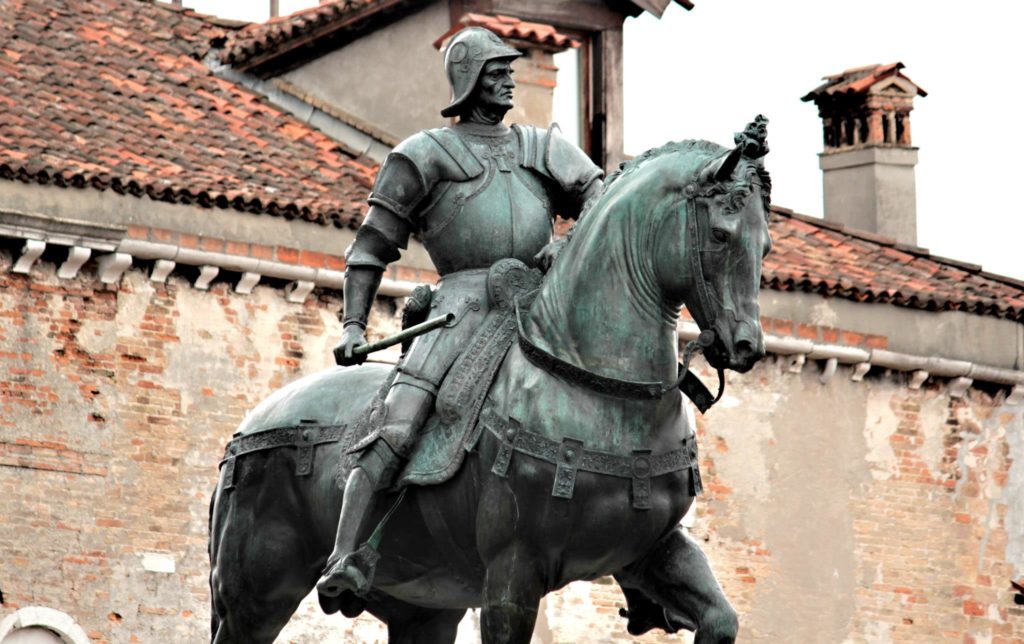

The sculpture overflows its pedestal. According to André Suarès quoted in The Majesty of Centaurs:
Colleone on horseback walks in the air, he will not fall. He cannot fall. He leads his earth with him. His base follows him […] He has all the strength and all the calm. Marcus Aurelius, in Rome, is too peaceful. He does not speak and does not command. Colleone is the order of the force, on horseback. The force is right, the man is accomplished. He goes a magnificent amble. His strong beast, with the fine head, is a battle horse; he does not run, but neither slow nor hasty, this nervous step ignores the fatigue. The condottiere is one with the glorious animal: he is the hero in arms.
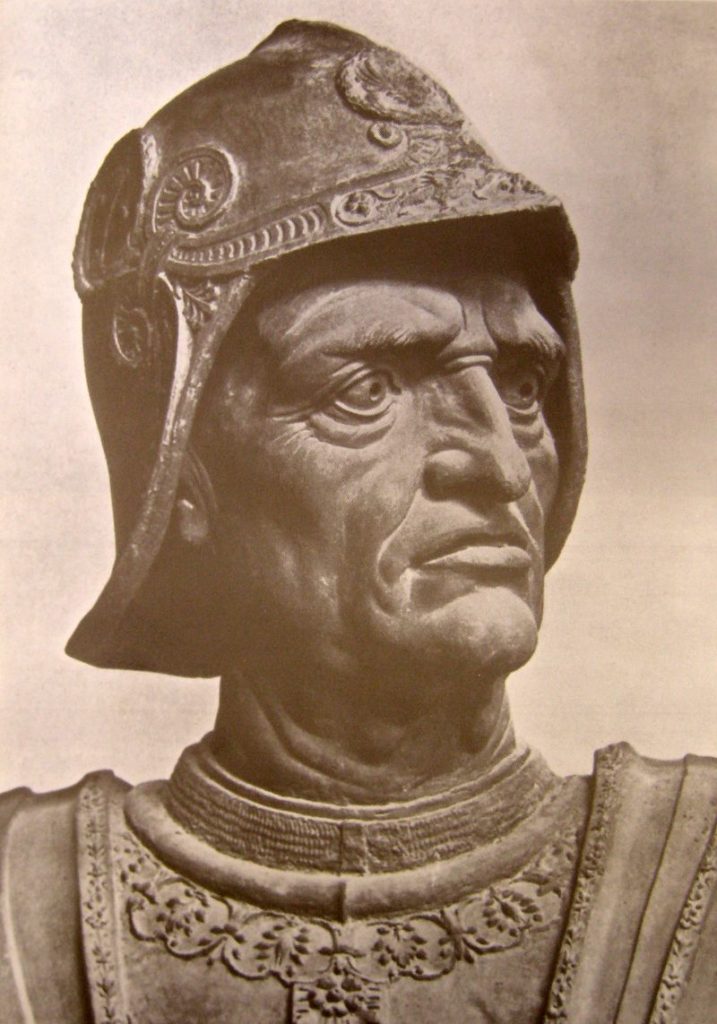

His baton of command is even metamorphosed into a bludgeon! But since it is not Verrocchio who finished this work, let us not blame the latter for the warlike fury that emanates from this statue.
Venice, a vicious slave-trading financial and maritime Empire fronting as a “Republic”, clearly took its revenge here on the beautiful conception developed during the Renaissance of a philosopher-king defending the nation-state.
On the aesthetic level, this mercenary smells like an animal. As a good observer, Leonardo warned us: when an artist represents a man entirely imprisoned by a single emotion (joy, rage, sadness, etc.), he ends up painting something that takes us away from the truly human soul. This is what we see in this equestrian statue.
If, on the contrary, the artist shows several emotions running through the figure represented, the human aspect will be emphasized. This is the case, as we have seen, with Donatello’s Gattamelata, uniting cunning, determination and prudence to overcome fear the face of threat.
Leonardo’s own, gigantic project to erect a gigantic bronze horse, on which he worked for years and developed new bronze casting techniques, unfortunately was never build, seen the hectic circumstances.
Finally, beyond all the interpretations, let us admire the admirable know-how of these artists. In terms of craft and skill, it generally took an entire life to become able to realize such great works, not even mentioning the patience and boundless passion required.
Up to us to bring it back to life !
Bibliography:
- Verrocchio, Sculptor and Painter of Renaissance Florence, Andrew Butterfield, National Gallery, Princeton University Press, 2020;
- Donatello, John Pope-Hennessy, Abbeville Press, 1993;
- Uccello, Franco and Stefano Borsi, Hazan, 2004;
- Les Commentaires de Lorenzo Ghiberti dans la culture florentine du Quattrocento, Pascal Dubourg-Glatigny, Histoire de l’Art, N° 23, 1993, Varia, pp. 15-26;
- Monumento Equestre al Gattamelata di Donatello: la Statua del Guerriero Astuto, blog de Dario Mastromattei, mars 2020;
- La sculpture florentine de la Renaissance, Charles Avery, Livre de poche, 1996 ;
- La sculpture de la Renaissance au XXe siècle, Taschen, 1999;
- Ateliers de la Renaissance, Zodiaque-Desclée de Brouwer, 1998;
- Rabelais et l’art de la guerre, Christine Bierre, 2007.
- The Greek language project, Plato and the Renaissance, Karel Vereycken, jan. 2021.