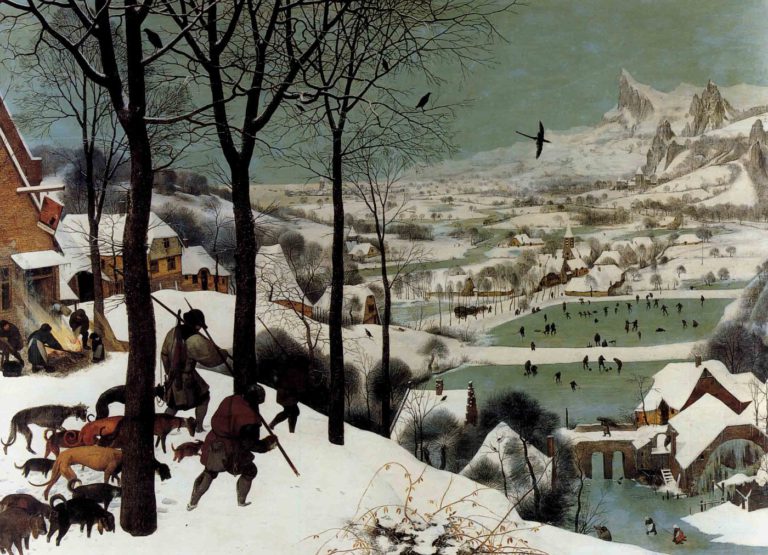
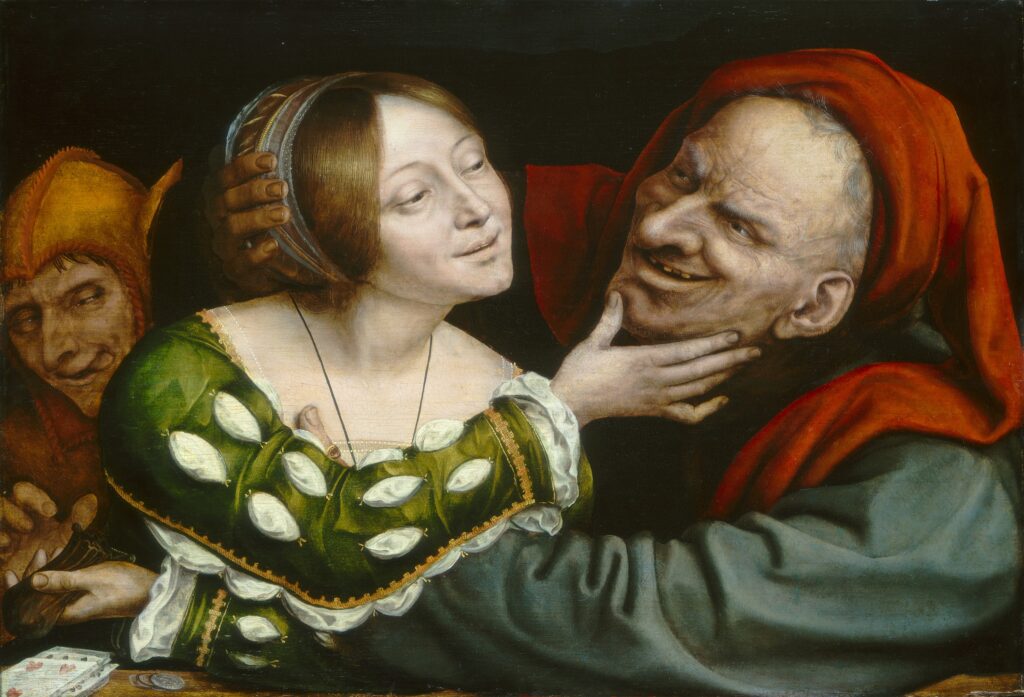
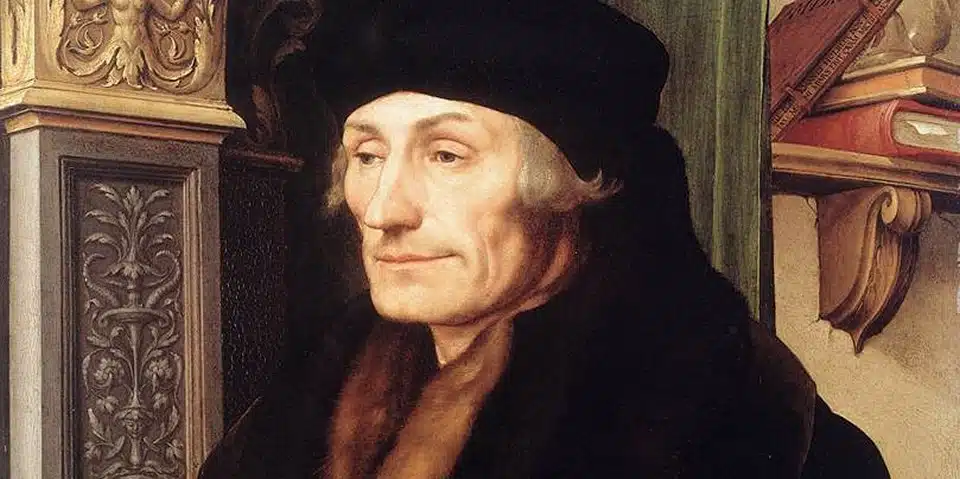
Étiquette : Erasmus
1512-2012: From Cosmography to the Cosmonauts, Mercator and Frisius


ARTKAREL AUDIO GUIDE — Matsys and the Art of « The Deal » (Berlin)


Comment on Quinten Matsys‘ painting « The Deal » (aka « The Contract ») in the Gemäldegalerie of Berlin, Germany. (June 2025)
For more on this artist, see my study on Matsys and Leonardo, the dawn of the Age of Laughter and Creativity.

Audio:
This Audio
Read:
- Quinten Matsys and Leonardo — The Dawn of the Age of Laugher and Creativity, (EN online);
- Квентин Массейс и Леонардо: на заре смехотворчества (RU pdf)
- Joachim Patinir et l’invention du paysage en peinture (FR en ligne).
- Joachim Patinir and the invention of landscape painting (EN online)
- Le Landjuweel d’Anvers de 1561 — Faire de l’art une arme pour la paix (FR en ligne)
- The 1561 Landjuweel of Antwerp that made art a weapon for Peace (EN online)
Quinten Matsys en Da Vinci – Dageraad van louterend gelach en creativiteit

DEZE TEKST
en français
in English
in Russian (pdf)

Inhoud
Inleiding
A. Culturele en filosofische kwesties van een context
- Cynische grappen of socratische dialogen?
- Wat is « Christelijk humanisme?«
- Petrarca en de “Triomf van de Dood«
- Dageraad van louterend gelach
- Sebastian Brant, Jheronimus Bosch en Het Narrenschip
- Rederijkers en Landjuweel
B. Quinten Matsys
- Biografische elementen
- Van smid tot schilder
- Hertogdom Brabant
- Opleiding: Bouts, Memling en/of Van der Goes?
- Debuten in Antwerpen en in het buitenland
C. Enkele werken, analyses en interpretaties
- De Maagd en het Kind, Gratie Gods en Vrije Wilskeuze
- Het altaarstuk van Sint-Anna
- Een nieuw perspectief
- Samenwerking met Joachim Patinir en Albrecht Dürer
- In de ban van Erasmus
- Utopia en Thomas More
- Pieter Gillis en het « Tweeluik der vriendschap«
- De « Da Vinci-connection » (I)
D. Erasmiaanse kunst van het groteske
- In religieuze schilderijen
- Bankiers, tollenaars en woekeraars
- De da Vinci-connection (II)
- De kunst van het groteske per se
- De metafoor van « Het ongepast koppel«
- Matsys, Da Vinci, wie schilderde de « De groteske oude vrouw »?
- Hans Liefrinck en Hieronymus Cock
- Dood gaan van het lachen, Zeuxis, Matsys en Rembrandt
E. Slotbeschouwing
Bibliografie
Begin 16e eeuw vestigde Quentin Matsys (1466-1530) 1 zich als een vooraanstaand schilder in Antwerpen. Hij werkte er meer dan 20 jaar. Via het werk van Matsys beïnvloedde Erasmus een hele generatie kunstenaars. Bidden en lachen waren de twee kanten van dezelfde munt, die van de « Filosofie van Christus. » Matsys schilderde diepreligieuze drieluiken, verbazingwekkend gedetailleerde portretten en enkele van de meest hilarische satirische werken uit de geschiedenis van de schilderkunst.
Matsys blijft een grote naam, maar zijn werk is bijna vergeten. Om deze grote kunstenaar recht te doen, zullen we hier zijn enthousiasme en zijn Erasmiaanse geest doorlichten. Ook bespreken we enkele van zijn meest originele artistieke bijdragen.

In 1550 was Antwerpen 2 met bijna 100.000 inwoners de grootste stad van het Westen. In het Oosten had Istanboel er al 200.000 in 1500…
Antwerpen was een belangrijke havenstad en het kloppend hart van een bloeiende internationale handel die op het einde van de 15de eeuw het oude Brugge 3 van de Medici overtrof. Antwerpen was een trekpleister voor talenten uit vele streken en landen. 4
Het was in die economische en culturele smeltkroes dat Quinten Matsys meerdere van de briljantste christelijke humanisten van zijn tijd kon ontmoeten, of het nu ging om geleerden en vredesactivisten als Erasmus van Rotterdam 5, Thomas More 6 en Pieter Gillis 7, innovatieve drukkers als Dirk Martens 8 van Aalst, hervormers als Gerard Geldenhouwer 9 en Cornelius Grapheus 10, Vlaamse kunstschilders als Gerard David 11 en Joachim Patinir 12 of buitenlandse schilder-graveurs en boekverluchters als Albrecht Dürer 13, Lucas van Leyden 14 en Hans Holbein de Jongere 15. Antwerpen was the place to be!
Boeken over Quinten Matsys en zijn milieu zijn vandaag moeilijk te vinden en meestal duur. De grote internationale uitgeversbedrijven, om tot zover onbekende redenen, schijnen hem tot eeuwige vergetelheid te hebben veroordeeld. Soms verschijnt zijn naam, maar slechts sporadisch en in de marge en dan nog alleen wanneer er sprake is van het « manierisme » van de « Antwerpse School » 16
Erger nog, er wordt niet naar zijn werken verwezen en zijn naam wordt slechts twee keer vermeld in L’art flamand et hollandais, le siècles des primitifs (1380-1520), een referentienaslagwerk over deze periode. 17
Het goede nieuws is dat het Interdisciplinair Centrum voor Kunst en Wetenschap in Gent, 18 België, sinds 2007 sleutelt aan een nieuwe « Catalogue raisonné » van zijn werk. Maar dat is nog even wachten.
De laatste uitgave van het volledig werk, verzorgd door de Amerikaanse kunsthistoricus Larry Silver, dateert van 1984 19 en wordt vandaag voor hoge prijzen op Amazon aan de man gebracht.
Er bestaat nog de mooie, zeldzame monografie van Andrée de Bosque 20, waarvan helaas de meeste afbeeldingen in zwart-wit zijn. Als troostprijs hebben de lezers nog het proefschrift 21 van Harald Brising uit 1908, herdrukt in 2019.
Om Quinten Matsys te eren en recht te doen, zullen we hier proberen een aantal vragen te beantwoorden die tot nu toe onbeantwoord zijn.
In hoeverre was het werk van Erasmus een directe inspiratiebron voor Matsys, Patinir en hun omgeving? Wat weten we over de uitwisselingen tussen deze kring in Antwerpen en vooraanstaande renaissancekunstenaars als Leonardo da Vinci en Albrecht Dürer? Welke invloed had de Erasmiaanse kunstenaar op zijn buitenlandse correspondenten?
Dit onderwerp roept meteen vragen op, aangezien Erasmus niet echt een liefhebber was van de « religieuze schilderkunst » van zijn eeuw. Hij gaf de voorkeur aan daadwerkelijke inzet en handelingen voor het algemeen belang, boven passieve bewondering en onderwerping aan religieuze rituelen en heiligenbeeldjes.
Zoals de Belgische kunstcriticus Georges Marlier (1898-1968) 22 in zijn gedocumenteerd boek benadrukt, was Erasmus geen amateur van kerkpropaganda, maar als een werk een authentiek gevoel van geloof, liefde en tederheid opriep, bracht hij daar eerbied voor op. Voor onze humanist was de innerlijke strijd van de mens veel belangrijker, gezien
« de ware navolging van Christus en zijn lijden bestaat in het uitdoven van de impulsen die tegenstrijdig zijn met de rede, en niet in het bewenen van Christus als een zielig object. » 23
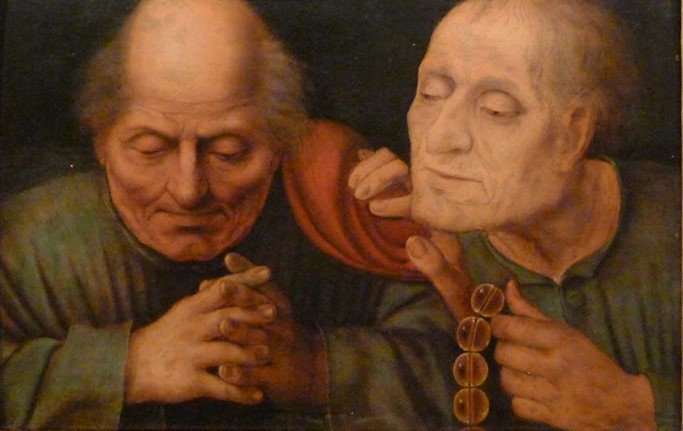

Dankzij eerder onderzoek naar de Italiaanse Renaissance, het levenswerk van Erasmus 24 en de kunst van Dürer 25 hebben we ons verdiept in de tijd van Matsys. We kunnen daar niet hier uitgebreid op terugkomen, maar het biedt ons wel een sterke basis om de buitengewone waarde van deze kunstenaar in te schatten.
A. Culturele en filosofische kwesties van een context
1. Cynische grappen of socratische dialogen?
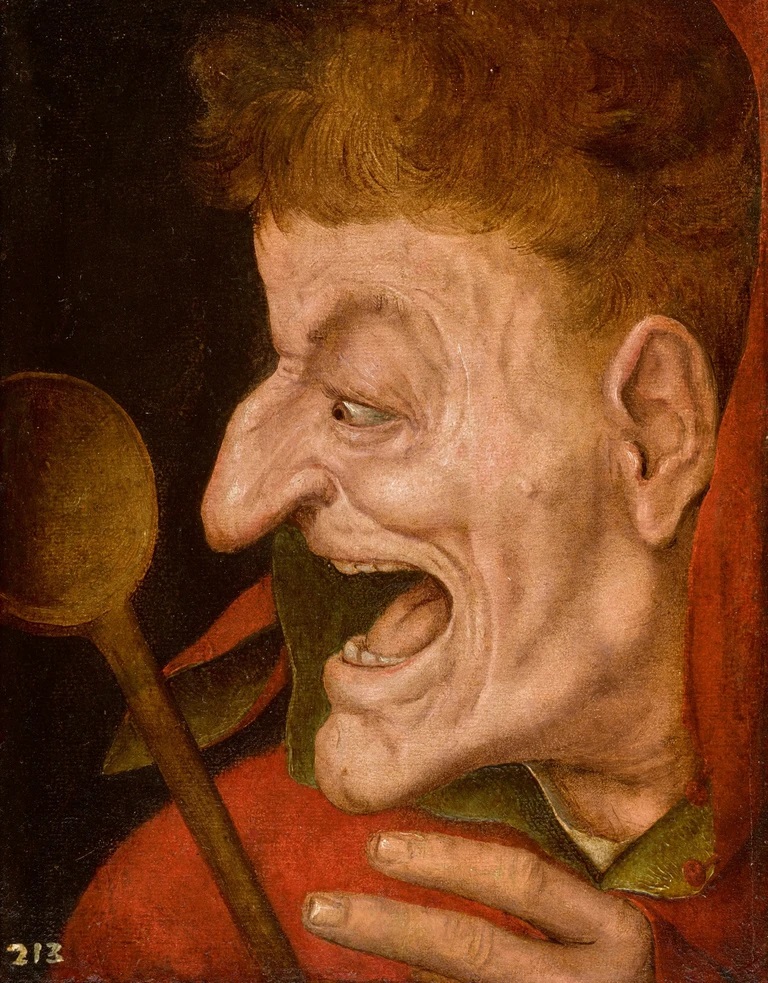

Voor de huidige « trash-cultuur », gebaseerd op emotionele effecten in een soort gevangenis van grenzeloos pessimisme, is het erg moeilijk om de culturele verfijndheid van een Matsys ten volle te waarderen.
Wat ontbreekt, is de morele en intellectuele integriteit die nodig is om de grappen, 26 ironie en metaforen 27 te begrijpen die de essentie vormden van het culturele leven in de Lage Landen van zijn tijd. 28
Veel mensen zien de wereld niet zoals hij is. Wel geven ze uitgebreid commentaar over de kleur van hun bril. Beknot door hun culturele vooroordelen, wanneer ze naar een geschilderd aangezicht kijken, zien ze niet de intentie, de ironisch knipoog of het idee dat de kunstenaar wil overbrengen. Een echte kunstenaar, schildert niet op doek of paneel, maar roept een beeld op in de geest van de toeschouwer. Moderne kijkers vluchten snel weg van het hogere domein van de metafoor. Ze klampen zich vast aan de veelvuldige details wiens symbolische interpretaties ze aan elkaar rijgen, in de hoop dat dit snoer de betekenis zal leveren voor het werk.
Wanneer ze een « grotesk » gezicht zien, houden ze vast aan het idee dat het over een portret gaat van een bepaalde persoon die echt heeft bestaan, in plaats van hardop te lachen! Omdat zij deze « onzichtbare » dimensie niet willen zien en het beeld « letterlijk » opvatten, zijn voor hen de « grotesken » van Erasmus, Matsys en Da Vinci slechts « cynische grappen » die getuigen van sluiks misprijzen en vermoedelijk van een sterk « gebrek van verdraagzaamheid » jegens « lelijke », « zieke », « abnormale », of gewoon « andere », mensen!
Laten we het hier luid en duidelijk herhalen: Erasmus en zijn drie belangrijkste geestelijke volgelingen, François Rabelais, 29 Miguel de Cervantes 30 en William Shakespeare 31, zijn de incarnaties, hoewel zelden erkend, van het « Christelijk humanisme » en de louterend gelach, een machtig politiek wapen en een instrument dat het mogelijk maakt « alle leden van het menselijk genre tot de waardigheid van het menszijn te verheffen », zoals de Franse generaal, medeoprichter van de Ecole Polytechnique, Lazare Carnot, dat formuleerde.
2. Wat is « Christelijk humanisme »?
De kern van Erasmus’ onderwijs- en politiek programma was het bevorderen van docta pietas, geleerde vroomheid, of wat hij de « Filosofie van Christus » noemde. Het is méér dan een overtuiging, een manier van zijn. 32
Deze filosofie kan worden samengevat als een « eedverbond » tussen de humanistische principes samengevat in Plato‘s Republiek 33 en het agape-mensbeeld 34 van het Evangelie en de geschriften van eerste kerkvaders zoals Hiëronymus 35 en Augustinus 36, die Plato en Socrates beschouwden als een van hun onvolmaakte voorlopers.
Het christelijk humanisme was een breuk met het zich onderwerpen aan een ‘blind’ en feodaal geloof, dat de redding van de mens, via de onsterfelijkheid van de ziel, uitsluitend zag in een bestaan na de dood.
Voor het christelijk humanisme is het de essentie van de menselijke natuur naar het hoogste goed te streven. « Hell is empty and all the devils are here » (De Hel is leeg en al de duivels staan hier), schreef William Shakespeare in 1610 in The Tempest.
De oorsprong van het kwaad is niet de mens op zichzelf of een externe « duivel », maar de ondeugden en morele kwalen die Plato al eeuwen vroeger had geïdentificeerd voordat de christenen ze de « zeven hoofdzonden » (ondeugden) noemden, kwalen die men kan beperken, bestrijden en zelfs overwinnen dankzij de « zeven hoofddeugden ». 37

Ter herinnering, deze hoofdzonden en hun tegengif zijn:
- Superbia (hoogmoed, hovaardigheid, ijdelheid, trots, hubris) tegenover Humilitas (nederigheid);
- Avaritia (hebzucht, gierigheid) tegenover Caritas, Agapè (naastenliefde);
- Luxuria (onkuisheid, lust, wellust, hoererij) tegenover Castitas (kuisheid);
- Invidia (nijd, jaloezie, afgunst) tegen Humanitas (goedheid);
- Gula (onmatigheid, gulzigheid, vraatzucht) tegenover Temperantia (matigheid);
- Ira (woede, toorn, wraak, gramschap) tegenover Patientia (geduld);
- Acedia (gemakzucht, traagheid, luiheid, vadsigheid, spleen, melancholie) tegenover Diligentia (ijver);
Het is veelzeggend voor onze tijd dat deze “zonden” (ondeugden of kwalen die ons ervan weerhouden het goede te doen), en niet hun tegengestelde deugden, op tragische wijze zijn geprezen als de « basiswaarden” die het goede functioneren van het huidige “neoliberale” financiële systeem en zijn “op regels gebaseerde” wereldorde garanderen!
“Particuliere ondeugden zorgen voor publieke voordelen,” betoogde Bernard Mandeville in 1705 in De Fabel van de bijen. Het is de dynamiek van particuliere belangen die de welvaart van een samenleving stimuleert, meende deze Nederlandse theoreticus die Adam Smith inspireerde en voor wie « moraliteit » alleen maar lusteloosheid uitlokt en de wereld ongelukkig maakt.
Het zijn hebzucht en het voortdurende nastreven van genot, en niet het algemeen belang, die zijn uitgeroepen tot de essentiële drijfveren van de mens, volgens de filosofische school die dominant werd: het Britse empirisme, verkondigd door Locke, Hume, Smith en hun soortgenoten. De zintuigen, en niet de menselijke rede, zijn de piloot van het menselijke vliegtuig!
Menselijke basiswaarden, zoals liefde voor de medemens en « humanitaire » hulp, worden aldus beperkt tot kortstondige activiteiten. Niet van de overheid, maar van liefdadigheidsinstellingen. Voor de oligarchie blijven ze instrumenten om het juk van het criminele systeem wat draagbaarder te maken voor het te onderwerpen « menselijk vee. » Meer en meer liefdadigheidsinstellingen zijn in de handen van grote patriciërsfamilies en belangrijke NGO’s. Alhoewel hun werk vaak uiterst nuttig is, blijven zij helaas instrumenten van overheersing, een betreurenswaardige realiteit.
3. Petrarca en de “Triomf van de Dood”
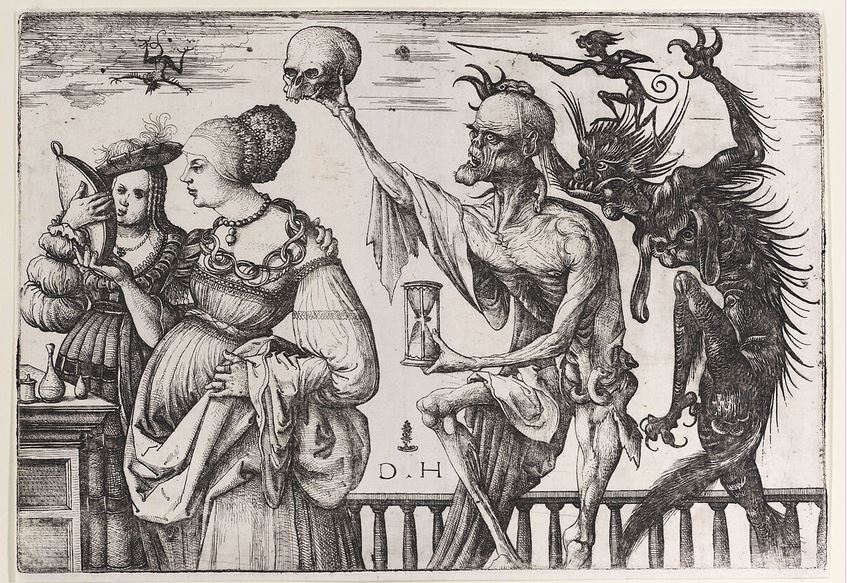

Het ware christendom, net als alle grote humanistische religies, streeft er onvermoeibaar naar om degenen die hun leven in zonde verspillen ertoe te brengen deze ondeugden van zich af te schudden. Dat kan door hen te laten inzien dat hun gedrag niet alleen tragisch, maar totaal lachwaardig is in het licht van de uiterste kortstondigheid van het menselijke fysieke bestaan.
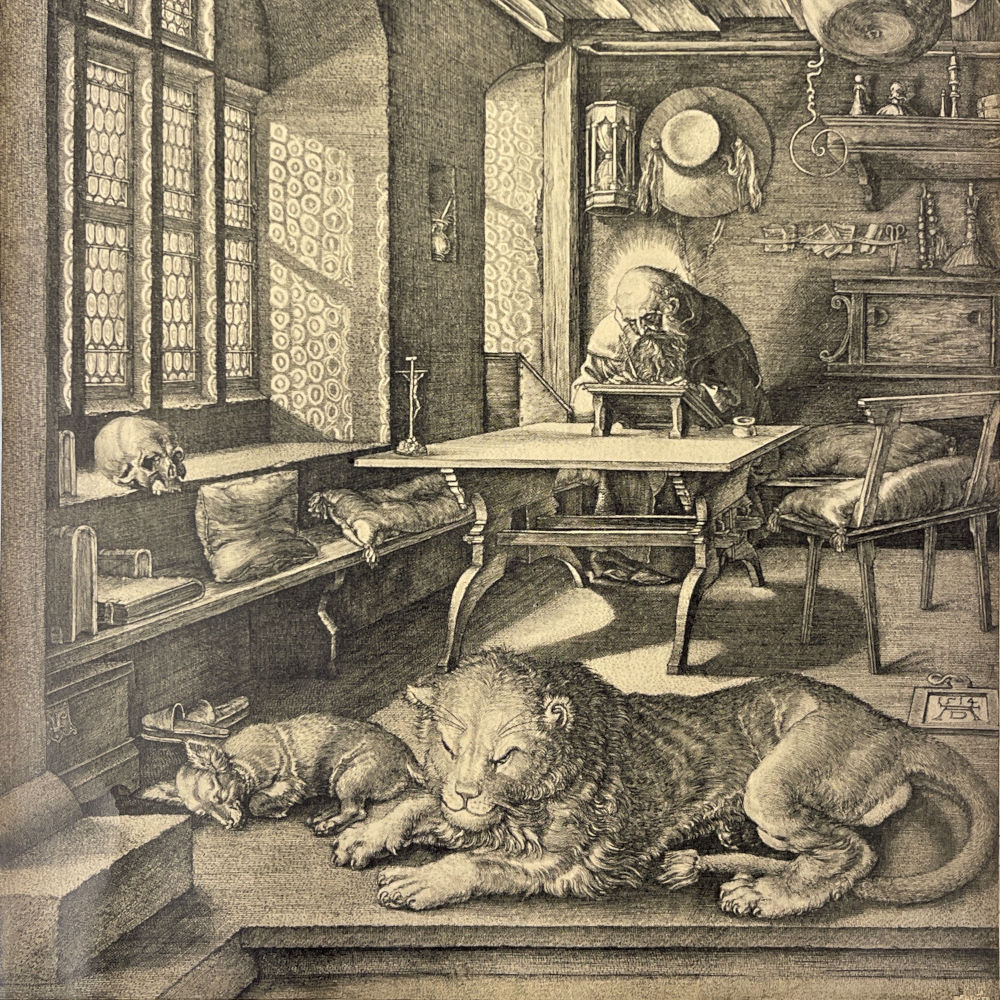



De Duitse kunstenaar Albrecht Dürer, in harmonie met dit Renaissanceparadigma, maakte het tot het centrale thema van zijn drie beroemde Meisterstiche (meestergravures), die als één geheel moeten worden begrepen: De ridder, de dood en de duivel (1513); Hiëronymus in zijn studeervertrek (1514) en Melencolia I (1514). 38
Op elk van deze gravures is een zandloper afgebeeld, een metafoor voor de onstuitbare stroom van de tijd. Door de zandloper (tijd) naast een schedel (dood), een kaars die uitgaat (laatste adem), een verwelkende bloem (de leegte van de passies) enz. te plaatsen, slagen de kunstenaars erin de metafoor van de « ijdelheid » (Vanitas) voor te stellen. 39
Erasmus, die het zandloper/schedelbeeld tot zijn persoonlijk embleem maakte, voegde er het motto aan toe: Concedi Nulli (Ik wijk voor niets, de dood zal niemand sparen, rijk of arm.) In die zin was het christelijk humanisme in de Renaissance een massabeweging die beoogde mensen te onderwijzen over geestelijke « onsterfelijkheid », tegen zowel religieus bijgeloof als tegen een sluipende terugkeer naar het Grieks-Romeinse heidendom.

Met deze filosofische eis treedt Erasmus hier direct in de voetsporen van Petrarca 40 en diens I Trionfi (1351-1374) 41, een gedichtencyclus die is opgebouwd uit zes elkaar opvolgende allegorische triomfen. De « Triomf der Liefde » wordt er overtroffen door de « Triomf der Kuisheid. » Op haar beurt wordt Kuisheid verslagen door de Dood; de Dood wordt overwonnen door Roem; Roem wordt veroverd door de Tijd; en zelfs de Tijd wordt uiteindelijk overwonnen door de Eeuwigheid en uiteindelijk staan we voor de « Triomf van God » over al deze louter aardse aangelegenheden.
Omdat de dood aan het einde van ons vluchtige fysieke bestaan zal « triomferen », is het in de pre-Renaissance visie de angst voor de dood en de vrees voor God die de mens moet helpen zich te richten op het bijdragen van iets onsterfelijks aan toekomstige generaties. Dat is veel beter dan te verdwalen in het labyrint van aardse genoegens en pijnen dat Jheronimus Bosch (1450-1516) 42 met zoveel ironie afbeeldt in zijn Tuin der Wereldse Lusten (1503-1515). 43
Leonardo da Vinci, wiens filosofisch-religieuze opvattingen door velen in het Vaticaan als ketters werden beschouwd, 44 schreef in zijn aantekeningen dat veel mannen en vrouwen, gezien hun gedrag, het prachtige lichaam dat God hen had gegeven niet eens verdienden:
“Zie, er zijn velen die zichzelf louter spijsverteringsstelsels, mestproducenten en latrine-vullers zouden kunnen noemen, want ze hebben geen andere bezigheid in deze wereld; Ze beoefenen geen enkele deugd, er blijft niets van hen over dan volle latrines [toiletten]. » 45
4. De dageraad van louterend gelach

Volgens woordenboeken spreekt men van « good laughter » wanneer we een situatie, die eerst vervelend en moeilijk blijkt, plotseling grappig vinden. Meestal is de oplossing zo eenvoudig, dat we ze niet zien! We lachen dan eigenlijk met de ironie van de situatie, met onszelf en met onze gebreken. Kortom, een goede lach is de beloning voor een authentiek creatief proces, wanneer de agonie van het uitputten van hypothesen in de zoektocht naar oplossingen, zowel voor wetenschappelijke als persoonlijke problemen, eindigt met een vreugdevol Eureka! De gure storm en de donkere wolken zijn door de creatieve winden weggeblazen en een helder licht toont ons plotseling een wijde horizon en een nieuw perspectief.
Op haar blog Angeles Earth, benadrukt de visuele kunstenares Angeles Nieto de innige verbondenheid tussen humor en creativiteit, twee basisingrediënten van de Renaissance:
« Humor volgt niet de lineaire, traditionele, gebruikelijke processen; humor stimuleert flexibel denken en creativiteit. De lach, kun je vergelijken als een schakelaar van jouw cognitieve gedachte, zodat je rationele kant op een bepaalde manier wordt verlamd. We lachen meestal als onze hersenen een verkeerd model herkennen, dat niet op zijn plaats is. Humor toont een nieuw standpunt dat de conventionele discussie ontwricht en bespot. De plotselinge mentale veranderingen die de humor veroorzaakt, zijn ook aanwezig in de creativiteit, we spelen met ideeën, op zoek naar verrassende ideeën. Humor is gebouwd op dissociatie, de mogelijkheid dat twee denkbeelden zich kruisen, zodat de tweede de betekenis van de eerste verandert. Creativiteit werkt onder dezelfde mechanismen als een grap. In beide gevallen gaat het om het verbinden van twee schijnbaar onverbonden ideeën. » 46
Volgens christelijke humanisten kan men de mens vleugels geven door hem te bevrijden van de ondeugd die hem verlaagt.
Een middel daarvoor is hem een spiegel voor te houden, een proces inherent aan de « socratische dialoog ». Ken uzelf! Als hij de moed heeft zichzelf te zien zoals hij is, zal hij misschien zijn onwetendheid aanvaarden. Dat is een eerste vorm van het soort wijsheid dat Cusanus De docta ignorantia 47 of « wetende onwetendheid » noemde.
Via zijn « vrije wilskeuze » kan ieder mens beslissen te handelen (of niet te handelen) in overeenstemming met zijn ware (goede) aard. Een totale toewijding aan het algemeen belang wordt dan een bron van immens plezier, zowel in onze persoonlijke relaties als in onze economische activiteiten. Het is dit doel, namelijk de vorming en de veredeling of verheffing van het persoonlijk karakter, dat de fundamentele doelstelling werd van zowel het christelijk als het republikeins onderwijs. Hoofden vullen met kennis en feiten, is geen doel op zichzelf. Gewetensvolle burgers met eigen kennis en oordeelsvermogen vormen is de echte uitdaging.
Maar door te beweren dat het leven van de mens volledig door God was voorbestemd, ontkende Luther het bestaan van de vrije wilskeuze en maakte hij de mens onverantwoordelijk voor zijn daden. 48
Deze opvatting was het tegenovergestelde van die van Erasmus, die de Kerk al lang vóór Luther had opgeroepen een einde te maken aan haar financiële uitbuiting van geloof, zoals de beroemde « aflaten » (indulgentia). 49
Christelijke humanisten beogen onze zielen te verheffen tot de hoogste graden van morele en intellectuele schoonheid. Ze trachten ons te bevrijden van onze overdreven gehechtheid aan aards plezier en aardse goederen – niet door doempreken, schuldgevoelens of de erg lucratieve handel van « aflaten », maar… dankzij de « louterende werking » (catharsis) van een bevrijdende lach! Keihard tegen de zonden, maar vol liefde en mededogen voor de zondaar die zich inzet voor zelfverbetering.
Oef, we kunnen ademen! Laten we even afstand nemen. Terwijl we serieus bezig zijn met onszelf te verbeteren, laat ons goedhartig lachen om onze onvolkomenheden. God heeft ons het leven gegeven en het is prachtig, zolang we maar weten hoe we het moeten benutten!
De Franse humanist, de socialist Jean Jaurès, vermoedelijk een lezer van Erasmus, zei zelfs:
« De vooruitgang van de mensheid wordt gemeten aan de toegevingen die de zotheid van de wijzen doet aan de wijsheid van de zotten. »
5. Sebastian Brant, Jheronimus Bosch en Het Narrenschip


« Genre-schilderkunst », welke gewone mensen afbeeldt in hun alledaagse activiteiten, ziet de dag met Quinten Matsys (men zou eerder moeten zeggen met het Erasmiaanse paradigma dat we zojuist hebben geïdentificeerd), benadrukt Larry Silver 50, die alzo bevestigt wat Georges Marlier 51 al in 1954 had geschreven.
Enkele jaren voordat Erasmus zijn Lof der Zotheid publiceerde (geschreven in 1509 en al in 1511 in Parijs uitgegeven) 52, opende de humanistische dichter en sociaal hervormer Sebastian Brant (1558-1921) uit Straatsburg het bal van de Socratische lach met zijn Narrenschiff (Het Narrenschip, uitgegeven in 1494 in Bazel, Straatsburg, Parijs en Antwerpen) 53, een hilarisch satirisch werk geïllustreerd door Holbein de Jongere (1497-1543) en Albrecht Dürer (1471-1528), die 73 van de 105 illustraties in de oorspronkelijke uitgave verzorgde.
Het Narrenschip werd een bestseller in heel Europa. De auteur was niet zomaar een simpele satiricus, maar een érudiet humanist wiens vertaling van de gedichten van Petrarca bekend is. 54
Brant was een sleutelfiguur en vriend van Johann Froben (1460-1529) en Johann Amerbach (1441-1513), afkomstig uit Zwitserse drukkersfamilies. Zij verwelkomden later Erasmus, toen de humanist, vervolgd in Leuven en de Lage Landen, gedwongen werd in ballingschap te gaan in Bazel.


Na de heiligen en de vorsten zijn het opeens gewone vrouwen, mannen en kinderen die in de werken verschijnen. Niet meer als « schenkers » die als getuigen aanwezig zijn bij een Bijbels of hemels tafereel, maar vanwege hun eigen kwaliteiten als verdienstelijke menselijke wezens.
Dürer maakte bijvoorbeeld een gravure, zij het enigszins ironisch, van « een kok en zijn vrouw ». 55 In het begin van de 15e eeuw duikt de klassieke Griekse taal terug op in West-Europa; in het begin van de 16de eeuw is het « de man van de straat » die opduikt in kunstwerken.
Met de opkomst van de kleine man, de ambachten en de burgerij verandert fundamenteel de klantenkring van de schilders. De opdrachten komen minder van religieuze orden en rijke kardinalen, meer van welvarende handelaars, burgers, gilden, gemeentes, steden, corporaties, broederschappen en ambachten die hun kapellen en huizen willen verfraaien en hun portretten aan vrienden willen schenken.
De uitbreiding van de Antwerpse markt, waarbij schilderkunst een luxeproduct voor de middenklasse werd, is een goed gedocumenteerd fenomeen. Onderzoek heeft de bewering van Lodovico Guicciardini (1521-1589) 56 bevestigd dat er in de jaren 1560 minstens 300 schilderateliers actief waren in Antwerpen.
Het Narrenschip van Brant was een mijlpaal en een keerpunt, het begin van een nieuw paradigma, van creativiteit, rede en opvoeding door middel van een oprechte, louterende en bevrijdende lach, waarvan de echo nog zeer luid zal weerklinken tot aan de dood van Pieter Bruegel de Oude in 1569. 57
Deze dynamiek kwam in gevaar toen Karel V in 1521 de Inquisitie nieuw leven inblies. Hij voerde de « plakkaten » in om zijn gezag en dat van de kerk te vrijwaren. Dat waren decreten die iedere burger die de Bijbel durfde te lezen en er commentaar op uitbracht, met de dood bestraften.

Het Narrenschip bestaat uit 113 delen. Elk deel, met uitzondering van een korte inleiding en twee afsluitende delen, handelt onafhankelijk van elkaar over een bepaalde klasse zotten, imbecielen of wrede mensen. Slechts af en toe wordt herinnerd aan het basisidee van het schip.
Geen enkele zotheid van de eeuw wordt vergeten. De auteur valt met nobele ijver de fouten en de buitensporigheden van de mens aan.
Het boek begint met de veroordeling van de allergrootste dwaas, degene die weigert de prachtige boeken te lezen die in zijn kas staan. Hij wil zijn hersenpan niet overladen met wijsheid. « Ik heb alles verkregen, » zegt de nar, « van een groot heer die de vermoeidheid van hen die in zijn plaats leren, in baar geld kan betalen. » 58
De derde zotheid (van de 113), die zich aansluit bij de eerste, is hebzucht en gierigheid:
« Het is absurde zotheid om rijkdommen te hamsteren en niet te genieten van de ware vreugde van het leven, de waanzin van de zot die niet weet, wie het goud dat hij opzij heeft gelegd, zal gebruiken op de dag dat hij in het graf zal afdalen. » 59

Deze visie is ook het thema van een drieluik van Jheronimus Bosch dat gedeeltelijk verloren is gegaan. Recentelijk onderzoek heeft aangetoond dat het huidige schilderij van Bosch, Het Narrenschip (Louvre, Parijs), dat mogelijk zelfs werd geschilderd voordat Brant 60 zijn satire schreef, mogelijkerwijs het linkerpaneel is van een drieluik waarvan het rechterpaneel De dood van de vrek (National Gallery, Washington) was. 61
Het interessante aan dit laatste paneel is dat niets fataal is! Zelfs de gierigaard kan tot zijn laatste ademtocht kiezen tussen het opslaan van zijn ogen naar Christus of het neerslaan van zijn ogen naar de duivel!
Dat de mens eeuwig vervolmaakbaar is en dat zijn lot ook afhangt van zijn persoonlijke, vrije wilskeuze, vormde de kern van de leer van de Zusters en Broeders des Gemene Leven, 62 een lekenbeweging van christelijke devotie waarmee Bosch, zonder er lid van te zijn, belangrijke affiniteiten had. Tot op heden blijft her raden naar het onderwerp et de titel van het middenpaneel. Voor het gesloten retabel, denkt men aan een afbeelding van een marskramer die wegloopt van slechte oorden.
Dat is reeds het thema van de buitenpanelen van Boschs drieluik De Hooiwagen. Op het centrale middenpaneel van dit werk ziet men koningen, prinsen en pausen die een kar achtervolgen die geladen is met een gigantische berg hooi (een metafoor voor geld) en door duivels naar de hel worden getrokken.
Het thema van de rondtrekkende marskramer 63 was zeer populair bij de Broeders van het Gemene Leven en de Devotio Moderna. 64 Voor hen, net als voor Augustinus, wordt de mens voortdurend geconfronteerd met een existentiële keuze. Hij bevindt zich voortdurend voor een tweesprong (het bivium). Ofwel kiest hij het moeilijke, rotsige pad dat naar boven loopt en hem dichter bij God brengt, ofwel kiest hij de gemakkelijke weg die naar beneden loopt naar aardse hartstochten, genegenheden, zonde en ondeugd.
Augustinus en later Dionysius de Kartuizer (1403-1471) verwierpen niet de schoonheid van mens en natuur. Ze waarschuwden wel dat we ervan moeten genieten als « een voorproef van de goddelijke wijsheid ». 65
De « marskramer » van Bosch en Patinir is daarom een metafoor voor de mens, die zich permanent onthecht en verder zoekt naar het juiste pad. Bosch schilderde verdwaasde mannen en vrouwen als hersenloze dieren die zich passioneel trachten te verzadigen met kleine vruchtjes zoals kersen, aardbeien en bessen, metaforen voor geld en aardse genoegens. Het bekomen plezier was intens, maar zo vluchtig en onvoldoende, dat men alleen maar dacht, bijna als drugverslaafden, deze ervaring zo snel mogelijk te hernieuwen. Alzo werd de ganse levensloop niets anders dan een permanente wedloop naar plezier dat nooit eindigde in waar geluk.
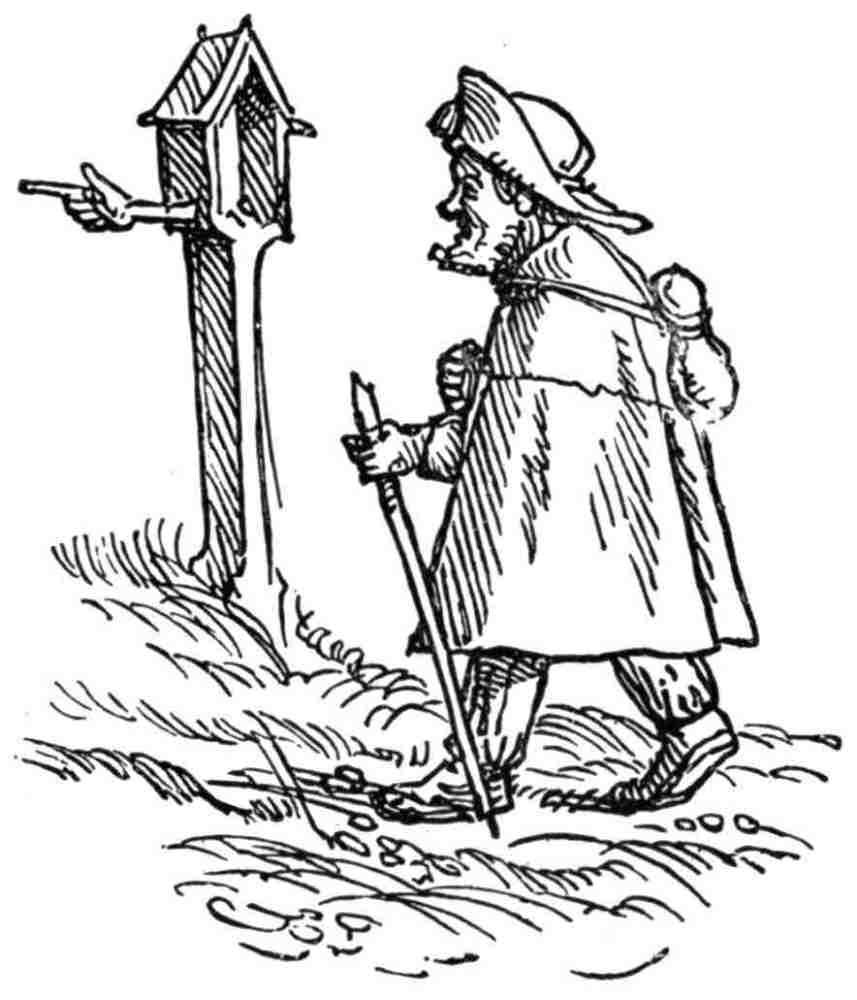

De marskramer gaat « op een slof en een schoen », dat wil zeggen dat hij zijn huis verlaat en de geschapen wereld van zonde (we zien een bordeel, dronkaards, enz.) en alle materiële goederen achter zich laat.
Met zijn « stok » (symbool van geloof) weet hij de « helse honden » (het kwaad) af te weren die hem in de kuiten bijten en hem trachten te weerhouden.
Een illustratie uit een Engels psalmenboek uit de 14e eeuw, het Luttrell Psalter, toont precies dezelfde allegorische voorstelling.
Deze metaforische beelden zijn dus niet het resultaat van een « zieke geest » of een losbandige verbeelding van Jheronimus Bosch, maar citaten van een gemeenschappelijke beeldentaal die we al aantreffen in de marges van verluchte boeken, maar die met Bosch een eigen leven kregen en op de voorgrond kwamen.
Hetzelfde thema, dat van de Homo Viator, de mens die zich onthecht van aardse goederen, komt ook steeds terug in de kunst en literatuur van deze periode, met name sinds de Nederlandse vertaling van De pelgrimstocht van de menselijke ziel, geschreven in 1358 door de Normandische cisterciënzer monnik Guillaume de Degulleville (1295-na 1358).
Christus verandert ons in pelgrims over de hele wereld. Samen met Hem doorkruisen wij de « aardse stad » met als enig doel de « hemelse stad. » Niet langer alleen homo sapiens, maar homo viator, een man op weg naar de hemel.
Hoewel de drie overgebleven delen van Bosch’ drieluik (Het Narrenschip, De dood van de Vrek en De Marskramer) op het eerste gezicht totaal los van elkaar lijken te staan, wordt hun samenhang duidelijk zodra de toeschouwer dit overkoepelende concept identificeert. 66
Voor een hedendaagse kunstenaar, met talent, techniek, humor, ironie en verbeelding, zou het wel eens leuk zijn om het verloren middenpaneel te trachten te schilderen op een passende manier. Het thema is mijns inziens noodzakelijkerwijs de val van de mens die zich niet kan onthechten van aardse goederen, de weg die de toeschouwer leidt van het Narrenschip naar De dood van de vrek.
6. Rederijkers en Landjuweel
De lach van sommigen maakt niet iedereen blij. Spitsige humor en ironie ondermijnen het onrechtmatig gezag van keizers, pausen, bankiers, hertogen en tirannen. Ironie, satire en humor zijn inderdaad de machtigste politieke wapens ooit bedacht. Vervolging, censuur, intimidatie, terreur en bestraffing moeten gedaan maken met humor en ironie.

De golf van culturele emancipatie in de Lage Landen, waar Erasmus en Matsys zelf deel van uitmaakten met hun eigen bijdragen, bereikte een hoogtepunt in de tweede helft van de 16de eeuw en lokte een brutale reactie uit.
Het « begin van het einde » van de Spaanse bezetting in de Lage Landen, aldus de historici, kondigde zich aan toen het Landjuweel 67 werd beknot. Al in de 13de en 14de eeuw waren Landjuwelen wedstrijden in de dichtkunst tussen schuttersgilden in het hertogdom Brabant. In de 15de en de 16de eeuw organiseerden de Rederijkers naar dit voorbeeld wedstrijden tussen de kamers.
Elke wedstrijd werd georganiseerd rond een centrale filosofische vraag, een zinne, bijvoorbeeld: “Wat de mens het meest tot de kunst aanzet » (Antwerpen, 1561) of « “wat de mens in het uur van zijn dood de meeste troost biedt” (Gent, 1539). De kamers moesten dan met een toneelstuk, een spel van zinne (waarbij de zinne de gestelde vraag is) een antwoord geven.
Andere wedstrijdcategorieën waren de vermakelijke, kluchtige toneelstukken, esbattementen, liederen en het rebusblazoen. Dat was een soort wapenschild met daarop een rebus. De oplossing van die rebus was een spreuk of een leus.
De louterende werking van catharsis (zuivering) in komedie en satire is algemeen bekend. Geconfronteerd met de angsten van het dagelijks leven of politieke onderdrukking, zorgt humor voor een onmiddellijke emotionele ontlading, terwijl het tegelijkertijd een kritische afstand biedt die zelfverbetering mogelijk maakt.
Louterend lachen, spot en satire werken bevrijdend, hoewel het gevaar bestaat dat ze ons demobiliseren als ze niet worden gevolgd door een oproep tot actie.

Een absoluut hoogtepunt van volkscultuur in de Lage Landen was het schitterende Landjuweel van 1561 in Antwerpen, op touw gezet door de Antwerpse rederijkerskamer De Violieren. Deze kamer was in feite niets anders dan de letterkundige afdeling van het Sint-Lucasgilde, dat wil zeggen het schildersgilde waarvan Matsys, Patinir, David en andere vrienden van Erasmus leden waren. 68
Veertien kamers van Brabant namen deel. Zo’n 1400 rederijkers te paard, in feestelijk kostuum, met muziek en zang, deden hun intrede in de stad. In de stoet reden 23 praalwagens en 200 andere rijtuigen.
Toneel, dichtkunst, muziek en schilderkunst hadden eenzelfde beeldentaal. Een van deze « punten » (sierlijk opgetuigde praalwagens met allegorisch-moralizerende voorstellingen) gedurende de Onze-Lieve-Vrouwe-ommegang van Antwerpen in 1563 werd omschreven als het soort hooiwagen dat Bosch centraal stelde in zijn schilderij De Hooiwagen (1501, Madrid), een allegorie voor het ziekelijk streven naar « aards gewin » :
« Eene Hoywaghen daer op sittende eene Sater,
ghenaempt Bedrieghelijck aen locken,
achter volghende alle Natie van volck, treckende aen het Hoy,
als Woekeners, Cassiers, Creemers &c. midts dat ertsch ghewin al hoy is »
(Een hooiwagen met daarop een sater met de naam « de Bedrieglijke Verleiding » en daarachter allerlei soorten volk, zoals woekeraars, bankiers en marskramers, die aan het hooi trekken, terwijl aards gewin allemaal hooi is). 69

Hetzelfde thema staat ook centraal in een gravure van Frans Hogenberg van 1559. Op deze prent is het volk rondom de hooiwagen in groepjes verdeeld en voorzien van bijschriften. Zo staat bij een van deze groepjes te lezen:
« Geestelyck weerlijck het sij in wat staten
Vint men ghebreck tot allen stonden
Daer om doeghet goet en willet quaet laten
Want anders (Ilaes) eest al hoy bevonden. »
(Geestelijke en wereldlijke personen van alle rangen blijken voortdurend gebreken te vertonen. Doe daarom het goede en vermijd het kwaad. Want anders zal het (helaas) allemaal hooi blijken te zijn). 70

De toneelvoorstellingen vinden plaats op een fraai versierd houten podium op de Grote Markt, voor de werf van het nieuwe stadhuis. Het is ontworpen door Cornelis II Floris de Vriendt (1514-1575). De inleidende spelen zijn geschreven door de « factor » van de Violieren, Willem van Haecht (c. 1530-1585).
Het spel van zinnen moet een antwoord geven op de vraag “wat de mens het meest tot de kunst aanzet”. Twee honderd jaar voor Immanuel Kant en Friedrich Schiller, beschouwde men de opwaardering van kunst als belangrijk instrument voor humanisering en politieke ontvoogding.
Het Landjuweel en de Ommegang waren volksfeesten waar « alles mocht », waar de « kleine man » met satires, vermommingen en spotliederen de verdrukker mocht beschimpen en voor de zot houden en alzo, al was het voor een héél kort moment, het juk van Spanje wat draagbaarder werd.
De meeste allegorische toneelstukken die werden opgevoerd, waren bijtende satires tegen de paus, monniken, aflaten, pelgrimstochten, enzovoort.
Zodra ze verschenen, werden ze verboden, en het was niet zonder reden dat het landjuweel van 1561 later werd aangehaald als het eerste (en het laatste) dat de literaire wereld ophitste ten gunste van de protestantse reformatie. Omdat deze werken verre van gunstig waren voor het Spaanse regime, beval de hertog van Alba hun afschaffing door de Index van 1571 en later verbood de regering zelfs theatervoorstellingen van retorische genootschappen.
B. Quinten Matsys, biografische elementen
Nu we vertrouwd zijn met de belangrijkste filosofische en culturele problematiek van zijn tijd, kunnen we met een gerust hart het leven 71 van Matsys en enkele van zijn werken onderzoeken.
1. Van smid tot schilder

Volgens de Historiae Lovaniensium van Joannes Molanus (1533-1585) werd Matsys geboren in Leuven tussen 4 april en 10 september 1466, als een van de vier kinderen van Joost Matsys (overleden 1483) en Catherine van Kincken.
De meeste verslagen over zijn leven vervlechten feiten en fabels. 72 De archieven zijn gierig aan sporen van zijn activiteiten of karakter.
In Leuven zou Quinten bescheiden zijn begonnen als kunstsmid. Volgens de legende werd hij verliefd op een mooi meisje, dat ook het hof werd gemaakt door een schilder. Het meisje gaf de voorkeur aan schilders boven smeden. Quinten zou het aambeeld al snel hebben ingeruild voor het penseel, aldus de legende.
De kroniekschrijver Karel Van Mander geeft een ander verhaal. Hij schreef in 1604 dat Quinten, die al sinds zijn twintigste jaar zwak en ziek was, in werkelijkheid « niet in staat was zijn brood te verdienen » als kunstsmid. Van Mander herinnert zich dat, op het moment van de feestvieringen van Vastenavond (Mardi Gras),
« De broeders die voor de zieken zorgden, gingen door de stad met grote, gesneden en beschilderde houten beelden en deelden gegraveerde en gekleurde afbeeldingen van heiligen uit aan de kinderen; Ze hadden er dus heel veel nodig. Toen een van de collega’s Quinten bezocht, vroeg hij aan hem deze afbeeldingen in te kleuren. Uiteindelijk probeerde Quinten zelf afbeeldingen te maken. Vanaf dit kleine begin kwam zijn voorkeur tot uiting en vanaf dat moment stortte hij zich met groot enthousiasme op het schilderen. In korte tijd boekte hij buitengewone vooruitgang en werd hij een volleerd meester. » 73


In Antwerpen, voor de Onze-Lieve-Vrouwekathedraal, op de Handschoenmarkt, kan men nog steeds de « putkevie » (versierd smeedijzeren hek op een waterput) vinden. Deze zou door Quinten Matsys zelf zijn gemaakt en stelt de legende van Silvius Brabo en Druon Antigoon voor. Dit zijn respectievelijk de namen van een mythische Romeinse officier die Antwerpen bevrijdde van de onderdrukking door een reus genaamd Antigoon. De reus Antigoon schaadde de handel in de stad door de toegang tot de rivier te blokkeren. Brabo kapte Antigoons hand af en wierp het in de Schelde.
Het opschrift op de waterput luidt: “Dese putkevie werd gesmeed door Quinten Matsijs. De liefde maeckte van den smidt eenen schilder.”
De archieven betreffende de bezittingen van Joost Matsys, de vader van Quinten, die smid en klokkenmaker was in de stad, tonen aan dat het gezin over een behoorlijk inkomen beschikte en dat financiële noodzaak niet de meest waarschijnlijke reden was waarom Matsys zich tot het schilderen wendde.
In 1897 schreef Edward van Even 74, zonder enig bewijs te leveren, dat Matsys ook muziek componeerde, gedichten schreef en gravures maakte.

Hoewel er geen bewijs is van een opleiding die Quinten Metsys heeft gehad vóór zijn inschrijving als vrij meester bij het Antwerpse schildersgilde in 1491, doen de bouwplannen van zijn broer Joos Matsys II in Leuven en de activiteiten van hun vader vermoeden dat de jonge kunstenaar binnen eigen familie leerde tekenen en zijn ideeën op papier zetten. Deze zou hem ook voor het eerst in aanraking hebben gebracht met architecturale vormen 75 en hun creatief gebruik.
Vooral uit zijn vroege werken blijkt duidelijk dat hij is opgeleid als bouwkundig tekenaar. Op zijn schilderij Madonna en kind op troon met vier engelen (1505, National Gallery, Londen) zitten de goddelijke figuren op een vergulde troon, waarvan de gotische omkadering lijkt op die van het raam op de tekening op perkament en het kalkstenen model van het Sint-Pietersproject, waaraan zijn broer ongeveer in dezelfde tijd heeft gewerkt.

Wat wel zeker is, is dat de kunstenaar prachtige bronzen medaillons heeft gemaakt waarop Erasmus, zijn zus Catarina en hijzelf zijn afgebeeld.
Rond 1492 trouwde onze schilder met Alyt van Tuylt die hem drie kinderen gaf: twee zonen, Quinten en Pawel, en een dochter, Katelijne. Alyt stierf in 1507 en Quinten hertrouwde een jaar later.
Nadien, met zijn nieuwe vrouw Catherina Heyns kreeg hij nog tien kinderen, vijf zonen en vijf dochters.
Kort na de dood van hun vader werden twee van zijn zonen, Jan (1509-1575) en Cornelis (1510-1556) 76 op hun beurt schilder en lid van het Antwerpse Gilde.
2. Het Hertogdom Brabant

Leuven was destijds de hoofdstad van het hertogdom Brabant, dat zich uitstrekte van Luttre, ten zuiden van Nijvel, tot ‘s-Hertogenbosch (het huidige Nederland). Tot deze regio behoorden de steden Aalst, Antwerpen, Mechelen, Brussel en Leuven, waar in 1425 een van de eerste universiteiten van Europa werd gesticht. Vijf jaar later, in 1430, erfde Filips de Goede van Bourgondië samen met de hertogdommen Neder-Lotharingen en Limburg, Brabant, dat deel uitmaakte van de Bourgondische Nederlanden. 77
In 1477, toen Matsys ongeveer 11 jaar oud was, viel het hertogdom Brabant onder Habsburgse heerschappij als deel van de bruidsschat van Maria van Bourgondië toen ze trouwde met Maximiliaan van Oostenrijk.
De latere geschiedenis van Brabant maakt deel uit van de geschiedenis van de Habsburgse « Zeventien Provinciën », die steeds meer onder controle kwamen van Augsburgse bankiersfamilies zoals de Fuggers 78 en de Welsers.



Als het tijdperk van Erasmus en Matsys een voorspoedige periode van de « Noordelijke Renaissance » was, dan werd het ook gekenmerkt door steeds grotere inspanningen van bankiersfamilies om het pausschap te « kopen » om zo de wereld te kunnen domineren.
De geopolitieke verdeling van de hele wereld (en haar grondstoffen) tussen het Spaanse Rijk (geregeerd door Venetiaanse bankiers) en het Portugese Rijk (onder leiding van Genuese bankiers) werd bezegeld door het Verdrag van Tordesillas, een akkoord dat in 1494 in het Vaticaan werd bekrachtigd door paus Alexander VI Borgia. Dit verdrag opende de deur voor de koloniale onderwerping van vele volkeren en landen, allemaal in naam van een zeer twijfelachtig gevoel van culturele en religieuze superioriteit.
Na herhaaldelijke staatsbankroeten werden de bewoners van de Lage Landen het doelwit van brutale economische en financiële plundering. De Fuggers leenden heel veel geld, zowel aan de keizer als de paus. Maar om nieuwe financieringen te verkrijgen, moesten de oudere worden terugbetaald. Door Luther, die steeds meer pleitte voor een breuk met Rome, overmatig te demoniseren, ontweek de heersende macht de prangende vragen die Erasmus en Thomas More stelden. Zij eisten dringende hervormingen om misbruik en corruptie binnen de katholieke kerk en de staat uit te roeien.
Het is niet ondenkbaar dat de abrupte weigering van paus Clemens VII om de eisen van Hendrik VIII voor een echtscheiding te honoreren, deel uitmaakte van een algehele strategie om het hele Europese continent in godsdienstoorlogen te storten, waaraan pas in 1648 een einde kwam met de Vrede van Westfalen ook wel Vrede van Münster genoemd.
3. Formatie: Memling, Bouts of Van der Goes?
De vroege, grote drieluiken die Matsys schilderde, leverden hem veel lof. Historici beschrijven hem als « een van de laatste Vlaamse primitieven ». Maar dat was in die tijd eigenlijk een spotnaam, gebruikt door Michelangelo 79 om alle niet-Italiaanse kunst, die hij als « gotisch » (barbaars) of « primitief » beschouwde, in wezen in diskrediet te brengen in vergelijking met de Italiaanse kunst die de ware antieke stijl imiteerde.
Omdat Matsys in Leuven werd geboren, is gesuggereerd dat hij zijn opleiding heeft genoten bij Aelbrecht Bouts (1452-1549), de zoon van de destijds dominante schilder in Leuven, Dieric Bouts de Oude (ca. 1415-1475). 80
In 1476, een jaar na de dood van zijn vader, zou Aelbrecht Leuven hebben verlaten om zijn opleiding te vervolgen bij een meester buiten de stad, hoogstwaarschijnlijk Hugo van der Goes (1440-1482), 81 wiens invloed op Aelbrecht Bouts, maar ook op Quinten Matsys, aannemelijk lijkt.
Van der Goes, die in 1474 deken werd van het schildersgilde van Gent en in 1482 overleed in het Rood Klooster bij Brussel, was een vurig aanhanger van de Broeders van het Gemene Leven en hun principes. 82
Als jonge assistent van Aelbrecht Bouts, zelf een leerling van Van der Goes, had Matsys de bakermat van het christelijk humanisme kunnen ontdekken.
Het bekendste werk van Van der Goes is het Portinari-drieluik (Uffizi, Florence), een altaarstuk dat Tommaso Portinari, hoofd van het Brugse filiaal van de Medici-bank, in opdracht van de kerk van Sant’Egidio in het ziekenhuis Santa Maria Nuova in Florence maakte.
De ruwe trekken van de drie herders (die elk een van de door de Broeders des Gemene Levens voorgeschreven stadia van spirituele verheffing uitdrukten 83) in de compositie van Van der Goes maakten diepe indruk op de schilders die in Florence werkten.

Matsys wordt ook beschouwd als een mogelijke leerling van Hans Memling (1430-1494), zelf een leerling was van Van der Weyden (1400-1464) 84 en een vooraanstaand schilder in Brugge.
De stijl van Memling en die van Matsys lijken zo veel op elkaar dat het moeilijk is om ze te onderscheiden.
Terwijl de Vlaamse kunsthistoricus Dirk de Vos in zijn catalogus van het werk van Hans Memling uit 1994 het portret van de musicus en componist Jacob Obrecht 85 (1496, Kimbell Art Museum, Fort Worth) beschreef als een zeer laat werk van Hans Memling, konden hedendaagse experts, waaronder Larry Silver 86, in 2018 vaststellen dat het veel waarschijnlijker is dat het portret het vroegst bekende werk van Quinten Matsys is.
Obrecht, die een grote invloed had op de Vlaamse polyfone (meerstemmige) en contrapuntische muziek uit de Renaissance, werd in 1492 benoemd tot koorleider van de Onze-Lieve-Vrouwekathedraal in Antwerpen. Rond 1476 was Erasmus toevallig een van Obrechts koorknapen.
Obrecht bezocht Italië minstens twee keer, in 1487 op uitnodiging van hertog Ercole d’Este I van Ferrara 87 en nadien, in 1504. Ercole had Obrechts muziek gehoord, waarvan bekend is dat deze tussen 1484 en 1487 in Italië circuleerde, en had verklaard dat hij deze meer waardeerde dan de muziek van alle andere componisten van zijn tijd; Daarom nodigde hij Obrecht uit. De componist overleed later in Italië aan de pest.
Al in de jaren 1460 reisde Erasmus’ leraar in Deventer, de componist en organist Rudolph Agricola (1443-1483), 88 naar Italië. Nadat hij burgerlijk recht had gestudeerd in Pavia en lessen had gevolgd bij de Italiaanse pedagoog Battista Guarino (1434-1505), vertrok hij naar Ferrara, waar hij een protegé werd van het hof van Este.


Rond 1499 maakte Leonardo een tekening van Ercole’s dochter, Isabella d’Este. Op de basis van die tekening, denken sommigen dat zij dezelfde persoon is als de Mona Lisa.
4. Debuten in Antwerpen en in het buitenland
Matsys werd in 1491 in Leuven ingeschreven, maar werd datzelfde jaar ook als meester-schilder toegelaten tot het Sint-Lucasgilde van Antwerpen. Op vijfentwintigjarige leeftijd besloot hij zich in de havenstad te vestigen. Hij schilderde er, zoals gezegd, in 1496 de kapelmeester Jacob Obrecht, zijn eerste bekende werk, en verschillende devotionele schilderijen met als onderwerp de Maagd Maria en het Kind.
Omdat de Liggeren (registers van de schildersgilden) geen informatie bevatten over Matsys’ activiteiten in de Lage Landen over een periode van meerdere jaren, is het verleidelijk om te veronderstellen dat Matsys een reis ondernam naar Italië. 89
Daar had hij grote meesters kunnen ontmoeten. Da Vinci woonde tussen 1482 en 1499 in Milaan en keerde daar in 1506 terug. Het is in Milaan waar Da Vinci zijn leerling Francesco Melzi (1491-1567) ontmoette, die hem vervolgens naar Frankrijk vergezelde. Matsys kan ook Colmar of Straatsburg hebben bezocht, steden die ook bezocht werden door Albrecht Dürer, een kunstenaar met wie hij blijkbaar vertrouwd was voor zijn komst in 1520 in onze gewesten.
Voor de Belgische kunsthistoricus Dirk de Vos (1943-2024), oud-conservator van het Groeningemuseum, was een reis naar Italië niet alleen mogelijk maar hoogstwaarschijnlijk:
« De vroege en de volwassen stijlen van Metsys contrasteren zo sterk dat we het verschil alleen kunnen verklaren door een beroep te doen op de hypothese van het ijverig bezoeken van de werken van de Italiaanse Renaissance, en meer bepaald die van Leonardo da Vinci en zijn discipelen uit de late 15e eeuw. We zien namelijk dat Metsys directe ontleningen aan Leonardo da Vinci heeft gedaan, zozeer zelfs dat een andere inspiratiebron uitgesloten lijkt. Hoewel er geen tastbaar bewijs is van een reis naar Italië, vertoont Metsys’ aanwezigheid in Antwerpen toch hiaten in de continuïteit die verenigbaar zijn met een langdurige afwezigheid, bijvoorbeeld tussen 1491 en 1507. Een reis naar Italië is dus helemaal niet onwaarschijnlijk. » 90
Dürer werd door zijn ouders naar Colmar in de Elzas gestuurd om daar een opleiding in de graveerkunst te volgen bij Martin Schongauer (1450-1491), veruit de meest bekwame graveur van zijn tijd. 91
Maar toen Dürer in de zomer van 1492 in Colmar aankwam, was Schongauer al overleden. Vanuit Colmar vertrok de kunstenaar naar Bazel, waar hij houtsneden maakte om boeken te illustreren en de indrukwekkende gravures van Jacob Burgkmair (1473-1531) en Hans Holbein de Oude (1460-1524) ontdekte. 92
Vervolgens ging hij naar Straatsburg, waar hij de hierboven genoemde erudiete dichter en humanist Sebastian Brant ontmoette en een portret van hem tekende.
C. Geselecteerde werken
1. De Maagd en het Kind, goddelijke genade en vrije wilskeuze


In 1495 schilderde Matsys Maria met Kind (Brussel). Hoewel het werk nog steeds zeer normatief is, verrijkt Matsys de devotionele beeldentaal met minder formele scènes uit het dagelijks leven. Het Kind, dat op speelse wijze nieuwe natuurkundige principes verkent, probeert onhandig de bladzijden van een boek om te slaan, terwijl een zeer ernstige Maagd Maria in een nis in gotische stijl zit, die ongetwijfeld is gekozen om aan te sluiten bij de architectuur en stijl van de zaal of kapel waar het schilderij geplaatst moest worden.
In een andere Maria met Kind (Rotterdam) gaat Matsys nog verder in deze richting. Men ziet er een zorgzame en gelukkige jonge moeder met een speels kind, zoon van God, maar ook zoon van de Mens. In een opstelling vlakbij de toeschouwer bemerkt men een brood en een kom melksoep met een lepel. Dit is ongetwijfeld een alledaags tafereel voor de meeste mensen van die tijd. God is niet alleen aanwezig in de kerk, maar in ons dagelijks bestaan.

In zijn Madonna met kind en melksoep (Brussel), dat Matsys’ vriend Gerard David (1460-1523) schilderde in 1520, toont hij met grote tederheid een jonge moeder die haar kind aanleert dat de achterkant van een lepel niet de beste manier is om de soep vanuit de kom in de mond te brengen!
Veel schilderijen over dit thema, zowel van Quinten Matsys (Maria met Kind, Louvre, 1529, Parijs) als van Gerard David (Rust tijdens de vlucht naar Egypte, National Gallery, Washington), tonen een kind dat met enorme inspanning doet om enkele druiven, kersen of ander fruit te bemachtigen.



In 1534 gebruikt Erasmus in zijn De libero arbitrio sive collatio (Gesprek of verzameling uitspraken over de vrije wilskeuze) dezelfde metafoor voor het fragiele evenwicht dat centraal staat in de verhouding tussen de vrije wil (die, los van een hoger doel, op zichzelf pure arrogantie kan worden) en de goddelijke genade (die als loutere voorbestemming kan worden geïnterpreteerd).
Om dit onderwerp, dat men zou denken dat alleen voor theologen is bestemd, voor zoveel mogelijk mensen toegankelijk te maken, gebruikt Erasmus een heel eenvoudige metafoor, vol tederheid en schoonheid:

“Een vader heeft een kind dat nog niet kan lopen; het valt; de vader tilt het op terwijl het kind haastige bewegingen maakt en moeite heeft om zijn evenwicht te bewaren; hij laat hem een vrucht zien die voor hem staat; het kind probeert het vast te pakken, maar door de zwakte van zijn ledematen zal het snel vallen als de vader zijn hand niet uitstrekt om het kind te ondersteunen en te begeleiden.
« Zo komt het kind, onder leiding van zijn vader, bij de vrucht die de vader bereidwillig in zijn handen legt als beloning voor zijn inspanning. Het kind zou nooit zijn opgestaan als de vader hem niet had opgetild; hij zou de vrucht nooit hebben gezien als de vader hem die niet had laten zien; hij had niet vooruit kunnen komen als zijn vader zijn zwakke stappen niet had gesteund; en hij zou de vrucht nooit hebben kunnen bereiken als zijn vader hem die niet in handen had gegeven.
« Wat zal het kind in dit geval als zijn eigen daden bestempelen? We kunnen niet zeggen dat hij niets gedaan heeft. Maar er is geen reden om zijn kracht te verheerlijken, aangezien hij alles wat hij is, aan zijn vader te danken heeft. » 93
Kortom, de vrije wilskeuze van de mens, welke Erasmus verdedigt, is essentieel, maar zonder God gaat de mens niet ver.
2. Altaarstuk van Sint-Anna



In Antwerpen beleefde Matsys’ activiteit een grote doorbraak met de eerste grote publieke bestellingen voor twee grote drieluik-altaarstukken:
- Het Drieluik van de Broederschap van Sint-Anna (1507-1509, Museum van Brussel), gesigneerd “Quinten Metsys screef dit”;
- Het Altaarstuk van het schrijnwerkersambacht (ook wel Nood Gods of Bewening van Christus genoemd, naam van het middenpaneel) (1507-1508, Museum van Antwerpen), geschilderd voor de kapel van het timmermansgilde in de kathedraal van Antwerpen, een werk dat grotendeels is geïnspireerd op de Kruisafname van Rogier Van der Weyden (Prado, Madrid). Johannes de Doper en Johannes de Evangelist, die verschijnen wanneer het drieluik gesloten is, zijn de patroonheiligen van de kerk.
Sint-Anna drieluik
Het thema en de iconografie van het Sint-Anna-drieluik werden, zoals gebruikelijk, volledig aan de schilder gedicteerd door de broederschap van Sint-Anna van Leuven, die hem deze opdracht gaf voor hun kapel in de Sint-Pieterskerk in dezelfde stad.
Het middenpaneel toont het verhaal van de familie van Sint-Anna, in een monumentaal gebouw met een afgeknotte koepel en een marmeren booggewelf die een breed uitzicht bieden op een bergachtig landschap. Het altaarstuk vertelt in vijf scènes het leven van Anna, de moeder van Maria, en haar man Joachim. Op het middenpaneel zijn de verschillende familieleden van de heilige afgebeeld.
De belangrijkste gebeurtenis in het leven van Anna en haar man Joachim, namelijk dat zij de ouders zouden worden van de Maagd Maria, terwijl zij zelf dachten dat zij geen kinderen konden krijgen, wordt afgebeeld op het linker- en rechterpaneel van het drieluik.
De kuise kus
De « onbevlekte ontvangenis » van Sint-Anna, moeder van Maria, uitgebeeld door de afbeelding van een « kuise kus » tussen de twee echtelieden (Anna en Joachim) voor de Gouden Poort van de muur van Jeruzalem, is een immens populair onderwerp in de geschiedenis van de schilderkunst, van Giotto tot Dürer.



Daarom werd het al snel getransformeerd naar de « onbevlekte ontvangenis » van Christus zelf. Vandaar dat er plotseling schilderijen verschenen waarop Maria « kuis » (maar toch op de lippen) haar kindje Jezus kuste.

De altaarstukkencyclus eindigt met de dood van Anna, die op het rechterbinnenpaneel is afgebeeld, omringd door haar kinderen en waar Christus zijn zegen geeft.
Ondanks de indrukwekkende omvang van dit werk en de conventionele verhaallijn, slaagt Matsys erin een vrijer en intiemer gevoel van contemplatie te creëren. Een voorbeeld hiervan is het neefje van Jezus in de linkerhoek, die plezier heeft in het verzamelen van heiligenbeeldjes en die, volledig geconcentreerd, probeert ze te lezen.
3. Een nieuw perspectief
In twee andere geschriften 94 heb ik aangetoond dat, in hun werk, zowel de Vlaamse schilder Jan Van Eyck 95 als de Italiaanse beeldhouwer en bronsgieter Lorenzo Ghiberti 96 zich vertrouwd hebben gemaakt met de « Arabische optica », in het bijzonder de wetenschappelijke werken van Ibn al-Haytham 97 (bekend onder zijn Latijnse naam Alhazen).
Tijdens de Renaissance probeerden verschillende scholen, met verschillende en soms tegenstrijdige benaderingen, de beste manier te vinden om drie dimensionele ruimte weer te geven door middel van perspectief.
Vanaf het begin van de 15e eeuw, voortbouwend op het werk van de Franciscanen van Oxford (Roger Bacon, Grosseteste, enz.), was er een school die uitging van de menselijke fysiognomie (twee ogen die een beeld creëren in de geest van de toeschouwer). In plaats van een mono-focaal (cyclopisch) model, hebben zijn, gebaseerd of Alhazen, een perspectief bedacht met twee centrale vluchtpunten (bi-focaal perspectief).
Dit perspectief is duidelijk herkenbaar in zekere werken van Van Eyck en Lorenzo Ghiberti, waarbij laatstgenoemde zelf wetenschappelijke teksten van Alhazen vertaalde in het Italiaans en opnam in zijn handboek voor schilders, de Commentarii, welke door Da Vinci werden geraadpleegd tijdens zijn opleiding in het atelier van Verrocchio, zelf een leerling van Ghiberti.
Een andere school, die verbonden is met Leon Battista Alberti, 98 beweerde dat « juist » perspectief, dat puur geometrisch en wiskundig is, een beroep doet op een uniek « centraal vluchtpunt ».
Ten slotte probeerde een derde school, die van Jean Fouquet in Frankrijk en Leonardo da Vinci, een curvilineair (kromlijnig) perspectief te hanteren, waarbij de beperkingen van het Albertiaanse model worden overkomen en de vervormingen vermeden.
In de moderne tijd wilden de volgelingen van Descartes en Galileo absoluut aantonen dat hun model van de lege ruimte geboren was in de Renaissance, met het Albertiaanse model. Zij beweerden dus dat alle andere benaderingen het werk was van boerse en onwetende « primitieven ».
Een onschatbare ontdekking
Zoals eerder vermeld, werkt het Gentse Interdisciplinair Centrum voor Kunst en Wetenschap (GICAS) sinds 2007 aan een nieuwe « Catalogue raisonné » van het werk van Quinten Matsys. In dit kader onderzochten Jochen Ketels en Maximiliaan Martens 99 in 2010 het Anna-altaarstuk van Matsys en de indrukwekkende Italiaanse portiek van het middenpaneel.
Laten we niet vergeten dat het geschilderde deel (in twee dimensies) op het centrale luik door de kunstenaar zo was ontworpen dat het harmonieus aansloot op een grote houten constructie (in drie dimensies) die als kader diende. Deze constructie is helaas verloren gegaan, maar we weten van zijn bestaan dankzij tekeningen.
« Toen we onze fotolampen op het centrale paneel richtten, » schrijven de twee onderzoekers, « liet het strijklicht iets zien wat in de literatuur helemaal niet was vermeld: in de gewelven van de architectuur aangebrachte constructielijnen. » 100
Infrarood benadrukte ook het bestaan,
« van een complexe reeks constructielijnen, getekend met de hand of met behulp van verschillende gereedschappen en technieken. Niet alleen was een dergelijk complex constructiesysteem niet te zien in de noordelijke schilderijen uit die tijd, maar Matsys moest ook een wiskundige procedure hebben gebruikt om de complexe loggia te construeren. » 101
Nog interessanter,
« Om de contouren van de afgeknotte koepel en de versiering ervan te tekenen, gebruikte Matsys nauwelijks lijnen, maar gaf hij de voorkeur aan stippen (…) onderaan het kapiteel voegde Matsys enkele losse letters toe, waarschijnlijk een ‘z’, een ‘e’ of een ‘c’ (…) Vanwege hun positie dicht bij het element en het feit dat Piero della Francesca bijvoorbeeld al een soortgelijk systeem met cijfers en letters had gebruikt in zijn tekeningen van De Prospectiva Pingendi (Over het perspectief van schilderijen, ca. 1480), is er reden om aan te nemen dat er een verband is met de omtrek of compositie van de zuil. » 102

In dit verband is het interessant om op te merken dat een van de weinige personen die op enig moment contact heeft gehad met Matsys en die Piero della Francesca‘s verhandeling103 over perspectief heeft gelezen en bestudeerd, niemand minder is dan Albrecht Dürer, wiens Vier boeken over de menselijke verhoudingen (1528) voortbouwt op Piero’s revolutionaire benadering.
Wat Dürer de « transfer-methode » van Piero noemt, zou later de basis vormen voor de projectieve meetkunde, met name aan de École Polytechnique onder leiding van Gaspard Monge, de belangrijkste wetenschap die de Industriële Revolutie mogelijk maakte.
De onderzoekers controleerden ook Matsys’ gebruik van het centrale vluchtpunt-perspectief met behulp van de « kruisverhouding-methode ».
Verbaasd, omdat het volgens de leer van de beste scholen onmogelijk zou zijn, stellen ze het volgende vast:
« Matsys toont zijn vaardigheid in perspectief, overeenkomend met de normen van de Italiaanse Renaissance, » een perspectief dat « inderdaad zeer correct is. » 104
Tot nu toe werd aangenomen dat de perspectiefwetenschap pas in de Lage Landen doordrong na de reis van Jan Gossaert naar Rome in 1508. Matsys, die blijk gaf van een meesterlijke en uitgebreide kennis van de perspectiefwetenschap, begon echter al in 1507 met de opbouw van dit werk.
4. Matsys’ samenwerking met Joachim Patinir en Albrecht Dürer


Een laatste opmerking over dit schilderij: het bergachtige landschap achter de figuren doet denken aan de typische en verontrustende landschappen van Matsys’ vriend Joachim Patinir (1480-1524), een andere weinig bekende maar grote kunstenaar in de geschiedenis van de schilderkunst.
In zijn tijd was Patinir’s vermaardheid niet klein. Felipe de Guevara, vriend en artistiek adviseur van Karel V en Filips II, noemt Patinir in zijn Commentaren op de schilderkunst (1540) als één van de drie grootste schilders van de regio, samen met Rogier van der Weyden en Jan van Eyck.
Patinir leidde een grote werkplaats met assistenten in Antwerpen. Onder degenen die onderhevig zijn aan de drievoudige invloed van Bosch, Matsys en Patinir, de volgende namen:
- Cornelis Matsys (1508-1556), zoon van Quinten, die trouwde met de dochter van Patinir;
- Herri met de Bles (1490-1566), actief in Antwerpen, mogelijke neef van Patinir;
- Lucas Gassel (1485-1568), actief in Brussel en Antwerpen;
- Jan Provoost (1465-1529), actief in Brugge en Antwerpen;
- Jan Mostaert (1475-1552), schilder werkzaam in Haarlem;
- Frans Mostaert (1528-1560), schilder actief in Antwerpen;
- Jan Wellens de Cock (1460-1521), schilder actief in Antwerpen;
- Matthijs Wellens de Cock (1509-1548), schilder-graveur werkzaam in Antwerpen;
- Hieronymus (Wellens de) Cock (1510-1570), schilder-graveur, die samen met zijn vrouw de Antwerpse uitgeversbedrijf In de Vier Winden oprichtte, destijds waarschijnlijk de grootste ten noorden van de Alpen, waar Pieter Bruegel de Oude werkzaam was.

Het is algemeen aanvaard dat Quinten Matsys de figuren in enkele van Patinir’s landschappen heeft geschilderd. Volgens de inventaris van het Escorial uit 1574 was dit het geval voor De verzoekingen van de Heilige Antonius (1520, Prado, Madrid).
Maar deze samenwerking kwam beide vrienden tegoed: Patinir ontwierp landschappen voor de werken van Matsys op diens verzoek. Deze realiteit ondermijnt enigszins de hardnekkige mythe van een Renaissance die wordt geprezen als het begin van competitief individualisme.
Dat Matsys en Patinir een hechte band hadden, blijkt wel uit het feit dat Matsys, na Patinirs vroege dood, de voogd werd van zijn twee dochters. Interessant is ook dat Gerard David, die na Memling de belangrijkste schilder in Brugge werd, in 1515 samen met Patinir lid werd van het Sint-Lucasgilde in Antwerpen, wat hem het recht gaf zijn werk te verkopen, niet alleen in Brugge, maar tevens op bloeiende Antwerpse kunstmarkt.
Moderne kunsthistorici beschouwen Patinir vaak als de vader en « uitvinder » van de landschapsschilderkunst. Ze beweren dat religieuze onderwerpen voor hem slechts een voorwendsel waren om te laten zien wat hem werkelijk interesseerde: landschappen. Men legt ook uit dat Rubens Adam en Eva schilderde alleen maar omdat hij graag naakten schilderde (en verkocht). Voor Rubens was dat misschien zo, maar voor Patinir ligt het duidelijk anders. Zoals de kunsthistoricus Reindert L. Falkenberg heeft aangetoond, 105 waren zijn « prachtige » landschappen niets meer zijn dan een soort geraffineerde, heel aantrekkelijke duivelse valstrik. De schoonheid van de wereld, een duivelse schepping volgens Patinir, bestaat enkel om mensen te verleiden en hen te laten bezwijken voor de zonde…
Ontmoeting met Albrecht Dürer

Dürers reisdagboek 106 van zijn bezoek in de Lage Landen is een trouwe bron van informatie.
Waarom kwam Dürer naar Brabant? Een mogelijke verklaring is dat de kunstenaar, na de dood van zijn belangrijkste opdrachtgever, keizer Maximiliaan I, zijn pensioen wou laten uitbetalen door Karel V.
Dürer kwam op 3 augustus 1520 in Antwerpen aan en bezocht Brussel en Mechelen, waar hij werd ontvangen door Margaretha van Oostenrijk (1480-1530), de tante van Karel V. Ze was verantwoordelijk voor het bestuur van de Bourgondische Nederlanden zolang Karel nog te jong was. Soms luisterde ze naar Erasmus, maar ze hield ook afstand.


In Mechelen bezocht Dürer zeker het prachtige paleis van Hieronymus (Jeroen) van Busleyden (1470-1517), de beschermheer die Erasmus de financiële steun gaf om in 1517 in Leuven het “Dry Tonghen College” op te richten. 107 Een grondige kennis van Latijn, Grieks en Hebreeuws, zou zowel misverstanden die het resultaat waren van slechte vertalingen, als religieuze conflicten kunnen vermijden, dacht Erasmus. Busleyden was een vriend van de bisschop van Londen, Cuthbert Tunstall (1475-1559), die hem voorstelde aan Thomas More (1478-1535).
Tijdens zijn verblijf bij Margaretha kon Dürer een prachtig schilderij uit haar collectie bewonderen: Het Arnolfini-echtpaar (1434) van Jan van Eyck.
Margaretha had net een pensioen toegekend aan de Venetiaanse schilder Jacopo de’ Barbari (1440-1515), 108 een diplomaat en politieke balling in Mechelen die een portret schilderde van Luca Pacioli (1445-1514), de Franciscaan die de Griekse teksten van Euclides aan Leonardo da Vince verklaarde. Pacioli was ook de auteur van De Divina Proportione (1509) (De Gulden Snede), een werk dat Da Vinci rijkelijk illustreerde.
De’ Barbari wordt door verschillende van zijn tijdgenoten vermeld, namelijk Dürer, Marcantonio Michiel (1584-1552) en Gerard Geldenhauer (1482-1542).
In 1504 ontmoette De’ Barbari Dürer in Neurenberg en ze bespraken de canon van de menselijke proporties, een centraal thema in het onderzoek van laatstgenoemde. 109 Uit een ongepubliceerd manuscript van Dürers verhandeling blijkt dat de Italiaan niet bereid was zijn bevindingen te delen:
« Ik heb niemand gevonden die iets heeft geschreven over de toepassing van de canon van menselijke proporties, behalve een man genaamd Jacob, geboren in Venetië en een charmante schilder. Hij liet mij [zijn gravure van] een man en een vrouw zien die hij met zijn systeem had gemaakt, zodat nu zou ik liever zien wat hij bedoelde dan van een nieuw koninkrijk te dromen… Jacobus wilde mij zijn principes niet duidelijk laten zien, dat zag ik duidelijk » 110
Volgens de archieven was de’ Barbari in maart 1510 in dienst van aartshertogin Margeretha in Brussel en Mechelen. In januari 1511 werd hij ziek en schreef een testament. In maart kende de aartshertogin hem een levenslang pensioen toe. Hij stierf in 1516 en liet de aartshertogin een serie van 23 gravureplaten na. Maar wanneer Dürer haar vroeg om hem een aantal van De’ Barbari’s geschriften over menselijke proporties te overhandigen, wijst ze zijn verzoek beleefd af. 111
De duitse historicus Matthias Mende is van mening dat:
“Dürers theoretische werken ondenkbaar zijn zonder directe of indirecte kennis van Leonardo da Vinci’s ideeën. Er zijn zelfs tekeningen van Leonardo’s anatomische platen gevonden in Dürers nalatenschap.” 112
Uit het reisdagboek van Dürer blijkt hoe hartelijk hij door zijn lokale collega’s werd ontvangen. 113



In Antwerpen schreef hij in zijn reisdagboek: « Ik ging Quinten Matsys in zijn huis opzoeken. » In dezelfde stad schetste hij een portret van Lucas van Leyden (1489-1533) 114 en vervaardigde hij het beroemde portret van de 93-jarige man die later als model zou dienen voor zijn Sint-Hiëronymus.
Hij ontmoet Erasmus minstens drie keer en tekent, schildert of graveert portretten die wederzijdse medeplichtigheid uitstralen. Erasmus gaf Dürer de opdracht omdat hij een groot aantal portretten nodig had om naar zijn correspondenten over heel Europa te sturen. Zoals hij in zijn dagboek aangeeft, schetste Dürer Erasmus tijdens deze ontmoetingen meerdere malen met houtskool. Zes jaar later zou hij er een wat onhandig gegraveerd portret van maken.

Ter gelegenheid van zijn tweede huwelijk, op 5 mei 1521, nodigde Patinir Dürer uit. Het is niet bekend wanneer en hoe hun vriendschap ontstond, of dat het gewoon toevallig was. De Meester van Neurenberg schetste een portret van Patinir en noemde hem « der gute Landschaftsmaler » (de goede landschapsschilder). Daarmee bedacht hij een nieuw woord voor wat een nieuw genre zou worden.
Tijdens het huwelijksfeest maakte hij kennis met Jan Provoost (1465-1529), Jan Gossaert (de Mabuse) (1462-1533) en Bernard van Orley (1491-1542), de twee laatste, populaire schilders aan het hof van Mechelen.
Maar Provoosts De vrek en de dood. (1515, Brugge) is duidelijk geïnspireerd door Erasmus.

De dichter, hoogleraar Latijn en filoloog Cornelis de Schryver (Grapheus) (1482-1558), medewerker van Erasmus’ drukker in Leuven en Antwerpen, Dirk Martens, is een figuur die Dürer in contact kon brengen met de schilders van Antwerpen, een stad waarvan hij in 1520 secretaris was.
Drukkers en uitgevers speelden een belangrijke rol in de Renaissance. Ze fungeerden als bemiddelaars tussen intellectuelen en geleerden enerzijds en illustratoren, graveurs, schilders en ambachtslieden anderzijds. Net als Dürer zelf voelde Grapheus zich aangetrokken tot de ideeën van de Reformatie, waarvan Luther en Erasmus de leiders waren. Grapheus heeft Dürer een exemplaar bezorgt van Luthers De Captivitate (Over de Babylonische gevangenschap van de kerk), een must-read voor iedereen die geïnteresseerd is in de toekomst van het christendom.
Net als Erasmus en vele andere humanisten was Dürer te gast bij Quinten Matsys in diens prachtige huis aan de Schuttershofstraat, versierd met Italiaanse ornamenten (guirlandes van bladeren, bloemen of vruchten) en decoratieve en symmetrische motieven van lijnen en figuren).

Een geïdealiseerde weergave van de ontmoeting tussen Dürer en Matsys (onder toeziend oog van Thomas More en Erasmus) is te zien op een schilderij van Nicaise de Keyser (1813-1887) in het Koninklijk Museum voor Schone Kunsten in Antwerpen.
Een ander tafereel, een tekening van Godfried Guffens (1823-1901) uit 1889, toont hoe de Antwerpse schepen Gérard van de Werve Albrecht Dürer ontvangt, die door Quinten Matsys aan hem wordt voorgesteld.

Toen Karel V uit Spanje terugkeerde en Antwerpen bezocht, schreef Grapheus een lofrede om zijn terugkomst te vieren. Maar in 1522 werd hij gearresteerd wegens ketterij, meegenomen naar Brussel voor verhoor en gevangengezet. Hij verloor toen zijn functie als secretaris. In 1523 werd hij vrijgelaten en keerde terug naar Antwerpen, waar hij hoogleraar Latijn werd. In 1540 werd hij opnieuw stadssecretaris van Antwerpen.
De zuster van Quinten Matsys, Catharina, en haar man werden in 1543 in Leuven ter dood veroordeeld. Hun misdaad? Het lezen van de Bijbel. Hij werd onthoofd en zij werd levend begraven op het plein voor de kerk.
Vanwege hun religieuze overtuigingen verlieten Matsys’ kinderen Antwerpen en gingen in 1544 in ballingschap. Cornelis bracht zijn laatste dagen door in het buitenland.
5. In de ban van Erasmus


In 1499 ontmoetten Thomas More en Erasmus elkaar in Londen. Hun eerste ontmoeting groeide uit tot een levenslange vriendschap en ze bleven regelmatig met elkaar corresponderen. In deze tijd werkten ze samen aan de vertaling in het Latijn en het drukken van enkele werken van de satiricus Lucianus van Samosata (ca. 125-180 n.Chr.), die ten onrechte de bijnaam « de Cynicus » kreeg.
Erasmus vertaalde Lucianus’ satirische tekst, Over hen die door de groten worden betaald,115 en liet deze naar zijn vriend Jean Desmarais sturen, hoogleraar Latijn aan de Universiteit Leuven en kanunnik van de Sint-Pieterskerk in die stad.
Lucien valt in zijn tekst de denkwijze aan van geleerden die hun ziel, hun geest en hun lichaam verkopen aan de dominante macht:
« Wat een vreugde om de eerste burgers van Rome tot je vrienden te mogen rekenen, om heerlijke diners te hebben, zonder dat het je iets kost, om te overnachten in een prachtig huis, om op je gemak te reizen, zachtjes liggend op een wagen getrokken door witte paarden, om bovendien een prachtige beloning te ontvangen voor deze vriendschap en het welzijn dat je mag genieten! Wat een goed werk, waar alles zo ontstaat zonder zaad of teelt. » 116
In een waar manifest tegen vrijwillige onderwerping, vooruitlopend op de soumission volontaire van La Boétie, valt Lucien hun perverse fantasie aan als de oorzaak van hun capitulatie:
« Er blijft slechts één motief over waarvan ik geloof dat het waar is, maar dat zij niet toegeven: de hoop om van duizend genoegens te genieten, jaagt hen naar deze huizen, getroffen door de schittering van het goud en zilver waarmee ze glimmen, volkomen gelukkig met de feesten en de luxe die ze zichzelf beloven; wanneer zij het goud uit de volle beker drinken, zonder belemmering.
Dit is wat hen drijft; Daarom ruilen ze hun vrijheid in voor slavernij. Het is niet, zoals ze zeggen, de behoefte aan het noodzakelijke, maar het verlangen naar het overbodige en al die pracht en praal.
Maar net als ongelukkige geliefden, net als ongelukkige aanbidders, worden ze door de rijken behandeld met de sluwe trots van een geliefd object, die de hartstocht van zijn achtervolgers in stand houdt, maar zich nauwelijks laat beroven van de amoureuze gunst van een kus, omdat hij weet dat genot de liefde vernietigt: hij weigert daarom dit genot, hij beschermt zich er met de grootste zorg tegen.
Om de geliefde echter een sprankje hoop te geven, uit angst dat buitensporige strengheid hem tot wanhoop zou drijven en hij zou kunnen ophouden met liefhebben, schenken we hem een glimlach, beloven we hem op een dag te doen wat hij wil, aardig te zijn en hem met alle mogelijke consideratie te behandelen; dan komt de leeftijd, en al snel zijn de liefde van de een en de gunsten van de ander niet meer op hun tijd. Hun hele leven bestaat dus uit hopen. » 117
Het was in 1515 dat Thomas More door de Engelse koning Hendrik VIII op een diplomatieke missie werd gestuurd om belangrijke internationale handelsgeschillen in Brugge te beslechten. In Antwerpen, ontmoette hij Erasmus’ vriend Pieter Gillis (1486-1533) (gelatiniseerd als Petrus Ægidius), een collega-humanist en secretaris (burgemeester) van de stad Antwerpen. Gillis, die op zeventienjarige leeftijd als proeflezer was begonnen in de drukkerij van Dirk Martens in Leuven en Antwerpen, kende Erasmus al sinds 1504. De humanist raadde hem aan om verder te studeren en ze hielden contact.
In Leuven gaf drukker Martens diverse boeken van humanisten uit, waaronder die van Dionysius de Kartuizer (1401-1471) en De inventione dialectica (1515) van Rudolphus Agricola, het meest gekochte en gebruikte handboek voor hoger onderwijs op scholen en universiteiten in heel Europa.
Net als Erasmus was Gillis een leerling en bewonderaar van Agricola, een emblematische figuur van de school van de Broeders van het Gemene Leven in Deventer. Agicola, Erasmus’ favoriete leraar, was een uitmuntend pedagoog, muzikant, orgelbouwer, dichter in het Latijn en de volkstaal, diplomaat, bokser en tegen het einde van zijn leven een Hebreeuws kenner. Hij was een inspiratiebron voor een hele generatie. Gillis’ huis in Antwerpen was ook een belangrijke ontmoetingsplaats voor humanisten, diplomaten en internationaal gerenommeerde kunstenaars.
Ook Quinten Matsys was daar altijd welkom. Ten slotte was het Gillis die de schilder Hans Holbein de Jongere aan het Engelse hof aanbeval, de jonge tekenaar die het Lof der Zotheid van Erasmus had geïllustreerd. Hierdoor werd hij in Engeland met groot enthousiasme ontvangen door Thomas More. Zijn broer Ambrosius Holbein (1494-1519) zou later More’s Utopia illustreren.
6. De utopie van Thomas More

Gillis deelt met More en Erasmus een sterk gevoel voor rechtvaardigheid, en ook een typisch humanistische bezorgdheid die zich toelegt op het zoeken naar betrouwbaardere bronnen van wijsheid. Hij is vooral bekend als een personage dat verschijnt in de openingspagina’s van Utopia, wanneer Thomas More hem presenteert als een toonbeeld van beleefdheid en een humanist die zowel aangenaam als serieus is:
« Tijdens dit verblijf [in Brugge] ontving ik, naast andere bezoekers en welkome gasten, vaak Pieter Gillis. Hij werd geboren in Antwerpen en geniet grote verdienste en een vooraanstaande positie onder zijn medeburgers, die de allergrootsten waardig is. De kennis en het karakter van deze jongeman zijn immers opmerkelijk. Hij is inderdaad vol vriendelijkheid en eruditie en verwelkomt iedereen met vrijgevigheid, maar als het om zijn vrienden gaat, doet hij dat met zoveel enthousiasme, genegenheid, trouw en oprechte toewijding, dat er maar weinig mensen zijn die qua vriendschap met hem te vergelijken zijn. Weinig mannen hebben zo’n bescheidenheid, zo’n gebrek aan gekunsteldheid, zo’n natuurlijk gezond verstand, zo’n charmante conversatie, zo’n scherpzinnigheid met zo weinig kwaadaardigheid. »

Het bekendste werk van Thomas More is natuurlijk Utopia, gecomponeerd in twee delen.
Het is een beschrijving van een fictief eiland dat niet werd geregeerd door aristocraten of een oligarchie zoals de meeste Europese staten, maar dat werd bestuurd op basis van de ideeën die Plato formuleerde in zijn dialoog De Republiek.
Terwijl Erasmus in Lof der Zotheid opriep tot hervorming van de kerk, riep More in Utopia (deels door Erasmus afgewerkt), een andere satire op de corruptie, hebzucht, hebberigheid en mislukkingen die zij om zich heen zagen, op tot hervorming van de staat en de economie.
Thomas More kreeg het idee voor het boek toen hij in 1515 in Gillis’ Antwerpse residentie Den Spieghel verbleef.



Het eerste deel van Utopia begint met briefwisseling tussen More en zijn vrienden, waaronder Pieter Gillis. Toen de Engelse humanist in 1516 naar Engeland terugkeerde, schreef hij het grootste deel van het werk.
Tussen december 1516 en november 1518 werden vier edities van Utopia samengesteld door Erasmus en Thomas More en in december 1516 gepubliceerd bij uitgever Dirk Martens in Leuven.
Bij de tekst is er een kaart van het eiland Utopia, verzen van Gillis en het « utopische alfabet » dat hij voor deze gelegenheid had bedacht. Verder vinden we verzen van Geldenhouwer, een geschiedschrijver en hervormer die eveneens een opleiding had genoten bij de Broeders van het Gemene Levens te Deventer, verzen van Grapheus en de brief van Thomas More waarin hij het boek aan Gillis opdroeg.
Enkele jaren na de dood van More en Erasmus, publiceerde Grapheus samen met Pieter Gillis zijn Enchiridio Principis Ac Magistratus Christiani (1541).
7. Pieter Gillis en het “Tweeluik der Vriendschap”

Naast drieluiken en religieuze schilderijen muntte Matsys uit in het schilderen van portretten. Een van Matsys’ mooiste werken is het dubbelportret van Erasmus en zijn vriend Gillis, geschilderd in 1517. 118
Dit vriendschapstweeluik zou dienen als een « virtueel » bezoek aan hun Engelse vriend Thomas More in Londen. Ze vroegen aan hun vriend Quinten Matsys om de twee portretten te maken, omdat hij in Antwerpen de beste schilder was. Het portret van Erasmus was het eerste dat voltooid werd. Het portret van Gillis vroeg meer tijd omdat het model tussen de poseer-sessies ziek werd. De twee humanisten hadden in hun correspondentie met Thomas More over dit dubbelportret gesproken, wat misschien geen goed idee was, omdat More voortdurend naar de evolutie van de werkzaamheden informeerde en erg ongeduldig werd om dit geschenk te ontvangen. Beide werken werden uiteindelijk voltooid en naar More gestuurd toen hij in Calais was. Hoewel de twee geleerde mannen op afzonderlijke panelen zijn afgebeeld, worden ze in een doorlopende studieruimte gepresenteerd. Als we de twee schilderijen naast elkaar zetten, zien we hoe Matsys de boekenkast achter de twee figuren heeft geplaatst. Hierdoor ontstaat de indruk dat de twee personen die op de twee afzonderlijke panelen zijn afgebeeld, zich in dezelfde ruimte bevinden en elkaar aankijken.
Erasmus is druk aan het schrijven en Pieter Gillis toont de Antibarbari, een boek dat Erasmus voorbereidde voor publicatie, terwijl hij in zijn linkerhand een brief van More vasthoudt. De voorstelling van Erasmus in zijn studeervertrek doet denken aan de voorstellingen van Sint-Hiëronymus, die met zijn vertaling van de Bijbel een voorbeeld was voor alle humanisten en wiens werk Erasmus net had gepubliceerd. Het is interessant om naar de boeken in de planken op de achtergrond te kijken.
Op de bovenste plank van het schilderij van Erasmus staat een boek met de tekst Novum Testamentum Graece, de eerste editie van het Nieuwe Testament in het Grieks, uitgegeven door Erasmus in 1516.
Op de onderste plank staat een stapel met drie boeken.
- Het onderste boek draagt het opschrift Hieronymus, dat verwijst naar de humanistische edities van de werken van deze kerkvader;
- Het middelste boek draagt het opschrift Lucianus, verwijzend naar de samenwerking tussen Erasmus en Thomas More bij de vertaling van Lucianus’ Dialogen.
- Het opschrift op het boek bovenaan de drie is het woord Hor, dat oorspronkelijk werd gelezen als Mor. De eerste letter werd waarschijnlijk veranderd tijdens een vroege restauratie, want naast het feit dat Mor de eerste letters zijn van de achternaam van Thomas More, verwijzen ze zeker naar de satirische essays die Erasmus schreef toen hij in 1509 bij Thomas More in Londen verbleef en die de titel Encomium Moriae (Lof der zotheid) droegen.
We zien Erasmus een boek schrijven. Aan deze weergave is speciale aandacht besteed, omdat de woorden op het papier een parafrase zijn van de brief van Paulus aan de Romeinen, het handschrift een nauwkeurige weergave is van dat van Erasmus en de rietpen die hij vasthoudt bekend stond als Erasmus’ favoriete schrijfmedium.
Als we beter kijken, zien we in de schaduwen een beurs in de plooien van Erasmus’ mantel. Erasmus wilde wellicht dat de kunstenaar dit verbeelde om zijn vrijgevigheid te illustreren. Erasmus en Gillis lieten Thomas More weten dat ze samen de kosten van het schilderij deelden, omdat ze wilden dat het een geschenk van hen beiden zou zijn.
Thomas More gaf in talloze brieven uiting aan zijn grote tevredenheid over deze portretten. Volgens hem schilderde Matsys de schilderijen met « zo’n grote virtuositeit dat alle schilders uit de oudheid erbij in het niet vallen ». Maar hij gaf toe dat hij zijn beeltenis liever in steen had zien gehouwen (in een vorm die hij minder vergankelijk achtte…).
8. De Da Vinci-connection (I)



Verschillende schilderijen tonen onomstotelijk aan dat Matsys en zijn gevolg over meer dan oppervlakkige kennis beschikten en zich deels lieten inspireren door de schilderijen en tekeningen van Leonardo da Vinci, zonder dat ze noodzakelijkerwijs de wetenschappelijke en filosofische bedoelingen en diepte van de auteur volledig begrepen.
Dat is duidelijk het geval bij Madonna met Kind in het Museum van Poznan (1513, Polen). Hier wordt, in de stijl van Patinir, de sierlijke en liefdevolle houding van Maria met Christus in haar armen afgebeeld, waarbij Christus het lam omhelst. Het is bijna een kopie van Leonardo da Vinci’s Sint-Anna en de Maagd Maria, een werk dat hij in 1503 begon en in 1517 naar Amboise in Frankrijk bracht. Zoals reeds vermeld, is het niet bekend hoe dit beeld de meester heeft bereikt, via prenten, tekeningen of persoonlijke contacten.

Een tweede voorbeeld vinden we in het Altaarstuk van het schrijnwerkersambacht (1508-1511).
Het centrale tafereel van het open drieluik doet denken aan De Kruisafname van Rogier van der Weyden (1435, Museo del Prado, Madrid). Op de achtergrond, een landschap. Het religieuze drama wordt tot in detail bestudeerd en op harmonieuze wijze opgevoerd.
Tegelijkertijd heeft Matsys eerbied voor de gelovigen die veel waarde hechten aan het verhaal van het religieus gebeuren zelf. Hoewel de scène aanzet tot nadenken en gebed, maakt Matsys ook gebruik van contrast. Hoewel sommige van de meer rustieke personages, met name de oosterse hoofden, mogelijk geïnspireerd zijn door de gezichten van zeelieden en kooplui die hij in de haven tegenkwam, zijn de gelaatstrekken van degenen die getroffen zijn door pijn en verdriet, vol gratie. Zoals van der Weyden, schildert ook Matsys ogen vol tranen.

Op het middelste paneel zien we niet het lijden, maar de klaagzang na het lijden. Het toont het moment waarop Jozef van Arimathea 119 de Maagd Maria om toestemming komt vragen om het lichaam van Christus te begraven. Achter de centrale handeling ligt de heuvel Golgotha, met zijn paar bomen, het kruis en de gekruisigde dieven.
Op het linkerpaneel is te zien hoe Salome het hoofd van Johannes de Doper aanbiedt aan Herodes de Grote 120 , koning van Judea, een vazalstaat van Rome.
Het rechterpaneel is een scène van buitengewone wreedheid. Het toont Johannes de Doper, wiens lichaam in een ketel met kokende olie wordt gedompeld. De heilige, naakt vanaf zijn middel, lijkt bijna engelachtig, alsof hij niet lijdt. Om hem heen een menigte sadistische gezichten, lelijke boeren in schreeuwerige kleding. De enige uitzondering op deze regel is de figuur van een jonge man, mogelijk een afbeelding van de schilder zelf, die het tafereel vanaf de kruin van een boom bekijkt.
De gezichten van de figuren die Johannes de Doper omringen, net als de gezichten van de figuren die de ketel verwarmen, zijn rechtstreeks overgenomen van een tekening van Leonardo da Vinci, Man misleid door zigeuners (vroegere titel: De vijf groteske koppen, circa 1494, Windsor Castle, Engeland).
Vlaamse ironie en humor verwelkomden die van Da Vinci!

Bij Da Vinci lijken de gezichten zelfs in lachen uit te barsten als ze naar elkaar en naar de gekroonde figuur in het midden kijken. De bladeren van deze kroon zijn niet die van de laurierbomen ter ere van dichters en helden, maar die van… een eik. De antihumanistische en oorlogszuchtige paus die in die tijd in Rome zegevierde, was Julius II, 121 die door Rabelais in de hel werd opgesloten omdat hij kleine pasteitjes verkocht. Giulio was een lid van een machtige Italiaanse adellijke familie, het Huis Della Rovere, letterlijk « van de eik »…
C. Erasmiaanse wetenschap van het groteske
1. In religieuze schilderkunst
Het gebruik van groteske koppen (tronies), die de lage passies uitdrukken die slechte mensen overweldigen en domineren, was een gangbare praktijk in religieuze schilderijen om de werken levendiger en contrastrijker te maken.
In 1505 reisde Dürer naar Venetië en de universiteitsstad Bologna om perspectief te leren. Vervolgens reisde hij verder naar het zuiden, naar Florence, waar hij, volgens de experten, de werken van Leonardo da Vinci en van de jonge Raphael ontdekte. Vervolgens reisde hij naar Rome.

Christus tussen de Schriftgeleerden (1506, Collectie Thyssen Bornemisza, Madrid) werd in vijf dagen in Rome geschilderd en weerspiegelt ook de mogelijke invloed van Da Vinci’s grotesken.
Dürer was begin 1507 terug in Venetië, alvorens hij datzelfde jaar naar Neurenberg terugkeerde.
Een ander sprekend voorbeeld is het schilderij De kruisdraging van Jheronimus Bosch (na 1510, Gent). Het hoofd van Christus wordt omgeven door een dynamische groep « tronies » of groteske gezichten.

Werd Bosch geïnspireerd door Da Vinci en Matsys, of was het andersom? Hoewel de compositie op het eerste gezicht chaotisch lijkt, is de structuur heel doordacht.
Het hoofd van Christus, in Bosch’s oeuvre, bevindt zich precies op het snijpunt van twee diagonalen. De balk van het kruis vormt een diagonaal, met linksboven de figuur van Simon van Cyrene die Christus helpt het kruis te dragen, en rechtsonder de « slechte » moordenaar.
De andere diagonaal verbindt de afdruk van het gezicht van Christus op de lijkwade van Veronica (linksonder) met de afdruk van de berouwvolle dief (rechtsboven). Hij wordt agressief bedreigt door een slechte charlatan of Farizeeër en een slechte monnik. Bosch verwijst hiermee duidelijk naar het religieuze fanatisme van zijn tijd.
De groteske koppen doen denken aan de maskers die vaak in de Passiespelen worden gebruikt en aan de karikaturen van Leonardo da Vinci. Het gezicht van Christus daarentegen is sereen en vol zachtheid. Hij is de lijdende Christus, door iedereen verlaten, die over alle kwaad in de wereld zal zegevieren. Deze voorstelling past perfect bij de ideeën van de Devotio Moderna. 122


Quinten Matsys, in zowel zijn Kruisdraging als zijn Ecce Homo (1526, Venetië, Italië) is duidelijk vertrouwd met de Bosch-traditie.
2. Bankiers, tollenaars en woekeraars

Matsys’ satirische veroordeling van woeker en hebzucht houdt rechtstreeks verband met de religieuze, filosofische, sociale en politieke kritiek van Erasmus en More.
Marlier beschrijft op meesterlijke wijze hoe woekeraars en speculanten de dominante spelers werden in het economische leven van die tijd in Antwerpen, een situatie die doet denken aan de huidige wereldwijde situatie:
« In de 16e eeuw ging de geleidelijke vervanging van het oude corporatieve regime door de nieuwe kapitalistische economie gepaard met een opeenvolging van crisissen, waaronder vooral de gewone mensen leden. Speculatie op de aandelenmarkt, monetaire manipulatie en geldhandel bevorderen de opbouw van aanzienlijke fortuinen, maar leiden ook tot verarming en vaak de ondergang van ambachtslieden en boeren. Rijke handelaren en financiers nemen de industrie over en verlagen de arbeider tot de rang van proletariër. Werknemers moeten zich nu onderwerpen aan de condities van de werkgevers. Lonen worden niet langer gerespecteerd en er is vaak sprake van grote werkloosheid, waardoor gezinnen in armoede terechtkomen.
De economische omwenteling ging gepaard met financiële problemen, veroorzaakt door de toestroom van edele metalen (goud en zilver) uit Amerika naar Spanje. In Antwerpen vonden gigantische banktransacties plaats. Onder Karel V groeide de stad uit tot de grootste geldmarkt van Europa. Vanaf het derde decennium van de eeuw begon de koopkracht van valuta te dalen [inflatie], wat leidde tot een voortdurende prijsstijging. De lonen blijven daarentegen gelijk. De financiers monopoliseren de goederen, houden de monopolies in handen en nemen zelfs het land in beslag, terwijl ze de pachters genadeloos uitknijpen. Dit zijn de nouveau riches, tegen wie de armen en de zwakken morren, maar die de keizer beschermt, omdat zij de enigen zijn die hem de fondsen kunnen voorschieten die hij nodig heeft voor zijn Europese politiek.
Karel V moest gehoor geven aan de draconische eisen van zijn bankiers en de exorbitante rente die hij moest betalen, dwong hem tot een belastingverhoging. Hij verdisconteert de opbrengsten van toekomstige belastingen en veilt bepaalde schatkistkantoren. We kunnen ons voorstellen welke misstanden hieruit voortkomen. Belastingen worden niet rechtstreeks door de overheid geheven, maar worden verpacht aan accijnsbetalers, die zichzelf door hun hoge belastingen haten. Ze zijn genadeloos tegenover de kleine mensen, die ze het weinige dat ze bezitten afpakken. »
« In zo’n situatie », concludeert Marlier, « waar crisissen zich vermenigvuldigen, waar van de ene op de andere dag een vals voorspoedige ondergang volgt, waar de handel wordt overspoeld door een groot aantal oneerlijke praktijken, moet woeker wel floreren. Van hoog tot laag op de maatschappelijke ladder worden veel mensen gedwongen om geld te lenen, tegen torenhoge rentetarieven. Op alle niveaus van de samenleving is de woekeraar actief op zoek naar winst. De slachtoffers vallen zowel onder de aristocratie als onder de boeren en arbeiders. In de steden is er nu een klasse mannen en vrouwen die alleen van woeker leven. » 123


Daarbij komt nog dat de Fuggers en vooral de Welsers 124 nauw betrokken waren bij de vroege slavenhandel van Afrika naar Amerika.
De Fuggers gebruikten hun mijnen in Oost-Europa en Duitsland om manillas te produceren. Dit waren koperen en bronzen armbanden die de geschiedenis ingingen als ruilobjecten en « handelsgeld » aan de kusten van West-Afrika.
De Welsers, die zich toelegden op de handel in specerijen en textiel, probeerden een kolonie te stichten in het huidige Venezuela (de Spaanse naam is afgeleid van het Italiaanse Venezziola, « Klein Venetië », dat later Welserland werd) en verscheepten meer dan 1.000 Afrikaanse slaven naar Amerika.
Ondertussen werden in de huizen van de welvarende burgers van Augsburg slaven van Indië gedwongen om voor hun « meesters » te werken.

Volgens de officiële website van de familie Fugger is het verhaal dat Anton Fugger in 1530 zijn schuldbewijzen in het vuur gooide, voor het oog van Karel V, om zo ruimhartig de terugbetaling van leningen kwijt te schelden, puur uitvindsel en propaganda.
Maar hij verleende de nieuwe keizer een kleine schuldvermindering (haircut). In ruil daarvoor zag Karel V af van de door hem voorgestelde « Keizerlijke Monopoliewet », die de macht van de banken en handelshuizen van het Heilige Roomse Rijk aanzienlijk zou hebben beperkt.
Volgens Fugger-onderzoeker Richard Ehrenberg ontstond het verhaal over Anton pas aan het einde van de 17e eeuw, alleen maar om aan te tonen hoe trouw zij waren aan de keizer. 125
Thomas More en Erasmus veroordelen de brutale opkomst van aasgier-kapitalisme, uitbuiting en criminele financiële praktijken in Utopia.
Zonder de opkomst van het moderne ondernemerskapitalisme te ontkennen, veroordeelt Erasmus botweg de misstanden van ongebreideld financieel winstbejag:
« Christus », zo verklaart hij, « verbiedt niet vindingrijke activiteiten, maar de tirannieke drang naar profijt. » 126
Ambtenaren, zo betoogde hij in zijn Opvoeding van een christelijke prins (1516), geschreven ter lering van de jonge Karel V die het boek nooit zal lezen, moesten worden gerekruteerd op basis van hun bekwaamheid en verdiensten, niet vanwege hun roemruchte naam of maatschappelijke status.
Voor Erasmus (satirisch sprekend door de mond van Zotheid):
« De meest dwaze en verachtelijke van alle menselijke klassen zijn de handelaren. Ze zijn voortdurend bezig met hun walgelijke liefde voor winst en gebruiken de meest doeltreffende middelen om die te bevredigen: liegen, meineed, diefstal, fraude en bedrog vullen hun hele leven. Ze beschouwen zichzelf echter wel een belangrijk persoon, want hun vingers zitten vol met gouden ringen en er zijn genoeg vleiende monniken die niet blozen om hen in het openbaar de meest eervolle titels te geven om zo een deel van hun oneerlijk verkregen rijkdom in te palmen. » 127

Volgens Larry Silver, op basis van de registers van de boekhouding die in dit werk zijn afgebeeld en het feit dat de belastinginning in die tijd aan privé agenten was toevertrouwd, zou men de naam van dit werk, De woekeraars moeten veranderen in De tollenaars.
Dat verandert niets aan het feit dat het centraal onderwerp van dit werk overeenkomt met de inhoud van een oud spreekwoord uit die tijd:
« Een woekeraar, een molenaar, een geldwisselaar en een tollenaar zijn de vier evangelisten van Lucifer. »
De man rechts (de woekeraar met een groteske uitdrukking) geeft hier een deel van de buit aan de gemeentesecretaris (de tollenaar, met een « normale » uitdrukking). De woekeraar, die zijn eigen leren beurs beschermd, toont hier het groteske en lelijke gezicht van hebzucht, gerechtvaardigd door de wet en wat in de officiële registers werd vastgelegd.
De actieve/passieve medeplichtigheid tussen de twee mannen is de ware lelijkheid van het verhaal. Silver geeft toe dat geldwisselaars vaak dezelfde rol speelden als bankiers, waarbij hij economisch historicus Raymond de Roover citeert.
Bovendien werd de vierde beschuldigde, de molenaar (doelwit van de schilderijen van Bosch en Bruegel), vaak gehekeld omdat de graanprijs een steeds terugkerend pijnpunt werd in tijden van schommelende prijzen voor basisproducten, zoals in deze periode het geval was.
Aangezien de verarming van de bevolking, in het bijzonder vanaf de jaren 1520, werden dergelijke satirische veroordelingen van financiële hebzucht natuurlijk heel populair. Het onderwerp werd vrijwel onmiddellijk overgenomen door de zoon van de schilder, Jan Matsys (1510-1575), die het vrijwel identiek kopieerde, Marinus van Reymerswaele (1490-1546) en Jan Sanders van Hemessen (1500-1566).
De bankier en zijn vrouw


In een meer « beschaafde » versie van deze metafoor, op hetzelfde thema, vinden we de beroemde Bankier en zijn vrouw van Quinten Matsys (1514, Louvre, Parijs). 128
In een hoofdstuk van zijn boek De Vlaamse Primitieven getiteld De erfgenamen van de grondleggers beschouwt kunsthistoricus Erwin Panofsky 129 dit werk als een « reconstructie » van een « verloren werk van Jan van Eyck (een « schilderij met halffiguren, voorstellende een baas die zijn rekeningen vereffent met zijn werknemer »), dat Marcantonio Michiel beweert te hebben gezien in de Casa Lampugnano in Milaan. »
Laten we nogmaals benadrukken dat dit geen dubbelportret is van een bankier en zijn vrouw, maar één metafoor.
Terwijl de bankier (in hetzelfde gebaar als Jacob Fugger op het schilderij van Lorenzo Lotto) controleert of het gewicht van het metaal van de munten overeenkomt met hun nominale waarde, werpt zijn vrouw, die de bladzijden van een getijdenboek omslaat, een trieste blik op de hebzuchtige activiteiten van haar zichtbaar ongelukkige echtgenoot.
In 1963 schreef Georges Marlier:
« Het schilderij van het Louvre heeft geen satirische toon, maar weerspiegelt een morele bekommering (…) De stichtelijke bedoeling wordt onderstreept door een inscriptie die op de lijst verscheen toen het schilderij zich in de collectie Stevens in Antwerpen bevond, rond het midden van de 17e eeuw: “Stature justa et aequa sint podere” (laat de weegschaal rechtvaardig zijn en de gewichten gelijk) 130
In Leviticus XIX, 35-36 kunnen we lezen:
« 35. Doe niets dat in strijd is met de billijkheid, noch in oordelen, noch in normen, noch in gewichten, noch in maten.
« 36. Laat de weegschaal rechtvaardig zijn en de gewichten zoals ze horen te zijn; Laat de korenmaat rechtvaardig zijn, en laat de bekerhouder zijn maat hebben. »
De bankier heeft, naast de weegschaal die hij gebruikt, ook een weegschaal aan de muur hangen achter zich. Voor christelijke humanisten is het gewicht van materiële rijkdom het tegenovergestelde van dat van geestelijke rijkdom. In Van der Weydens Laatste Oordeel in Beaune toont de schilder ironisch genoeg een engel die de herrezen zielen weegt en de zwaarste onder hen… naar de hel stuurt.
Anderen beweren dat de vrouw van de bankier niet helemaal ongevoelig is voor de geldstukken, maar dat haar ogen meer op de handen van haar man gericht zijn dan op de voorwerpen die op tafel liggen. Vroomheid of het genot van rijkdom? Een stuk fruit op de plank (een appel of sinaasappel), net boven haar man, zou kunnen verwijzen naar de verboden vrucht, maar de kaars die niet brandt op de plank achter haar, herinnert aan de kortstondigheid van aardse genoegens.

Wanneer Marinus van Reymerswaele dit thema (hierboven) opneemt, lijkt de verleiding voor de vrouw om geld op tafel te leggen nog wat groter.

We kunnen aannemen dat de bolle (convexe) spiegel, 131 die op de voorgrond op de tafel van het echtpaar is geplaatst, functioneert als een « mise en abyme » (een « kamer in een kamer » of « een schilderij in een schilderij »). We zien een man (de bankier?) die zelf een boek (religieus?) leest.
De bolle spiegel toont niet noodzakelijkerwijs een bestaande, reële ruimte, maar kan ook een denkbeeldige plaats buiten de ruimte-tijd van de hoofdscène weergeven. Het kan eventueel de bankier in zijn toekomstige leven laten zien, vrij van hebzucht, die met grote passie een religieus boek leest?
Terwijl het gebruik van bolle spiegels (waarvan de optische wetten werden beschreven door Arabische wetenschappers zoals Alhazen en bestudeerd door Franciscanen uit Oxford, zoals Roger Bacon). 132 doet Matsys’ werk denken aan Van Eycks’ Echtpaar Arnolfini (1434, National Gallery, Londen) 133 en Petrus Christus’ (1410-1475) Goudsmid in zijn atelier of Sint-Eligius 134 (1449, Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York) en is een oprecht en zeer geslaagd eerbetoon aan Van Eyck.
Het goede nieuws is dat de tot nu toe meest aanvaarde hypothese over de betekenis van dit schilderij is dat het een religieus en moraliserend werk is, met als thema de ijdelheid van aardse goederen in tegenstelling tot tijdloze christelijke waarden, en een veroordeling van hebzucht als een doodzonde.
De roeping van Mattheüs.
Inhoudelijk gezien kan het schilderij ook in verband worden gebracht met een gemeenschappelijk en populair thema uit die tijd, namelijk De roeping van Mattheüs.135
« 9. Toen Jezus daar wegging, zag Hij een man, Mattheüs genaamd, in het huisje van de tollenaar zitten. Hij zei tegen hem: ‘Volg Mij’, en Mattheüs stond op en volgde hem.
« 10. Terwijl Jezus in het huis van Mattheüs zat te eten, kwamen er veel tollenaars en zondaars bij Hem en zijn discipelen eten.
« 11. Toen de Farizeeën dit zagen, vroegen ze zijn leerlingen: ‘Waarom eet uw Meester met tollenaars en zondaars?’
« 12 Toen Jezus dit hoorde, zei hij: ‘Gezonde mensen hebben geen dokter nodig, maar zieke mensen wel.’
« 13. ‘Ga daarom op weg en leer wat dit betekent: Barmhartigheid wil Ik en geen offers’[a]; want Ik ben niet gekomen om rechtvaardigen te roepen, maar zondaars.‘ «
(Mattheüs 9, 9-13)
De bovenstaande passage is waarschijnlijk autobiografisch, omdat het de roeping beschrijft van Matteüs om Jezus te volgen als apostel. Zoals bekend, reageerde Mattheüs positief op de roeping van Jezus en werd hij een van de twaalf apostelen.
Volgens het Evangelie heette Mattheüs oorspronkelijk Levi. Hij was een belastinginner (tollenaar) in dienst van Herodes en was daarom niet erg geliefd. De Romeinen dwongen het Joodse volk om belasting te betalen. Het was bekend dat tollenaars de bevolking oplichtten door meer te vragen dan vereist en het verschil in eigen zak stoken. Toen Levi eenmaal de roeping om Jezus te volgen had aanvaard, werd hij vergeven en kreeg hij de naam Mattheüs, wat « geschenk van Jahweh » betekent.
Dit thema kon Erasmus alleen maar bevallen, sinds het niet de nadruk legde op straf of zonde zelf, maar op positieve transformatie en verandering als resultaat van vrije wilskeuze.


Zowel Marinus van Reymerswaele (in 1530) als Jan van Hemessen (in 1536), die Matsys na diens dood kopieerden en door hem werden geïnspireerd, namen het onderwerp over. Op het schilderij van Van Hemessen, net als op het werk van Matsys, zien we ook de vrouw van de belastinginner vooraan staan, eveneens met haar hand op een open boek.
3. De Da Vinci-connection (II)


Samengevat kunnen we zeggen dat er tot nu toe drie elementen in Matsys’ werk zijn die ons in staat stellen zijn nauwe banden met Italië en Da Vinci vast te stellen.
- Zijn goede kennis van perspectief, in het bijzonder die van Piero della Francesca, zoals blijkt uit het marmeren gewelf in Italiaanse stijl dat voorkomt in het Triptiek van Sint-Anna (Antwerpen); 136
- Zijn overname van Da Vinci’s vijf groteske koppen, in de sadisten aan het werk in het zijluik van het Sint-Anna retabel (Antwerpen)
- De overname van de houding van de Maria met kind en Sint-Anna van Da Vinci (Louvre) in Matsys’ Madonna met Kind (Poznan, Polen).
Hoe deze invloed tot stand kwam, blijft een raadsel. Er zijn meerdere hypothesen toegestaan, die elkaar kunnen aanvullen:
- Hij kon met andere kunstenaars die dergelijke reizen hadden gemaakt, van gedachten wisselen en in Italië contacten leggen. Een andere hypothese die onderzocht moet worden, is de vraag of Dürer, die zelf contacten in Italië had, mogelijk als tussenpersoon heeft gehandeld. Er wordt gezegd dat sommige anatomische tekeningen van Dürer naar Leonardo zijn gemaakt. Jacopo de’ Barbari schilderde een portret van Luca Pacioli, de franciscaan die Leonardo had geholpen Euclides in het Grieks te lezen. Dürer had Barbari in Neurenberg ontmoet, maar zoals we hierboven hebben gezien, was hun relatie niet erg coöperatief.
- Op vrij jonge leeftijd ging hij naar Italië (Milaan, Venetië, enz.) waar hij direct contact kon leggen met Leonardo of met een of meerdere van diens studenten. Volgens Philippe d’Aarschot werd Matsys, « zonder ooit een voet in Italië te hebben gezet, beïnvloed door Leonardo da Vinci. Is zijn Maria Magdalena (Museum Antwerpen) niet een replica van de Mona Lisa? « 137 Er wordt ook gezegd dat ook Holbein de Jongere beïnvloed werd door Leonardo, zoals blijkt uit enkele van zijn composities.138
- Matsys kreeg gravures te zien die door Italiaanse en Noord-Italiaanse kunstenaars waren gemaakt en verspreid. Hoewel de originele tekeningen en manuscripten na de dood van Leonardo’s meester in 1519 in Amboise werden gekopieerd en later verkocht door Melzi’s zoon, is Leonardo’s invloed op Matsys al vanaf 1507 merkbaar.

Het werk van Leonardo wekte de interesse van heel Europa. Zo werd in 1545 een levensgrote replica van het fresco Het Laatste Avondmaal van Leonardo da Vinci aangekocht door de Norbertijnerabdij van Tongerlo. Andrea Solario (1460-1524), een leerling van Leonardo da Vinci, zou het werk samen met andere kunstenaars hebben gemaakt. Uit recentelijk wetenschappelijk onderzoek blijkt echter dat Leonardo delen van deze replica zelf heeft geschilderd.

Professor Jean-Pierre Isbouts 139 en een team wetenschappers van onderzoeksinstituut IMEC onderzochten het doek met multispectrale camera’s. Daarmee kunnen de verschillende lagen van een schilderij worden gereconstrueerd en kunnen restauraties worden onderscheiden van het origineel.
Volgens de onderzoekers trekt één personage in het bijzonder de aandacht. Johannes, de apostel links van Jezus, is geschilderd met de speciale « sfumato »-techniek. Het is dezelfde techniek die werd gebruikt om de Mona Lisa te schilderen, en die alleen Leonardo beheerste, meent Isbouts.

Op vergelijkbare wijze neemt Joos Van Cleve in het onderste luik van zijn Bewening (1520-1525) de compositie van Leonardo da Vinci’s Laatste Avondmaal over, wat duidelijk aantoont dat dit schilderij bij de meeste schilders in het Noorden bekend was.
Tenslotte, zoals Silver opmerkt, verschijnt één van Leonardo’s Vijf groteske koppen, in spiegelbeeld ten opzichte van het origineel, opnieuw voor de oude man in Matsys’ later schilderij, het Ongepast koppel!
Dat het in spiegelbeeld verschijnt, zou verklaard kunnen worden als Matsys het in een gravure zag. Bij het afdrukken van de plaat verschijnt het afgedrukte beeld daadwerkelijk negatief ten opzichte van het origineel.




Ook een studie van Leonardo da Vinci van een (niet-grotesk) hoofd van een apostel voor het Laatste Avondmaal, vertoont kenmerken die dicht bij die van Matsys liggen.

4. De kunst van het groteske per se

Leonardo da Vinci’s werk betreffende visi monstruosi (monsterlijke gezichten), dateert in ieder geval uit de vroege Milanese periode (jaren 1490), toen hij op zoek ging naar een model om « Judas » op het fresco van het Laatste Avondmaal (1495-1498) te schilderen.
Er wordt gezegd dat Da Vinci zich bij de schepping van de personages in het schilderij liet inspireren door echte mensen in en rond Milaan. Toen het schilderij bijna klaar was, had de meester nog steeds geen model voor Judas. Er wordt gezegd dat hij rondhing in de gevangenissen van Milaan en bij criminelen op zoek naar een passend gezicht en een passende uitdrukking voor Judas, de vierde figuur van links en de apostel die uiteindelijk Jezus verraadde.
Da Vinci adviseerde kunstenaars om altijd een notaboekje bij de hand te hebben en mensen te tekenen die « ruziemakend, lachend of vechtend » waren. Hij lette op de vreemde gezichten op het plein. In een briefje waarin hij uitlegt hoe je vreemden kunt tekenen, voegt hij toe:
« Ik zal niets zeggen over monsterlijke gezichten, omdat die van nature in het geheugen blijven hangen. »
Wanneer de prior van het klooster bij Ludovico Sforza klaagt over Da Vinci’s « luiheid » bij het ronddwalen door de straten op zoek naar een crimineel die Judas kan voorstellen, antwoordt de kunstenaar dat als hij niemand anders kan vinden, de prior zelf een ideaalmodel kan worden… Tijdens de uitvoering van het schilderij is Da Vinci’s vriend, de Franciscaanse wiskundige Luca Pacioli, in de stad en heeft contact met de meester.
Voor de laatstgenoemde, die altijd gretig was om de dynamiek van de contrasten in de natuur te verkennen en vast te leggen, is lelijkheid niet zomaar een spel, maar inherent aan de rol van de kunstenaar:
« Als de schilder schoonheden wil zien die hem betoveren », schrijft hij in zijn notitieboek, « dan is hij is de meester van hun productie, en als hij monsterlijke dingen wil zien die hem bang zouden kunnen maken of die belachelijk en lachwekkend of werkelijk zielig zouden zijn, dan is hij hun Heer en God. »
Da Vinci en anderen humanisten vroegen zich af wat de relatie was tussen innerlijke schoonheid (deugdzaamheid) en uiterlijke, lichamelijke schoonheid. Op de achterkant van Da Vinci’s portret van Genivra de Benci (Washington DC), ziet men een vaandel met daarop de Latijnse tekst: « Virtutem forma decorat » (Schoonheid siert de deugd). En dus ook omgekeerd, vroeg men zich af hoe iemands lelijk uiterlijk de uitdrukking was van zijn ondeugdzaamheid.
De Italiaanse experte Sara Taglialagamba meent dat het groteske, dat abnormaal of « buiten de normen » is, niet door Leonardo werd bedoeld « om zich tegen schoonheid te verzetten », maar als een contrast, als « het tegenovergestelde van evenwicht en harmonie ». 140
De misvormingen die kenmerkend zijn voor de figuren van Da Vinci, komen zowel bij mannen als vrouwen voor. Ze komen voor bij zowel jonge als oude mensen (hoewel ze zich vooral op oudere mensen concentreren). Geen enkel lichaamsdeel wordt gespaard en ze worden vaak gecombineerd om de geportretteerden een nog dierlijker uiterlijk te geven.

Dürer, die vandaag de dag wordt beschuldigd van racial profiling, nam de studie van de canon van de menselijke proporties zeer ernstig. Deze studie werd, met name door de ontdekking van Vitruvius’ boek De Architectura, beschouwd als de sleutel tot harmonieuze verhoudingen voor zowel de schilderkunst als de architectuur en de stedenbouw.
« Schoonheid, schreef Vitruvius, wordt geproduceerd door het aangename uiterlijk en de goede smaak van het geheel, en door de afmetingen van alle onderdelen die op de juiste wijze in verhouding tot elkaar staan. » 141
Dürer heeft alle delen van het menselijk lichaam systematisch gemeten om harmonische relaties tussen de delen vast te stellen. Hij concludeert dat de variaties in de verhoudingen van gezichten en lichamen overeenkomen met de variaties die door geometrische projecties worden gegenereerd. Ze veranderen niet qua harmonie, maar ze zien er anders uit, zelfs grotesk, als ze vanuit een bepaalde hoek worden geprojecteerd.
Da Vinci en Dürer, en later Holbein de Jongere in zijn schilderij De ambassadeurs (1533, National Gallery, Londen), waren meesters in de wetenschap van de « anamorfosen », dat wil zeggen geometrische projecties vanuit raaklijnen waardoor een afbeelding zo vervormd wordt dat ze moeilijk te herkennen is voor de toeschouwer die rechtstreeks naar het platte oppervlak kijkt, terwijl de afbeelding alleen te begrijpen is wanneer deze vanuit deze verrassende hoek wordt bekeken.

Het feit dat meesters die geraffineerd mooie figuren creëren, zoals Da Vinci of Matsys, zich plotseling uitten met gekke karikaturen en bizarre tronies, lijkt misschien verontrustend, maar dat hoeft niet. Elke karikatuur is gebaseerd op metaforische gedachten, net als alle grote kunst. Renaissancekunst wordt vaak gezien als ordelijk en geruststellend, maar de grotesken zijn slechts een voortzetting van de spuiers van de kathedraalbouwers. En de « monsters » in de marge van zoveel verluchte manuscripten die Bosch uitlicht, zijn een voorbode van die van François Rabelais, Francesco Goya en James Ensor. 142
Zijn tronies zijn zo misvormd en afwijkend van de gebruikelijke normen dat ze als « grotesk » worden beschreven. Ze kunnen ons doen huiveren maar ze kunnen ons ook aan het lachen krijgen als we met tegenzin instemmen om neer de kijken op onze eigen onvolkomenheden of die van onze dierbaren die we liever niet willen zien. Laten we eerlijk zijn. Ons uiterlijk staat heel ver van de beelden die we in tijdschriften en op schermen zien en die we voor de werkelijkheid aanzien.
In de Lof der Zotheid van Erasmus prijst de verteller (de personificatie van de Zotheid) voor het eerst, naast vele andere prestaties, zijn eigen leidende rol bij het bereiken van dingen die met pure logica, menselijke rede, formele wijsheid en intellect zouden mislukken, zoals de belachelijke handelingen die nodig zijn om de menselijke voortplanting te bewerkstelligen.
Pas op, waarschuwt de Zotheid, als iedereen wijs en vrij van zotheid zou zijn, zou de wereld snel ontvolkt worden!
5. De metafoor van « Het ongepast koppel »

Als Erasmus met bijtende ironie de corruptie en zotheid van koningen, pausen, hertogen en prinsen aan de kaak stelt, legt hij ook dezelfde corruptie bloot die de gewone man treft, bijvoorbeeld oudere mannen die hun vrouw verlaten om bij jongere vrouwen in te trekken, een praktijk die zo wijdverbreid was, betreurde de Zotheid, « dat het bijna een onderwerp van lof is. »
De Zotheid feliciteert zichzelf met satirische ironie voor het uitstekende werk dat het doet door senioren, zowel mannen als vrouwen, enkele flinke korrels zotheid te geven:
« Het is werkelijk mijn edelmoedigheid als je overal oude mannen ziet, zo oud als Nestor, die zelfs geen menselijk gezicht meer hebben, trillend, warrig, tandeloos, grijs, kaal, of liever, om de beschrijving van Aristophanes te gebruiken: smerig, krom, ellendig, verwelkt, zonder haar of tanden of seks, die zoveel plezier in het leven hebben, zo vol jeugdige hartstocht dat de een zijn haar wit verft, de ander zijn kaalheid verbergt onder een pruik, weer een ander tanden gebruikt die hij misschien van een varken heeft geleend, weer een ander sterft van liefde voor een jong meisje en elke jongere overtreft in amoureuze onzin. We zien stervende lijken die trouwen met een jong meisje, zelfs zonder bruidsschat, die van nut zal zijn voor anderen; Het is zo wijdverbreid dat het bijna een onderwerp van lof is.
« Maar het is nog veel aangenamer om oude vrouwen te zien die al dood zijn van aftakeling, zo lijkbleek dat je zou denken dat ze uit de hel zijn teruggekeerd, en die ondanks alles maar blijven herhalen: Wat is het licht van de dag toch mooi! ze zijn nog steeds loops en zelfs, zoals de Grieken zeggen, in de bronsttijd nodigen ze een goedbetaald hertenkalf uit in hun huis, maken zich ijverig op, bergen nooit hun spiegel op, plukken hun schaamhaar, tonen hun zachte en stinkende borsten, ontlokken een trillende kreet uit een kwijnend verlangen, stoppen nooit met drinken, mengen zich onder de dansen van jonge meisjes en schrijven slechte liefdesbrieven. Dit zorgt ervoor dat iedereen moet lachen; wij vinden ze volkomen zot en dat zijn ze ook; maar ze zijn tevreden met zichzelf, voor het moment ondergedompeld in de grootste genoegens, badend in honing en, dankzij mij [Zotheid], gelukkig. » 143
De vorming van ongelijke paren in de literatuurgeschiedenis gaat terug tot de oudheid, toen Plautus, een Romeinse komische dichter uit de 3e eeuw voor Christus, oudere mannen afraadde om jongere vrouwen het hof te maken. Erasmus neemt slechts één thema uit de satirische literatuur over, met name Het Narrenschip, dat in hoofdstuk 52, waarin afgunst en hebzucht worden gecombineerd, het thema « huwelijk om geld » aansnijdt.
Naast de Lof der Zotheid wijdde Erasmus in 1529, in dialogen die hij schreef om Latijn aan kinderen te leren, een Colloquium getiteld Het ongepast koppel. (Uittreksel, hieronder)
« Het ongepast koppel »
Gabriel: Ken jij Lampride Eubule?
Petronius: Er is geen betere of meer fortuinlijke burger in deze stad.
Gabriel: En zijn dochter Iphigenia?
Petronius: Je gaf de bloem een naam aan jonge dames van haar leeftijd.
Gabriel: Dat klopt. Goed! Weet je met wie ze getrouwd is?
Petronius: Ik weet het als je het mij vertelt.
Gabriel: Aan Pompilius Blenus.
Petronius: Deze opschepper, die met zijn opschepperij voortdurend iedereen irriteert?
Gabriel: Zelf.
Petronius: Maar hij is hier al lang beroemd, vooral om twee redenen: zijn leugens en zijn ziekte, die nog steeds geen echte naam heeft, ondanks het grote aantal mensen dat eraan lijdt!
Gabriel: Dit is een zeer trotse jeuk, die niet zou wijken voor lepra, elefantiasis, impetigo, jicht of jicht van de kin, als er een conflict was om de eerste rang.
Petronius: Dat is wat de stam van de artsen verkondigt.
Gabriel: Wat heeft het nu voor zin om het jonge meisje aan u te beschrijven, aangezien u haar kent, en dit ondanks het feit dat haar opsmuk veel plezier heeft toegevoegd aan haar natuurlijke charmes? Beste Petronius, je zou haar voor een godin aanzien: haar kleding stond haar wonderwel. Intussen kwam de gelukkige verloofde bij ons aan, met een gebroken neus, slepend met zijn been – maar met minder gratie dan Zwitserse huurlingen doorgaans doen – met vuile handen, een vieze adem, doffe ogen, een verbonden hoofd en pus uit zijn neus en oren. Sommige mensen dragen ringen aan hun vingers, hij heeft ze zelfs aan zijn benen.
Petronius: Wat is er met de ouders gebeurd dat ze zo’n kind aan zo’n monster toevertrouwen?
Gabriel: Ik weet het niet, behalve dat de meeste mensen tegenwoordig hun verstand lijken te zijn verloren.
Petronius: Misschien is hij wel heel rijk?
Gabriel: Hij is extreem rijk, maar vooral aan schulden.
Petronius: Als het meisje haar vier grootouders van vaders- en moederskant had vergiftigd, welke wredere martelingen had ze dan kunnen ondergaan?
Gabriel: Als ze op de as van haar vader had gepist, zou ze gestraft zijn door gedwongen te worden om zo’n monster maar één keer te kussen.
Petronius: Ik ben het er helemaal mee eens.
Gabriel: Naar mijn mening is deze behandeling veel wreder dan haar bloot te stellen aan beren, leeuwen of krokodillen. Want deze wilde beesten zouden haar zo’n opmerkelijke schoonheid hebben gespaard, of een snelle dood zou een einde hebben gemaakt aan haar martelingen.
Petronius: Je hebt gelijk. Deze daad lijkt mij absoluut Mezentius waardig, die volgens Vergilius de levenden aan de doden koppelde, handen op handen en mond op mond. Maar zelfs deze tiran zou, tenzij ik in de war was, niet zo barbaars zijn geweest om zo’n mooi jong meisje met een lijk te verenigen. Bovendien is er geen lijk waaraan men niet liever gehecht zou willen zijn dan aan dit stinkende karkas: want zijn adem is een waar gif, zijn spraak een wond en zijn aanraking brengt de dood.144
Dit Erasmiaanse thema van « niet bij elkaar passende geliefden » is erg populair geworden. Volgens kunsthistoricus Max J. Friedlander 145 was Matsys de eerste die dit thema in onze gewesten propageerde. Matsys beeldt dit thema uit door een oudere man af te beelden die verliefd wordt op een jongere, mooiere vrouw. Hij kijkt haar vol bewondering aan, maar merkt niet dat ze zijn beurs steelt. In werkelijkheid komt de groteske lelijkheid van de man, verblind door zijn verlangen naar de jonge vrouw, overeen met de lelijkheid van zijn ziel. De jonge vrouw, verblind door haar hebzucht, lijkt oppervlakkig gezien een tof meisje, maar in werkelijkheid misbruikt ze de naïeve dwaas.
Van buitenaf ziet de toeschouwer al snel dat het geld dat ze van de oude gek steelt, direct in de handen van de nar terechtkomt die achter haar staat, wiens gezicht zowel lust als hebzucht uitdrukt. De moraal dit werk is dat alle winst noch naar hem noch naar haar gaat, maar naar de zotheid zelf (De Nar)! Een situatie die doet denken aan Bosch’ schilderij uit 1502, De Goochelaar (1475, St Germain-en-Laye).
Véél meer dan « ongelijke » liefde (een oude man met een jonge vrouw), benadrukt het schilderij van Matsys een soort van « wederzijdse corruptie » sinds elkeen alleen maar denkt aan zijn eigenbelang. Net als in de geopolitiek, denken beide partijen dat ze ten koste van elkaar winnen, maar in werkelijkheid verliezen ze beiden. Vanuit dit oogpunt gaat de « moraal » van het gebeuren veel verder dan vreemdgaan tussen partners.
Zoals we al zeiden, werden de kwalen (zoals wellust en hebzucht), die tot dan toe door de Kerk waren beschouwd als « zonden », voor de christelijke humanisten een onderwerp van hartelijk gelach, waarbij het schilderij fungeerde als een « spiegel », waardoor de toeschouwer over zichzelf kon nadenken en zijn eigen karakter kon verbeteren.
In de folklore van Saksen en later voornamelijk in Vlaanderen is Tyl Uylenspieghel een belangrijke figuur. In het woord Uyl-en-spieghel betekent Uyl de wijsheid en spieghel de weerkaatsing. Zijn fratsen zijn in werkelijkheid een afspiegeling van volkswijsheid. Zijn fratsen zijn in werkelijkheid een afspiegeling van volkswijsheid.


Het thema van het ongepast koppel komt al voor in een kopergravure van Dürer uit 1495, waarop een jong meisje haar hand opent om geld uit de beurs van de oude man naar haar eigen hand over te hevelen. In 1503 pakte Jacopo de’ Barbari het onderwerp opnieuw op met De oude man en de jonge vrouw (Philadelphia).
Cranach de Oudere, 146 die Antwerpen in 1508 bezocht en duidelijk werd geïnspireerd door de grotesken van Matsys, maakte ontelbare variaties op dit thema (inclusief het gebruik van de grotesken van Da Vinci die door Matsys waren overgenomen!). Cranach reageerde op de groeiende vraag in het protestantse Duitsland, een productie die werd voortgezet door zijn zoon Cranach de Jongere. 147




Cranach zou zijn eigen variaties op het thema schilderen, waarbij hij het vaak alleen tot « wellust » beperkte en de geldkwestie wegliet. Hoe lelijker en ouder de man, en hoe mooier en jonger de vrouw, hoe meer het resulterende contrast een emotionele impact heeft die het storende karakter van de gebeurtenis benadrukt. Cranach vindt het leuk om de rollen om te draaien en laat een rijke oude vrouw zien, vergezeld door haar bediende, die een verleidelijke jongeman verleidt…

Jan Matsys, een van de zonen van Quinten Matsys, die ook met Erasmus bevriend was, heeft ons een interessante interpretatie van het thema nagelaten. Hij heeft er een sociale dimensie aan toegevoegd: arme gezinnen gebruiken hun dochters als lokaas om oudere, rijke heren te lokken, die met hun rijkdom en geld in staat zijn om de familie te voeden. Dit thema van « koppelaarsters » is ook door Goya aangesproken.
In een van Cranachs versies heeft de rijke man al een brood op tafel voor zich staan, een waar symbool van voedselchantage. Wat opvalt in de versie van Jan is de moeder, die achter de gekke oude man staat en naar het brood en het fruit op tafel staart. Hoewel hebzucht en lust nog steeds reëel zijn, dramatiseert Jan een gegeven context die niet zomaar belachelijk gemaakt kan worden.
Tot de vele andere kunstenaars die dit thema opnamen, behoren onder meer Hans Baldung Grien (1485-1545), Christian Richter (1587-1667) en Wolfgang Krodel de Oude (1500-1561). Geen van hen slaagde erin de metafoor van Matsys, die het meest trouw bleef aan de geest van Erasmus, volledig weer te geven: de zotheid die het spel wint. Een werkelijk lachwekkende situatie! De triomf van de zotheid! Ook hier baseert Matsys zich, zoals we al zeiden, voor het gezicht van de oude zot op Da Vinci’s schetsen van groteske koppen.
6. De “groteske oude vrouw”, auteurschap van Da Vinci

De oude man (rechts), Quinten Matsys, Musée Jacquemart André, Paris.
Op dit punt kunnen we de bespreking aandurven van wat misschien het meest schandalige schilderij ooit is, afwisselend genoemd de « groteske oude vrouw » of de « lelijke hertogin ».
Er is veel inkt gevloeid om te speculeren over zijn identiteit, zijn « ziekte » (de ziekte van Paget, volgens een dokter), zijn « geslacht », vooral om de blik van de toeschouwer te richten op een letterlijke, « op feiten gebaseerde » interpretatie, in plaats van om de hilarische metafoor te waarderen en te ontdekken die de kunstenaar schildert, niet op het paneel, maar zoals gezegd in het hoofd van de toeschouwer.
Het schilderij moet worden geanalyseerd en begrepen in samenhang met zijn tegenhanger – een begeleidend schilderij – waarop een oude man is afgebeeld, wiens aandacht deze oude vrouw wil afdwingen. Verrassend genoeg kan men op het eerste gezicht zeggen dat Matsys, lang vóór Cranach, hier de gebruikelijke genderrollen omdraait. We zien immers niet een oude man die een jong meisje probeert te verleiden, maar een oude vrouw die een rijke oude man probeert te versieren.
Ten eerste is er de oude dame, die in een staat van ultieme aftakeling verkeert en wanhopig probeert een rijke oude man te verleiden. Het uiterlijk van de persoon roept, net als bij Domenico Ghirlandaio‘s Oude man en jongen (1490, Louvre, Parijs), bij de toeschouwer meteen vragen op over de relatie tussen innerlijke en uiterlijke schoonheid.
« Vanuit een uiterlijk standpunt », schrijft een waarnemer, « is deze vrouw theoretisch gezien mooi, gezien haar prachtige jurk, met juwelen versierde accessoires en ontluikende bloem. Haar innerlijke schoonheid wordt echter weerspiegeld in haar overdreven en onaangename fysieke verschijning. » 148
Opnieuw is de literaire invloed duidelijk te zien in Lof der Zotheid (1511), dat vrouwen op de hak neemt die « nog steeds de coquette spelen », die « zich niet los kunnen maken van hun spiegels » en welke « niet aarzelen hun afstotelijke verschrompelde borsten te tonen ». 149

De kleding van de vrouw is duur. Ze is gekleed om indruk te maken, met onder andere een bolvormig hoofddeksel dat haar bijzondere gelaatstrekken accentueert. Ze tart de bescheidenheid die van oudere vrouwen tijdens de Renaissance werd verwacht en draagt een strak geregen lijfje dat haar gerimpelde decolleté benadrukt.
Haar haar is verborgen in de horens van een hartvormig kapje, waarover ze een witte sluier heeft geplaatst, vastgehouden door een grote broche versierd met juwelen.
Hoe goed ze ook gekleed was, toen dit paneel begin 16e eeuw werd geschilderd, waren haar kleren waarschijnlijk al tientallen jaren verouderd. Ze deden denken aan de kleren op het portret dat Van Eyck een eeuw eerder van zijn vrouw Margaret had gemaakt. Ze wekten eerder gelach dan bewondering op.
In De Ciceronianus, een fictieve dialoog gepubliceerd in 1528, stelt Erasmus dat literaire stijl, net als mode, van de ene op de andere dag verandert. Een van zijn personages, Nosophon, wordt geciteerd als hij zegt:
“Kijk maar naar beelden die niet zo oud zijn, geschilderd, laten we zeggen, zestig jaar geleden en zie wat gedragen werd door mensen van het schone geslacht die tot vooraanstaande families behoorden of aan het hof leefden. Als een vrouw nu zo gekleed in het openbaar kwam, zouden de dorpsgekken en straatjongens haar bekogelen met rot fruit.”
Hypologus, zijn gesprekspartner antwoordt dan:
“Wie zou het nu pikken als een fatsoenlijke getrouwde vrouw van die enorme hoorns en piramides en kegels boven op haar hoofd zou dragen en haar wenkbrauwen en slapen zou laten plukken zodat bijna haar halve hoofd kaal is.” 150
Deze hoofdtooi was een iconografisch symbool geworden van vrouwelijke ijdelheid. De horens werden vergeleken met die van de duivel of, in het beste geval, met de horens die aangaven dat zij door haar minnaars was bedrogen (cornuto). Het lijkt erop dat ze zichzelf verkoopt op basis van haar uiterlijk, want ze biedt een bloem aan. In de Renaissance-kunst staat deze bloem vaak symbool voor seksualiteit.
Het tragische lot van de afgesneden roos illustreert op de meest verontrustende manier het verstrijken van de tijd en daarmee ook het fysieke verval. Fris of kwetsbaar, de roos roept op tot onmiddellijk genot, maar lijkt tegelijkertijd te protesteren tegen de dood die haar wacht.

Er zijn verschillende namen genoemd om de vrouw te identificeren. In de 17e eeuw werd het schilderij verward met het portret van Margarete Maultasch (1318-1369) die, gescheiden van haar eerste echtgenoot Jean Henri van Luxemburg, hertrouwde met Lodewijk I, markgraaf van Brandenburg, na duizend-en-een verwikkelingen die resulteerden in de excommunicatie van het echtpaar door Clemens VI.
Een ingewikkeld verhaal in roerige tijden, waaraan Margarete de bijnaam « muil-tas’ (grote mond) of « hoer » in het Beierse dialect overhield. Het probleem is dat we andere portretten van Margarete kennen waarop ze op haar mooist is… Ze werd niettemin omschreven als « de lelijkste vrouw uit de geschiedenis » en kreeg de bijnaam « de lelijke hertogin ».
In de Victoriaanse tijd inspireerde deze afbeelding (of een van de vele versies ervan) John Tenniels afbeelding van de hertogin in zijn illustraties voor Lewis Carrolls Alice’s Adventures in Wonderland (1865). Dit hielp om de bijnaam te bevestigen en het personage tot een icoon te maken voor generaties lezers.

Ten tweede is er de oude man, wiens met bont afgezette gewaad en gouden ringen, hoewel niet zo duidelijk ouderwets of absurd als het kostuum van de vrouw, toch opzichtig rijkdom suggereren.
Zijn opvallende profiel doet denken aan het bekende profiel van de belangrijkste Europese zakenbankier in de 15e eeuw, de overleden Cosimo de’ Medici van Florence. Deze laatste, die een belangrijke rol had gespeeld als beschermheer van de kunsten en als voorstander van het Oecumenisch Concilie van Florence, verloor op latere leeftijd zowel zijn verstand als zijn waardigheid.
Het is opmerkelijk dat in 1513, het jaar dat het schilderij werd voltooid, de oorlogslustige paus Julius II, de grote vijand van Erasmus, stierf en Giovanni di Lorenzo de’ Medici de nieuwe paus werd onder de naam Leo X.

De figuur van de oude man doet ook denken aan de verloren gegane portretten uit het begin van de 15e eeuw van hertog Filips de Stoute van Bourgondië.
Als je nog een keer kijkt en de borsten van de vrouw vergeet, zie je dat haar gezicht, een gezicht is van… een vreselijke man.
Het zou een gehate politicus of theoloog uit die tijd kunnen zijn, die de een aan de ander verkoopt in een vlaag van hebzucht en lust.
Is de lelijke oude hoer misschien een verwijzing naar de bankier Jacob de Rijke, de perverse bankier van het Vaticaan? Laten we voor nu accepteren dat we het niet weten.
De Boheemse kunstenaar Wenceslaus Hollar (1607-1677) zag het dubbelportret van Matsys en maakte er in 1645 een gravure van. Hij voegde er de titel « Koning en koningin van Tunis, bedacht door Leonardo da Vinci, uitgevoerd door Hollar » aan toe.

Da Vinci’s « vaderschap » van dit werk was dus blijkbaar een publiek geheim.
In de carnavalsperiode, waarin mensen zich een paar dagen mochten onttrekken aan de regels van de maatschappij, althans in de Lage landen en de regio Noordrijn-Westfalen, werd er met veel plezier van rolwisselingen genoten. Arme boeren konden zich voordoen als rijke kooplieden, leken als geestelijken, dieven als politieagenten, mannen als vrouwen, enzovoort.

Het oorspronkelijke idee voor deze metafoor komt duidelijk van Da Vinci, die een klein schetsje maakte van een lelijke vrouw, mogelijk een oude hoer, opvallend genoeg met horens, een kapje en een klein bloemetje tussen haar borsten. Precies dezelfde attributen, metaforen en symbolen die Matsys later in zijn werk gebruikte!

Melzi, de leerling van Da Vinci, maar ook andere leerlingen of discipelen hebben hoogst waarschijnlijk het werk van hun meester gekopieerd of gebruikt. Het plaatsen van de oude geile vrouw tegenover een rijke Florentijnse koopman is dus misschien een originele grap van Melzi of Salai (« kleine duivel »), een lievelingsleerling van Da Vinci vooral bekend als een grapjas. Werden er onder de mantel tekeningen verkocht? Het blijft maar gissen.


Er zijn over de hele wereld verschillende grappige versies van het thema te vinden in zowel particuliere als openbare collecties.
Een andere schets, gemaakt door Da Vinci zelf of door zijn discipelen, toont een groteske wildeman, met overeind staand haar, vergezeld door een reeks grotesk ogende geleerden, van wie er één op Dante lijkt!

Da Vinci, die zijn geschriften altijd ondertekende met de woorden « man zonder letteren » (omo sanza lettere) 151, voelde zich verdrukt in zijn statuut als ambachtsman en werd nooit ernstig genomen door de boekgeleerden die Lucianus veroordeelde omdat zij hun ziel hadden verkocht aan de gevestigde orde.
Dit alles laat zien dat er niets « ziekelijk » was aan wat Matsys schilderde, maar dat hij deel uitmaakte van een « cultuur » van groteske gezichten waarvan variaties werden gebruikt om de metaforische inhoud en verbeelding van de humanistische cultuur te verrijken.
De impact van Matsys behandeling van dit kluchtig onderwerp was en blijft explosief. Van vluchtige schetsen van Da Vinci, maakte hij levensgrote en adembenemend hyperrealistische voorstellingen!
In de Windsor-collectie van de koningin bevindt zich een tekening met rood krijt waarop de vrouw vrijwel exact hetzelfde is afgebeeld als in het werk van Matsys.

Tot voor kort waren historici ervan overtuigd dat Quentin Matsys deze tekening, toegeschreven aan da Vinci, had « gekopieerd » en had vergroot als onderwerp van zijn olieverfschilderij.
« Da Vinci tekende dit unieke karakter, tot aan de gerimpelde borst die uit haar jurk tevoorschijn komt. Matsys heeft het alleen vergroot in olieverf. » 152
Recentelijk onderzoek suggereert echter dat het anders ging!
In werkelijkheid zou Melzi, of Da Vinci zelf, de rode krijt tekening naar het schilderij van Matsys hebben kunnen gemaakt, hetzij door er direct naar te kijken, hetzij op basis van reproducties. Kunt u zich voorstellen dat een Italiaan een Vlaamse schilder kopieert?
Susan Foister, adjunct-directeur en conservator van Oudhollandse, Duitse en Britse schilderijen bij de National Gallery in Londen, die ook de tentoonstelling Renaissance Faces: Van Eyck tot Titiaan uit 2008 cureerde, vertelde destijds aan The Guardian:
« We kunnen nu met zekerheid zeggen dat Leonardo – of in ieder geval een van zijn leerlingen – het prachtige schilderij van Matsys heeft gekopieerd, en niet andersom. Dit is een zeer opwindende ontdekking. » 153
Volgens Foister ontdekten ze dat Matsys tijdens het proces wijzigingen aanbracht aan zijn schilderij. Dit suggereert dat de Vlaming het zelf maakte in plaats van een sjabloon te kopiëren. Bovendien zijn in de rode krijt tekening de vormen van het lichaam en de kleding te simplistisch afgebeeld en ontbreekt het linkeroog van de vrouw in de oogkas.
« Er werd altijd aangenomen dat een minder bekende kunstenaar uit Noord-Europa Leonardo zou hebben gekopieerd, en er werd niet echt rekening mee gehouden dat het andersom zou kunnen zijn », vat Foister samen. 154
Ze voegde toe dat beide kunstenaars bekend stonden om hun interesse in grotesken en dat ze tekeningen uitwisselden, « maar de eer voor dit meesterlijke werk gaat naar Matsys. » 155
Emma Capron, Associate Curator of Renaissance Painting in de National Gallery in Londen, schreef in 2023:
“Door grappige figuren te behandelen met de serieuze attributen van een portret, parodieerde Massys het genre en stak hij misschien impliciet de draak met de zelfoverschatting die inherent is aan het zitten voor een portret. De spanning tussen een waardige vorm en een obscene inhoud was een fundamenteel komisch element dat werd uitgelegd door de Romeinse redenaar Cicero en satiricus Lucianus. Het was gebaseerd op een retorische methode die bekend staat als ‘paradoxaal encomium’ (paradoxale lofzang), die bestond uit de verheerlijking van een onderwerp dat voor de grap werd verheerlijkt. Deze methode werd tijdens de Renaissance opnieuw toegepast in spottende odes aan vergane schoonheden en, het beroemdst, in Erasmus’ Lof der Zotheid.” 156
7. Liefrinck en Cock
In een commentaar157 geeft Jan Muylle enkele interessante gegevens over het werk van de Antwerpse houtsnijder-graveur en prentenuitgever Hans Liefrinck (ca. 1518-1573).
Liefrinck maakte onder meer de tweede staat van Pieter Bruegels ontwerpen De Vette Keuken en De Magere Keuken, en hij werkte samen met meester drukker Christoffel Plantijn.
Hij publiceerde ook, gedrukt op twee vellen, vier nauwelijks bekende kopergravuren met groteske koppen ontleend aan tekeningen van of naar Leonardo da Vinci.

“We zijn ervan overtuigd dat hun belang deze terloopse vermeldingen ver overstijgt,” schrijft Muylle. Deze gravuren “vertonen soms – en dit is nergens gesignaleerd – sterke overeenkomsten met enkele groteske koppen in schilderijen van Quinten Metsijs (1465-1530) –van wie men sinds geruime tijd weet dat hij schatplichtig was aan Da Vinci — en met een prent van Liefrincks befaamde collega-uitgever Hieronymus Cock (ca. 1510-1570), tevens de opdrachtgever van Bruegel. De groteske koppen van Metsijs, Cock en Liefrinck tonen namelijk aan hoe snel Da Vinci’s voorbeelden – de meester overleed op 2 mei 1519 in Amboise – door Zuidnederlandse meesters, allen werkzaam in Antwerpen, zijn opgenomen in hun artistieke traditie.”
De bijschriften en epigrammen van Liefrinck’s en Cock’s gravures geven ook “een hoogstnoodzakelijke houvast bij het formuleren van een interpretatie. Dit is welkom, omdat het hier een representatief corpus van werken betreft.”

In de cartouche van Liefrincks tweede onderschrift leest men iets wat Da Vinci ook bijna zegde : “Deformes, bone spectator, ne despice vultus. Sic natura homines sic variare solet.” (Waarde kijker, veracht deze misvormde gezichten niet. Zo zorgt de natuur er gewoonlijk voor dat de mensen onderling verschillen.)



Hieronymus Cock (ca. 1510-1570) neemt ook de groteske verbeelding over van “Het ongepast koppel” (Ongelijke Liefde) in een gravure. Er wordt gezegd dat hij ze kopieerde van de Italiaan Agostino Veniziano (1490-1550). Het epigram van Veniziano is typische Venitiaanse “humor” : “Chi non ci vol veder si cavi gli occhi“ (Wie ons niet wil zien, trek zijn ogen uit). Welke versie er eerst is gemaakt blijft voorlopig onduidelijk. In de epigrammen maken beide kunstenaars eigenlijk geen referentie meer naar het oorspronkelijk thema.
Wat duidelijk is, is het feit dat het epigram onderaan Cocks prent, veel humanistischer is :
“Al ben ick leelyck, ick ben sier plesant, Wilt ghij wel doen houet u aen mijnen kant.”
De onderschriften bij de gravures van Liefrinck en Cock sluiten goed aan met het humanisme van Erasmus en de visie van Da Vinci.
8. Dood gaan van het lachen, Zeuxis, Matsys en Rembrandt
Tot slot trok het lezen van Daniel Ménagers boek De Renaissance en de Lach 158 onze aandacht op het relaas van het leven van de Griekse schilder Zeuxis. Deze historische anekdote biedt naar onze mening een belangrijke sleutel tot het begrijpen van Matsys’ schilderij « De lelijke oude vrouw ».
Zeuxis van Heraclea (464-398 v. Chr.) was een van de beroemdste Griekse schilders uit de oudheid. Hij was geboren in Heraclea en zijn kunst overtrof die van bijna alle andere schilders uit zijn tijd.
Volgens de legende schilderde Zeuxis tijdens een kunstenaarswedstrijd druiven zo waarheidsgetrouw dat vogels eraan kwamen pikken. Een concurrerende schilder, Parrhasios van Efeze , presenteerde echter een gordijnschilderij dat zo levensecht was dat Zeuxis, trots op het oordeel van de vogels, vroeg of het gordijn dichtgetrokken kon worden zodat hij het schilderij kon zien. Hij erkende zijn waan en gaf met openhartige bescheidenheid zijn nederlaag toe, aangezien hij alleen dieren had misleid, terwijl Parrhasios mensen had misleid.

Zoals zowel Plinius de Oudere als Cicero vertellen, werd Zeuxis, wiens werk niet bewaard is gebleven, gevraagd om de Tempel van Hera in Crotona te decoreren. De schilder stelde voor om daar het ideaal van vrouwelijke schoonheid te schilderen: een voorstelling van Helena van Troje, de kanunnik van die tijd. Om dit ideaal van schoonheid te creëren, zou Zeuxis de meest sublieme aspecten van vijf vrouwen hebben geëxtraheerd en in één figuur hebben verenigd.
De scène verscheen in 1525 in een verluchting van een manuscript van de Roman de la Rose, uitgevoerd voor Koning Frans I.
In de tweede eeuw berichtte Sextus Pompeius Festus dat Zeuxis ooit Aphrodite schilderde, de Griekse godin van de voortplanting, het genot, de liefde en de schoonheid. Het schilderij was in opdracht van een oude vrouw die erop stond dat zij zelf model zou staan voor de jonge, mooie en rondingen hebbende Aphrodite.
Zeuxis stemde toe, maar toen ze het eindresultaat zag, een Aphrodite, afgebeeld als een gerimpelde oude vrouw, barstte hij in lachen uit en stierf. Het was de koppigheid van oude vrouwen om te geloven dat ze eeuwig waren in hun uiterlijk, een thema dat Goya in zijn tijd opnieuw zou oppakken, die zo’n heftige lach opriep dat het levensgevaarlijk werd!
Het verhaal ontging ook Erasmus niet. Hij vermeldt het in zijn Lof der Zotheid (uitgegeven in 1511) in een passage die in verband kan worden gebracht met het schilderij van Matsijs, dat dateert van omstreeks 1513.
Erasmus speelt de bal terug in het mannenveld:
« Een vrouw die zo lelijk is dat haar man er bang voor is, lijkt net zo mooi als Venus; zou hij nog mooier zijn als ze echt zo mooi was? Een man bezit een bepaald verdorven schilderij en houdt het voor een Zeuxis of een Apelles aan; hij blijft ernaar kijken en het bewonderen; is hij niet net zo tevreden als de kenner die zijn gewicht in goud heeft betaald voor een authentiek schilderij van deze meesters, en die er misschien minder plezier in heeft? » 159
De man, de tegenhanger van Matsys’ dubbelportret met de « lelijke oude vrouw », is duidelijk het type man dat door waanzin is getroffen en gelooft dat zijn geliefde de godin Venus is, terwijl zij in werkelijkheid een « angstaanjagend lelijke vrouw » is. De man, net als veel toeschouwers, realiseert zich niet eens dat dit lichaam van zijn geliefde bekroond is met een mannenhoofd! De waanzin is dus dubbelzinnig en breed gedeeld, ook onder de toeschouwers.
De humanist is niet onkundig van de oorzaken van de dood van Zeuxis, die hij terloops vermeldt in Adagium 2401 over ‘Het sardonisch lachen’:
« De schilder Zeuxis stierf omdat hij niet kon stoppen met lachen om de oude vrouw die hij schilderde, net als Chrysippus toen hij een ezel vijgen zag eten. »

Matsys, lid van het Sint-Lucasgilde en volgens sommigen van de literaire afdeling daarvan, de Rederijkerskamer De Violieren, heeft mogelijk inspiratie gehaald uit dit verhaal.
Door de « lelijke oude vrouw » te schilderen, zoals Zeuxis vóór hem had gedaan, wilde Matsys ons doen sterven van het lachen (om ijdelheid)! Een lofzang op de waanzin, omgezet in schilderkunst!
Het onderwerp heeft veel interesse gewekt.
In 1662, Rembrandt, op ongeveer 56-jarige leeftijd, beeldde zichzelf op een werk slechts zeven jaar voor zijn dood in 1669 af als Zeuxis terwijl hij zichzelf doodlacht. Rembrandt schilderde een oude vrouw van wie de neus en juwelen zichtbaar zijn. 160
Het thema werd in 1685 overgenomen door Rembrandt’s laatste leerling, Aert de Gelder. Hoewel Rembrandt het profiel van de oude vrouw in de schaduw tekende, is De Gelders onderwerp onomstotelijk helder.

E. Slotbeschouwing
Het werk van Quinten Matsys en zijn visuele dialoog met dat van Leonard da Vinci levert ons een duidelijk bewijs dat de Lage Landen zich niet hermetisch afsloten tegen de invloed van de Italiaanse Renaissance. In deze gewesten koos men eerder wat men zag als een meerwaarde voor onze nationale cultuur: de liefde voor God, schoonheid en de mens van Petrarca, de wetenschap van perspectief van Piero della Francesca, de hilarische tronies van Leonardo da Vinci. Dat alles vond in de Lage Landen veel aandacht en bewondering. Dit was niet het land van achterlijke boeren zonder cultuur zoals dat weleens beweerd werd in aristocratische kringen die helemaal niets begrepen hebben van Bruegels diepere boodschap.
Op cultureel gebied moet men helaas vaststellen dat de « Zeven hoofdzonden » die More en Erasmus vijf eeuwen geleden probeerden in te dijken, zijn verheven tot de axiomatische « waarden » van de hedendaagse « westerse » samenleving!
Totaal het tegenovergestelde van de universele mensenwaarden die de kern vormen van de filosofische, religieuze of agnostische overtuigingen van de grote meerderheid.
« Vrijheid » werd losgekoppeld van « noodzakelijkheid », « rechten » van « plichten. » Alles mag. Lust, afgunst, hebzucht, luiheid, vraatzucht, hebzucht, woede, geweld, wreedheid, verslaafdheid, enz. worden dagelijks in een positief licht gezet op televisie en internet, met inbegrip voor laagjarige kinderen. Het mag allemaal en wordt zelfs aangemoedigd, zolang het niet indruist tegen de dominante machtsstructuur.
Erasmus zou zich in zijn graf omdraaien als hij wist dat zijn naam in 2024 vooral verbonden is aan een studiebeurs die de EU aanbiedt aan jongeren die in andere EU-lidstaten willen gaan studeren. Zoals een Belgische professor voorstelde, zouden deze beurzen een periode van verplichte training in het gedachtegoed van Erasmus moeten bevatten, en in het bijzonder in zijn vergevorderde concepten van vredesopbouw. 161
Kortom, om een nieuwe renaissance te realiseren, moeten we onze medeburgers bevrijden van Angst. Ze negeren reële gevaren, zoals een kernoorlog, en leven in angst voor denkbeeldige bedreigingen.
Redelijkheid alleen is niet genoeg. Zonder humor zou de Renaissance, met zijn ongeëvenaarde bloei van ontdekkingen en uitvindingen in wetenschap, kunst en maatschappij, nooit hebben plaatsgevonden. Humor is een katalysator voor creativiteit. Zoals sommige hedendaagse Chinese wetenschappers zeggen: “Effectief Ha-ha [lachen] helpt mensen naar A-Ha [ontdekken]”. 162
Door ons gevoel voor humor te ontwikkelen, ontwikkelen we een nieuw vermogen om problemen vanuit verschillende invalshoeken te begrijpen, en dit type denken leidt tot meer creativiteit. Problemen op een lineaire, traditionele manier benaderen leidt tot conventionele, zelfs triviale oplossingen. Maar, zoals Albert Einstein suggereerde: “Om creativiteit te stimuleren, moeten we een kinderlijke liefde voor spel ontwikkelen”.
Humor is een creatieve daad omdat creativiteit, net als humor, verrassing uitlokt door bepaalde kaders te doorbreken. In beide gevallen is het doel om niet voor de hand liggende verbanden te leggen tussen ongerijmde elementen. En wat is een grap anders dan een combinatie van verschillende en/of contrasterende ideeën die ironie creëren, een verschuiving, een ongehoorzaamheid aan conventionele verwachtingen. Humor maakt ons bewust van de ongerijmdheid tussen twee elementen. En het vermogen om van het ene element naar het andere te gaan is een cognitief proces dat creativiteit bevordert. Met andere woorden, humor verandert de manier waarop we denken en vergemakkelijkt onverwachte manieren van denken, zoals het “gedachte-experiment” dat Einstein ertoe bracht zich voor te stellen dat hij “op een lichtstraal” reed.
En het “spelinstinct” van de mens, zoals Friedrich Schiller aangeeft in zijn werk Over de esthetische opvoeding van de mens in een reeks brieven (1795), als een eerste ontmoeting met een afwezigheid van beperkingen, dient een breder project van menselijke vooruitgang, waarin de vrijheid die nodig is voor de mens om zichzelf adequaat te besturen wordt uitgeoefend door de interactie van de vermogens die zich manifesteren in de loop van de esthetische ervaring. Kortom, de ontwikkeling van zowel “spelinstinct” als humor zijn essentieel voor creativiteit en kunst, inclusief de kunst van zelfbestuur.
De Nederlandse historicus Herman Pleij zegt het goed: « Eigenlijk zou men de huidige wereld meer zotheid toewensen. Niet voor niets biedt de nar op het vroegmoderne toneel de medespelers en toeschouwers graag de spiegel aan die hij in de hand houdt. Ken uzelf. En toon u bewust van de betrekkelijkheid der dingen. Al is het maar voor even. » 163
Laten we stoppen met onder onze adem lachen en hartelijk lachen. De meeste wetenschappelijke studies zijn het erover eens dat lachen goed is voor je gezondheid en dat plotselinge sterfgevallen door lachaanvallen zeldzaam zijn.
Voor hen die, net als wij, streven naar vrede door de ontwikkeling van ieder individu en iedere staat, is het tijd om de visie van Erasmus, Rabelais, Da Vinci en Matsys over de « hartelijke lach » heel, heel, heel serieus te nemen. Dat is de weg naar ontvoogding !

Tot slot, een visuele rebus van Jan Matsys.
Oplossing:
- De “D” is een afkorting van “de »;
- De wereldbol betekent “wereld”;
- De voet, in het Nederlands, is de naam van het lichaamsdeel “voet”, maar het woord ligt dicht bij het woord “voedt” (voedsel geven);
- De vedel (snaarinstrument), waarvan de betekenis dicht bij het woord “vele” ligt;
- Hieronder… de twee narren of zotten die wijzen naar wat er gebeurt « tussen neus en lepel » (tussendoor, en passant).
De oplossing van de reubus is dus: « De wereld voedt veel zotten. »
En jij, toeschouwer, jij bent één van ons, vertellen ons de zotten. Ze weten het en adviseren ons om het aan niemand te vertellen! Mondeke Toe!
Bibliografie
- ACCATINO, (datum ?)
Sandra Accatino, Quentin Massys, Anciana grotesca o La duquesa fea, in « El Arte del Mirar », Academia.edu. - AGRICOLA, 2016
Rudolf Agricola, Brieven, Levens en Lof, Uitgeverij Wereldbibliotheek, Amsterdam. - AINSWORTH, MARTENS, 1995
Maryan W. Ainsworth, Maximiliaan P. J. Martens, Petrus Christus, Ludion and Metropolitan Museum of Art, Gent-New York. - ALBERTI, 1435
Leon Baptitta Alberti, De Pictura, Macula Dédale, 1992, Paris. - ANOUILH, 1987
Jean Anouilh, Thomas More ou l’Homme libre, Editions de la Table ronde, Paris. - ANTOINE-KÖNIG, POGAM, 2024
Elisabeth Antoine-König, Pierre-Yves Le Pogam. Figures du Fou. Du Moyen Âge aux Romantiques, Musée du Louvre, Gallimard, Paris. - ARASSE, 1997
Daniel Arasse, Léonard de Vinci, Hazan, Paris. - BAKKER, 2004
Boudewijn Bakker, Landschap en Wereldbeeld, van Van Eyck tot Rembrandt, Uitgeverij Thoth, Bussem. - BATAILLON, 1998
Marcel Bataillon, Erasme et l’Espagne, Droz, Genève. - BAX, 1978
Dirk Bax, Bosch, his picture-writing deciphered, A.A.Balkema, Rotterdam. - BIALOSTOCKI, 1993
Jan Bialostocki, L’Art du XVe siècle des Parler à Dürer, Librairie générale française, Paris. - BLOCH, 2016
Amy R. Bloch, Lorenzo Ghiberti’s Gates of Paradise: Humanism, History, and Artistic Philosophy in the Italian Renaissance, Cambridge University Press. - BORCHERT, 2010
Till-Holger Borchert, Cranach der Ältere und die Niederlande, in DIe Welt von Lucas Cranach, editions G. Messling. - BOSQUE, 1975
Andrée de Bosque, Quinten Metsys, Arcade Press, Brussels. - BRANT, 1494
Sébastien Brant, La Nef des Fous, Editions Seghers et Nuée Bleue, Paris, 1979. - BRISING, 1908
Harald Brising, Quinten Matsys; essai sur l’origine de l’italianisme dans l’art des Pays-Bas, Brising, Harald, 1908, Leopold Classic Library, reprint 2015. - BROWN, 2008
Mark Brown, Solved: mystery of The Ugly Duchess – and the Da Vinci connection, The Guardian, Oct. 11, 2008, London. - BRUCKER, 1993
Gene Adam Brucker, Florence, six siècles de splendeur et de gloire, Editions de la Martinière, Paris. - BRUYN, 2001
Eric de Bruyn, De vergeten beeldentaal van Jheronimus Bosch, Heinen, ‘s-Hertogenbosch. - BRUYN, BEECK, 2003
Eric de Bruyn and Jan Op de Beeck, De Zotte Schilders, ‘t Vliegend Peerd, Mechelen. - BRUYN, 2013
Yanice de Bruyn, Masterthesis ‘Gebaar en wereldbeeld: Een onderzoek naar de herkomst en betekenis van het gebaar van de Man met bril van Quinten Metsys, Universiteit van Gent. - BUCK, 1999
Stéphanie Buck, Hans Holbein, Maîtres de l’Art allemande, Könemann, Cologne. - BUTTERFIELD, 2019
Andrew Butterfield, Verrochio, Sculptor and Painter of Renaissance Florence, National Gallery of Art and Princeton University Press, Washington. - CAUTEREN, HUTS, 2016
Katherina Van Cauteren and Fernand Huts, Voor God & Geld, Gouden tijd van de zuidelijke Nederlanden, Lannoo. - CAMPBELL, STOCK, 2009
Lorne Campbell, Jan van der Stock, Rogier van der Weyden 1400-1464, Maître des passions, Davidsfonds. - CAPRON, 2023
Emma Capron, Quinten Massys and the Art of Satire, in The Ugly Duchess, Beauty & Satire in the Renaissance, published by the National Galery Global, Yale University Press to accompagny the exhibition of the same name; - CHASTEL, KLEIN, 1995
André Chastel, Robert Klein, L’Humanisme, l’Europe de la Renaissance, Skira, Genève. - CHATELET, 1988
Albert Châtelet, Early Dutch Painting, Painting in the Northern Netherlands in the Fifteenth Century, Montreux Fine Art Publications, Lausanne. - CHATELET, 1994
Albert Châtelet, Le beau Martin – études et mises au point, Actes du colloque, Musée d’Unterlinden, Berlin. - CHAUNU, 1975
Pierre Chaunu, Le temps des réformes, Histoire religieuse et système de civilisation, La Crise de la chrétienté, L’éclatement, Pluriel, Fayard, Paris. - CLARK, PEDRETTI, 1969
Kenneth Clark and Carlo Pedretti, Leonardo da Vinci drawings at Windsor Castle, Phaidon Press. - CLAYTON, 2003
Martin Clayton, Leonardo da Vinci, the Divine and the Grotesque, The Royal Collection, London. - CLELAND, 2014
Elisabeth Cleland, Pieter Coecke van Aelst, Fonds Mercator, The Metropolitan Museum of Art. - CLOULAS, 1990
Iva Cloulas, Jules II, Fayard, Paris. - COLE, 1894
Timothy Cole, Quinten Massys, Century Magazine, Volume 48, Issue 4, Old Dutch Masters. - COOLS, 2016
Hans Cools, Europa-Amerika-Utopia: visioenen van een ideale wereld in de zestiende eeuw, in Op zoek naar Utopia, Jan Van der Stock, Davidsfonds, Leuven. - CUSANUS, 1543
Nicolaas of Cusa (Cusanus), Het Zien van God, vertaald door Inigo Bocken, Uitgeverij De Kok, Pelckmans. - CUSANUS, 2008
Nicolas de Cues, La Docte Ignorance, traduction d’Hervé Pasqua, Bibliothèque Rivages. - CUSANUS, 2012
Nicolas de Cues, Anthologie, Marie-Anne Vannier, Editions du CERF, Paris. - CUSANUS, 2023
Nicolaas van Cusa, Cusanus, Over de wetende onwetendheid, vertaald door Gert den Hertogh, voorwoord Inigo Bocken, Damon. - DEGUILEVILLE, LYDGATE, 1426
Guillaume De Deguileville, The Pilgrimage of Man (the Soul), Kessinger Reprints. - DELCOURT, 1986
Marie Delcourt, Erasme, Editions Labor, Bruxelles. - DHANENS, 1980
Elisabeth Dhanens, Van Eyck, Mercatorfonds, Albin Michel, Antwerpen. - DHANENS, 1998
Elisabeth Dhanens, Hugo van der Goes, Mercatorfonds, Antwerpen. - D’IETEREN, 2005
Catheline Périer D’Ieteren, Thierry Bouts, Fonds Mercator, Bruxelles. - DLABACOVA, HOFMAN, BOER, HOGESTIJN, HORST, 2018
Anna Dlabacova, Rijcklof Hofman, Erik de Boer, Clemens Hogestijn, Ewout van der Horst, De Moderne Devotie, Spiritualiteit en cultuur vanaf de late Middeleeuwen, WBooks, Zwolle. - DOMINICI, 2013
Tamara Dominici, Erasmo da Rotterdam e Quintin Metsys, ipotesi per un incontro, doctoral thesis, Università degli Studi di Urbino « Carlo Bo ». - DOMINICI, 2016
Tamara Dominici, Quentin Metsys e l’Italia: immagini di un viaggio, Studiolo. - DOMINICI, 2019
Tamara, Dominici, Erasmus of Rotterdam and Quentin Metsys: a Reassessment, P. FORESTA, F. MELONI (a cura), Arts, Portraits and Representation in the Reformation Era. Proceedings of the Fourth Reformation Research Consortium Conference. - DRIFT, 2023
Lucia Van der Drift, A mindfull Look at the Ugly Duchess, video, National Gallery of Art, London. - DÜRER, 1613
Albrecht Dürer, Les Quatre Livres d’Albert Dürer, Peintre & Géometricien tres excellent, De la proportion des parties & pourtraicts des corps humains, chez Jan Janszoon, Arnhem, reprint Roger Dacosta, Paris, 1975. - DÜRER, 1995
Albrecht Dürer, Géométrie, Presented and translated by Jeanne Peiffer, Sources du savoir, Editions du Seuil, Paris. - EICHLER, 1999
Anja-Franziska Eichler, Albrecht Dürer, Könemann, Cologne. - ENENKEL, PAPY, 2006
Karl A. E. Enenkel, Jan Papy, Petrarch and His Readers in the Renaissance, Brill. - ERASMUS, 1900
Desiderius Erasmus, The Colloquies of Erasmus, Translated by N. Bailey, Gibbing & Company, London. - ERASMUS, 1964
Desiderius Erasmus, Eloge de la Folie, Garnier-Flammarion, Paris. - ERASMUS, 1967
Desiderius Erasmus, La Correspondance d’Érasme (XII volumes), translation and notes after Opus Epistolarum of P.S. Allen, H.M. Allen and H.W. Garrod; french translation under the direction of Alois Gerlo and Paul Foriers, Bruxelles, Presses académiques européennes, Bruxelles - ERASMUS, 1991
Desiderius Erasmus, Oeuvres choisies, annotations by Jacques Chomarat, Livre de Poche, Paris. - ERASMUS, 1992
Desiderius Erasmus, Erasme, Collection Bouquins, Robert Laffont, Paris. - ERASMUS, 1992
Desiderius Erasmus, Erasme, Colloques (II volumes), Imprimerie nationale éditions, Paris. - ERASMUS, 1997
Desiderius Erasmus, The Education of a Christian Prince, Cambridge Texts in the History of Political Thought, Cambridge University Press. - ERASMUS, LUTHER, 2000
Erasmus-Luther, Discours on Free Will, The Continuing Publishing Company, New York. - ERASMUS, 2013
Desiderius Erasmus, Les Adages, sous la direction de Jean-Christophe Saladin, Le Miroir des Humanistes, Les Belles Lettres, Paris. - ESTAMPES, 1977
Cabinet des Estampes, Diables et diableries, La représentation du diable dans la gravure des XVe et XVIe siècle, Genève. - EWING, 1990
Dan Ewing, Marketing Art in Antwerp, 1460-1560: Our Lady’s Pand, The Art Bulletin, Vol. 72, N° 4, pp. 558-584. - FALKENBURG, 1985
Reindert L. Falkenburg, Joachim Patinir, Het landschap als beeld van de levenspelgrimage, Nijmegen. - FALKENBURG, 2015
Reindert Falkenburg, Bosch, le jardin des délices, Hazan, Paris. - FERRETTI-BOCQUILLON, 2003
Marina Ferretti-Bocquillon, L’horrible et l’exquis, les portraits, in Léonard de Vinci, dessins et manuscrits, Connaissance des Arts, Louvre, Paris. - FLORENKI, 2021
Pavel Florenski, La Perspective inversée, Editions Allia, Paris. - FOLL, 2012
Joséphine Le Foll, Raphaël, sa vie, son oeuvre, son temps, Editions Hazan, Paris. - FRANCESCA, 1998
Piero della Francesca, De la Perspective en Peinture, In Medias Res, Paris. - FRAENGER, 1997
Wilhelm Fraenger, Hieronymus Bosch, new edition, G&B Arts International. - FRIEDLANDER, 1971
Max J. Friedländer, Early Netherlandish Painting. volume 7, Quentin Massys, Editions de la Connaissance, Bruxelles. - GALASSI, 2024
Maria Clelia Galassi, Jan Massys (c. 1510-1573): Renaissance Painter of Flemish Female Beauty, Brepols. - GASSIER, WILSON, 1970
Pierre Gassier and Juliette Wilson, Goya, Office du Livre, Editions Vilo, Paris. - GEERTS, 1987
Katelijne Geerts, De spelende mens in de Boergondische Nederlanden, Genootschap van de geschiedenis, Brugge. - GERARD, 1978
Jo Gérard, Bruegel l’ancien et son époque, Editions Paul Legrain, Bruxelles. - GERLO, 1969
Alois Gerlo, Erasme et Ses Portraitistes: Metsijs, Durer, Holbein, Hes & de Graaf Publishers bv. - GIBSON, 1980
Michael Gibson, Bruegel, Nouvelles Editions française, Paris. - GILBERT, 1905
Felix Gilbert, The Pope, His Banker and Venice, A vivid account of men, money, and states in the High Renaissance, Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massasuchusetts, London, England. - GONDINET-WALLSTEIN, 1990
Eliane Gondinet-Wallstein, Un retable pour l’Au-delà, Editions Mame. - GREILSAMMER, 1990
Myriam Greilsammer, L’Envers du tableau. Mariage et maternité en Flandre médiévale, Armand Colin, Paris. - GRIEKEN, LUIJTEN, STOCK, 2013
Joris van Grieken, Ger Luijten and Jan Van der Stock, Hieronymus Cock, De Renaissance in prent, Mercatorfonds. - GROOTE, MALAISE
Gerard Groote, Joseph Malaise, The Following of Christ, the Spiritual Diary of Gerard Groote (1340-1384), Kessinger Reprints. - GROTE, 1998
Lettres et traités. Aux origines de la Devotio Moderna, Gérard Grote, fondateur de la Dévotion Moderne, Brepols. - HALE, 1993
John Hale, The Civilisation of Europe in the Renaissance, Fontana Press/HarperCollins Publishers, London. - HALKIN, 1987
Léon E. Halkin, Erasme parmi nous, Fayard, Paris. - HAY, 1967
Denys Hay, The Age of the Renaissance, Thames & Hudson. - HECK, 2003
Christian Heck, L’art flamand et hollandais, Le siècle des primitifs (1380-1520), Citadelles & Mazenod, Paris. - HEYDEN, 1968
Dr. M. C. A. Van der Heijden, O Muze kom nu voort, Ontluiking van de Renaissance, Uitgeverij Spectrum, Utrecht/Antwerpen. - HERRE, 1985
Franz Herre, The Age of the Fuggers, Presse-Druck- und Verlag-GmbH Augsburg. - HILLS, 1980
Paul Hills, Leonardo & Flemish Painting, Burlington Magazine. - HUET, 2021
Leen Huet, Pieter Bruegel, la biographie, CFC, Bruxelles. - HUIZINGA, 1955
Johan Huizinga, Erasme, Gallimard, Paris. - JADRANKA, 2003
Bentini Jadranka, Une Renaissance Singulière – La Cour Des Este À Ferrare – Bentini Jadranka, Quo Vadis. - JANSSEN, KOK, MAESSCHALK, ROEY, SCHEPPER, 1996
Paul Janssen, Harry de Kok, Edward De Maesschalk, Jan Van Roey and Hugo De Schepper, Le Delta d’Or des Plats Pays, Vingt siècles de civilisation entre Seine et Rhin, Fonds Mercator. - JENSMA, BLOCKMANS, WEILAND, DRESDEN, NUCHELMANS, KOLDEWEIJ, FRIJHOFF, 1996
G. Th. Jensma, W.P.Blockmans, J.Sperna Weiland, S. Dresden, J. Nuchelmans, A.M. Koldeweij and W.Th.M.Frijhoff, Erasmus. De actualiteit van zijn denken, Walburg Pers, Zuthphen. - KEMP, 2019
Martin Kemp, Léonard de Vinci, Citadelles & Mazenod, Paris. - KEMPIS, 1905
Thomas A. Kempis, The Founders of The New Devotion: Being The Lives of Gerard Groote, Florentius Radewin and Their Followers, Kessinger reprints. - KETELS, MARTENS, 2014
Jochen Ketels and Maximiliaan Martens, Foundations of Renaissance, Architecture and Treatises in Quentin Matsys’ S. Anne Altarpiece (1509). European Architectural Historians Network, EAHN: Investigating and Writing architectural history : subjects, Methodologies and Frontiers. pp. 1072-1083. - KLIBANSKY, PANOFSKY, SAHL, 1989
Raymond Klibansky, Erwin Panofsky and Fritz Sahl. Saturne et la Mélancolie, Bibliothèque illustrée des histoires, Gallimard, Paris. - KOLDEWIJ, VANDENBROECK, VERMET
Jos Koldewij, Paul Vandenbroeck and Bernard Vermet, Jérôme Bosch, l’oeuvre complet, Ludion/Flammarion, Gand, Amsterdam. - KWAKKELSTEIN, 2023
Michael W. Kwakkelstein, Heads in Histories. From Likeness to Type in Verrocchio, Leonardo, Durer, Massys and a Follower of Bosch, Academia.edu. - LEVENSON, OBERHUBER, SHEEHAN, 1971
Jay A. Levenson, Konrad Oberhuber, Jacquelyn L. Sheehan, Italian Engravings from the National Gallery of Art, National Gallery of Art. - LAUR, 1872
H. Durand de Laur, Erasme, précurseur de l’esprit moderne (II volumes), Didier et Cie, Libraires-éditeurs, Paris. - LUCCO, 2011
Mauro Lucco, Antonello de Messine, Editions Hazan, Paris. - LUTHER, ERASME, 1526, 1525
Martin Luther, Du serf arbitre; Desiderius Erasmus, Diatribe du Libre Arbitre, Folio Essais, Gallimard, Paris - MAKOWSKI, 1999
Claude Makowski, Albrecht Dürer, Le songe du Docteur et La Sorcière, Editions Jacqueline Chambon/Slatkine, Genève. - MARGOLIN, 1995
Jean-Claude Margolin, Erasme, précepteur de l’Europe, Editions Julliard, Paris. - MANDER, 1604
Karel van Mander, Le Livre des peintres, Vies des plus illustres peintres des Pays-Bas et d’Allemagne, Les Belles Lettres, 2001. - MANDEVILLE, 1732
Bernard Mandeville, The Fable of the Bees, Penguin classics, Reprint Edition. - MANN, 1984
Nicolas Mann, Petrarch, Oxford University Press. - MARIJNISSEN, SEIDEL, 1984
Roger H. Marijnissen and Max Seidel, Bruegel, Artabas Book, Crown Publishers. - MARIJNISSEN, 1987
Roger H. Marijnissen, Bosch, The Complete Works, Mercatorfonds, Antwerp. - MARIJNISSEN, 1988
Roger H. Marijnissen, Bruegel, Fonds Mercator, Albin Michel, Anvers. - MARLIER, 1954
Georges Marlier, Erasme et la peinture flamande de son temps, Editions van Maerlant, Damme. - MARTENS, 1998
Maximiliaan P.J. Martens, Bruges et la Renaissance: De Memling à Pourbus, Stichting Kunstboek, Ludion, Flammarion. - MARTENS, BORCHERT, DUMOLYN, SMET, DAM, 2020
Maximiliaan Martens, Till-Holger Borchert, Jan Dumolyn, Johan De Smet, Frederica Van Dam, Van Eyck, une révolution optique, Hannibal, MSK Gent. - MELCHIOR-BONNET
Sabine Melchior-Bonnet, Histoire du miroir, Imago, Paris. - MEGANCK, 2014
Tine Luk Meganck, Pieter Bruegel the Elder, Fall of the Rebel Angels, Art, Knowledge and Politics on the Eve of the Dutch Revolt, SilvanaEditoriale, Royal Museums of Fine Arts of Belgium. - MENAGER, Daniel, 1995
Daniel Ménager, La Renaissance et le rire, Perspectives littérairer, PUF. - MESSLING, SANDER, 2023
Guido Messling, Jochen Sander. Renaissance in the North. Holbein, Burgkmair, and the Age of the Fuggers, Hirmer. - MICHELET, 1982
Jules Michelet, Renaissance et Réforme, Histoire de la France au XVIe siècle, Bouquins, Robert Laffont, Paris. - MIEGROET, 1989
Hans J. Van Miegroet, Gerard David, Fonds Mercator, Anvers. - MILLNER KAHR, 1973
Madlyn Milner Kahr, La peinture hollandaise du siècle d’or, Livre de Poche, Librairie générale française. - MORE, 2012
Thomas More, Utopia, Penguin Classics. - MULS, 1953
Jozef Muls, Erasmus en Quinten Matsijs, Uitgeverij NV Standaard Boekhandel. - OBERHUBER, 1999
Konrad Oberhuber, Raphaël, Editions du Regard, Paris. - PANOFSKY, 1971
Erwin Panofsky, Early Netherlandish Painting, Harvard University Press. - PAPY, 2016
Jan Papy, Thomas More, Utopia en Leuven: sporen naar de intellectuele en culturele contextn, Het boek Utopia in Leuven en in de Nederlanden and Utopia en het Europees humanisme, in Op zoek naar Utopia, Jan Van der Stock, Davidsfonds, Leuven. - PAPY, 2018
Jan Papy, Le Collège des Trois langues de Louvain (1517-1797), Editions Peeters, Louvain. - PANOFSKY, 1971
Erwin Panofsky, The Life and Art of Albrecht Durer, Princeton University Press. - PATOUL, SCHOUTE, 1994
Brigitte de Patoul and Roger Van Schoute, Les Primitifs flamands et leur temps, La Renaissance du livre. - PETRARCA, 2001
De mooiste van Petrarca, Uitgeverij Lannoo/Atlas. - PETRARCH, 2022
Francis Petrarch (Francesco Petrarca), The Triumphs of Petrarch, Legare Street Press. - PHILIPPOT, 1994
Paul Philippot, La peinture dans les anciens Pays-Bas, XVe-XVIe siècles, Flammarion, Paris. - PINELLI, 1996
Antonio Pinelli, La Belle Manière, Anticlassicisme et maniérisme dans l’art du XVIe siècle, Livre de Poche, Librairie générale française. - PIRENNE, 1932
Henri Pirenne, Histoire de Belgique, Vol. II, La Renaissance du Livre, Bruxelles. - PLEIJ, 2007
Herman Pleij, De Eeuw van de Zotheid, over de nar als maatschappelijke houvast in de vroegmoderne tijd, Uitgeverij Bert Bakker, Amsterdam. - PREVENIER, BLOCKMANS, 1983
Walter Prevenier en Wim Blockmans, Les Pays-bas bourguignons, Fonds Mercator et Albin Michel. - PONS, BARRET, 1980
Maurice Pons and André Barret, Patinir ou l’harmonie du monde, Robert Laffont, Paris. - RAYAUD, 1988
Dominque Raynaud, L’hypothèse d’Oxford, Presses Universitaires de France, Paris. - RAYNAUD, 2003
Dominique Raynaud, Ibn al-Haytham on binocular vision: a precursor of physiological optics, Arabic Sciences and Philosophy, Raynaud, Cambridge University Press (CUP). - RENAUDET, 1998
Augustin Renaudet, Erasme et l’Italie, Droz, Genève. - REVEL, 1995
Emmanuelle Revel, Le prêteur et sa femme de Quinten Metsys, Collection Arrêt sur œuvre, Service culturel, Action éducative, Louvre, Paris. - RETI, 1974
Ladislao Reti, Léonard de Vinci, L’Humaniste, l’artiste, l’inventeur, Mc Graw Hill et Robert Laffont, Paris. - RIDDERBOS, 2014
Berhard Ridderbos, Schilderkunst in de Bourgondische Nederlanden, Davidsfonds, Leuven. - ROBERTS-JONES, 1997
Philippe and Françoise Roberts-Jones, Bruegel, Flammarion, Paris. - RUUSBROEC, 2010
Jan van Ruusbroec, La Pierre brilliante, Ornement des Noces spirituelles, Sources mystiques, Centre Saint-Jean-de-la-Croix, Editions du Carmel. - SAMOSATE, 1905
Lucian of Samosata, De Mercene Conductis (The Dependant Scholar). Translated by Fowler, H W and F G. Oxford: The Clarendon Press. 1905. - SCHNEIDER, 1995
Norbert Schneider, Portretschilderkunst, Taschen/Librero. - SCHOUTE, VERBOOMEN, 2000
Roger Van Schoute and Monique Verboomen, Jérôme Bosch, La Renaissance du Livre, Tournai. - SHAFFER, 2015
Katie Shaffer, The Ugly Duchess by Quinten Massys, An Analyses, Academia.edu. - SILVER, 1978
Larry Silver, « Prayer and Laughter: Erasmian Elements in Two Late Massys Panels, » Erasmus in English 9, pp. 17-23. - SILVER, 1984
Larry Silver, The Paintings of Quinten Massys : With Catalogue Raisonné, Montclair, Allanheld & Schram. - SILVER, 2006
Larry Silver, Hieronymous Bosch, Abbeville Press Inc. - SILVER, 2011
Larry Silver, Bruegel, Citadelles & Mazenod, Paris. - SILVER, 2015
Larry Silver, Massys and Money, The Tax Collectors Rediscovered, Journal of Historians of Netherlandish Art (JHNA) Volume 7, Issue 2, Summer. - SILVER, 2018
Larry Silver, Metsys’s Musician: A Newly Recognized Early Work, Journal of Historians of Netherlandish Art (JHNA), Volume 10, Issue 2, Summer. - SILVER, 2021
Larry Silver, Keep Your Mouth Shut – Quinten Metsys (c. 1465–1530) and the Fool in the Sixteenth Century, Hannibal Editions, Antwerp. - STOCK, 1985
Jan Van der Stock, Cornelis Matsys 1510/11-1556/57: Grafisch werk. Tentoonstellingscatalogus. - STOCK, 2016
Jan Van der Stock, Op zoek naar Utopia, Davidsfonds, Leuven. - STOUTEN, GOEDEGEBUURE, OOSTROM, 1999
Hanna Stouten, Jaap Goedegebuure and Frits Van Oostrom, Le bas Moyen Âge et le temps de la rhétorique, in Histoire de la littérature néerlandaise, Fayard, Paris. - STRIEDER, 1990
Peter Strieder, Dürer, Fonds Mercator, Albin Michel. - TAGLIALAGAMBA, 2014
Sara Taglialagamba, Leonardo, Metsys e le teste grottesche. Rinascenza antigraziosa, in “Art Dossier”, N° 309, pp. 72-77. - TOMAN, 1995
Rolf Toman, Renaissance italienne, Architecture, Sculpture, Peinture, Dessin, Editions de la Martinière, Paris, Könemann, Cologne. - TRACY, 1996
James D. Tracy, Erasmus of the Low Countries, University of California Press, Berkely. - VANDENBROECK, 1987
Paul Vandenbroeck, Jheronimus Bosch, tussent volksleven en stadscultuur, EPO, Berchem. - VANDENBROECK, 2002
Paul Vandenbroeck, Jheronimus Bosch, de verlossing van de wereld, Ludion Gent-Amsterdam. - VANDENBROECK, 2016
Paul Vandenbroeck, Erotische utopie: de ‘Tuin der Lusten’ in context, in Op zoek naar Utopia, Jan Van der Stock, Davidsfonds, Leuven. - VANNIER, EULER, REINHARDT, SCHWAETZER, 2010
Marie-Anne Vannier, Walter Euler, Klaus Reinhardt and Harald Schwaetzer, Les mystiques rhénans, Eckhart, Tauler, Suso, Anthologie, Editions du CERF, Paris. - VANNIER, EULER, REINHARDT, SCHWAETZER, 2011
Marie-Anne Vannier, Walter Euler, Klaus Reinhardt and Harald Schwaetzer, Encyclopédie des mystiques rhénans, d’Eckhart à Nicolas de Cues et leur réception, Editions de CERF, Paris. - VASARI, 1549
Giorgio Vasari, The Lives of the Artists, Oxford University Press. - VERDEYEN, 1997
Paul Verdeyen, Jan van Ruusbroec, Mystiek licht uit de Middeleeuwen, Davidsfonds, Leuven. - VEREYCKEN, 2002
Karel Vereycken, Leonardo da Vinci, painter of movement, Fidelio, Schiller Institute, Washington; - VEREYCKEN, 2005
Karel Vereycken, How Erasmus Folly Saved Our Civilization, website Schiller Institute, Washington. - VEREYCKEN, 2007
Karel Vereycken, Albrecht Dürers fight against Neo-Platonic Melancholia, Academia.edu. - VEREYCKEN, 2019
Karel Vereycken, Dirk Martens, L’imprimeur d’Erasme qui diffusa les livres de poche, Academia.edu. - VERMEERSCH, 1981
Valentin Vermeersch, Brugge, duizend jaar kunst, Mercatorfonds, Antwerpen. - VINCI, RICHTER, 1970
Leonardo da Vinci, Notebooks, two volumes, compiled and edited by Jean-Paul Richter, Dover Editions - VINCI, 1987
Léonard de Vinci, Traité de la Peinture, traduit par André Chastel, Editions Berger-Levrault, Paris. - VLIEGHE, 1986
Hans Vlieghe, Centrum van de nieuwe kunst, in Antwerpen, Twaalf eeuwen geschiedenis en cultuur, p. 133-162, Mercatorfonds, Antwerp. - VOET, 1976
Léon Voet, L’âge d’or d’Anvers, Fonds Mercator, Anvers. - VOS, 1985
Dirk de Vos, L’Art flamand, Peinture, p. 95-138, Fonds Mercator, Antwerp. - VOS, 1994
Dirk de Vos, Hans Memling, Fonds Mercator, Albin Michel. - VOS, 1999,
Dirk de Vos, Rogier van der Weyden, Mercatorfonds, Antwerpen. - WEEMANS, 2013
Michel Weemans, Herri met de Bles, Les ruses du paysage au temps de Bruegel et d’Erasme, Hazan, Paris. - WANGERMEE, 1968
Robert Wangermée, Flemish Music, Arcade, Brussels. - ZWEIG, 1935
Stephan Zweig, Erasme, Grandeur et décadence d’une idée, Editions Bernard Grasset, Paris.
VERKLARENDE VOETNOTEN:
- De spelling van de naam van de kunstenaar verschilt in de loop van de tijd en per taalcultuur. In het Frans heet hij Quentin Metsys, in het Engels Quinten Massys en in het Nederlands Quinten (Kwinten) Matsijs. In Grobbendonk heet hij Matsys. Omdat de « ij » aan het einde van de 15e eeuw nog niet bestond, koos de auteur voor deze tekst « Quinten Matsys », identiek aan de spelling die Harald Brising in 1908 gebruikte en die Matsys zelf gebruikte om zijn schilderij De bankier en zijn vrouw (1514, Louvre) te signeren. ↩︎
- Antwerpen, Twaalf eeuwen geschiedenis en cultuur, Karel Van Isacker en Raymond van Uytven, Mercatorfonds, Antwerpen, 1986. ↩︎
- Brugge, duizend jaar kunst, Valentin Vermeersch, Mercatorfonds, Antwerpen, 1981. ↩︎
- L’âge d’or d’Anvers, Léon Voet, Fonds Mercator, Antwerpen, 1976. ↩︎
- Erasmus (1466-1536) is een van de grootste denkers uit de geschiedenis van de Lage landen. Hij was priester, theoloog, filosoof, schrijver en humanist. Twee centrale motieven bepalen Erasmus’ denken: de vrijheid van mensen en vrede. In 1517 schreef hij Querela Pacis, “De Klacht van de Vrede”, waarin hij de vredesengel aan het woord laat. De engel spreekt zich uit tegen strikt nationalisme, vooral wanneer dit misbruikt wordt om oorlog te voeren, en ten gunste van internationale samenwerking. ↩︎
- Jean Anouilh, Thomas More of de vrije man, Editions de la Table ronde, Parijs, 1987. ↩︎
- Pieter Gillis (1486-1533), beter bekend onder zijn Latijnse naam Petrus Ægidius, was een humanist, jurist, proeflezer en redacteur die werkte voor Dirk Martens. Hij is een vriend van Erasmus en komt voor in de Utopia van Thomas More. Hij beveelde de schilder Holbein de Jongere aan bij Thomas More en werd stadssecretaris (burgemeester) van de stad Antwerpen. ↩︎
- Dirk Martens (1446-1534) van Aalst was een geleerde, humanist, uitgever en boekdrukker in Vlaanderen, gevestigd in Leuven en Antwerpen. Hij publiceerde de eerste brief van Christoffel Columbus, waarin hij verslag doet van zijn reis, en een vijftigtal werken van Erasmus, evenals de eerste druk van Utopia van Thomas More. Om studenten gemakkelijk toegang te geven tot kennis, liet Martens veel klassiekers drukken in zakformaat. Zie Dirk Martens, de drukker van Erasmus die de paperback verspreidde, Karel Vereycken, Artkarel, 2019. ↩︎
- Gerard Geldenhouwer (1482-1442), ook bekend als Gerhardus Noviomagus, was een humanist en satiricus met erasmiaanse inspiratie. Net als Erasmus kreeg hij onderwijs aan de beroemde Latijnse school van de Broeders van het Gemene Leven in Deventer. In Leuven schreef hij zijn eerste publicaties, waaronder een bundel Satires in de traditie van Erasmus’ Lof der Zotheid. Hij hield toezicht op het drukken van diverse werken van Erasmus en Thomas More. Later sloot Geldenhouwer zich aan bij de protestantse Reformatie, meer bepaald bij de tolerante stroming van Philipp Melanchthon in Maagdenburg. ↩︎
- De Nederlandse historicus Cornelius de Schryver (1482-1558), beter bekend als Cornelius Grapheaus, was een humanist, dichter, filoloog en hoogleraar Latijn. Oorspronkelijk afkomstig uit Nijmegen, vestigde hij zich in Antwerpen. Toen hij jong was, ging hij naar Italië. Als vriend van Erasmus, Gillis en Geldenhouwer leverde hij zes elegische verzen voor de uitgave van Thomas More’s Utopia, uitgegeven door Dirk Martens. Hij was meermaals stadssecretaris (burgemeester) van Antwerpen. ↩︎
- Na de dood van Hans Memling in 1494 werd Gerard David (1460-1523) de belangrijkste schilder van Brugge. In 1501 werd hij deken van het gilde. Ondanks zijn succes in Brugge, liet hij zich samen met Patinir inschrijven als meester in Antwerpen, waardoor hij zijn werken ook op de bloeiende kunstmarkt van die stad kon verkopen. Zie Gerard David, Hans J. Van Miegroet, Mercator Fonds, Antwerpen, 1989. ↩︎
- De Antwerpse schilder Joachim Patinir (1483-1524), afkomstig van Dinant, was een goede vriend van Quinten Matsys. Zie Patinir ou l’harmonie du monde, Maurice Pons en André Barret, Robert Laffont, Parijs, 1980. ↩︎
- De Neurenbergse schilder-graveur en meetkundige Albrecht Dürer (1471-1528) woonde elf maanden in Antwerpen: van 2 augustus 1520 tot 2 juli 1521. In zijn reisdagboek lezen we over de mensen die hij in Antwerpen ontmoette, onder wie de beroemde kunstenaars Quinten Matsys, Bernard van Orley en Lucas van Leyden. Zijn terugkeer naar Neurenberg viel samen met de aankondiging van de ‘plakkaten’ (decreten) van Karel V, die katholieken verboden de Bijbel te lezen. Omdat Dürers inkomsten grotendeels afkomstig waren van het illustreren van Bijbelteksten, waren de vooruitzichten om er zijn brood mee te verdienen vrijwel nihil. ↩︎
- In 1510 produceerde de in Leiden geboren en door Dürer beïnvloede Lucas van Leyden (1489-1533) twee meesterlijke gravures, Het melkmeisje en Ecce Homo. Laatstgenoemde werd door Rembrandt zeer bewonderd. Lucas ontmoette Dürer in 1521 in Antwerpen en profiteerde opnieuw van zijn invloed, zoals blijkt uit de Passieserie uit datzelfde jaar. Het is mogelijk dat Lucas zijn graveervaardigheden met de hulp van Dürer heeft verbeterd, aangezien hij na hun ontmoeting een aantal etsen heeft gemaakt. ↩︎
- Holbein de Jongere (1497-1543) was een schilder uit Bazel. Als tiener werd hem gevraagd om een exemplaar van Erasmus’ Lof der Zotheid te voorzien van tekeningen, wat hem zeer goed lukte. Holbein schilderde meerdere olieverfportretten van de humanist en kwam naar Antwerpen om Pieter Gillis te ontmoeten. Later sloot hij zich aan bij Thomas More in Engeland. ↩︎
- De stijl van de Antwerpse maniëristen wordt bekritiseerd vanwege het gebrek aan karakter en individuele expressie. Er wordt gezegd dat het ‘gemanierd’ is en, erger nog, dat het gekenmerkt wordt door een kunstmatige elegantie. Zie Les Primitifs flamands et leur temps, pages 621-622-623-624, Editions Renaissance du Livre, 1994. ↩︎
- L’art flamand et hollandais, le siècles des primitifs (1380-1520), Christian Heck, Citadelles & Mazenod, Parijs. ↩︎
- De onderzoeksgroep Ghent Interdisciplinary Centre for Art and Science (GICAS) is een samenwerking tussen leden van de faculteiten Letteren en Wijsbegeerte (Kunstgeschiedenis, Archeologie, Geschiedenis), Wetenschappen (Analytische Chemie) en Architectuur en Ingenieurswetenschappen (Beeldverwerking). Het onderzoek richt zich op de materiële aspecten van kunstwerken, met een bijzondere nadruk op de Nederlandse schilderkunst (15e-17e eeuw). Het centrum past zowel beeldvorming als beeldverwerkingstechniek toe, als ook materiaalanalyse in relatie tot kunsthistorische kwesties en toepassingen in conservering en restauratie. ↩︎
- The Paintings of Quinten Massys: With Catalogue Raisonne, Larry Silver, Allanheld & Schram, 1984. ↩︎
- Quentin Metsys, Andrée de Bosque, Arcade Press, Brussel, 1975. ↩︎
- Quinten Matsys; essai sur l’origine de l’italianisme dans l’art des Pays-Bas, Harald Brising, proefschrift van 1908, Leopold Classic Library, herdrukt in 2015. ↩︎
- Erasme et la peinture flamande de son temps, Georges Marlier, Editions van Maerlant, Damme, 1954. ↩︎
- Georges Marlier, ibid. p. 163. ↩︎
- Hoe Erasmus’ zotheid onze beschaving redde, Karel Vereycken, Artkarel, 2005. ↩︎
- Albrecht Dürers strijd tegen neoplatoonse melancholie, Karel Vereycken, Solidarité & Progrès webpagina, 2007. ↩︎
- De Eeuw van de Zotheid, over de nar als maatschappelijke houvast in de vroegmoderne tijd, Herman Pleij, Uitgeverij Bert Bakker, Amsterdam, 2007. ↩︎
- Le bas Moyen Âge et le temps de la rhétorique, Hanna Stouten, Jaap Goedegebuure, Frits Van Oostrom, in Histoire de la littérature néerlandaise, Fayard, 1999. ↩︎
- De vergeten beeldentaal van Jheronimus Bosch, Dr Eric de Bruyn, Heinen, ‘s-Hertogenbosch, 2001; Bosch, his picture-writing deciphered, Dirk Bax, A.A.Balkema, Rotterdam, 1978. ↩︎
- De Franse schrijver en christelijk humanist François Rabelais (1483-1553) in zijn brief aan Salignac (in werkelijkheid Erasmus) zijn « vader » en zelfs zijn « moeder » en vergelijkt zichzelf liefdevol met een soort baby die in zijn baarmoeder groeide, Rabelais, Oeuvres complètes, p. 947, Editions du Seuil, Parijs, 1973. ↩︎
- Het Spaanse literaire genie Miguel de Cervantes (1546-1616) kreeg zijn opleiding van zijn schoolmeester Juan Lopez de Hoyos (1511-1583), een fervent volgeling van Erasmus, wiens visie hij overbracht op zijn meest geliefde leerling.
↩︎ - Het is overtuigend aangetoond dat de Engelse toneelschrijver en dichter William Shakespeare (1564-1616) het toneelstuk Sir Thomas More uit 1595 schreef, of er in ieder geval een substantiële bijdrage aan leverde. Hij beschouwde zich, in geest en daad, als de « tweelingbroer » van Erasmus. ↩︎
- Erasmus of the Low Countries, James D. Tracy, p. 104, Erasmus begon rond 1515 in zijn werken te spreken over « de filosofie van Christus ». Al in Julius Exclusus (Paus Julius II uitgesloten van de hemel, 1514) introduceert hij het idee wanneer Sint-Petrus de goddelijke eenvoud van Christus’ leer contrasteert met de wereldse arrogantie van de krijger-Paus Julius II. « Dit soort filosofie » (van Christus) komt « meer tot uitdrukking in emoties [affectibus] dan in syllogismen », het gaat « meer over inspiratie dan over leren, meer over transformatie dan over redeneren. » ↩︎
- Over Plato‘s humanisme: Bierre, Christine, Platon contre Aristote, la République contre l’oligarchie, webpage Solidarité & Progrès, 2004.
↩︎ - Martin Luther King, in een sermoen, herinnert er ons aan dat in het oude Griekenland onderscheidde men drie verschillende vormen van liefde: eros, voor geslachtelijke liefd, philia voor (broederlijke) vriendschap en agape, vertaald in het latijn als caritas voor grenzeloze naastenliefde. Agape kiest ervoor de ander te beschouwen zoals in 1 Korintiërs 13 gebeurt: altijd bereid het beste van de ander te denken, klaar om te vergeven, bereid het beste voor de ander te zoeken. Een belangrijke eigenschap van agape, is dat ze niet gebaseerd is op de eigen behoeften. ↩︎
- Tussen 339 en 397 n. Chr. studeerde en schreef kerkvader Hiëronymus van Stridon, waarbij hij gebruikmaakte van veel historische en filosofische werken uit zijn eigen bibliotheek. Hieronymus bleef zijn klassieke geleerdheid inzetten in dienst van het christendom, en de intellectuele discipline die daarbij kwam kijken werd gewaardeerd zolang deze het christelijke doel kon dienen – en zonder de nieuwe christelijke samenleving in gevaar te brengen. ↩︎
- De epistemologie van Augustinus van Hippo was duidelijk Platonisch. Volgens hem is God, ondanks het feit dat Hij buiten de mens staat, zich van Hem bewust vanwege zijn directe handelen op hen (wat tot uiting komt in de straling van zijn licht op de geest of soms in zijn onderricht) en niet vanwege redeneringen of het leren uit louter empirische zintuiglijke ervaringen. ↩︎
- Tot de grootste successen van Pieter Bruegel de Oude behoren De zeven hoofdzonden en De deugden, twee series tekeningen, gegraveerd en gedrukt door zijn vrienden en medewerkers in drukkerij In de Vier Winden van Hieronymus Cock in Antwerpen, in een beeldtaal die hij overnam van zijn inspiratiebron, de schilder Hieronymus Bosch. ↩︎
- Het leven en de kunst van Albrecht Dürer, Erwin Panofsky, Princeton University Press, 1971. ↩︎
- Vanitas (van het Latijnse ‘ijdelheid’, wat in deze context nutteloosheid of zinloosheid betekent) is een soort memento mori of symbolische metafoor die herinnert aan de onvermijdelijkheid van de dood. Het symboliseert de vergankelijkheid van het leven, de zinloosheid van genot en daarmee de ijdelheid van een bestaan dat wordt gedefinieerd door de permanente zoektocht naar aards genot. ↩︎
- Over de strijd van Petrarca en zijn boezemvriend Boccaccio voor de introductie van het klassieke Grieks in Europa: De revolutie van het antieke Grieks, Plato en de Renaissance, Karel Vereycken, Artkarel, 2021. ↩︎
- De immense populariteit en daarmee het historische belang van deze cycli, vooral in Frankrijk, mag niet worden onderschat. In Nederland is de vaak verkeerd begrepen beeldtaal van Pieter Brueghel de Oude voor zijn schilderij De triomf van de dood (Prado, Madrid) vrijwel rechtstreeks ontleend aan de dichtbundel van Petrarca. ↩︎
- Met Hieronymus Bosch op het spoor van het Sublieme, Karel Vereycken, Archiefwebpagina, Schiller Instituut, Washington. ↩︎
- Bosch, De Tuin der Lusten, Reindert Falkenburg, Hazan, Parijs, 2015. ↩︎
- In zijn magnum opus, Il Cortegiano (De hoveling), Boek XXXIX, bespot de pauselijke nuntius Baldassar Castiglione (1478-1519) Leonardo da Vinci en betreurt « dat een van de eerste schilders ter wereld de kunst waarin hij uniek is, verachtte en filosofie begon te studeren, waarin hij concepten en hersenschimmen smeedde die zo vreemd waren dat hij ze nooit in zijn werk kon schilderen. » ↩︎
- Leonardo da Vinci’s notitieboeken, Richter, 1888, XIX filosofische stelregels. Moraal. Controverses en speculaties, nr. 1178, Dover Editions, Vol. II., 1970. ↩︎
- Het geheim om creatief te zijn: lachen, Angeles Nieto, Angeles Earth; ↩︎
- De Docta Ignorantia (Over aangeleerde onwetendheid), Nicolaas van Cusa, 1440. Cusanus volgt hier Socrates, die volgens Plato zei: « Ik weet dat ik niets weet » (Plato, Apologie, 22d). ↩︎
- Met zijn De servo arbitrio (De Verslaafde Wil) reageerde Maarten Luther in 1525 op Erasmus’ De libero arbitrio (Over de Vrije Wil) die een jaar eerder, in 1524, werd gepubliceerd. ↩︎
- Op 31 oktober 1517 schreef Luther een brief aan zijn bisschop, Albert van Brandenburg, om te protesteren tegen de verkoop van aflaten. Bij zijn brief voegde hij een kopie van zijn Dispuut over de kracht en doeltreffendheid van aflaten, beter bekend als de 95 stellingen. Erasmus en anderen hadden deze oplichterij al uitgebreid veroordeeld, met name in zijn Lof der Zotheid uit 1509. ↩︎
- Massys and Money: Tax Collectors Rediscovered, Larry Silver, JHNA, Volume 7, Number 2 (zomer 2015), Silver schrijft: « Toch wordt de invloed van Massys’ schilderkunst op de geschiedenis van de genreschilderkunst al enige tijd erkend. Het onderwerp werd vrijwel onmiddellijk opgenomen door de zoon van de schilder, Jan Massys, door Marinus van Reymerswaele en door Jan van Hemessen. » ↩︎
- Ibid, noot nr. 22. ↩︎
- Het werk werd in een paar dagen geschreven in de residentie van Thomas More in Bucklersbury bij Londen en drukt de diepe schok van Erasmus uit toen hij ontdekte in welke erbarmelijke staat hij « zijn » Kerk en « zijn » Italië aantrof toen hij in 1506 naar Rome kwam. Voor Erasmus, in tegenstelling tot de scholastici, moest emotie niet genegeerd of onderdrukt worden, maar verheven en opgeleid, een thema dat later door Friedrich Schiller werd ontwikkeld in zijn Brieven over de esthetische opvoeding van de mens (1795). Stultitia (de Latijnse naam voor Zotheid) is de personificatie van Waanzin die voortdurend heen en weer slingert tussen schijnbare zotheid = echte wijsheid en schijnbare wijsheid = echte zotheid, zichzelf uitdrukt en stellig aanspraak maakt op haar vaderschap en op haar vaderschap van alles. Van de « zachte » zotheid van de zwakken, van vrouwen en kinderen, van mannen die door hun zonde de rede hebben verlaten, gaat Erasmus over tot het mobiliseren van al zijn ironie en vernuft om de « harde » criminele zotheid van de machtigen, van de « philo-sofisten », van kooplieden, bankiers, prinsen, koningen, pausen, theologen en monniken te kastijden. ↩︎
- La Nef des Fous, Sebastian Brant, Editions Seghers en Nuée Bleue, herdruk, 1979, Straatsburg. ↩︎
- Sebastian Brant, Forschungsbeiträge zu seinem Leben, zum Narrenschiff und zum übrigen Werk, Thomas Wilhelmi, Schwabe Verlag, p. 34, 2002, Basel. ↩︎
- Dürer maakte deze gravure ter illustratie van een populaire bundel met de titel Het Boek van de Torenridder, een handleiding voor goed gedrag voor jonge meisjes. Volgens het verhaal at de vrouw van de kok een paling die bedoeld was voor een speciale gast, maar in plaats van het aan haar man te vertellen, loog ze. Er wordt gezegd dat een ekster het geheim van de vrouw aan haar man vertelde en dat de wraakzuchtige vrouw hem als straf zijn veren liet uitplukken. De kok, afgebeeld met alle attributen van zijn vak: mes, pan en lepel, luistert naar de vogel met een uitdrukking van toenemende verbazing op zijn gezicht, terwijl zijn vrouw haar blik opzij richt in afwachting die grenst aan een oplossing. ↩︎
- Het feit dat de Florentijnse schrijver en koopman Lodovico Guicciardini (1521-1589) het grootste deel van zijn leven in Antwerpen woonde, zij het na 1542, maakt hem een waardevolle bron van informatie. ↩︎
- For Bruegel, his World is Vast, Interview van de auteur met Bruegel expert Michael Gibson, kunstcriticus voor de International Herald Tribune, Fidelio, Vol. 8, N° 4, Winter 1998. ↩︎
- Sebastian Brant, Ibid., p. 23. ↩︎
- Sebastian Brant, Ibid., p. 27. ↩︎
- Dendrochronologisch onderzoek van Peter Klein heeft het hout gedateerd op 1491, dus voor de publicatie van Brants Narrenschip. Meestal ziet men Bosch’s oeuvre als een illustratie van de eerste editie van 1493. Een andere mogelijke bron voor de allegorie van het schip is de Bedevaart van de ziel, een werk van de 14e-eeuwse cisterciënzer Guillaume de Deguileville, gedrukt in het Nederlands in 1486. ↩︎
- Dendrochronological Analysis of Works by Hieronymus Bosch and His Followers, Peter Klein, Museum Boijmans Van Beuningen-NAi Publishers-Ludion, Rotterdam, 2001; ↩︎
- See Moderne Devotie et Broeders en van het Gemene Leven, bakermat van het Humanisme, lezing van Karel Vereycken, 2011, Artkarel.com. ↩︎
- Dit thema, verder ontwikkeld door Joachim Patinir, Herri met de Bles en anderen, staat centraal in De Bedevaart van de ziel, Guillaume De Deguileville, 14de eeuw. ↩︎
- De Moderne Devotie, Spiritualiteit en cultuur vanaf de late Middeleeuwen, collectief werk, WBooks, Zwolle, 2018. ↩︎
- Dionysus de Kartuizer (1401-1471) ging op 13-jarige leeftijd naar Zwolle om les te volgens aan de Latijnse school van de Broeders van het Gemene Leven, die werd geleid door Johannes Cele. Hij vergezelde Cusanus op zijn reis door de Nederlanden in 1451. Hij was bechtvader en raadsman van Hertog Filips de Goede. Hij was waarschijnlijk de theologische adviseur van Jan van Eyck voor de compositie van het Lam Gods. Dionysus schreef De Venustate Mundi et Pulchritudine Dei (Over de aantrekkingskracht van de wereld en de schoonheid van God). Een ander bekend traktaat van hem is Speculum amatorum mundi, vertaald als Spieghel der liefhebbers deser werelt (verschenen in 1535). Het is een moralistisch-didactisch werk dat de dwaasheid van aardse genietingen uitlegt. Wie de wereld liefheeft is verdoemd, want de weg naar de hemel is smal. Een zuiver hart kan geen vreugde vinden op aarde en begrijpt dat de eeuwige vreugde alleen is weggelegd voor wie tijdens het leven godvruchtig lijdt. ↩︎
- Hier moeten we het baanbrekende werk van Prof. Eric de Bruyn erkennen in zijn opmerkelijke boek De vergeten beeldentaal van Jheronimus Bosch, Heinen, ‘s-Hertogenbosch, 2001, waarin hij onomstotelijk aantoonde dat het onderwerp van de achterkant van Bosch’ schilderij « De hooiwagen » niet de « Terugkeer van de verloren zoon » was, zoals jarenlang werd gedacht, maar eerder « De marskramer » ↩︎
- Les Flamands de France, Louis de Baecker, Messager des sciences historiques et archives des arts de Belgique, p. 181, Gent, Vanderhaeghen, 1850. ↩︎
- Le Landjuweel d’Anvers de 1561 — Faire de l’art une arme pour la paix, Karel Vereycken, Artkarel.com, 2025; ↩︎
- Eigentijdse beschrijving, in De vergeten beeldentaal van Jheronimus Bosch, p. 23. Dr. Eric de Bruyn, Adriaan Heinen Uitgevers, s’Hertogenbosch, 2001 ↩︎
- De Bruyn, Ibid. p. 23; ↩︎
- Voor een gedetailleerd relaas van Matsys’ jeugd, zie Quinten Metsys, Andrée de Bosque, p. 33, Arcade Press, Brussel, 1975. ↩︎
- De legende begon met Dominicus Lampsonius (1536-1599), die in zijn Gelijkenissen van enige bekende schilders uit Neder-Duitsland, uitgegeven in 1572 door de weduwe van Hieronymus Cock in Antwerpen, een gegraveerd portret van Matsys opnam, gemaakt door Jan Wierix, vergezeld van een gedicht over hoe Matsys’ vriendin de voorkeur gaf aan het geluid van het stille penseel boven het zware geluid van de hamerslagen van een smid. Het verhaal wordt in 1604 opgenomen door Karel van Mander in zijn Schilder-Boeck en later door Alexander van Fornenberg (1621-1663) in zijn enthousiaste presentatie van Matsys, Den Antwerpschen Protheus, vaak Cyclopshen Apelles; dat wil zeggen; Het leven, het einde van de koninklijke familie, het einde van het land, het einde van het hoge land, de heer Quinten Matsys: Van Grof-Smidt, in Fyn-Schilder, Antwerpen, uitgegeven door Hendrick van Soest, 1658. ↩︎
- Het schildersboek, Karel Van Mander, 1604. ↩︎
- Quinten Metsys, Edward van Even, in Het Belfort, Jaargang 12, 1897, Digitale Bibliotheek voor Nederlandse Letteren, webpagina. ↩︎
- Architectuurtekeningen uit Nederland: 15e-16e eeuw, Oliver Kik, CODART eZine, nr. 8, herfst 2016. ↩︎
- Voor meer: Cornelis Matsys 1510/11-1556/57: Grafisch werk, Jan Van der Stock, Tentoonstellingscatalogus. ↩︎
- De Bourgondische Nederlanden, Walter Prevenier en Wim Blockmans, Mercator en Albin Michel Fonds, 1983. ↩︎
- Zie The Age of the Fuggers, Franz Herre, Presse-Druck- und Verlag-GmbH Augsburg, 1985. ↩︎
- In 1548 vermeld Francisco de Hollanda (1517-1585), in zijn De Pinture Antigua (1548), het gesprek tussen Vittoria Colonna en de beroemde schilder Michelangelo waarin ze de kunst van het noorden bespraken. Michelangelo: « Over het algemeen, mevrouw, zal de Vlaamse schilderkunst de liefhebber beter bevallen dan welke schilderkunst uit Italië dan ook, die hem nooit een traan zal doen laten, terwijl die uit Vlaanderen hem er vele zal doen laten; en dit niet vanwege de levendigheid en de vaardigheid van het schilderen, maar vanwege de goedheid van de vrome persoon. In Vlaanderen schildert men omwille van de uiterlijke precisie of van dingen die je blij kunnen maken en waarover niemand kwaad mag spreken, zoals heiligen en profeten. Zij schilderen voorwerpen en metselwerk, het groene gras van de velden, de schaduwen van bomen, rivieren en bruggen. Dit noemen zij landschappen, met veel figuren aan de ene kant en veel figuren aan de andere kant. En dit alles, hoewel het sommigen bevalt, gebeurt zonder enige vakkundige keuze van stoutmoedigheid en, in laatste analyse, zonder inhoud of kracht. » ↩︎
- Over deze kunstenaar: zie Dieric Bouts, Catheline Périer D’Ieteren, Mercator Fonds, Brussel, 2005. ↩︎
- Over deze kunstenaar: zie Hugo van der Goes, Elisabeth Dhanens, Mercatorfonds, Antwerpen, 1998. Ook Hugo van der Goes en de Moderne Devotie, Karel Vereycken, Artkarel.com. ↩︎
- Zie Schilderijen in de Bourgondische Nederlanden, Bernhard Ridderbos, Davidsfonds, Leuven, 2014. ↩︎
- De drie graden van visie volgens Ruusbroec de Wonderbare en de herders in Van der Goes’ Portinari Triptiek, Delphine Rabier, Studies in Spirituality, nr. 27, pp. 163-179, 2017. In zijn tweede Brusselse werk, Die geestelike brulocht (ca. 1335/40) legt Ruusbroec uit dat het geestelijke leven in drie stadia verloopt waarin de liefde tot God zich telkens verdiept: het werkende leven, het innige leven en het Godschouwende leven. Ruusbroec beklemtoont dat de mysticus die het hoogste stadium heeft bereikt de vorige twee nooit achterlaat, maar ze beoefent vanuit de vereniging met God. Dit noemt Ruusbroec het ‘gemene’ leven. ↩︎
- Over deze kunstenaar: zie Rogier van der Weyden, Dirk De Vos, Mercatorfonds, Antwerpen, 1999. ↩︎
- Over de muziekcomposities van Jacob Obrecht (1457-1505), zie Vlaamse Muziek, Robert Wangermée, Arcade, Brussel, 1968. ↩︎
- Metsys’s Musician: A Newly Recognized Early Work, Larry Silver, Journal of Historians of Netherlandish Art (JHNA), Volume 10, N° 2, Zomer 2018. ↩︎
- Over de Renaissance en het hof van Ferrara: Een unieke Renaissance, Het Este-hof in Ferrara, Bentini Jadranka, Quo Vadis, 2003. ↩︎
- De Latijnse school van de Broeders des Gemene Leven in Deventer werd ten tijde van Erasmus geleid door Alexander Hegius (1433-1498), een leerling van de beroemde Rudolf Agricola (Huisman) (1442-1485), een leerling van Cusa en een vurig verdediger van de Italiaanse Renaissance en de klassieke literatuur. Erasmus noemde het een ‘goddelijk intellect’. Op 24-jarige leeftijd reisde Agricola door Italië om orgelconcerten te geven en ontmoette daar Ercole d’Este I (1431-1505), heerser van het hof van Ferrara. Aan de Universiteit van Pavia ontdekte hij ook de verschrikkingen van de aristotelische scholastiek. Toen Agricola in Deventer doceerde, begon hij zijn lezing met de woorden: « Vertrouw niets van wat je tot op heden hebt geleerd. Wijs alles af! Begin met het standpunt dat alles moet worden afgeleerd, behalve datgene wat u opnieuw kunt ontdekken op basis van uw eigen autoriteit of op basis van decreten van hogere auteurs. » ↩︎
- De hypothese dat Quentin Matsys een reis naar Italië heeft gemaakt, is met name geopperd door de Italiaanse auteur Limentani Virdis. Hij schrijft de schilder zelfs het vaderschap toe van een fresco in het Milanese oratorium van de abdij van Santa Maria di Rovegnano. ↩︎
- Vlaamse Kunst, p. 261, Dirk de Vos, Mercatorfonds, 1985. ↩︎
- Le Beau Martin, Gravures et dessins, Musée d’Unterlinden, Colmar, 1991; ↩︎
- Renaissance in the North, Holbein, Burgkmair, and the Age of the Fuggers, Guido Messling, Jochen Sanders (eds), Hirmer, 2023; ↩︎
- Over de vrije wilskeuze, Erasmus. ↩︎
- Van Eyck, Vlaams schilder die de Arabische optica gebruikte, Karel Vereycken, lezing over het thema « Perspectief in de Vlaamse religieuze schilderkunst van de 15e eeuw » aan de Sorbonne Universiteit van Parijs, 26-28 april 2006. ↩︎
- Van Eyck, een optische revolutie, Maximiliaan Martens, Till-Holger Borchert, Jan Dumolyn, Johan De Smet en Frederica Van Dam, Hannibal, MSK Gent, 2020. ↩︎
- De rol van Avicenna en Ghiberti bij de uitvinding van het perspectief in de Renaissance, Karel Vereycken, Artkarel, 2022. ↩︎
- Ibn al-Haytham over binoculaire visie: een voorloper van de fysiologische optica, Arabische Wetenschappen en Filosofie, pp. 79-99, Raynaud, Dominique, Cambridge University Press, 2003. ↩︎
- Leon Battista Alberti (1404-1472) publiceerde zijn De Pictura in 1435. Hoewel het werk belangrijke geometrische concepten uitwerkt die gebruikt worden in perspectiefweergave, ontbreekt elke vorm van illustratie of beeldspraak en gaat het niet in op de vorming van beelden in de geest van de toeschouwer. Leonardo nam de tijd om de beperkingen van het Albertiaanse systeem te demonstreren en presenteerde enkele alternatieven. ↩︎
- Grondslagen van de Renaissance, architectuur en verhandelingen in het altaarstuk van Anna van Quentin Matsys (1509), Jochen Ketels en Maximiliaan Martens, European Architectural Historians Network, EAHN: Onderzoeken en schrijven van architectuurgeschiedenis: onderwerpen, methodologieën en grenzen. blz. 1072-1083. ↩︎
- Ketels, Martens, Ibid.; ↩︎
- Ketels, Martens, Ibid.; ↩︎
- Ketels, Martens, Ibid.; ↩︎
- De prospectiva pingendi (Over het perspectief van de schilderkunst), geschreven door Piero della Francesca (1415-1492), is het eerste Italiaanse Renaissance-traktaat dat aan het onderwerp perspectief is gewijd. Zie Het ei zonder schaduw van Piero della Francesca, Karel Vereycken, Fidelio, Vol. 9, nr. 1, voorjaar 2000, Schiller Institute, Washington. ↩︎
- Ketels, Martens, Ibid.; ↩︎
- Joachim Patinir, Het landschap als beeld van de levende wereld, Reindert L. Falkenburg, Nijmegen, 1985. ↩︎
- In Albrecht Dürer, Anja-Franziska Eichler, Könemann, 1999, Keulen, p. 112. ↩︎
- Zie Erasmus’ droom, het « Drietalen college » van Leuven (1517-1797), Pr. Jan Papy, Editions Peeters, Leuven, 2018. ↩︎
- Jacopo de’ Barbari en de vroege zestiende-eeuwse noordelijke kunst, Jay A. Levenson, New York University, 1978. ↩︎
- Vier boeken over menselijke verhoudingen, Albrecht Dürer, 1528. Het is de moeite waard om op te merken, voor ons onderwerp hier, dat de kunstenaar in het derde boek principes geeft waarmee de verhoudingen van figuren kunnen worden veranderd, inclusief de wiskundige simulatie van convexe (bolle) en concave (holle) spiegels. ↩︎
- Citaat uit Italiaanse prenten uit de National Gallery of Art, Jay A. Levenson, Konrad Oberhuber, Jacquelyn L. Sheehan, National Gallery of Art, 1971. ↩︎
- Les premières gravures italiennes, Quattrocento-début du cinquecento. Venise, Vicence, Padoue : Jacopo de Barbari, Girolamo Mocetto, p. 312-348, Inventaire de la collection du département des Estampes et de la Photographie, Éditions de la Bibliothèque nationale de France, 2015. ↩︎
- Albert Dürer et ses rencontres avec les artistes des Pays-Bas, Matthias Mende, Stadtgeschiedliches Museum-Nürnberg, in Albert Dürer aux Pays-Bas, son voyage (1520-1521), son influence, Paleis voor Schone Kunsten, Brussel, 1977, p. 149. ↩︎
- Albrecht Dürer, Dagboek van zijn reis naar de Lage landen, 1520-1521. Vergezeld van het zilverstift schetsboek en de schilderijen en tekeningen gemaakt tijdens zijn reis, New York Graphic Society, Greenwich, 1996. ↩︎
- Ibid, Noot nr. 14. ↩︎
- Over hen die in dienst staan van de groten, Lucianus van Samosata, vertaald door Eugène Talbot, Hachette, Parijs, 1866. ↩︎
- Lucianus van Samosata, Ibid. ;
↩︎ - Lucianus van Samosata, Ibid. ; ↩︎
- Erasme parmi nous, p. 72-73, Léon E. Halkin, Fayard, Parijs, 1987. ↩︎
- Jozef van Arimathea is een Bijbelse figuur die verantwoordelijk was voor de begrafenis van Jezus na zijn kruisiging.
↩︎ - Herodes de Grote (ca. 72 – ca. 4 v.Chr.) was een Romeins-Joodse ‘cliëntkoning’ (satraap) van het koninkrijk Judea. Hij staat bekend om zijn kolossale bouwprojecten, waaronder de herbouw van de Tweede Tempel in Jeruzalem. ↩︎
- Over de rol van Julius II bij de wederopbouw van Rome, zie What Humanity Can Learn from Raphael’s School of Athens, Karel Vereycken, Artkarel.com, 2022. ↩︎
- Ibid, noot nr. 88 betreffende Moderne Devotie. ↩︎
- Marlier, Ibid, p. 252.. ↩︎
- Over de rol van de Fuggers en de Welsers in de financiële en fysieke slavernij in die tijd, zie Jacob the Rich, father of financial fascism, Karel Vereycken, Artkarel, 2024. ↩︎
- Ehrenberg, Richard, Capital et finance à l’âge de la Renaissance : A Study of the Fuggers, and Their Connections, 1923 ; ↩︎
- Marlier, Ibid., p. 252 ↩︎
- Geciteerd door Marlier, Ibid. ↩︎
- Le prêteur et sa femme de Quinten Metsys, Emmanuelle Revel, Collection Arrêt sur œuvre, Service culturel, Action éducative, Louvre, Paris, 1995. ↩︎
- Les primitifs flamands, Erwin Panofsky, Harvard University Press, 1971, vertaald van het Engels door Dominique Le Bourg, Hazan, collection « 35/37 », Parijs, 1992, pp. 280-282. ↩︎
- Le siècle de Bruegel. La Peinture en Belgique qu XVIe siècle, catalogue d’exposition 27 septembre – 24 novembre 1963, Musées royaux des Beaux-Arts de Belgique, Bruxelles, nota van Georges Marlier. ↩︎
- Voor een bespreking van dit onderwerp en tegenstrijdige interpretaties: voor de duivelse aard van spiegels, zie Histoire du miroir, Sabine Melchior-Bonnet, Imago, Paris, 1994; voor spiegels als bemiddeling van het goddelijke, zie Cusanus, Het zien van God, 1453. ↩︎
- L’hypothèse d’Oxford, Dominque Raynaud, Presses Universitaires de France, Paris, 1988. ↩︎
- Jan van Eyck, a Flemish painter using Arab Optics, Karel Vereycken, lezing, 2006 Sorbonne Universiteit, Parijs, Artkarel, France. ↩︎
- Zie Petrus Christus, Maryan W. Ainsworth and Maximiliaan P. J. Martens, p. 96. ↩︎
- Iconographie de l’art chrétien, Louis Réau, Presses Universitaires de France, 1958, tome III, Iconographie des saints, pp. 927-928. ↩︎
- Ketels, Martens, Ibid. ↩︎
- Gids voor de Kunst in België, Philippe d’Aarschot, p. 105, Spectrum, 1965. ↩︎
- Holbeins De Lais van Corintië uit 1526 toont de invloed van Leonardo da Vinci. Pierre Vays, hoogleraar kunstgeschiedenis aan de faculteit van Genève, benadrukt ook de “Leonardesque toets van sommige van zijn composities”, in Holbein de Jongere, op https://www.clio.fr ↩︎
- Da Vinci likely painted part of Belgium’s ‘The Last Supper’ replica, Maïthé Chini, The Brussels Times, May 2, 2019. ↩︎
- In Les grotesques et mouvements de l’âme, Léonard de Vinci conçu par Wenceslaus Hollar à la Fondation Pedretti, Federico Giannini, Finstre Sull’Arte, 26 mars 2019. ↩︎
- De Tien Boeken over Architectuur, Vitruvius. ↩︎
- Figures du fou, Du Moyen Âge aux Romantiques, Elisabeth Antoine-König, Pierre-Yves Le Pogam, Musée du Louvre, Gallimard, 2024; ↩︎
- Erasmus, Lof der zotheid, hoofdstuk. XXXI. ↩︎
- The Colloquies of Erasmus, door de auteur vertaald van het engels, Gibbing & Company, London, 1900. ↩︎
- Early Netherlandish Painting. volume 7, Quentin Massys, Max J. Friedländer, Editions de la Connaissance, Bruxelles, 1971. ↩︎
- Cranach der Ältere und die Niederlande, Till-Holger Borchert, in DIe Welt von Lucas Cranach, editions G. Messling, 2010. ↩︎
- Les couples mal assortis – Lucas Cranach, Perceval, eve-adam.over-blog.com, 2016 ↩︎
- The Ugly Duchess by Quinten Massys, An Analysis, Katie Shaffer, Academia.edu, 2015. ↩︎
- In Picturing women in late Medieval and Renaissance art, Christa Grössinger, Manchester University Press, 1997. p. 136. ↩︎
- Quinten Massys and the Art of Satire, Emma Capron, in The Ugly Duchess, Beauty & Satire in the Renaissance, p. 20-21, uitgegeven in 2023 door National Galery Global en Yale University Press ter gelegenheid van de eponieme tentoonstelling; ↩︎
- Léonard de Vinci, Daniel Arasse, p. 36, Hazan, Paris, 1997. ↩︎
- De Larousse Encyclopedie merkt op dat « de invloed van Leonardo zichtbaar is in een Maria met kind (Museum van Poznań), geïnspireerd op de Maagd Maria en Sint-Anna, en ook te zien is in het vakmanschap van de Maagd van Rattier (1529, Louvre) of de Madeleine (Museum van Antwerpen). Het kan de karikaturale tendens hebben geïnspireerd van De oude man (1514, Parijs, Jacquemart-André Museum), van De lelijke vrouw (kopie in Londen, NG) en misschien zelfs genretaferelen zoals De oude Galant (Washington, NG) of De woekeraar (Rome, Gal. Doria-Pamphili). » ↩︎
- Opgelost: Het mysterie van de boze hertogin – en de Da Vinci-connectie, Mark Brown, The Guardian, 11 oktober 2008. ↩︎
- Mark Brown, Ibid. ; ↩︎
- Mark Brown, Ibid. ; ↩︎
- Emma Capron, Ibid. ; ↩︎
- Groteske koppen van Quinten Metsijs, Hieronymus Cock en Hans Liefrinck naar Leonardo da Vinci, De Zeventiende Eeuw, Jaargang 10, 1994. ↩︎
- Daniel Ménager, La Renaissance et le rire, PUF, 1995, Paris; ↩︎
- Erasmus, Lof der Zotheid; ↩︎
- Rembrandt database, IV 25, Self-portrait as Zeuxis laughing, p. 551, Ernst van de Wetering, Rembrandt Research Project. ↩︎
- Erasmus, De Klacht van de Vrede, Ibid. ↩︎
- Creativity and Humor, Chapter 4 – Why Humor Enhances Creativity From Theoretical Explanations to an Empirical Humor Training Program: Effective “Ha-Ha” Helps People to “A-Ha”, Ching-Hui Chen, Hsueh-Chih Chen, Anne M. Roberts, pages 83-108, Explorations in Creativity Research, 2019; ↩︎
- De Eeuw van de Zotheid, over de nar als maatschappelijke houvast in de vroegmoderne tijd, Herman Pleij, p. 11, Uitgeverij Bert Bakker, Amsterdam. ↩︎
ArtistCloseUp interviews Karel Vereycken on the creative method



In its september 2024 issue #22, the Contemporary Art Magazine ArtistCloseUp, widely read among professionnals, presented some works of the French-Belgian Painter-engraver Karel Vereycken.
On July 23, the magazine published an online interview with Karel on what motivates him and his creative method.
Karel Vereycken
Born in 1957 in Antwerp, Karel graduated from the Institut Saint-Luc in Brussels and trained in engraving at the Académie Royale des Beaux-Arts, where he obtained a certificate of passage « with distinction. » In France, as a member of the Fédération nationale de l’estampe, he confirmed his technical mastery at Atelier63 and continued to perfect his skills in the Paris workshop of Danish engraver Bo Halbirk.
Complete biography


Written By Editorial Team
What is your background and how did you start your journey in the art world?
“I was born in 1957 in Antwerp. My parents worked in the port and the ship repair industry. Their adolescence, studies and careers were reduced to zero by the war period and the need to bring an income and feed their brothers, parents and family. So for their children, my parents thought we should have the occasion to fully enjoy and explore the cultural dimensions.
My mother, who was prevented by the war to become an opera singer, got me into a music school. But at that time, the teaching methods, basically learning to read scores for two years before ever being allowed to sing, were so repugnant that I ran away from that. As an alternative, my mother sent me to a communal drawing school directed by a talented sculptor named Herman Cornelis. The bearded cigar-smoking giant would rip pages out of old books and stick them in my hands saying “copy this!”
At the same time, my father would take me every weekend to visit the numerous museums of Antwerp where paintings of Bruegel, Rembrandt, Bosch, Rubens, Van Eyck and many other Flemish masters were on show. Father couldn’t really explain why but knew this was somehow very important.
Antwerp has also a well preserved XVIth century print shop of Christopher Plantin, a French humanist who worked in that city in the 16th century with many cartographers such as Mercator and Ortelius, whose engraved globes and printed maps impressed me deeply.
Then, at age 12, I won my first art prize and my teacher convinced my mother “there was precious talent” in me. With that advice, my mother sent me to Brussels to attend the Saint Luke Art School and study Plastic Arts. Some teachers were quite annoying but others got us into deep study of anatomy, examining Leonardo da Vinci and Albrecht Dürer’s groundbreaking studies. I continued another two years at the Ecole Royale des Beaux Arts of Brussels to study copper engraving and got graduated “with distinction.”
I then moved to Paris and worked as a journalist and editor of a non-commercial militant paper. But after some years, I found out art was really lacking in my life so I returned to it. First by producing copies of old masters painting on wooden oak panels with hand-made egg tempera, venitian turpentine and various other ancient oil techniques I rediscovered with a friend of mine.
Since the people that ordered these painting took them home, at the end, I had nothing to put on show. Therefore, I returned to watercolors and etching. I also gave a three year course of drawing for some of my friends, mainly amateurs and beginners.”
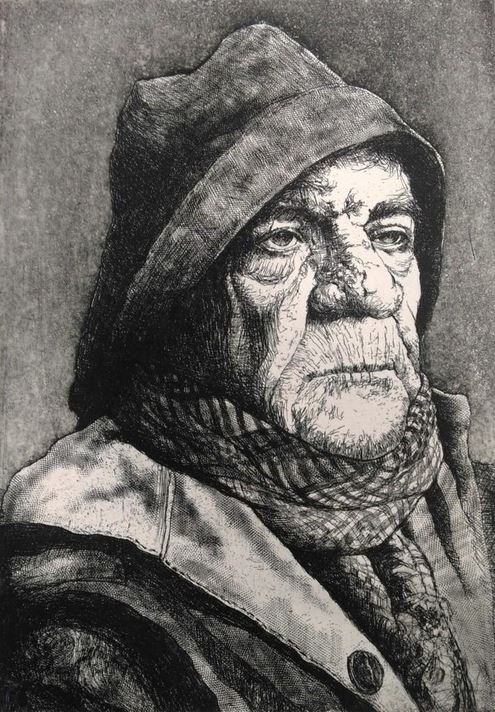

What inspires you?
“What always attracted me in painting and imagining is the way art “makes visible” things and ideas that are “not visible” as such in the simple visible world but which “appear” in the minds of the viewer.
It took me over twenty years to sort out the difference between “symbols” (a “convention” accepted among a group or a code system designed to communicate a secret meaning), and “metaphor” which by assembling things unusual, by irony and paradox, allows the individual mind to “discover” the meaning the painter intended to transmit.
Such an approach offers the joy of discovery and surprise, a deep human quality. Modern art started as a non-figurative form of symbolism till “contemporary” art brought many artists to put an axe into the very idea of poetical meaning.
In 1957, the CIA sponsored, under various covers and often without the artists even knowing about it, many “abstract” artists to promote a form of art that it considered coherent with its ideology of “free enterprise.”
So what inspires me is true human culture, be it Chinese painting of the Song dynasty, the Buddhist sculptures of Gandhara, the early Flemish masters or the magnificent bronze heads of Ifé in current Nigeria. Bridging the distances in space and time, religion and philosophy, stands the celebration of unique human capacities, that of compassion, empathy and love.”
What themes do you pursue? Is there an underlying message in your work?
“I don’t pursue themes, they pursue me! My aim is to shock people by showing them that nothing is more “modern” and “revolutionary” than “classical” art, not understood as annoying academic formalism, but as a science of composition based on non-cynical, liberating ironical poetical metaphors, who are the key to all forms of art be it in the domain of the visual arts or music. Art is always a “gift” from the artist to the viewers and the act of giving is an act of love. That is the message.”
How would you describe your work?
“I consider my work as part of a teaching activity, as a sort of humanistic intellectual guerrilla “warfare.” Even if I appreciate selling my works, and get more resources available for my art work, I’m definitely not out to please a given public or to market an aesthetic object. What counts for me is to get viewers to reflect on how “art” can be a “window” to a dimension people intuitively know as important but were never given access to.
I also took dozens and dozens of friends on guided tours at the Louvre in Paris, to the Frankfurt Museum or to the Metropolitan in New York. Some of these guided visits have been audio-taped and are available on my website. After these tours, most of those I guided thanked me warmly saying “I never even suspected to what degree ideas are transmittable through paintings.””
Which artists influence you most?
“I have studied in depth the European renaissance in the works of Ghiberti, Van Eyck, Leonardo, followed by Piero della Francesca and Dürer, arab optical science gave us the science of perspective representation. I wrote several book-length articles on Rembrandt whose tenderness and profoundness moved me to tears. But if one looks to his life, he’s main quality was not his natural talent alone but the fact that he was such a hard worker. For example, to have your portrait done by Rembrandt, you had to pause for some time every day in his studio during at least three months! Having natural talents makes artists lazy! But having good results after much hard work is the trait of genius.
Deciphering Hieronymus Bosch images in his paintings brought me to explore all the ironies of the 15th Century’s Dutch language brought up by Erasmus and his circles. Viewing all of Goya’s work on show in Madrid was another shock to the degree that his painting is so political while remaining beautiful visual poetry in its own right. Emotionally, I identify mostly with him who saw, just as me, both Rembrandt, Erasmus and Bosch as the sources of his elan. Today, Gandhara Buddhist art is adding new dimensions I ignored and helps me to add the required nuances to my views mostly centered on European art.”

What is your creative process like?
“It takes a lot of courage to overcome the fear to be “completely alone” while you walk a road nobody ever walked on. Everything starts by having a “spark” of imagination and forge it into paradoxical metaphors. As an example, the way I created my work Stairway to Heaven (color etching on zinc, image 3). It started with my examination of the fantastic Chinese landscape paintings. Going through pictures of Chinese landscapes, I realized some of these paintings were not pure imagination but based on landscapes that really existed. The most fascinating of them are certainly those of an area called “Yellow mountains.”
Now at that time, I was also unraveling the way the Flemish painter Joachim Patinir painted his landscapes, as objects for religious contemplation. In the latter’s painting, man is seen, as in Augustinian philosophy, as a pilgrim, who has to learn how to detach himself from earthly possessions, that attachment considered a source of evil. The pilgrim is at the crossroads. By his free will he has to decide, either to take the easy road downhill or the difficult road uphill where he will reach out by going through a small gate.
So in my etching, I “married” a landscape from this Flemish school (on the left) with a view of China’s Yellow mountain. Initially, I had left out the pilgrim, but by working on the landscape, the idea came back to my mind. To accentuate that the road downhill was the road to evil, I added an owl, in Flemish folk art a symbol of evil since able to see in the dark and to grab you in your weakness. So, as one of my friends says, “behind Karel’s works, there’s always a story,” but it is up to you to discover it !”
What is an artist’s role in society and how do you see that evolving?
“I see on the internet dozens of very talented artists, the world is full of them! But what is required is a turn. What we need are political and financial elites willing to promote a culture that give these talents the chance and the means to shape the public and urban living space. We need a “culture of art” that makes people more and not less human.
As the German poet Friedrich Schiller said in his poem “The artists,” it is them that have the dignity of mankind in their hands, with them humanity rises or falls. Today, a much required turn is desirable. The despicable dictatorship of a handful of greedy gallerist sitting in London, Zurich, Venice and Geneva and deciding who is or is not a valuable artist should be brought to an end and I’m not even mentioning the laundering of criminal money it involves.”
Have you had any noteworthy exhibitions you’d like to share?
“With my colleagues from the workshop of Bo Halbirk in Montreuil, it was really nice in June 2024, to present my works at the 6th Exhibit of Contemporary Prints at the Paris Saint-Sulpice market. Going public, meeting art lovers and fellow artists is always a pleasure and a way to open new avenues. I need more of that!”
Website: artkarel.com
Instagram: @karelvereycken
Other links: www.facebook.com/karel.vereycken
ARTKAREL AUDIO GUIDE: Why Vermeer was hiding his convictions (Paris)


Listen:
To the audio on this website
Read:
ARTKAREL AUDIO GUIDE: How Bosch’s Ship of Fools drove the Jester out of business (Paris)


Liste:
To the audio on this website;
Read:
- With Hieronymous Bosh on the track of the Sublime;
- Comment la folie d’Erasme sauva notre civilisation (FR en ligne) + NL pdf (Agora Erasmus) + EN pdf (Schiller Institute Archive Website) + DE pdf (Neue Solidarität).
- Le rêve d’Erasme: le Collège des Trois Langues de Louvain (FR en ligne)
- Erasmus‘ dream: the Leuven Three Language College (EN online)
- ENTRETIEN: Jan Papy: Erasme, le grec et la Renaissance des sciences (FR en ligne)
- Dirk Martens, l’imprimeur d’Erasme qui diffusa le livre de poche (FR en ligne).
- 1512-2012 : Mercator et Frisius, des cosmographes aux cosmonautes + NL pdf (Agora Erasmus) + EN pdf (Schiller Institute Archive Website).
- La nef des fous de Sébastian Brant (FR en ligne), un livre d’une grande actualité !
- Avec Jérôme Bosch sur la trace du Sublime (FR en ligne) + EN pdf.
- Joachim Patinir et l’invention du paysage en peinture (FR en ligne).
- Joachim Patinir and the invention of landscape painting (EN online)
- Exposition de Lille : ce que nous apprennent les fabuleux paysages flamands (FR en ligne).
- Portement de croix: redécouvrir Bruegel grâce au livre de Michael Gibson (FR en ligne) + EN pdf (Fidelio).
- ENTRETIEN Michael Gibson: Pour Bruegel, le monde est vaste (FR en ligne) + EN pdf (Fidelio)
- Pierre Bruegel l’ancien, Pétrarque et le Triomphe de la Mort (FR en ligne) + EN online.
- A propos du film « Bruegel, le moulin et la croix » (FR en ligne).
- L’ange Bruegel et la chute du cardinal Granvelle (FR en ligne).
- Albrecht Dürer contre la mélancolie néo-platonicienne + EN pdf.
ARTKAREL AUDIO GUIDE: Why Erasmus had no time to pause for portraits (Paris)
Rembrandt: 400 years old and still young!


Rembrandt H. van Ryn, was born on July 15, 1606, as the son of a not so poor miller living in the revolutionary city of Leyden in the Netherlands.
Today (2006), four hundred years later, even without any knowledge of the specific historical context, few are those that remain indifferent to his artistic message and skill. Why Rembrandt? What particular quality of his paintings, engravings and drawings gave him the power to reach over centuries of time?
As we will document here, Rembrandt, a precocious intellectual, became already quite « universal » as a young adult. But let’s try to find out what « universal » means.
The Revolt of the Netherlands
The revolt of the Burgundian Netherlands (Note 1) against the tyranny the Fuggers, bankers at the helm of the Spanish and Austrian Habsburg empire, resulted in the tragic break-up of this « nation-state in the making » between the north (today’s Netherlands) and the south (the territory that today includes Belgium and part of northern France).
The Habsburg empire, while brutally sticking to the rich southern part (Flanders), cynically offered the « insurgents » that, if they wished to have a country, they could settle in the malaria-infested swamps of the North, where 75% of the territory lies below sea level, but nevertheless an area slowly domesticated by generations of hardworking farmers thanks to a vast system of canals, dikes and locks, patiently erected since the end of the thirteenth century.
But Charles V, and even worse, his son Philip II of Spain, didn’t believe in the power of mind or that of work. Instead, they believed in the power of the sword and the terror of the Inquisition. After a long war and much unnecessary bloodshed, their policies had reached an impasse, and on April 9, 1609, the semi-bankrupt Habsburgs were forced to sign a twelve-year truce with the new Republic of the Netherlands.
Education
That same year, Rembrandt, hardly 3 years old, entered basic school, where girls and boys learn to read, to write and to calculate. School opens at 6 a.m. in the summer, at 7 a.m. in winter, and finishes only at 7 p.m. Classes start with prayer, the reading and discussion of passages of the Bible and the singing of psalms. Here Rembrandt develops an elegant handwriting and more than rudiments of the Bible.
The Netherlands want to survive. Its leaders wisely used the 12 year truce (1609-1621) to fulfill their commitment to the general welfare. This way, early XVIIth century Holland became maybe the first country of the world where everybody got the chance to learn how to read, write and calculate.
That universal school system, whatever its inadequacies, offered to both poor and rich alike, was the secret of the Dutch « Golden Century ». It’s schooling will also create the generations of Dutch immigrants that will participate a hundred years afterwards in the American Revolution
Others would enter the secondary school at the age of 12, but Rembrandt precociously enters Leyden’s Latin School at the age of 7. There, pupils generally, besides rhetoric, logic and calligraphy, learn, not only Greek and Latin, but English, French, Spanish or Portuguese. Then, in 1620, at the age of 14, since no age limit in the Netherlands bridled young talents, Rembrandt inscribed at the Leyden University. His choice is not Theology, Law, Science, nor Medicine, but Literature.
Did Rembrandt want to add to his knowledge of Latin, the mastery of Greek and Hebrew philology and perhaps Chaldean, Coptic or Arabic? After all, Leyden was already publishing Arabic-Latin dictionaries, while the Netherlands were increasingly growing to become the book printing centre of the world.
From its foundation in 1585, after a historic battle for the city’s freedom, Leyden University became a rallying point for humanists worldwide and a center for new discoveries in optics, physics, anatomy and cartography, offering the world such famous scientists as Christian Huygens (1629-1695) and Antonie van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723), both correspondents of Leibniz.
People flocked in from Flanders, Germany, Denmark, Sweden, England and even Hungary. By 1621, over fifty Frenchmen were teaching in Leyden. In a desperate effort to pollute this source of creativity, in 1630, René Descartes registered as a « mathematician » at the University of Leyden. (Note 2)
But the big trouble had already started way before. A disastrous theological « debate » degenerated into a conflict akin to civil war. On the one side, Jacob Arminius, founder of the « Remonstrant » current upholding the Erasmian-Rabelaisian concept of man endowed with a free will although that free will remained to be fine-tuned with the grace of God. This view was also held by the elder general and capable national leader, Johan van Oldenbarnevelt (1547-1619).
On the opposing side, one Franciscus Gomarus, defender of the fatalist Calvinist doctrine of « predestination », a doctrine adhered to by Prince Maurits, the young incoming son of the founder of the nation, William the Silent. While leaders were strongly divided, the 1619 « Dordrecht Synod » installed the radical Calvinist doctrine as the law.

But Leyden was mostly « Arminian » and so was Rembrandt. Rembrandt’s 1633 and 1635 portraits of Johannes Uytenbogaert, the main reverend leading the Arminians who was obliged to spent several years of his life in exile to escape from persecution, show how closely Rembrandt was connected to this movement.
So, when Rembrandt entered University, the situation was very hot. Arminian-minded teachers are on the leave and often forced to do so. So was Rembrandt, and after two months, at age 14, he quitted University and went full time into painting and set up his own workshop.
By 1621, the truce had come to an end, and the Spanish army was once again conducting an all-out war against the Netherlands, which was accused, not without reason, of supporting the Bohemian revolt and harboring the leaders of its resistance. (Note 3)
As a young intellectual confronted with injustice and political and religious madness, Rembrandt entered the studio of Jacob Isaaczoon van Swanenburg, a learned Dutch painter who lived in Venice and Naples, where he worked from 1600 to 1617 before running into trouble with the Inquisition, which accused him of « painting on Sundays ».
Few works have survived from this master, renowned for his city views and portraits. But his subjects and style resemble those of the great humanist Hieronymus Bosch. For three long years, Rembrandt learned how to grind pigments, master essences, varnishes, brushes, canvases and panels.
But above all, Swanenburgh made his pupil a master in the art of engraving and etching.
Pelgrims of Emmaus
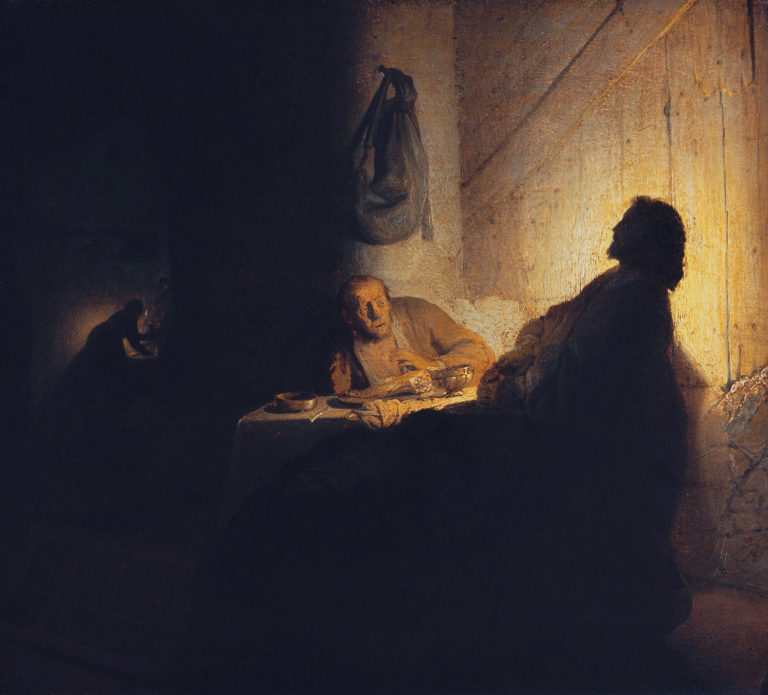

Rembrandt’s interest in the power of ideas clearly appears in the « Pilgrims at Emmaus », where an atmosphere of astonishment and horror break out when Christ reveals himself to the disbelievers.

Then, before setting up his studio, Rembrandt will spend six months in the workshop of Pieter Lastman in Amsterdam. With Lastman, Rembrandt finally finds a master that departs from the traditional Dutch landscapes, still-lives and boring group portraits.
Building on the theatrical settings of Caravaggio, Lastman paints biblical, Greek and Roman mythology. He paints history! And Rembrandt always desired to become a historieschilder. Now, Rembrandt finally found in painting the literature he was looking for when inscribing in the University.
Also, in Lastman’s workshop, he meets the talented Jan Lievens, with whom he will work for a while.
Knowing how to know thyself
Rembrandts reputation is largely the fruit of the near to one hundred multiform self-portraits, including about twenty engravings, covering the walls of numerous museums around the world. Some pragmatists tell us Rembrandt did that many self-portraits because he just was the cheapest model in town, and probably the most patient one. Others claim he was simply noting down his unending grimaces, the famous tronies, to prepare future dramatic historical paintings.
We think there is more to it and we approve Simon Schama who wrote that, « The reason for the multiplication of his self-image was not a relentless, almost monomaniacal assertion of the artistic ego but something like the exact opposite. »
The self-portrait, an art expression that has nearly disappeared from today’s practice, always throws an extremely daring challenge to the painter looking into the mirror. Is this me? I didn’t realize I look that way. I’ve changed again! What is wrong? The a priori ideas in the mind of the perceiver or the sense perceptions he’s confronted with? Real thinking, in essence, comes down to confronting not just those burning paradoxes, but the joy of overcoming them with self reflexive irony, and a truthful commitment to the permanent discovery and communication of that increasing irony through a Socratic dialogue.
Rembrandt, at the age of 22 starts training his first pupil, Gerrit Dou, only fifteen years old. Samuel van Hoogstraten, who was another young pupil, reported Rembrandt advising him:
« Try to learn introducing in your work what you know already. Then, very soon, you will discover what escapes you and want to discover. »

Hoogstraten’s self-portrait at age 17 demonstrates what a contagious genius Rembrandt became rapidly as a teacher.
But Rembrandt’s main problem was to show movement. Anima means soul and for Rembrandt animating the mind of the viewer was the art of making that viewer conscious of his own quality of moving the soul, i.e. moving the mover. Through this process of teaching and self-teaching Rembrandt works out various ways to tell his-stories.
One funny way to put faces into motion is to wrap them into clothing, put on jewelry, and choose a specific light setting that generates interesting eye-attracting shadows bringing into light the plastic volumes. Explore facial expressions evoking anger, fear, happiness, self-doubt, laughter, etc.
The real subject is not Rembrandt, but the discovery of human consciousness through self-consciousness. The mirror image permits oneself to look over one’s shoulder down on oneself. Leonardo and others advised artists to view their own work in a mirror, since the « fresh » mirror image offered the artist another « viewpoint », revealing those remaining imperfections that had escaped from his attention.

Also, the compassion and self esteem one is forced to develop in that process becomes a basic ingredient for promethean and agapic character formation. Then, Rembrandt’s joyful process of self-discovery spills naturally over into the portraits done of others.
Look how funny Saskia smiles, when she dresses up « as Rembrandt » with a feathered reddish hat, carrying a golden chain and with her little hand lost in Rembrandt’s large glove.
Then, there are also the self-portraits in assistenza, where the painter’s face pops up uninvited in a larger painting, such as in Velazquez‘ « Las Meninas ».
The Stoning of Saint-Stephen

One of Rembrandt’s grimacing faces appears behind the martyr in the first known painting by the young Rembrandt, The Stoning of Saint-Stephen. Executed at the age of 19, the work powerfully expresses the basis of Rembrandt’s ideas. Loaded with some twenty figures, the subject had previously been treated by Lastman and Adam Elsheimer, a young German Mannerist living in Rome, whose works Rembrandt had admired while contemplating reproductions in Swanenburgh’s studio.
But why Saint-Stephen? Rembrandt’s choice stems directly from the subject. This Greek-speaking Jewish convert, the first Christian martyr, was tried by a court of law for blasphemy. He unabashedly told the Sanhedrin judges that they were « stiff-necked and uncircumcised in heart and ears » and that they were people who had « received the law by the disposition of angels, and have not kept it… »
Stephen also told them that God could not be kept « locked up in a temple ». At one point, Stephen,
« being full of the Holy Spirit, and having his eyes fixed on heaven, saw the glory of God, and Jesus standing at the right hand of God, and he said: ‘Behold, I see the heavens opened, and the Son of Man standing at the right hand of God’.
« And crying aloud, they stopped their ears, and with one accord rushed upon him; and having pushed him out of the city, they stoned him; and the witnesses laid their garments at the feet of a young man called Saul. And they stoned Stephen, who prayed and said: Lord Jesus, receive my spirit. And kneeling down, he cried aloud: Lord, do not impute this sin to them. »
The painting leaves the left side entirely in shadow, in a partially failed attempt to evoke the idea of Stephen seeing the « open heavens. » Saul is in the shadows because he is the one encouraging the execution. Later, on the road to Damascus, he would have his own vision of the « heavens opening » and in turn convert to Christianity, since Saul is none other than the future St. Paul.
In short, as we have said, at the age of 19, Rembrandt powerfully asserts the principles for which he wants to live and for which he is prepared to die, ideas that he must have discovered at the age of fourteen during the great Sophist event, the great « theological debate » that was the beginning of the end of the Republic.
Ideas
Historians might scream there is no space here for political manifestos. They are right. Rembrandt’s ideas go far beyond simple minded militantism, and their political impact is much more profound.
In 1641, an artist, Philips Angel, adressing the painting guild, honored Rembrandt and underscored the artist’s « elevated and profound reflection ». What were these « elevated and profound » ideas all about?
- Truth. Somebody must mobilize the courage to stand up and tell the truth in front of established authorities or misleading public opinion. That theme comes regularly back, notably with « Suzanna and the Elders ». Daniel, a witness of injustice will speak up and saves Suzanna from the death sentence.
- Reason. Faith and religion do not always coincide with religious rites. Look to the angry angel preventing Abraham from killing his own son in « The sacrifice of Isaac ». Think before acting! Reason, love of God and love for mankind must guide any religious practice and on the basis of reason, a dialogue of cultures can enrich humanity.
- Self-perfection. Change, yes. People can find in themselves the means to identify their errors and change for the better. The example of Saint-Paul will stand as a permanent reference for Rembrandt, who painted him several times and even represented himself as the Church father.
- Love, Repentance, Pardon. In a period of permanent danger of « religious wars », Rembrandt strongly identifies with Saint Stephen’s demand « Lord, lay not this sin to their charge. » Rembrandt will paint several times « The return of the prodigal son ». The father gives a great feast for the returning son because he « who was dead came back to life ». The notion of pardon, and acting in the advantage of the other, will become the key concept for the success of the world Peace of Westphalia concluded in 1648 ending the thirty years war, including the recognition of the Netherlands as a sovereign state.
The Night Watch
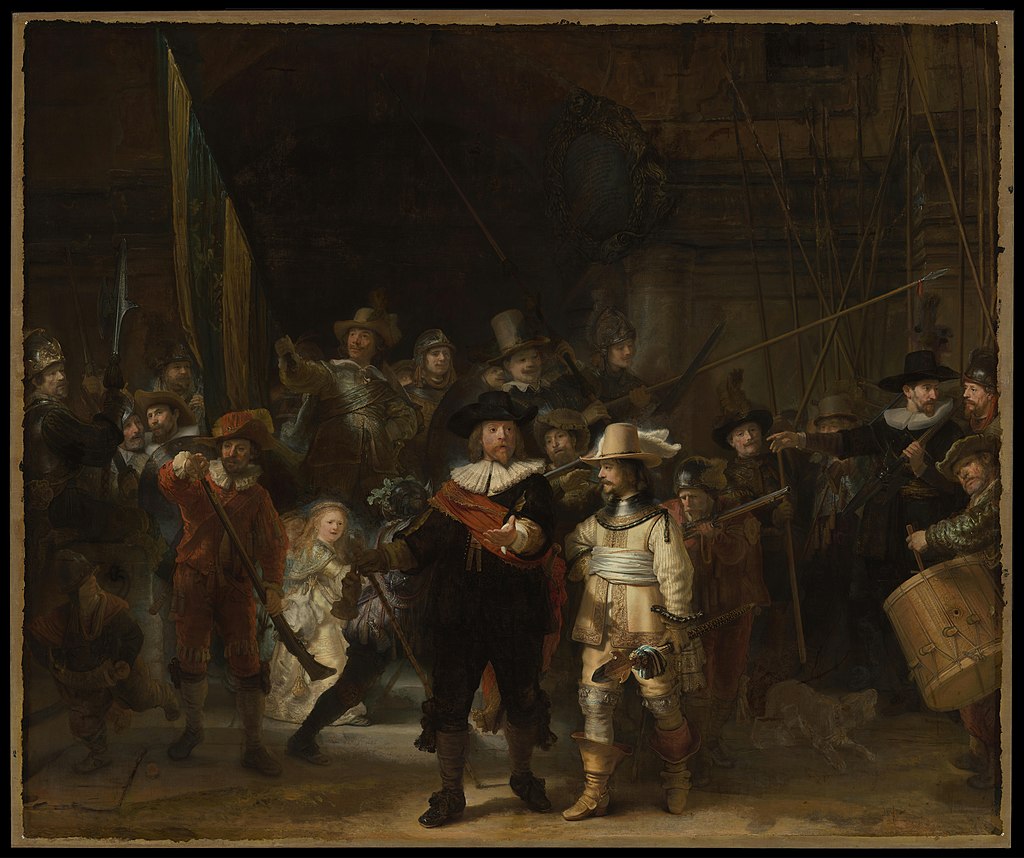

Misrepresented as a nocturnal scene, the Night Watch is probably one of the greatest intellectual provocations against cold Aristotelian classicism.
The Netherlands was at war. Amsterdam, like most major cities, maintained a considerable militia of archers, crossbowmen and harquebusiers. These small citizen armies had a firing range and a meeting hall, the Kloveniersdoelen, where soldiers could rest after training.
Obviously, such glorious gatherings deserved to be immortalized in vast group portraits, where all the members of the company was presented in such a way that, as van Hoogstraten put it, « you could, as it were, behead them all with a single cannon shot. »
Rembrandt completely overturned this traditional representation. Firstly, apart from the 2 captains and their 16 companions (who each paid for their presence on the canvas), Rembrandt added another third of figures to the original number.
Secondly, the revolutionary concept implemented is the idea of depicting the whole group as « on the march », not just advancing, but raising flags and weapons after passing under a circular arch seen just behind them.
Thirdly, a spectacular sense of movement emanates from the rapid oscillation of a chiaro-oscura, illuminating one part, casting another into shadow.
Finally, the show seems formally a confused, chaotic scene. People enter from all sides. In infinite heteronomy, one loads his rifle, another beats the drum, another raises his spear while another stares at his rifle.
Beyond this apparent hectic confusion, what remains is the spirit of a republican citizenry called to arms and moving from chaos to unity, a subject Rembrandt represented the same year in an allegorical oil sketch, Concord of the State.
Against narrow academic rigor, the spirit of inclusion of the multitude so common to Flemish painters like Bruegel was once again manifesting itself.
Van Hoogstraten, defending Rembrandt against these critics (as usual, those who were jealous of his brilliant performance) commented:
« Rembrandt observed this requirement [of unity] very well… and although in the opinion of many he went too far, making the painting more according to his personal taste than according to the individual portraits he had been commissioned to paint.
Nevertheless, the painting, no matter how harsh the critics, will stand, in my judgment, against all these rivals because it is so picturesque in its conception and because it is so powerful that, according to some, all the other doelen works look like playing cards in comparison. »
Immortality
We took here just a few examples to demonstrate that Rembrandts universal character derives directly from his ruthless commitment, directed to make us conscious of the creative potential given to all human beings, men and women, old and young, Christians, Jews, Muslims or others, a creative and creating human nature called the soul.
This commitment is once again available in today’s new generation and can therefore be mobilized for great achievements.
From this point of view, Rembrandt is in a good position to become a reference individual capable of leading us out of the current cultural « dark age », where video games teach our children to take perverse pleasure in gratuitous violence and push them to become « naturally born killers ».
In contrast, a Rembrandt who catches life and loves mankind will trace the divine in the slightest spark of light. As some sort of 5th apostel, without ever painting God directly, Rembrandt reveals the harmony of his creation.
Those who took time studying his paintings can tell themselves: « God exists, I just met Rembrandt », since through Rembrandt’s art God’s tender love and blessing power are revealed to us in our human reality.
That « immortal » nature of Rembrandt’s soul will doubtlessly nourish the « immortality » of the creative geniuses he will inspire. Let us not wait another four hundred years to celebrate such a genius, for what he brings us is living and not to be buried in the history of art
Notes:
- Friedrich Schiller, The revolt of the Netherlands; Karel Vereycken, How Erasmus Folly saved our Civilization; Karel Vereycken, « Rembrandt, bâtisseur de nations » in Nouvelle Solidarité, June 10 and 17, 1985.
- Years earlier, René Descartes, using his own funds, made a trip to Bohemia and in 1620 took part in the battle of Montagne Blanche, leading to the massacre of Prague, the capital of Bohemia. One biographer reports that Descartes, entering Prague, immediately appropriated Kepler’s Brahe scientific instruments.
- For a detailed report on the links between Rembrandt and Comenius and the Bohemian revolt, see Karel Vereycken, The light of Agapê, Rembrandt and Comenius versus Rubens, Ibykus N°85, 2003.
- Ernst van Wetering, director of the Rembrandt Research Project (RRP), on the basis of scientific examinations of Rembrandt’s works, estimates that the master required his models to pose for three hours a day for at least three months.
- Karel Vereycken, Leonardo, painter of movement, Fusion N°108, 2006.
Devotio Moderna, Brothers of the Common Life: the cradle of humanism in the North


Presentation of Karel Vereycken, founder of Agora Erasmus, at a meeting with friends in the Netherlands on September 10, 2011.
The current financial system is bankrupt and will collapse in the coming days, weeks, months or years if nothing is done to end the paradigm of financial globalization, monetarism and free trade.
To exit this crisis implies organizing a break-up of the banks according to principles of the Glass-Steagall Act, an indispensable lever to recreate a true credit system in opposition to the current monetarist system. The objective is to guarantee real investments generating physical and human wealth, thanks to large infrastructure projects and highly qualified and well-paid jobs.
Can this be done? Yes, we can! However, the true challenge is neither economic, nor political, but cultural and educational: how to lay the foundations of a new Renaissance, how to effect a civilizational shift away from green and Malthusian pessimism towards a culture that sets itself the sacred mission of fully developing the creative powers of each individual, whether here, in Africa, or elsewhere.
Is there a historical precedent? Yes, and especially here, from where I am speaking to you this morning (Naarden, Netherlands) with a certain emotion. It probably overwhelms me because I have a rather well informed and precise sense of the role that several key individuals from the region where we are gathered this morning have played and how, in the fourteenth century, they made Deventer, Zwolle and Windesheim an intellectual hotbed and the cradle of the Renaissance of the North which inspired so many worldwide.
Let me summarize for you the history of this movement of lay clerics and teachers: the Brothers and Sisters of the Common Life, a movement that nurished our beloved Erasmus of Rotterdam, the humanist giant from whom we borrowed the name to create our political movement in Belgium.
As very often, it all begins with an individual decision of someone to overcome his shortcomings and give up those « little compromises » that end up making most of us slaves. In doing so, this individual quickly appears as a « natural » leader. Do you want to become a leader? Start by cleaning up your own mess before giving lessons to others!
Geert Groote, the founder

The spiritual father of the Brothers is Geert Groote, born in 1340 and son of a wealthy textile merchant in Deventer, which at that time, like Zwolle, Kampen and Roermond, were prosperous cities of the Hanseatic League.
In 1345, as a result of the international financial crash, the Black Death spread throughout Europe and arrived in the Netherlands around 1449-50. Between a third and a half of the population died and, according to some sources, Groote lost both parents. He abhorred the hypocrisy of the hordes of flagellants who invaded the streets and later advocated a less conspicuous, more interior spirituality.
Groote had talent for intellectual matters and was soon sent to study in Paris. In 1358, at the age of eighteen, he obtained the title of Master of Arts, even though the statutes of the University stipulated that the minimum age required was twenty-one.
He stayed eight years in Paris where he taught, while making a few excursions to Cologne and Prague. During this time, he assimilated all that could be known about philosophy, theology, medicine, canon law and astronomy. He also learned Latin, Greek and Hebrew and was considered one of the greatest scholars of the time.
Around 1362 he became canon of Aachen Cathedral and in 1371 of that of Utrecht. At the age of 27, he was sent as a diplomat to Cologne and to the Court of Avignon to settle the dispute between the city of Deventer and the bishop of Utrecht with Pope Urban V. In principle, he could have met the Italian humanist Petrarch who was there at that time.
Full of knowledge and success, Groote got a big head. His best friends, conscious of his talents, kindly suggested him to detach himself from his obsession with « Earthly Paradise ». The first one was his friend Guillaume de Salvarvilla, the choirmaster of Notre-Dame of Paris. The second was Henri Eger of Kalkar (1328-1408) with whom Groote shared the benches of the Sorbonne.
In 1374, Groote got seriously ill. However, the priest of Deventer refused to administer the last sacraments to him as long as he refused to burn some of the books in his possession. Fearing for his life (after death), he decided to burn his collection of books on black magic. Finally, he felt better and healed. He also gave up living in comfort and lucre through fictitious jobs that allowed him to get rich without working too hard.
After this radical conversion, Groote decides to selfperfect. In his Conclusions and Resolutions he wrote:
« It is to the glory, honor and service of God that I propose to order my life and the salvation of my soul. (…) In the first place, not to desire any other benefit and not to put my hope and expectation from now on in any temporal profit. The more goods I have, the more I will probably want more. For according to the primitive Church, you cannot have several benefits. Of all the sciences of the Gentiles, the moral sciences are the least detestable: many of them are often useful and profitable both for oneself and for teaching others. The wisest, like Socrates and Plato, brought all philosophy back to ethics. And if they spoke of high things, they transmitted them (according to St. Augustine and my own experience) by moralizing them lightly and figuratively, so that morality always shines through in knowledge… ».
Groote then undertakes a spiritual retreat at the Carthusian monastery of Monnikshuizen near Arnhem where he devotes himself to prayer and study.
However, after a three-year stay in isolation, the prior, his Parisian friend Eger of Kalkar, told him to go out and teach :
« Instead of remaining cloistered here, you will be able to do greater good by going out into the world to preach, an activity for which God has given you a great talent. »
Ruusbroec, the inspirer

Groote accepted the challenge. However, before taking action, he decided to make a last trip to Paris in 1378 to obtain the books he needed.
According to Pomerius, prior of Groenendael between 1431 and 1432, he undertook this trip with his friend from Zwolle, the teacher Joan Cele (around 1350-1417), the historical founder of the excellent Dutch public education system, the Latin School.
On their way to Paris, they visit Jan van Ruusbroec (1293-1381), a Flemish “mystic” who lived in the Groenendael Priory on the edge of the Soignes Forest near Brussels.
Groote, still living in fear of God and the authorities, initially tries to make « more acceptable » some of the old sage’s writings while recognizing Ruusbroec as closer to the Lord than he is. In a letter to the community of Groenendael, he requested the prayer of the prior:
« I would like to recommend myself to the prayer of your provost and prior. For the time of eternity, I would like to be ‘the prior’s stepladder’, as long as my soul is united to him in love and respect.” (Note 1)
Back in Deventer, Groote concentrated on study and preaching. First he presented himself to the bishop to be ordained a deacon. In this function, he obtained the right to preach in the entire bishopric of Utrecht (basically the whole part of today’s Netherlands north of the great rivers, except for the area around Groningen).
First he preached in Deventer, then in Zwolle, Kampen, Zutphen and later in Amsterdam, Haarlem, Gouda and Delft. His success is so great that jealousy is felt in the church. Moreover, with the chaos caused by the great schism (1378 to 1417) installing two popes at the head of the church, the believers are looking for a new generation of leaders.
As early as 1374, Groote offered part of his parents’ house to accommodate a group of pious women. Endowed with a by-law, the first house of sisters was born in Deventer. He named them « Sisters of the Common Life », a concept developed in several works of Ruusbroec, notably in the final paragraph Of the Shining Stone (Van den blinckende Steen)
« The man who is sent from this height to the world below, is full of truth, and rich in all virtues. And he does not seek his own, but the honor of the one who sent him. And that is why he is upright and truthful in all things. And he has a rich and benevolent foundation grounded in the riches of God. And so he must always convey the spirit of God to those who need it; for the living fountain of the Holy Spirit is not a wealth that can be wasted. And he is a willing instrument of God with whom the Lord works as He wills, and how He wills. And it is not for sale, but leaves the honor to God. And for this reason he remains ready to do whatever God commands; and to do and tolerate with strength whatever God entrusts to him. And so he has a common life; for to him seeing [via contemplativa] and working [via activa] are equal, for in both things he is perfect.”
Radewijns, the organizer

Following one of his first sermons, Groote recruited Florens Radewijns (1350-1400). Born in Utrecht, the latter received his training in Prague where, also at the early age of 18, he was awarded the title of Magister Artium.
Groote then sent him to the German city of Worms to be consecrated priest there. In 1380 Groote moved with about ten pupils to the house of Radewijns in Deventer; it would later be known as the « Sir Florens House” (Heer Florenshuis), the first house of the Brothers and above all its base of operation?
When Groote died of the plague in 1384, Radewijns decided to expand the movement which became the Brothers and Sisters of the Common Life. Soon it will be branded the Devotio Moderna (Modern Devotion).
Books and beguinages


A number of parallels can be drawn with the phenomenon of the Beguines which flourished from the 13th century onward. (Note 2)
The first beguines were independent women, living alone (without a man or a rule), animated by a deep spirituality and daring to venture into the enormous adventure of a personal relationship with God. (Note 3)
Operating outside the official religious hierarchy, they didn’t beg but worked various jobs to earn their daily bread. The same goes for the Brothers of the Common Life, except that for them, books were at the center of all activities. Thus, apart from teaching, the copying and production of books represented a major source of income while allowing spreading the word to the many.
Lay Brothers and Sisters focused on education and their priests on preaching. Thanks to the scriptorium and printing houses, their literature and music will spread everywhere.
Windesheim
To protect the movement from unfair attacks and criticism, Radewijns founded a congregation of canons regular obeying the Augustinian rule.
In Windesheim, between Zwolle and Deventer, on land belonging to Berthold ten Hove, one of the members, a first cloister is erected. A second one, for women this time, is built in Diepenveen near Arnhem. The construction of Windesheim took several years and a group of brothers lived temporarily on the building site, in huts.
In 1399 Johannes van Kempen, who had stayed at Groote’s house in Deventer, became the first prior of the cloister of Mont Saint-Agnès near Zwolle and gave the movement new momentum. From Zwolle, Deventer and Windesheim, the new recruits spread all over the Netherlands and Northern Europe to found new branches of the movement.
In 1412, the congregation had 16 cloisters and their number reached 97 in 1500: 84 priories for men and 13 for women. To this must be added a large number of cloisters for canonesses which, although not formally associated with the Windesheim Congregation, were run by rectors trained by them.
Windesheim was not recognized by the Bishop of Utrecht until 1423 and in Belgium, Groenendael, associated with the Red Cloister and Korsendonc, wanted to be part of it as early as 1402.
Thomas a Kempis, Cusanus and Erasmus

Johannes van Kempen was the brother of the famous Thomas a Kempis (1379-1471). The latter, trained in Windesheim, animated the cloister of Mont Saint-Agnès near Zwolle and was one of the towering figures of the movement for seventy years. In addition to a biography he wrote of Groote and his account of the movement, his Imitatione Christi (The Imitation of Christ) became the most widely read work in history after the Bible.
Both Rudolf Agricola (1444-1485) and Alexander Hegius (1433-1498), two of Erasmus’ tutors during his training in Deventer, were direct pupils of Thomas a Kempis. The Latin School of Deventer, of which Hegius was rector, was the first school in Northern Europe to teach the ancient Greek language to children.
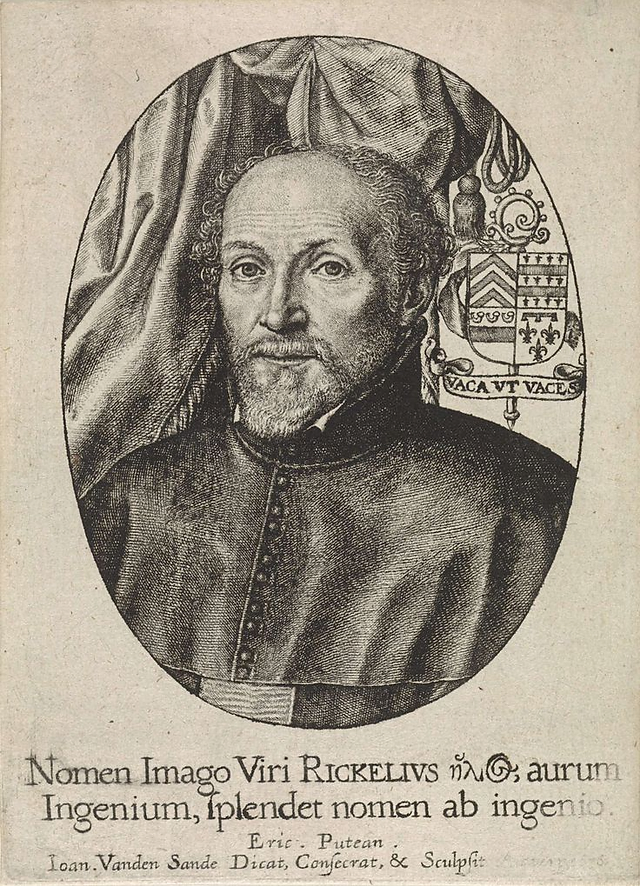

While no formal prove exists, it is tempting to believe that Cusanus (1401-1464), who protected Agricola and, in his last will, via his Bursa Cusanus, offered a scholarship for the training of orphans and poor students of the Brothers of the Common Life in Deventer, was also trained by this humanist network.
What is known is that when Cusanus came in 1451 to the Netherlands to put the affairs of the Church in order, he traveled with his friend Denis the Carthusian (van Rijkel) (1402-1471), a disciple of Ruusbroec, whom he commissioned to carry on this task.
A native of Limburg, trained at the famous Cele school in Zwolle, Dionysius the Carthusian also became the confessor of the Duke of Burgundy and is thought to be the “theological advisor” of the Duke’s ambassador and court painter, Jan Van Eyck. (Note 4)
Gansfort

Wessel Gansfort (1419-1489), another exceptional figure of this movement was at the service of the Greek Cardinal Bessarion, the main collaborator of Nicolas of Cusa (Cusanus) at the Council of Ferrara-Florence of 1437. Gansfort, after attending the Brothers’ school in Groningen, was also trained by Joan Cele‘s Latin school in Zwolle.
The same goes for the first and only Dutch pope, Adrianus VI, who was trained in the same school before completing his training with Hegius in Deventer. This pope was very open to Erasmus’ reformist ideas… before arriving in Rome.
Hegius, in a letter to Gansfort, which he calls Lux Mundi (Light of the World), wrote:
« I send you, most honorable lord, the homilies of John Chrysostom. I hope that you will enjoy reading them, since the golden words have always been more pleasing to you than the pieces of this metal. As you know, I went to the library of Cusanus. There I found some books that I didn’t know existed (…) Farewell, and if I can do you a favor, let me know and consider it done.”
Rembrandt

A quick look on Rembrandt’s intellectual training indicates that he too was a late product of this educational epic. In 1609, Rembrandt, barely three years old, entered elementary school where, like other boys and girls of his generation, he learned to read, write and… draw.
The school opened at 6 in the morning, at 7 in the winter, and closes at 7 in the evening. Classes begin with prayer, reading and discussion of a passage from the Bible followed by the singing of psalms. Here Rembrandt acquired an elegant writing style and much more than a rudimentary knowledge of the Gospels.
The Netherlands wanted to survive. Its leaders take advantage of the twelve-year truce (1608-1618) to fulfill their commitment to the public interest.
In doing so, the Netherlands at the beginning of the XVIIth century became the first country in the world where everyone had the chance to learn to read, write, calculate, sing and draw.
This universal educational system, no matter what its shortcomings, available to both rich and poor, boys and girls alike, stands as the secret behind the Dutch « Golden Century ». This high level of education also created those generations of active Dutch emigrants a century later in the American Revolution.
While others started secondary school at the age of twelve, Rembrandt entered the Leyden Latin School at the age of 7. There, the students, apart from rhetoric, logic and calligraphy, learn not only Greek and Latin, but also foreign languages such as English, French, Spanish or Portuguese. Then, in 1620, at the age of 14, with no laws restricting young talents, Rembrandt enrolled in University. The subject he chose was not Theology, Law, Science or Medicine, but… Literature.
Did he want to add to his knowledge of Latin the mastery of Greek or Hebrew philology, or possibly Chaldean, Coptic or Arabic? After all, Arabic/Latin dictionaries were already being published in Leiden at a time the city was becoming a major printing center in the world.
Thus, one realizes that the Netherlands and Belgium, first with Ruusbroec and Groote and later with Erasmus and Rembrandt, made an essential contribution in the not so distant past to the kind of humanism that can raise today humanity to its true dignity.
Hence, failing to extend our influence here, clearly seems to me something in the realm of the impossible.

Footnotes:
- Geert Groote, who discovered Ruusbroec’s work during his spiritual retreat at the Carthusian monastery of Monnikshuizen, near Arnhem, has translated at least three of his works into Latin. He sent The Book of the Spiritual Tabernacle to the Cistercian Cloister of Altencamp and his friends in Amsterdam. The Spiritual Marriage of Ruusbroec being under attack, Groote personally defends it. Thus, thanks to his authority, Ruusbroec’s works are copied in number and carefully preserved. Ruusbroec’s teaching became popularized by the writings of the Modern Devotion and especially by the Imitation of Christ.
- At the beginning of the 13th century the Beguines were accused of heresy and persecuted, except… in the Burgundian Netherlands. In Flanders, they are cleared and obtain official status. In reality, they benefit from the protection of two important women: Jeanne and Margaret of Constantinople, Countess of Flanders. They organized the foundation of the Beguinages of Louvain (1232), Gent (1234), Antwerp (1234), Kortrijk (1238), Ypres (1240), Lille (1240), Zoutleeuw (1240), Bruges (1243), Douai (1245), Geraardsbergen (1245), Hasselt (1245), Diest (1253), Mechelen (1258) and in 1271 it was Jan I, Count of Flanders, in person, who deposited the statutes of the great Beguinage of Brussels. In 1321, the Pope estimated the number of Beguines at 200,000.
- The platonic poetry of the Beguine, Hadewijch of Antwerp (XIIIth Century) has a decisive influence on Jan van Ruusbroec.
- It is significant that the first book printed in Flanders in 1473, by Erasmus’ friend and printer Dirk Martens, is precisely a work of Denis the Carthusian.
Erasmus’ dream: the Leuven Three Language College


In autumn 2017, a major exhibit organized at the University library of Leuven and later in Arlon, also in Belgium, attracted many people. Showing many historical documents, the primary intent of the event was to honor the activities of the famous Three Language College (Collegium Trilingue), founded in 1517 by the efforts of the Christian Humanist Erasmus of Rotterdam (1467-1536) and his allies. Though modest in size and scope, Erasmus’ initiative stands out as one of the cradles of European civilization, as you will discover here.

Revolutionary political figures, such as William the Silent (1533-1584), organizer of the Revolt of the Netherlands against the Habsburg tyranny, humanist poets and writers such as Thomas More, François Rabelais, Miguel Cervantes and William Shakespeare, all of them, recognized their intellectual debt to the great Erasmus of Rotterdam, his exemplary fight, his humor and his great pedagogical project.
For the occasion, the Leuven publishing house Peeters has taken through its presses several nice catalogues and essays, published in Flemish, French as well as English, bringing together the contributions of many specialists under the wise (and passionate) guidance of Pr Jan Papy, a professor of Latin literature of the Renaissance at the Leuven University, with the assistance of a “three language team” of Latinists which took a fresh look at close to all the relevant and inclusively some new documents scattered over various archives.
“The Leuven Collegium Trilingue: an appealing story of courageous vision and an unseen international success. Thanks to the legacy of Hieronymus Busleyden, counselor at the Great Council in Mechelen, Erasmus launched the foundation of a new college where international experts would teach Latin, Greek and Hebrew for free, and where bursaries would live together with their professors”, reads the back cover of one of the books.

For the researchers, the issue was not necessarily to track down every detail of this institution but rather to answer the key question: “What was the ‘magical recipe’ which attracted rapidly to Leuven between three and six hundred students from all over Europe?”
Erasmus’ initiative was unprecedented. Having an institution, teaching publicly Latin and, on top, for free, Greek and Hebrew, two languages considered “heretic” by the Vatican, was already tantamount to starting a revolution.
Was it that entirely new? Not really. As early as the beginning of the XIVth century, for the Italian humanists in contact with Greek erudites in exile in Venice, the rigorous study of Greek, Hebraic and Latin sources as well as the Fathers and the New Testament, was the method chosen by the humanists to free mankind from the Aristotelian worldview suffocating Christianity and returning to the ideals, beauty and spirit of the “Primitive Church”.
For Erasmus, as for his inspirer, the Italian humanist Lorenzo Valla (1403-1457), the « Philosophy of Christ » (agapic love), has to come first and opens the road to end the internal divisions of Christianity and to uproot the evil practices of greed (indulgences, simony) and religious superstition (cult of relics) infecting the Church from the top to the bottom, and especially the mendicant orders.
To succeed, Erasmus sets out to clarify the meaning of the Holy Writings by comparing the originals written in Greek, Hebrew and Latin, often polluted following a thousand years of clumsy translations, incompetent copying and scholastic commentaries.
Brothers of the Common Life



My own research allows me to recall that Erasmus was a true disciple of the Sisters and Brothers of the Common Life of Deventer in the Netherlands, a hotbed of humanism in Northern Europe. The towering figures that founded this lay teaching order are Geert Groote (1340-1384), Florent Radewijns (1350-1400) and Wessel Gansfort (1420-1489), all three said to be fluent in precisely these three languages.
The religious faith of this current, also known as the “Modern Devotion”, centered on interiority, as beautifully expressed in the little book of Thomas a Kempis (1380-1471), the Imitation of Christ. This most read book after the Bible, underlines the importance for the believer to conform one owns life to that of Christ who gave his life for mankind.
Rudolph Agricola
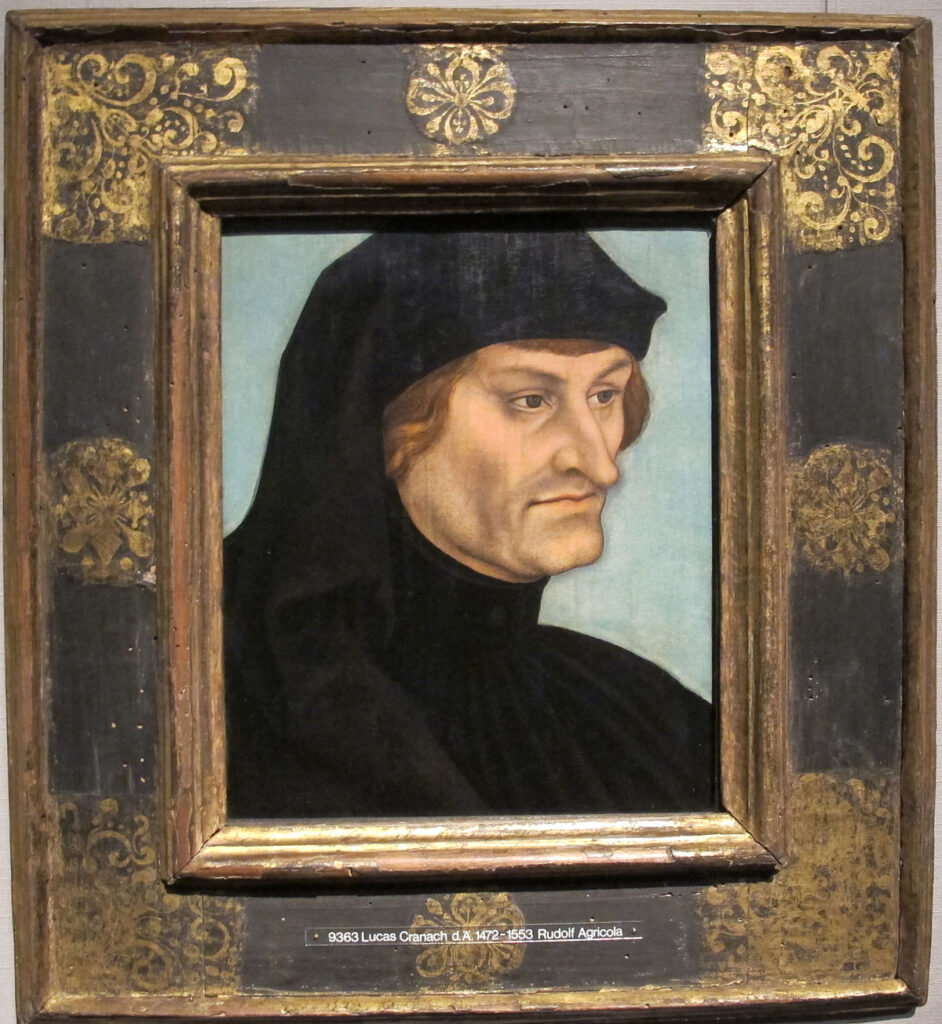

Hence, in 1475, Erasmus father, fluent in Greek and influenced by famous Italian humanists, sends his son to the chapter of the Brothers of the Common Life in Deventer, at that time under the direction of Alexander Hegius (1433-1499), himself a pupil of the famous Rudolph Agricola (1442-1485) which Erasmus had the chance to listen to and which he calls a “divine intellect”.
Follower of the cardinal-philosopher Nicolas of Cusa (1401-1464), enthusiastic advocate of the Italian Renaissance and the Good Letters, Agricola would tease his students by saying:
“Be cautious in respect to all that you learned so far. Reject everything! Start from the standpoint you will have to un-learn everything, except that what is based on your sovereign authority, or on the basis of decrees by superior authors, you have been capable of re-appropriating yourself”.
Erasmus, with the foundation of the Collegium Trilingue will carry this ambition at a level unreached before. To do so, Erasmus and his friend apply a new pedagogy. Hence, instead of learning by heart medieval commentaries, pupils are called to formulate their proper judgment and take inspiration of the great thinkers of the Classical period, especially “Saint Socrates”. Latin, a language that degenerated during the Roman Empire, will be purified from barbarisms.
With this approach, for pupils, reading a major text in its original language is only the start. An explorative work is required: one has to know the history and the motivations of the author, his epoch, the history of the laws of his country, its geography, cosmography, all considered to be indispensable instruments to put each text in its specific literary and historical context and allowing reading, beyond the words, the intention of their author.

This “modern” approach (questioning, critical study of sources, etc.) of the Collegium Trilingue, after having demonstrated its efficiency by clarifying the message of the Gospel, will rapidly travel over Europe and reach many other domains of knowledge, notably scientific issues! By uplifting young talents, out of the small and sleepy world of scholastic certitudes, this institution rapidly grew into a hotbed for creative minds.
For the ignorant reader who often considers Erasmus as some kind of comical writer praising madness which lost it after an endless theological dispute with Martin Luther, such a statement might come as a surprise.
Scientific Renaissance

While Belgium’s contributions to science, under Emperor Charles Vth, are broadly recognized and respected, few are those understanding the connection uniting Erasmus with a mathematician as Gemma Frisius and his pupil and friend Gerard Mercator, an anatomist such as Andreas Vesalius or a botanist such as Rembert Dodonaeus.
Hence, as already thoroughly documented in 2011 by Professor Jan Papy in a remarkable article, the scientific renaissance which bloomed in the Netherlands and Belgium in the early XVIth century, could not have taken place if it were for the “linguistic revolution” provoked by the Collegium Trilingue.
Because, beyond the mastery of their vernacular languages (French and Dutch), hundreds of youth, by studying Greek, Latin and Hebrew, suddenly got access to all the scientific treasures of Greek Philosophy and the best authors in those newly discovered languages.

At last, they could read Plato in the text, but also Anaxagoras, Heraclites, Thales of Millet, Eudoxus of Cnidus, Pythagoras, Eratosthenes, Archimedes, Galen, Vitruvius, Pliny the elder, Euclid and Ptolemy whose work they will master and eventually correct.
As the books published by Peeters account in great detail, during the first century of its existence, the Collegium Trilingue had a rough time confronting political uproar and religious strife. Heavy critique came especially form the “traditionalists”, a handful of theologians for which the Greeks were nothing but schismatics and the Jews the assassins of Christ and esoterics.
The opposition was such that Erasmus himself never could teach at the Collegium and, while keeping in close contact, decided to settle in Basel, Switzerland, in 1521.
Despite all of this, the Erasmian revolution conquered Europe overnight and a major part of the humanists of that period were trained or influenced by this institution. From abroad, hundreds of pupils arrived to follow classes given by professors of international reputation.
27 European universities integrated pupils of the Collegium in their teaching staff: among them stood Jena, Wittenberg, Cologne, Douai, Bologna, Avignon, Franeker, Ingolstadt, Marburg, etc.
Teachers at the Collegium were secured a decent income so that they weren’t obliged to give private lectures to secure a living and could offer public classes for free. As was the common practice of the Brothers of the Common Life in Deventer, a system of bursa allowed talented though poor students, including many orphans, to have access to higher learning. “Something not necessarily unusual those days, says Pr Jan Papy, and done for the sake of the soul of the founder (of the Collegium, reference to Busleyden)”.

While visiting Leuven and contemplating the worn-out steps of the spiral staircase (wentelsteen), one of the last remains of the building that had a hard time resisting the assaults of time and ignorance, one can easily imagine those young minds jumping down the stairs with enthusiasm going from the dormitory to the classroom. Looking at the old shopping list of the school’s kitchen one can conclude the food was excellent with lots of meat, poultry but also vegetables and fruits, and sometimes wine from Beaune in Burgundy, especially when Erasmus came for a visit! While over the years, of course, the quality of the learning transmitted, would vary in accordance with the excellence of its teachers, the Collegium Trilingue, whose activity would last till the French revolution, gave its imprint in history by giving birth to what some have called the “Little Renaissance” of the first half of the XVIth century.
In France, the Sorbonne University reacted with fear and in 1523, the study of Greek was outlawed in France.

François Rabelais, at that time a monk in Vendée, saw his books confiscated by the prior of his monastery and deserts his order. Later, as a doctor, he translated the medical writings of the Greek scientist Galen from Greek into French. Rabelais’s letter to Erasmus shows the highest possible respect and intellectual debt to Erasmus.
In 1530, Marguerite de Navarre, sister of King Francis, and reader and admirer of Erasmus, at war with the Sorbonne, convinced her brother to allow Guillaume Budé, a friend of Erasmus, to create the “Collège des Lecteurs Royaux” (ancestor of the Collège de France) on the model of the Collegium Trilingue. And to protect its teachers, many coming directly from Leuven, they got the title of “advisors” of the King. The Collège taught Latin, Hebrew and Greek, and rapidly added Arab, Syriac, medicine, botany and philosophy to its curriculum.
Dirk Martens

Also celebrated for the occasion, Dirk Martens (1446-1534), rightly considered as one of the first humanists to introduce printing in the Southern Netherlands.
Born in Aalst in a respected family, the young Dirk got his training at the local convent of the Hermits of Saint William. Eager to know the world and to study, Dirk went abroad. In Venice, at that time a cosmopolite center harboring many Greek erudite in exile, Dirk made his first steps into the art of printing at the workshop of Gerardus de Lisa, a Flemish musician who set up a small printing shop in Treviso, close to Venice.
Back in Aalst, together with his partner John of Westphalia, Martens printed in 1473 the first book in the country with a movable type printing press, a treatise of Dionysius the Carthusian (1401-1471), a friend and collaborator of cardinal-philosopher Nicolas of Cusa, as well as the spiritual advisor of Philip the Good, the Duke of Burgundy and thought to be the occasional « theological » advisor of the latter’s court painter, Jan Van Eyck.
If the oldest printed book known to us is a Chinese Buddhist writing dating from 868, the first movable printing types, made first out of wood and then out of hardened porcelain and metal, came from China and Korea in 1234.

The history of two lovers, a poem written by Aeneas Piccolomini before he became the humanist Pope Pius II, was another early production of Marten’s print shop in Aalst.
Proud to have introduced this new technique allowing a vast increase in the spreading of good and virtuous ideas, Martens wrote in one of the prefaces: “This book was printed by me, Dirk Martens of Aalst, the one who offered the Flemish people all the know-how of Venice”.
After some years in Spain, Martens returned to Aalst and started producing breviaries, psalm books and other liturgical texts. While technically elaborate, the business never reached significant commercial success.
Martens then moved to Antwerp, at that time one of the main ports and cross-roads of trade and culture. Several other Flemish humanists born in Aalst played eminent roles in that city and animate its intellectual and cultural life. Among these:
—Cornelis De Schrijver (1482-1558), the secretary of the City of Aalst, better known under his latin name Scribonius and later as Cornelius Grapheus. Writer, translator, poet, musician and friend of Erasmus, he was accused of heresy and hardly escaped from being burned at the stake.
—Pieter Gillis (1486-1533), known as Petrus Aegidius. Pupil of Martens, he worked as a corrector in his company before becoming Antwerp’s chief town clerk. Friend of Erasmus and Thomas More, he appears with Erasmus in the double portrait painted by another friend of both, Quinten Metsys (1466-1530).
—Pieter Coecke van Aelst (1502-1550), editor, painter and scenographer. After a trip to Italy, he set up a workshop in Antwerp. Pieter will produce patrons for tapestries, translated with the help of his wife the works of the Roman architect Vitruvius into Dutch and trained the young Flemish painter Bruegel the Elder who will marry his daughter.
Invention of pocket books
In Antwerp, Martens became part of this milieu and his workshop became a meeting place for painters, musicians, scientists, poets and writers. With the Collegium Trilingue, Martens opens a second shop, this time in Leuven to work with Erasmus. In order to provide adequate books to the Collegium, Martens proudly became, in the footsteps of the Venetian Printer Aldo Manuce, one of the first printers to concentrate on in-octavo 8° (22 x 12 cm), i.e. “pocket” size books affordable by all and which students could take home !
For the specialists of the Erasmus house of Anderlecht, close to Brussels,
“Martens innovated in nearly all domains. As well as in terms of printing types as lay-out. He was the first to introduce Italics, Greek and Hebrew letter types. He also generalized the use of ‘New Roman’ letter type so familiar today. During the first thirty years of the XVIth century, he also operated the revolution in lay-out (chapters and paragraphs) that gave birth to the modern book as we know it today. All this progress, he achieved in close cooperation with Erasmus”.
Thomas More’s Utopia

In 1516, it was Dirk Martens who printed the first edition of Thomas More’s Utopia. Among the hundreds of editions he printed mostly alone, 61 books and writings of Erasmus, notably In Praise of Folly. He also produced More’s edition of the roman satirist Lucian and Columbus’ account of the discovery of the new world. In 1423, Martens printed the complete works of Homer, quite a challenge!
In 1520, a papal bull of Leo X condemned the errors of Martin Luther and ordered the confiscation of his writings to be burned in public in front of the clergy and the people.
For Erasmus, burning books didn’t automatically erased their their content from the minds of the people. “One starts by burning books, one finishes by burning people” Erasmus warned years before Heinrich Heine said that “There, were one burns books, one ends up burning people”.
Printers and friends of Erasmus, especially in France, died on the stake opening the doors for the religious wars that will ravage Europe for the century to come.
What Erasmus feared above all, is that with the Vatican’s brutal war against Luther, it is the entire cultural renaissance and the learning of languages that got threatened with extinction.
In July 1521, confronted with the book burning, the German painter and engraver Albrecht Dürer, who made his living with bible illustrations, left Antwerp with his wife to return to his native Nuremberg.
Thirty years later, in 1552, the great cartographer Gerardus Mercator, a brilliant pupil of the Collegium Trilingue, for having called into question the views of Aristotle, went into exile and settled in Duisbourg, Germany.
In 1521, at the request of his friends who feared for his life, Erasmus left Leuven for Basel and settled in the workshop of another humanist, the Swiss printer Johann Froben.
In 1530, with a foreword of Erasmus, Froben published Georgius Agricola’s inventory of mining techniques, De Re Metallica, a key book that vastly contributed to the industrial revolution of Saxen, Switzerland, Germany and the whole of Europe.
Conclusion
If certain Catholic historians try to downplay the hostility of their Church towards Erasmus, the fact remains that between 1559 and 1900, the full works of Erasmus were on the “Index Vaticanus” and therefore “forbidden readings” for Catholics.
If Thomas More, whom Erasmus considered as his twin brother, was canonized by Pius XI in 1935 and recognized as the patron saint of the political leaders, Erasmus himself was never rehabilitated.
Interrogated by this author in a letter, the Pope Francis returned a polite but evasive answer.

Let’s rebuild the Collegium Trilingue !
With the exception of the staircase, only a few stones remain of the historical building housing the Collegium Trilingue. In 1909, the University of Louvain planned to buy up and rebuild the site but the First World War changed priorities. Before becoming social housing, part of the building was used as a factory. As a result, today, there is no overwhelming charm. However, seeing the historical value of the site, we cannot but fully support a full reconstruction plan of the building and its immediate environment.
It would make the historical center of Leuven so much nicer, so much more attractive and very much more loyal to its own history. On top, such a reconstruction wouldn’t cost much and might interest private investors. The images in 3 dimensions produced for the Leuven exhibit show a nice Flemish Renaissance building, much in the style of the marvels constructed by architect Rombout II Keldermans.
Every period has the right to honestly “re-write” its own history, without falsifications, according to its own vision of the future.
It has to be noted here that the world famous “Rubenshuis” in Antwerp, is not at all the original building, but a scrupulous reconstruction of the late 1930s.
With Kondiaronk and Leibniz, re-inventing a society without oligarchy


By Karel Vereycken, May 2023.
Helga Zepp-LaRouche, the founder of the Schiller Institute, in her keynote address to the Schiller Institute’s Nov. 22, 2022 videoconference, “For World Peace—Stop the Danger of Nuclear War: Third Seminar of Political and Social Leaders of the World,” called on world leaders to eradicate the evil principle of oligarchy.
Oligarchy is defined as a power structure in which power rests with a small number of people having certain characteristics (nobility, fame, wealth, education, or corporate, religious, political, or military control) and who impose their own power over that of their people.
To be precise, Zepp-LaRouche said :
“For 600 years, there has been a continuous battle between two forms of government, between the sovereign nation state and the oligarchical form of society, vacillating back and forth with sometimes a greater emphasis in this or that direction.
All empires based on the oligarchical model have been oriented towards protecting the privileges of the ruling elite, while trying to keep the masses of the population as backward as possible,
because as sheep they are easier to control (…)”
Now, unfortunately, most of the citizens of the transatlantic world and elsewhere will tell you that abolishing the oligarchical principle is “a good idea”, a “beautiful dream”, but that reality tells us “it can’t happen” for the very simple reason that “it never happened before”.
Societies, by definition, they argue, are in-egalitarian. Kings and Presidents of Republics, they argue, eventually might have “pretended” they ruled over the masses for their “common good”, but in reality, our fellow-citizens think, it was always the rule of a handful favoring their own interest over the majority.
The BRICS
Interesting for all of us, is that some leading thinkers involved in the BRICS movement, are trying to imagine new ways of collective rule excluding oligarchical principles.
For example, going in that direction, economist Pedro Paez, former advisor to Ecuador’s Rafael Correa, in his intervention at the April 15-16 Schiller Institute’s video conference, defended
“a new concept of currency based on monetary arrangements of clearing houses for regional payments, that can be joined into a world clearing house system, which could also prevent another type of unilateral, unipolar hegemony from arising, such as the one that was established with Bretton Woods, and that would instead open the doors to multipolar management”.
Also Belgian philosopher and theologian Marc Luyckx, a former member of the Jacques Delors famous taskforce « Cellule de Prospective » of the European Commission, in a video interview on the de-dollarization of the world economy, underlined that the BRICS countries are creating a world order whose nature makes it so that not a single member of their own group can become the dominant power.
The Dawn of Everything

The good news is that a mind-provoking, 700-page book, titled “The Dawn of Everything: A New History of Humanity”, written and published in 2021 by the American anthropologist David Graeber and the British archaeologist David Wengrow, destroys the conventional notions of ancient human cultures making linear progress toward the neo-liberal economic model and therefore, by implication, high levels of inequality.
Even better, based on hard facts, the book largely debunks the “narrative” that oligarchical rule is somehow “natural”. Of course, the oligarchical principle ruled often and often for a long time. But, surprisingly, the book offers overwhelming indications and “hard facts” proving that in ancient times, some societies, though not all, which eventually prospered over centuries, through political choices, consciously adopted modes of governance preventing minority groups from permanently keeping a hegemonic grip over societies.
Zepp-LaRouche’s 10th point

The subject matter of this issue is intimately linked to the 10th point raised by Helga Zepp-LaRouche, which, in order to demonstrate that all sources of evil can be eradicated by education and political decision, that man’s natural inclination, is intrinsically to do the good. The very existence of historical precedents of societies surviving without oligarchy over hundreds of years, is of course, the “practical” proof of man’s axiomatic inclination to do the good.
Unsurprisingly, some argue that the issue of “good” and “evil” is nothing but a “theological debate”, since the concepts of “good” and “evil” are concepts made up by humans in order to compare themselves with one another. They argue it would never occur to anyone to argue about whether a fish, or a tree, were good or evil, since they lack any form of self-conscience enabling them to measure if their deeds and actions fulfill their own inclination or that of their creator.
Now, part of the “Biblical answer” to this question, if man is bad or evil, claims that people “once lived in a state of innocence”, yet were tainted by original sin. We desired to be godlike and have been punished for it; now we live in a fallen state while hoping for future redemption.
Overturning the evil Rousseau and Hobbes
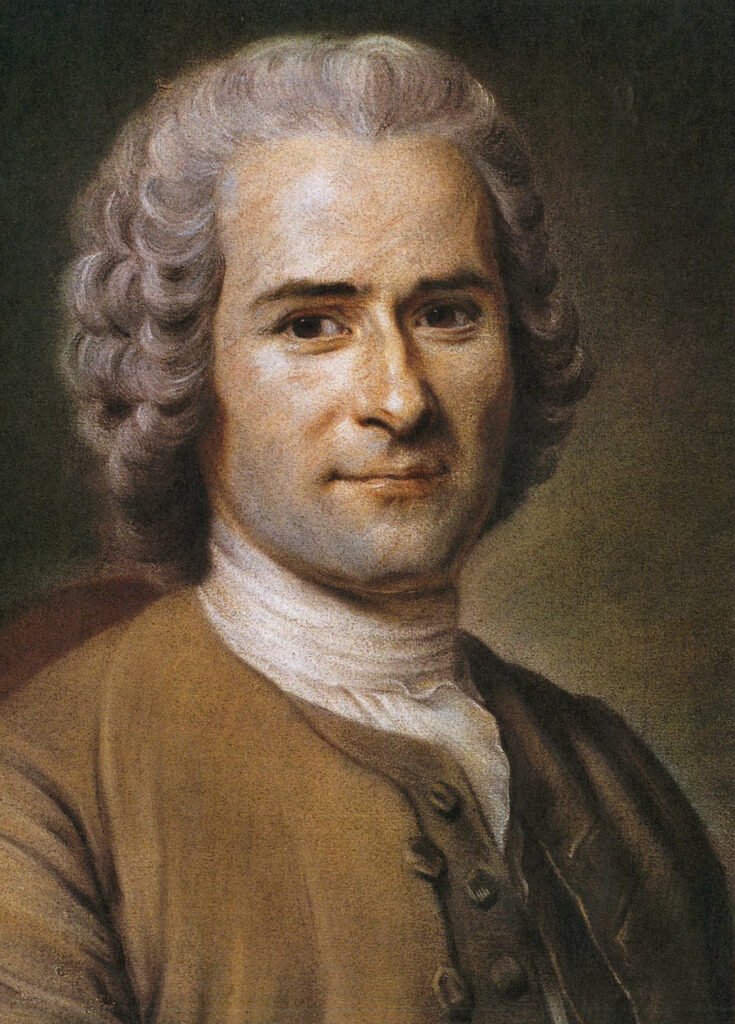


Graeber and Wengrow, establishing the core argument of their entire book, demonstrate in a very provocative way how we got brainwashed by the pessimistic and destructive oligarchical ideology, especially that promoted by both Rousseau and Hobbes, for whom inequality is the natural state of man, a humanity which might have eventually been good as “a noble savage”, before becoming “civilized” and a society only surviving thanks to a “social contract” (voluntary bottom-up submission) or a “Leviathan” (top down dictatorship) :
“Today, the popular version of this [biblical] story [of man thrown out of the Garden of Eden] is typically some updated variation on Jean-Jacques Rousseau’s Discourse on the Origin and the Foundation of Inequality Among Mankind, which he wrote in 1754. Once upon a time, the story goes, we were hunter-gatherers, living in a prolonged state of childlike innocence, in tiny bands. These bands were egalitarian; they could be for the very reason that they were so small. It was only after the “Agricultural Revolution,” and then still more the rise of cities, that this happy condition came to an end, ushering in ‘civilization’ and ‘the state’—which also meant the appearance of written literature, science and philosophy, but at the same time, almost everything bad in human life: patriarchy, standing armies, mass executions and annoying bureaucrats demanding that we spend much of our lives filling in forms.
“Of course, this is a very crude simplification, but it really does seem to be the foundational story that rises to the surface whenever anyone, from industrial psychologists to revolutionary theorists, says something like ‘but of course human beings spent most of their evolutionary history living in groups of ten or twenty people,’ or ‘agriculture was perhaps humanity’s worst mistake.’ And as we’ll see, many popular writers make the argument quite explicitly. The problem is that anyone seeking an alternative to this rather depressing view of history will quickly find that the only one on offer is actually even worse: if not Rousseau, then Thomas Hobbes.
“Hobbes’s Leviathan, published in 1651, is in many ways the founding text of modern political theory. It held that, humans being the selfish creatures they are, life in an original State of Nature was in no sense innocent; it must instead have been ‘solitary, poor, nasty, brutish, and short’—basically, a state of war, with everybody fighting against everybody else. Insofar as there has been any progress from this benighted state of affairs, a Hobbesian would argue, it has been largely due to exactly those repressive mechanisms that Rousseau was complaining about: governments, courts, bureaucracies, police. This view of things has been around for a very long time as well. There’s a reason why, in English, the words ‘politics’ ‘polite’ and ‘police’ all sound the same—they’re all derived from the Greek word polis, or city, the Latin equivalent of which is civitas, which also gives us ‘civility,’ ‘civic’ and a certain modern understanding of ‘civilization.
“Human society, in this view, is founded on the collective repression of our baser instincts, which becomes all the more necessary when humans are living in large numbers in the same place. The modern-day Hobbesian, then, would argue that, yes, we did live most of our evolutionary history in tiny bands, who could get along mainly because they shared a common interest in the survival of their offspring (‘parental investment,’ as evolutionary biologists call it). But even these were in no sense founded on equality. There was always, in this version, some ‘alpha-male’ leader. Hierarchy and domination, and cynical self-interest, have always been the basis of human society. It’s just that, collectively, we have learned it’s to our advantage to prioritize our long-term interests over our short-term instincts; or, better, to create laws that force us to confine our worst impulses to socially useful areas like the economy, while forbidding them everywhere else
“As the reader can probably detect from our tone, we don’t much like the choice between these two alternatives. Our objections can be classified into three broad categories. As accounts of the general course of human history, they:
1) simply aren’t true;
2) have dire political implications and
3) make the past needlessly dull.”
As a consequence of the victory of imperial models of political power, the only accepted “narrative” of man’s “evolution”, automatically validating an oligarchical grip over society, is that which allows “confirming” the pre-agreed-upon dogma erected as immortal “truth”. And any historical findings or artifacts contradicting or invalidating the Rousseau-Hobbes narrative will be, at best, declared anomalies.
Open our eyes
Graeber and Wengrow’s book is an attempt
“to tell another, more hopeful and more interesting story; one which, at the same time, takes better account of what the last few decades of research have taught us. Partly, this is a matter of bringing together evidence that has accumulated in archaeology, anthropology and kindred disciplines; evidence that points towards a completely new account of how human societies developed over roughly the last 30,000 years. Almost all of this research goes against the familiar narrative, but too often the most remarkable discoveries remain confined to the work of specialists, or have to be teased out by reading between the lines of scientific publications.”
To give just a sense of how different the emerging picture is:
“[I]t is clear now that human societies before the advent of farming were not confined to small, egalitarian bands. On the contrary, the world of hunter-gatherers as it existed before the coming of agriculture was one of bold social experiments, resembling a carnival parade of political forms, far more than it does the drab abstractions of evolutionary theory. Agriculture, in turn, did not mean the inception of private property, nor did it mark an irreversible step towards inequality. In fact, many of the first farming communities were relatively free of ranks and hierarchies. And far from setting class differences in stone, a surprising number of the world’s earliest cities were organized on robustly egalitarian lines, with no need for authoritarian rulers,
ambitious warrior-politicians, or even bossy administrators.”
Kondiaronk, Leibniz and the Enlightenment


In fact, Rousseau’s story, argue the authors, was in part a response to critiques of European civilization, which began in the early decades of the 18th century. “The origins of that critique, however, lie not with the philosophers of the Enlightenment (much though they initially admired and imitated it), but with indigenous commentators and observers of European society, such as the Native American (Huron-Wendat) statesman Kondiaronk,” and many others.
And when prominent thinkers, such as Leibniz, “urged his patriots to adopt Chinese models of statecraft, there is a tendency for contemporary historians to insist they weren’t really serious”.
However, many influential Enlightenment thinkers did in fact claim that some of their ideas on the subject of inequality were directly taken from Chinese or Native American sources!
Just as Leibniz became familiar with Chinese civilization through his contact with the Jesuit missions, the ideas from Native Americans reached Europe by way of books such as the widely read seventy-one-volume report The Jesuit Relations, published between 1633 and 1673.
While today, we would think personal freedom is a good thing, this was not the case for the Jesuits complaining about the Native Americans. The Jesuits were opposed to freedom in principle:
“This, without doubt, is a disposition quite contrary to the spirit of the Faith, which requires us to submit not only our wills, but our minds, our judgments, and all the sentiments of man
to a power unknown to the laws and sentiments of corrupt nature.”
Jesuit father Jérôme Lallemant, whose correspondence provided an initial model for The Jesuit Relations, noted of the Wendat Indians in 1644: “I do not believe that there is a people on earth freer than they, and less able to allow to the subjection of their wills to any power whatever”.

Even more worrisome, their high level of intelligence. Father Paul Le Jeune, Superior of the Jesuits in Canada in the 1630:
“There are almost none of them incapable of conversing or reasoning very well, and in good terms, on matters within their knowledge. The councils, held almost every day in the Villages, and on almost all matters, improve their capacity for talking”.
Or in Lallemant’s words:
“I can say in truth that, as regards intelligence, they are in no ways inferior to Europeans and to those who dwell in France. I would never have believed that, without instruction, nature could have supplied a most ready and vigorous eloquence, which I have admired in many Hurons (American Natives); or more clear-nearsightedness in public affairs, or a more discreet management in things to which they are accustomed”.
(The Jesuit Relations, vol. XXVIII, p. 62.)
Some Jesuits went much further, noting – not without a trace of frustration – that New World “savages” seemed rather cleverer overall than the people they were used to dealing with at home.

The ideas of Native Indian statesman Kondiaronk (c. 1649–1701), known as “The Rat” and the Chief of the Native American Wendat people at Michilimackinac in New France, reached Leibniz via an impoverished French aristocrat named Louis-Armand de Lom d’Arce, Baron de la Hontan, better known as Lahontan.
In 1683, Lahontan, age 17, joined the French army and was posted in Canada. In his various missions, he became fluent in both Algonkian and Wendat and good friends with a number of indigenous political figures, including the brilliant Wendat statesman Kondiaronk. The latter impressed many French observers with his eloquence and brilliance and frequently met with the royal governor, Count Louis de Buade de Frontenac. Kondiaronk himself, as Speaker of the Council (their governing body) of the Wendat Confederation, is thought to have been sent as an ambassador to the Court of the French King, Louis XIV, in 1691.
The Great Peace of Montreal

Even after being betrayed by the French, and obliged to conduct his own wars to secure his fellow men, Kondiaronk, played a key role in what is remembered as the “Great Peace of Montreal” of August 1, 1701, which ended the bloody Beaver Wars, in reality proxy wars between the British and the French, each of them using the native Indians as “cannon fodder” for their own geopolitical schemes
France was increasingly cornered by the British. Therefore, at the request of the French, in the summer of 1701, more than 1,300 Indians, from forty different nations, gathered near Montreal, dispite the fact that the city was ravaged by influenza. They came from the Mississippi Valley, the Great Lakes, and Acadia. Many were lifelong enemies, but all had responded to an invitation from the French governor. Their future and the fate of the colony were at stake. Their goal was to negotiate a comprehensive peace, among themselves and with the French. The negotiations dragged on for days, and peace was far from being guaranteed. The chiefs were wary. The main stumbling block to peace was the return of prisoners who had been captured during previous campaigns and enslaved or adopted.
Without Kondiaronk’s support, peace was unattainable. On August 1, seriously ill, he spoke for two hours in favor of a peace treaty that would be guaranteed by the French. Many were moved by his speech. The following night, Kondiaronk died, struck down by influenza at the age of 52.

But the next day, the peace treaty was signed. From now on there would be no more wars between the French and the Indians. Thirty-eight nations signed the treaty, including the Iroquois. The Iroquois promised to remain neutral in any future conflict between the French and the Iroquois’ former allies, the English colonists of New England.
Kondiaronk was praised by the French and presented as a “model” of peace-loving natives. The Jesuits immediately put out the lie that, just before dying, he had “converted” to the Catholic faith in the hope other natives would follow his model.
Lahontan from Amsterdam to Hanover

Now, following various events, Lahontan ended up in Amsterdam. In order to make a living he wrote a series of books about his adventures in Canada, the third one entitled Curious Dialogues with a Savage of Good Sense Who Has Travelled (1703), comprising four dialogues with a fictional figure, “Adario” (in reality Kondiaronk), which were rapidly translated into German, Dutch, English, and Italian. Lahontan, himself, gaining some sort of celebrity, settled in Hannover, where he befriended the great philosopher and scientist Wilhelm Gottfried Leibniz.
On the lookout for everything that was being discussed in Europe, the philosopher, then 64 years old, seems to have been put on the track of Lahontan by Dutch and German journalists, but also by the text of an obscure theologian from Helmstedt, Conrad Schramm, whose introductory lecture, the « The Stammering Philosophy of the Canadians », had been published in Latin in 1707. Referring first to Plato and Aristotle (which he abandoned almost immediately), Schramm used the Dialogues and the Memoirs of Lahontan to show how the « Canadian barbarians knock on the door of philosophy but do not enter because they lack the means or are locked into their customs”.

Far less narrow-minded, Leibniz saw in Lahontan a confirmation of his own political optimism, which allowed him to affirm that the birth of society does not come from the need to get out of a terrible state of war, as Thomas Hobbes believed, but from a natural aspiration to concord.
But what captured his main interest, was not so much whether the “American savages” were capable, or not, of philosophizing, but whether they really lived in concord without government.
To his correspondent Wilhelm Bierling, who asked him how the Indians of Canada could live “in peace although they have neither laws nor public magistracies [tribunals]”, Leibniz replied:
“It is quite true […] that the Americans of these regions live together without any government but in peace; they know neither fights, nor hatreds, nor battles, or very few, except against men of different nations and languages.
I would almost say that this is a political miracle,
unknown to Aristotle and ignored by Hobbes.”
Leibniz, who claimed to know Lahontan well, underlined that Adario, “who came in France a few years ago and who, even if he belongs to the Huron nation, judged its institutions superior to ours.”
This conviction of Leibniz will be expressed again in his Judgment on the works of M. le Comte Shaftesbury, published in London in 1711 under the title of Charactersticks:
« The Iroquois and the Hurons, savages neighboring New France and New England, have overturned the too universal political maxims of Aristotle and Hobbes. They have shown, by their super-prominent conduct, that entire peoples can be without magistrates and without quarrels, and that consequently men are neither sufficiently motivated by their good nature, nor sufficiently forced by their wickedness to provide themselves with a government and to renounce their liberty. But these savages shows that it is not so much the necessity, as the inclination to go to the best and to approach felicity, by mutual assistance, which makes the foundation of societies and states; and it must be admitted that security is the most essential point”.
While these dialogues are often downplayed as fictional and therefore merely invented for the sake of literature, Leibniz, in a letter to Bierling dated November 10, 1719, responded: « The Lahontan’s Dialogues, although not entirely true, are not completely invented either.”
As a matter of fact, Lahontan himself, in the preface to the dialogues, wrote:
“When I was in the village of this [Native] American, I took on the agreeable task of carefully noting all his arguments. No sooner had I returned from my trip to the Canadian lakes than I showed my manuscript to Count Frontenac, who was so pleased to read it that he made the effort to help me put these Dialogues into their present state.”
People today tend to forget that tape-recorders weren’t around in those days.
For Leibniz, of course, political institutions were born of a natural aspiration to happiness and harmony. In this perspective, Lahontan’s work does not contribute to the construction of a new knowledge; it only confirms a thesis Leibniz had already constituted.
A critical view on the Europeans and the French in particular

Hence, Lahontan, in his memoirs, says that Native Americans, such as Kondiaronk, who had been in France,
“were continually teasing us with the faults and disorders they observed in our towns, as being occasioned by money. There’s no point in trying to remonstrate with them about how useful the distinction of property is for the support of society: they make a joke of everything you say on that account. In short, they neither quarrel nor fight, nor slander one another; they scoff at arts and sciences, and laugh at the difference of ranks which is observed with us. They brand us for slaves, and call us miserable souls, whose life is not worth having, alleging that we degrade ourselves in subjecting ourselves to one man [the king] who possesses all power, and is bound by no law but his own will.”
Lahontan continues:
“They think it unaccountable that one man should have more than another,
and that the rich should have more respect than the poor.
In short, they say, the name of savages, which we bestow upon them, would fit ourselves better,
since there is nothing in our actions that bears an appearance of wisdom.”
In his dialogue with Kondiaronk, Lahontan tells him that if the wicked remained unpunished, we would become the most miserable people of the earth. Kondiaronk responds:
“For my part, I find it hard to see how you could be much more miserable than you already are. What kind of human, what species or creature, most Europeans be, that they have to be forced to do the good, and only refrain from evil because of fear of punishment?… You have observed we lack judges. What is the reason for that? Well, we never bring lawsuits against one another. And why do we never bring lawsuits? Well because we made a decision neither to accept or make use of money. And why do we refuse to allow money in our communities? The reason is this: we are determined not to have laws – because, since the world was a world, our ancestors have been able to live contentedly without them.”
Brother Gabriel Sagard, a French Recollect Friar, reported that the Wendat people were particularly offended by the French lack of generosity to one another:
“They reciprocate hospitality and give such assistance to one another that the necessities of all are provided for without there being any indigent beggar in their towns and villages;
and they considered it a very bad thing when they heard it said
that there were in France a great many of these needy beggars,
and thought that this was for lack of charity in us, and blamed us for it severely”.

Money, thinks Kondiaronk, creates an environment that encourages people to behave badly:
“I have spent six years reflecting on the state of European society and I still can’t think of a single way they act that’s not inhuman, and I genuinely think this can only be the case, as long as you stick to your distinctions of ‘mine’ and ‘thine’. I affirm that what you call money is the devil of devils; the tyrant of the French, the source of all evils; the bane of souls and the slaughterhouse of the living. To imagine one can live in the country of money and preserve one’s soul is like imagining one could preserve one’s life at the bottom of a lake. Money is the father of luxury, lasciviousness, intrigues, trickery, lies, betrayal, insincerity, – all of the world’s worst behaviors. Fathers sell their children, husbands their wives, wives betray their husbands, brothers kill each other, friends are false, and all because of money. In the light of all this, tell me that we Wendat are not right in refusing to touch, or so much as to look at money?”
In the third footnote of his speech on the origins on inequality, Jean-Jacques Rousseau, who invented the idea of the “noble savage” presumably existing before man engaged in agriculture, himself refers to
“those happy nations, who do not know even the names of the vices
which we have such trouble controlling,
of those American savages whose simple and natural ways of keeping public order
Montaigne does not hesitate to prefer to Plato’s laws…”
Europeans refusing to return

Another observation is that of Swedish botanist Peher Kalm, who, in 1749, was astonished by the fact that a large number of Europeans, exposed to Aboriginal life, did not want to return:
“It is also remarkable that the greater part of the European prisoners who, on the occasion of the war, were taken in this way and mixed with the Indians, especially if they were taken at a young age, never wanted to return to their country of origin afterwards, even though their father and mother or close relatives came to see them to try to persuade them to do so, and they themselves had every freedom to do so. But they found the Indians’ independent way of life preferable to that of the Europeans; they adopted native clothing and conformed in every way to the Indians, to the point where it is difficult to distinguish them from the Indians, except that their skin and complexion are slightly whiter. We also know of several examples of Frenchmen who have voluntarily married native women and adopted their way of life; on the other hand, we have no example of an Indian marrying a European woman and adopting her way of life; if he happens to be taken prisoner by the Europeans during a war, he always looks for an opportunity, on the contrary, to return home, even if he has been detained for several years and has enjoyed all the freedoms that a European can enjoy.”
Before Lahontan:
Thomas More’s Utopians

In 1492, as the joke goes, “America discovered Columbus, a Genoese captain lost at sea”. The mission he had been entrusted with was motivated by a variety of intentions, not least the idea of reaching, by traveling west, China, a continent thought to be populated by vast populations unaware of Christ’s inspiring and optimistic message, and therefore in urgent need of evangelization.
Unfortunately, two years later, a less theological interest arose when, on June 7, 1494, the Portuguese and Spanish signed the Treaty of Tordesillas at the Vatican, under the supervision of Pope Alexander IV (Borgia), dividing the entire world between two dominant world powers:
- the Spanish Empire under top-down control of the continental Habsburg/Venice alliance;
- the Portuguese Empire under that of the banking cartel of Genoese maritime slave traders.
This didn’t stop the best European humanists, two centuries before Lahontan, from raising their voices and showing that some of the so-called “savages” of the United States had virtues and qualities absolutely worthy of consideration and possibly lacking here in Europe.

Such was the case with Erasmus of Rotterdam and his close friend and collaborator Thomas More, who shared what are thought to be their views on America in a little book entitled “U-topia” (meaning ‘any’ place), jointly written and published in 1516 in Leuven, Belgium.
By instinct, the reports they received of America and the cultural characteristics of its natives, led them to believe that they were dealing with some lost colony of Greeks or even the famous lost continent of Atlantis described by Plato in both his Timaeus and Critias.
In More’s Utopia, the Portuguese captain Hythlodeus describes a highly organized civilization: it has flat-hulled ships and “sails made of sewn papyrus”, made up of people who “like to be informed about what’s going on in the world” and whom he “believes to be Greek by origin”.
At one point he says:
“Ah, if I were to propose what Plato imagined in his Republic, or what the Utopians put into practice in theirs, these principles, although far superior to ours – and they certainly are –
might come as a surprise, since with us, everyone owns his property,
whereas there, everything is held in common.”
(no private property).
As far as religion is concerned, the Utopians (like the Native Americans)
“have different religions but, just as many roads lead to one and the same place, all their aspects, despite their multiplicity and variety, converge towards the worship of the divine essence. That’s why nothing can be seen or heard in their temples except what is consistent with all beliefs.
The particular rites of each sect are performed in each person’s home;
public ceremonies are performed in a common place;
Public ceremonies are performed in a form that in no way contradicts them.«
And to conclude :
“Some worship the Sun, others the Moon or some other planet (…) The majority, however, and by far the wisest, reject these beliefs, but recognize a unique god, unknown, eternal, in-commensurable, impenetrable, inaccessible to human reason, spread throughout our universe in the manner, not of a body, but of a power. They call him Father, and relate to him alone the origins, growth, progress, vicissitudes and decline of all things. They bestow divine honors on him alone (…) Moreover, despite the multiplicity of their beliefs, the other Utopians at least agree on the existence of a supreme being, creator and protector of the world.”
Exposing the trap of woke ideology
Does that mean that “all Europeans were evil” and that “all Native Americans were good”? Not at all! The authors don’t fall for such simplistic generalizations and “woke” ideology in general.
For example, even with major similarities, the cultural difference between the First Nation of the Canadian Northwest Coast and those of California, was as big as that between Athens and Sparta in Greek antiquity, the first a republic, the latter an oligarchy.
Different people and different societies, at different times, made experiments and different political choices about the axiomatics of their culture.
While in California, forms of egalitarian and anti-oligarchical self-government erupted, in some areas of the north, oligarchical rule prevailed:
“[F]rom the Klamath River northwards, there existed societies dominated by warrior aristocrats engaged in frequent inter-group raiding, an in which, traditionally, a significant portion of the population had consisted of chattel slaves. This apparently had been true as long as anyone living there could remember.”
Northwest societies took delight in displays of excess, notably during festivals known as “potlach” sometimes culminating in
“the sacrificial killing of slaves (…) In many ways, the behavior or Northwest Coast aristocrats resembles that of Mafia dons, with their strict codes of honor and patronage relations; or what sociologists speak of as ‘court societies’ – the sort of arrangement one might expect in, say, feudal Sicily, from which the Mafia derived many of its cultural codes.”
So, the first point made by the authors is that the infinite diversity of human societies has to be taken into account. Second, instead of merely observing the fact, the authors underline that these diversities very often didn’t result from “objective” conditions, but from political choices. That also carries the very optimistic message, that choices different from the current world system, can become reality if people rise to the challenge of changing them for the better.
Urbanization before agriculture

In the largest part of the book, the authors depict the life of hunter-gatherers living thousands of years before the agricultural revolution but able to create huge urban complexes and eventually ruling without a dominant oligarchy.
The book identifies examples in China, Peru, the Indus Valley (Mohenjo-Daru), Ukraine ((Taljanki, Maidenetske, Nebelivka), Mexico (Tlaxcala), the USA (Poverty Point), and Turkey (Catalhoyuk), where large-scale, city-level living was taking place (from about 10,000 BC to 6,000 BC).
But these didn’t involve a ruling caste or aristocratic class; they were explicitly egalitarian in their house building and market trading; made many innovations in plumbing and street design; and were part of continental networks which shared best practice. The agricultural revolution was not a “revolution”, the book argues, but rather a continual transformative process spread across thousands of years when hunter-gatherers were able to flexibly organize themselves into mega-sites (several thousand inhabitants), organized without centers or monumental buildings, but built with standardized houses, comfortable for daily life, all of this achieved without static hierarchies, kings, or overwhelming bureaucracy.
Another case in point is the example of Teotihuacan, which rivaled Rome in grandeur between about 100 BC and 600 AD, where, following a political revolution in 300 AD, an egalitarian culture embarked on a massive social housing program designed to give all residents decent quarters.
Conclusion
Living today, it is very difficult for most of us to imagine that a society, a culture, or a civilization, could survive over centuries without a centralized, forcibly hierarchical power structure.
While, as the authors indicate, archaeological evidence, if we are ready to look at it, tell us the contrary. But are we ready to challenge our own prejudices?

As an example of such self-inflicted blindness, worth mentioning is the case of the “King-Priest”, a small male carved figure showing a neatly bearded man, found during the excavation of the ruined Bronze Age city of Mohenjo-daro (Pakistan), dated to around 2000 BC and considered « the most famous stone sculpture » of the Indus Valley civilization. While in Mohenjo-Daro there exists neither a royal palace or tomb, nor a religious temple of any nature, British archaeologists immediately called it a “King-Priest”, because very simply “it can’t be otherwise”.
Reading Graeber and Wengrow’s book obliges us to adjust our views and become optimistic. They show that radically different human systems are not only possible but have been tried many times by our species. In a public talk in 2022, Wengrow presented what he sees as lessons for the political present from the past, where human beings were much more fluid, conscious and experimental with their social and economic structures :
“Now what do all these details amount to? What does it all mean? Well, at the very least, I’d suggest it’s really a bit far-fetched these days to cling to this notion that the invention of agriculture meant a departure from some egalitarian Eden. Or to cling to the idea that small-scale societies are especially likely to be egalitarian, while large-scale ones must necessarily have kings, presidents and top-down structures of management. And there are also some contemporary implications. Take, for example, the commonplace notion that participatory democracy is somehow natural in a small community—or perhaps an activist group—but couldn’t possibly have a scale-up for anything like a city, a nation or even a region. Well, actually, the evidence of human history, if we’re prepared to look at it, suggests the opposite. If cities and regional confederacies, held together mostly by consensus and cooperation, existed thousands of years ago, who’s to stop us creating them again today with technologies that allow us to overcome the friction of distance and numbers? Perhaps it’s not too late to begin learning from all this new evidence of the human past, even to begin imagining what other kinds of civilization we might create if we can just stop telling ourselves that this particular world is the only one possible.”